Structured Threat Information Expression (STIX™) is a
language and serialization format used to exchange cyber threat intelligence
(CTI). STIX enables organizations to share CTI with one another in a consistent
and machine-readable manner, allowing security communities to better understand
what computer-based attacks they are most likely to see and to anticipate
and/or respond to those attacks faster and more effectively. STIX is designed
to improve many different capabilities, such as collaborative threat analysis,
automated threat exchange, automated detection and response, and more.
The objects and features added for inclusion in STIX 2.1
represent an iterative approach to fulfilling basic consumer and producer
requirements for CTI sharing. Objects and properties not included in this
version of STIX, but deemed necessary by the community, will be included in
future releases.
This specification is provided under the Non-Assertion Mode of the OASIS IPR Policy, the mode chosen when the
Technical Committee was established. For information on whether any patents
have been disclosed that may be essential to implementing this specification,
and any offers of patent licensing terms, please refer to the Intellectual
Property Rights section of the TC’s web page (https://www.oasis-open.org/committees/cti/ipr.php).
The key words "MUST", "MUST NOT",
"REQUIRED", "SHALL", "SHALL NOT",
"SHOULD", "SHOULD NOT", "RECOMMENDED",
"NOT RECOMMENDED", "MAY", and "OPTIONAL"
in this document are to be interpreted as described in BCP 14 [RFC2119] [RFC8174] when, and only when, they appear
in all capitals, as shown here.
All text is
normative except for examples, the overview (section 1.5), and any text marked non-normative.
[Character Sets] "N. Freed and
M. Dürst, “Character Sets”, IANA, December 2013, [Online]. Available: http://www.iana.org/assignments/character-sets/character-sets.xhtml
[Davis] M. Davis and
K. Whistler, "UNICODE NORMALIZATION FORMS", Unicode® Standard Annex
#15, February 2016. [Online] Available: http://unicode.org/reports/tr15/
[FIPS202] “SHA-3 Standard:
Permutation-Based Hash and Extendable-Output Functions”, FIPS PUB 202, August
2015, Information Technology Laboratory, National Institute of Standards and
Technology (NIST). [Online]. Available: http://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/FIPS/NIST.FIPS.202.pdf
[IEEE 754-2008] “IEEE Standard for
Floating-Point Arithmetic”, IEEE 754-2008, August 2008. [Online]. Available:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4610935/
[IPFIX] IANA, “IP
Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Entities”, December 2016, [Online]. Available: http://www.iana.org/assignments/ipfix/ipfix.xhtml
[ISO639-2] “ISO 639-2:1998
Codes for the representation of names of languages -- Part 2: Alpha-3 code”,
1998. [Online]. Available: http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail?csnumber=4767
[ISO3166-1] “ISO ISO
3166-1:2013 Country Codes”, 2013. [Online]. Available:https://www.iso.org/standard/63545.html
[ISO10646] “ISO/IEC
10646:2014 Information technology -- Universal Coded Character Set (UCS)”,
2014. [Online]. Available: http://standards.iso.org/ittf/PubliclyAvailableStandards/c063182_ISO_IEC_10646_2014.zip
[JCS] "JSON
Canonicalization Scheme version 06", 2019. [Online]. Available: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-rundgren-json-canonicalization-scheme/
[Media Types] N. Freed, M.
Kucherawy, M. Baker and B. Hoehrmann, “Media Types”, IANA, December 2016.
[Online]. Available: http://www.iana.org/assignments/media-types/media-types.xhtml
[NIST SP800-38D] M. Dworkin,
“Recommendation for Block Cipher Modes of Operation:Galois/Counter Mode (GCM)
and GMAC”, NIST Special Publication 800-38D, November 2007. [Online].
Available: http://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/Legacy/SP/nistspecialpublication800-38d.pdf
[NVD] Official
Common Platform Enumeration (CPE) Dictionary, National Vulnerability Database
[Online]. Available: https://nvd.nist.gov/cpe.cfm
[Port Numbers] J.Touch, A. Mankin,
E. Kohler, et. al., “Service Name and Transport Protocol Port Number Registry”,
IANA, January 2017. [Online]. Available: http://www.iana.org/assignments/service-names-port-numbers/service-names-port-numbers.xhtml
[RFC1034] Mockapetris, P.,
"Domain names - concepts and facilities", STD 13, RFC 1034, DOI
10.17487/RFC1034, November 1987, http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc1034.
[RFC1321] Rivest, R.,
"The MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm", RFC 1321, DOI 10.17487/RFC1321,
April 1992, http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc1321.
[RFC2047] Moore, K.,
"MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) Part Three: Message Header
Extensions for Non-ASCII Text", RFC 2047, DOI 10.17487/RFC2047, November
1996,
http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc2047.
[RFC2119] Bradner, S.,
"Key words for use in RFCs to Indicate Requirement Levels", BCP 14,
RFC 2119, DOI 10.17487/RFC2119, March 1997, http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc2119.
[RFC3174] Eastlake 3rd, D.
and P. Jones, "US Secure Hash Algorithm 1 (SHA1)", RFC 3174, DOI
10.17487/RFC3174, September 2001, http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc3174.
[RFC3339] Klyne,
G. and C. Newman, "Date and Time on the Internet: Timestamps", RFC
3339, DOI 10.17487/RFC3339, July 2002, http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc3339.
[RFC3986] Berners-Lee,
T., Fielding, R., and L. Masinter, "Uniform Resource Identifier (URI):
Generic Syntax", STD 66, RFC 3986, DOI 10.17487/RFC3986, January 2005, http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc3986.
[RFC4122] Leach,
P., Mealling, M., and R. Salz, "A Universally Unique IDentifier (UUID) URN
Namespace", RFC 4122, DOI 10.17487/RFC4122, July 2005, http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc4122.
[RFC4648] Josefsson, S.,
"The Base16, Base32, and Base64 Data Encodings", RFC 4648, DOI
10.17487/RFC4648, October 2006, http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc4648.
[RFC5322] Resnick, P., Ed.,
"Internet Message Format", RFC 5322, DOI 10.17487/RFC5322, October
2008,
http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc5322.
[RFC5646]
Phillips, A., Ed., and M. Davis, Ed., "Tags for
Identifying Languages", BCP 47, RFC 5646, DOI 10.17487/RFC5646, September
2009, http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc5646.
[RFC5890] Klensin, J.,
"Internationalized Domain Names for Applications (IDNA): Definitions and
Document Framework", RFC 5890, DOI 10.17487/RFC5890, August 2010, http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc5890.
[RFC6234] Eastlake 3rd, D.
and T. Hansen, "US Secure Hash Algorithms (SHA and SHA-based HMAC and
HKDF)", RFC 6234, DOI 10.17487/RFC6234, May 2011, http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc6234.
[RFC7493] Bray, T., Ed., "The
I-JSON Message Format", RFC 7493, DOI\ 10.17487/RFC7493, March 2015, https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc7493.
[RFC7539] Nir, Y. and A.
Langley, "ChaCha20 and Poly1305 for IETF Protocols", RFC 7539, DOI
10.17487/RFC7539, May 2015, http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc7539.
[RFC8174] Leiba, B.,
"Ambiguity of Uppercase vs Lowercase in RFC 2119 Key Words", BCP 14,
RFC 8174, DOI 10.17487/RFC8174, May 2017, https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc8174.
[RFC8259] Bray,
T., Ed., "The JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Data Interchange
Format", RFC 8259, DOI 10.17487/RFC8259, December 2017. http://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc8259.txt.
[SSDEEP] J. Kornblum,
“Identifying Almost Identical Files Using Context Triggered Piecewise Hashing”,
Proceedings of The Digital Forensic Research Conference (DFRWS) 2006. [Online].
Available: http://dfrws.org/sites/default/files/session-files/paper-identifying_almost_identical_files_using_context_triggered_piecewise_hashing.pdf
[TLP] Traffic
Light Protocol, Version 1.0 (TLP). (2016, Aug. 25). FIRST. [Online]. Available: https://first.org/tlp
[UNSD M49] Standard country or
area codes for statistical use (M49), UN Statistics Division (UNSD), Available:
https://unstats.un.org/unsd/methodology/m49/
[WGS84] National
Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA), Department of Defense World Geodetic System
1984, NIMA TR8350.2, January 2000. Available: http://earth-info.nga.mil/GandG/publications/tr8350.2/wgs84fin.pdf
[X.509] X.509
: Information technology - Open Systems Interconnection - The Directory:
Public-key and attribute certificate frameworks, ITU, October 2016. [Online].
Available: https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-X.509/
[CAPEC] Common
Attack Pattern Enumeration and Classification (CAPEC). (2014, Nov. 7). The
MITRE Corporation. [Online]. Available: http://capec.mitre.org.
[Casey
2007] Casey, T., Threat Agent Library Helps Identify
Information Security Risks September 2007. [Online]. Available: https://communities.intel.com/servlet/JiveServlet/downloadBody/1151-102-1-1111/Threat
Agent Library_07-2202w.pdf.
[Casey 2015] Casey, T.,
“Understanding Cyberthreat Motivations to Improve Defense”, Intel, February
2015. [Online]. Available: https://communities.intel.com/servlet/JiveServlet/previewBody/23856-102-1-28290/understanding-cyberthreat-motivations-to-improve-defense-paper-l.pdf.
[CVE] Common
Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE). The MITRE Corporation. [Online].
Available: http://cve.mitre.org.
[FM 2-22.3] "US Army
Field Manual - Human Intelligence Collector Operations", FM 2-22.3,
September 2006. [Online]. Available: https://fas.org/irp/doddir/army/fm2-22-3.pdf.
[Goessner 2007] Goessner, S.,
“JSONPath - XPath for JSON”, February 2007. [Online]. Available: http://goessner.net/articles/JsonPath/.
[ICD 203] "Analytic
Standards", ICD 203, January 2015. [Online]. Available: https://www.dni.gov/files/documents/ICD/ICD%20203%20Analytic%20Standards.pdf
[JSON Schema] OASIS Cyber Threat
Intelligence (CTI) TC, “cti-stix2-json-schemas”, OASIS. [Online]. Available: https://github.com/oasis-open/cti-stix2-json-schemas.
[NIST800-83] M.
Souppaya and K. Scarfone, “Guide to Malware Incident Prevention and Handling
for Desktops and Laptops”, NIST Special Publication 800-83, 2013. [Online].
Available: https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-83/rev-1/final
[Pattern Grammar] OASIS Cyber Threat
Intelligence (CTI) TC, "STIX Pattern Grammar", OASIS. [Online].
Available: https://github.com/oasis-open/cti-stix2-json-schemas/tree/master/pattern_grammar
[RFC7515] Jones, M.,
Bradley, J., and N. Sakimura, "JSON Web Signature (JWS)", RFC 7515,
DOI 10.17487/RFC7515, May 2015, https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc7515.
[RFC7516] Jones, M. and J.
Hildebrand, "JSON Web Encryption (JWE)", RFC 7516, DOI
10.17487/RFC7516, May 2015, https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc7516.
[RFC8322] Field, J., Banghart,
S., and D. Waltermire, "Resource-Oriented Lightweight Information Exchange
(ROLIE)", RFC 8322, DOI 10.17487/RFC8322, February 2018, https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc8322.
[SWID] ISO/IEC
19770-2:2015 Information technology -- IT asset management -- Part 2: Software
identification tag, 2015. [Online]. Available: https://www.iso.org/standard/65666.html
[VERIS] VERIS Community Database.
(n.d.). [Online]. Available: http://vcdb.org/
[WEP] "Words
of Estimative Probability", Kent, Sherman, March 2007. [Online].
Available: https://www.cia.gov/library/center-for-the-study-of-intelligence/csi-publications/books-and-monographs/sherman-kent-and-the-board-of-national-estimates-collected-essays/6words.html
The following color, font and
font style conventions are used in this document:
● The Consolas font is used for all type names,
property names and literals.
○
type names are in red with a light red background – threat-actor
○
property names are in bold style – created_at
○
literals (values) are in blue with a blue background – malicious-activity
○
All relationship types are string literals; therefore, they will
also appear in blue with a blue background – related-to
● In
an object's property table, if a common property is being redefined in some
way, then the background is dark grey.
● All
examples in this document are expressed in JSON. They are in Consolas 9-point font, with straight
quotes, black text and a light grey background,
and using 2-space indentation. JSON examples in this document are
representations of JSON objects [RFC8259]. They should not be interpreted
as string literals. The ordering of object keys is insignificant. Whitespace
before or after JSON structural characters in the examples are insignificant [RFC8259].
● Parts
of the example may be omitted for conciseness and clarity. These omitted parts
are denoted with the ellipses (...).
● The
term “hyphen” is used throughout this document to refer to the ASCII hyphen or
minus character, which in Unicode is “hyphen-minus”, U+002D.
STIX is a schema that defines a taxonomy of cyber threat
intelligence that is represented by the following objects:
|
STIX Objects
|
STIX Bundle Object
|
|
STIX Core Objects
|
STIX Meta Objects
|
|
STIX
Domain Objects
(SDO)
|
STIX
Cyber-observable Objects
(SCO)
|
STIX Relationship
Objects
(SRO)
|
Language
Content Objects
|
Marking
Definition Objects
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STIX Core Objects
Any SDO, SCO, or SRO.
STIX Domain Objects
Higher Level Intelligence Objects that represent behaviors
and constructs that threat analysts would typically create or work with while
understanding the threat landscape.
STIX Cyber-observable Objects
Objects that represent observed facts about a network or
host that may be used and related to higher level intelligence to form a more
complete understanding of the threat landscape.
STIX Relationship Objects
Objects that connect STIX Domain Objects together, STIX
Cyber-observable Objects together, and connect STIX Domain Objects and STIX
Cyber-observable Objects together to form a more complete understanding of the
threat landscape.
STIX Meta Objects
A STIX Object that provides the necessary glue and
associated metadata to enrich STIX Core Objects to support user and system
workflows.
STIX Bundle Object
An object that provides a wrapper mechanism for packaging
arbitrary STIX content together.
STIX is a connected graph of nodes and edges. STIX Domain
Objects and STIX Cyber-observable Objects define the graph nodes and STIX
relationships (including both external STIX Relationship Objects and embedded
relationships) define the edges. This graph-based language conforms to common
analysis approaches and allows for flexible, modular, structured, and
consistent representations of CTI.
STIX defines a set of STIX Domain Objects (SDOs): Attack
Pattern, Campaign, Course of Action, Grouping, Identity, Indicator,
Infrastructure, Intrusion Set, Location, Malware, Malware Analysis, Note,
Observed Data, Opinion, Report, Threat Actor, Tool, and Vulnerability. Each of
these objects corresponds to a concept commonly used in CTI.
STIX Domain Objects are defined in section 4.
STIX defines a set of STIX Cyber-observable Objects (SCOs)
for characterizing host-based and network-based information. SCOs are used by
various STIX Domain Objects (SDOs) to provide supporting context. The Observed
Data SDO, for example, indicates that the raw data was observed at a particular
time.
STIX Cyber-observable Objects (SCOs) document the facts
concerning what happened on a network or host, and do not capture the who,
when, or why. By associating SCOs with STIX Domain Objects (SDOs), it is
possible to convey a higher-level understanding of the threat landscape, and to
potentially provide insight as to the who and the why particular intelligence
may be relevant to an organization. For example, information about a file that
existed, a process that was observed running, or that network traffic occurred
between two IPs can all be captured as SCOs.
STIX Cyber-observable Objects (SCOs) are defined in section 6.
Previously, in STIX 2.0, Cyber-observable Objects could only
exist as objects within an Observed Data object. It is still possible to
represent Cyber-observable Objects in this way, but this method has been
deprecated. See section 2.13.
A relationship is a link between STIX Domain Objects (SDOs),
STIX Cyber-observable Objects (SCOs), or between an SDO and a SCO that
describes the way in which the objects are related. Relationships can be
represented using an external STIX Relationship Object (SRO) or, in some cases,
through certain properties which store an identifier reference that comprises
an embedded relationship, (for example the created_by_ref
property).
The generic STIX Relationship Object (SRO) is one of two
SROs and is used for most relationships in STIX. This generic SRO contains a
property called relationship_type
to describe more specifically what the relationship represents. This
specification defines a set of known terms to use for the relationship_type property between SDOs
of specific types. For example, the Indicator SDO defines a relationship from
itself to Malware via a relationship_type
of indicates
to describe how the Indicator can be used to detect the presence of the
corresponding Malware. In addition to the terms defined in the specification,
STIX also allows for user-defined terms to be used as the relationship type.
Currently the only other SRO (besides a generic
Relationship) is the Sighting SRO. The Sighting object is used to capture cases
where an entity has "seen" an SDO, such as sighting an indicator.
Sighting is a separate SRO because it contains additional properties such as count that are only applicable to
Sighting relationships. Other SROs may be defined in future versions of STIX if
new relationships are identified that also require additional properties not
present on the generic Relationship object.
In addition to relationships created using the SROs
(Relationship and Sighting), STIX also uses ID references to represent embedded
relationships. Embedded relationships are simply ID reference properties on
STIX Objects that contain the ID of a different STIX Object. Embedded
relationships are used when the property is an inherent part of the object and
not something that a third party might add or something that might require the
inclusion of a confidence score. Because they represent an inherent linkage and
have no other properties, an SRO is not needed to represent them. An embedded
relationship can only be asserted by the creator of the object ("object
creator") it is contained in.
For example, the entity that created a STIX Object is an
inherent, factual part of that object and therefore that information is
captured in an embedded relationship contained in the created_by_ref property rather than
through the use of an SRO.
Embedded relationships (ID references) are described in
section 3.4 and STIX Relationship Objects (SROs) are defined in section 5.
While refining STIX for the 2.1 specification, the CTI TC
reached consensus that the STIX 2.0 Cyber Observable Container (see section 2.13) and
the Observed Data object's graph within a graph model was insufficient to
support critical CTI use cases. Consequently, in STIX 2.1, the Cyber Observable
Container is deprecated, and implementers are encouraged to use STIX
Relationship Objects (SROs) instead. Within the context of the (deprecated)
Cyber Observable Container's graph within a graph model, an object relationship
is a reference linking two (or more) related SCOs and these relationships are
constrained to SCOs contained within the same Cyber Observable Container.
A Cyber Observable Container relationship should not be
confused with STIX Relationship Objects (SROs) that are defined in section 5.
Each STIX Cyber-observable Object (SCO) defines a set of
base properties that are generally applicable for any instance of that object.
However, there is also a need to encode additional data beyond the base
definition of the object data models. To enable this, STIX permits the
specification of additional properties through the set of predefined SCO
Extensions. Where applicable, predefined SCO Extensions are included within the
definition of the corresponding SCOs. For example, the File SCO includes
predefined Extensions for characterizing PDF files, raster image files, archive
files, NTFS files, and Windows PE binary files.
Producers may also define and include their own Custom SCO
Extensions. For further information, refer to section 11.3 (Custom Object Extensions.)
The STIX Patterning language enables the detection of
activity on networks and endpoints. This language allows matching against time
stamped cyber observable data collected by a threat intelligence platform or
other similar system. STIX Patterning is currently only used by the STIX
Indicator object, but it can be employed in other use cases.
Before undertaking work on STIX Patterning, a thorough
effort to evaluate existing patterning languages (e.g., Snort or Yara) was
performed. This effort identified that no existing patterning language solves
or supports the STIX use cases. Extending other language was ruled out as
unfeasible, both from a technical perspective as well as taking into
consideration that from a licensing/IPR perspective, extending an existing
language under the auspices of OASIS would have been problematic.
STIX Patterning was primarily designed to support STIX
Indicators. As such it is a mechanism for communicating how to find malicious
code and/or threat actors active within a given network or endpoint.
This language release is focused on supporting a common set
of use cases and therefore allows for the expression of an initial set of
patterns that producers and consumers of STIX can utilize. As more complex
patterns are deemed necessary, the STIX patterning language will be extended in
future releases to improve its effectiveness as an automated
detection/remediation method.
STIX Patterning is defined in section 9.
The latest ANTLR grammar for the patterning specification
can be found on Github in the Pattern Grammar repository [Pattern Grammar].
Note that this grammar is non-normative and is intended solely as an aid to
implementers.
STIX Domain Objects (SDOs) and Relationship Objects (SROs)
all share a common set of properties which provide core capabilities such as
versioning and data markings (representing how data can be shared and used).
All STIX Cyber-observable Objects (SCOs) likewise share a common set of
properties that are applicable for all SCOs. Similarly, STIX Meta Object use
some but not all of the common properties.
Some STIX properties are defined using open vocabularies or
enumerations. Enumerations and open vocabularies are defined in STIX in order
to enhance interoperability by increasing the likelihood that different
entities use the same exact string to represent the same concept. If used
consistently, open vocabularies make it less likely that one entity refers to
the energy sector as “Energy” and another as “Energy Sector”, thereby making comparison
and correlation easier.
While using predefined values from STIX vocabularies is
strongly encouraged, in some cases this may not be feasible. To address this,
producers are permitted to use values outside of the open vocabulary. In the
case of enumerations, producers are required to use only the values defined
within the STIX specification.
STIX open vocabularies and enumerations are defined in
section 10.
Properties that are defined as open vocabularies
identify a suggested vocabulary from that section. For example, the Threat
Actor sophistication property, as defined in section 4.16, uses the Threat Actor Sophistication vocabulary as
defined in section 10.24.
Reserved property names are marked with a type called RESERVED
and a description text of “RESERVED FOR FUTURE USE”. For more information
please see section 3.8.
STIX is defined independent of any specific storage or
serialization. However, the mandatory-to-implement (MTI) serialization for STIX
2.1 is UTF-8 encoded JSON as defined in [RFC7493] and [RFC8259], which uses the JSON Object type
described within when representing all STIX Objects. In other words, all
STIX-conformant tools have to implement support for JSON but can implement
support for other serializations.
STIX 2.1 is transport-agnostic, i.e., the structures and
serializations do not rely on any specific transport mechanism. A companion CTI
specification, TAXII™,
is designed specifically to transport STIX Objects. STIX provides a Bundle (see
section 8)
as a container for STIX Objects to allow for transportation of bulk STIX data,
especially over non-TAXII communication mechanisms.
JSON schemas have been developed by members of the Cyber
Threat Intelligence Technical Committee and are available in the
cti-stix2-json-schemas OASIS Open Repository [JSON Schema]. The JSON schemas are
informative and serve as a best effort attempt to validate that STIX 2.1
content meets the structural requirements identified in this specification.
This specification is the normative description of STIX 2.1.
TC EDITORS: PLEASE REMOVE THIS SECTION BEFORE CS BALLOT
While the eventual version indicator for this version of the
specification will be "2.1", implementations of draft versions (CSDs)
of this specification SHOULD instead advertise "2.1-draft02" in all
places where the specification version is referenced (for example, spec_version property,
API-roots, media types, etc). This allows implementations to safely perform
content negotiation with each other, even if they would otherwise be
incompatible. When this specification is marked as final by the Technical
Committee, having advanced to either a CS (committee specification) or an OASIS
Standard, implementations MUST only advertise "2.1" to
represent this specification. Any content that was used prior to this
specification becoming final and has a designation of "-draftXX") MAY
be converted to the final version or deleted.
This section lists all of the major changes from the previous
2.0 version of STIX.
STIX 2.1 differs from STIX 2.0 in the following ways:
- New objects: Grouping, Infrastructure,
Language-Content (internationalization), Location, Malware-Analysis, Note,
Opinion
- Objects that have undergone significant change:
Course of Actions, Malware, all SCOs
- New concepts: Confidence
- STIX Cyber-observable Objects can now be
directly related using STIX Relationship Objects
- Renamed conflicting properties on Directory
Object, File Object, Process Object, and Windows Registry Key Object.
- Added relationship from Indicator to Observed
Data called "based-on".
- Added a description to Sighting and added a name
to Location.
- Made some SCO relationships external on
Domain-Name, IPv4-Addr, and IPv6-Addr.
AV - Anti-Virus / Anti-Malware solution
CAPEC - Common Attack Pattern Enumeration and
Classification
Consumer - Any entity that receives STIX content
CTI - Cyber Threat Intelligence
Deprecated - STIX features or properties that are in
the process of being replaced by newer ones.
Embedded Relationship - A link (an "edge"
in a graph) between one STIX Object and another represented as a property on
one object containing the ID of another object
Entity - Anything that has a separately identifiable
existence (e.g., organization, person, group, etc.)
IEP - FIRST (Forum of Incident Response and Security
Teams) Information Exchange Policy
Instance - A single occurrence of a STIX Object version
MTI - Mandatory To Implement
Object Creator - The entity that created or updated a
STIX Object (see section 3.3)
Object Representation - An instance of an object
version that is serialized as STIX
Producer - Any entity that distributes STIX content,
including object creators as well as those passing along existing content
SCO - STIX Cyber-observable Object
SDO - STIX Domain Object (a "node" in a
graph)
SRO - STIX Relationship Object (one mechanism to
represent an "edge" in a graph)
STIX - Structured Threat Information Expression
STIX Content - STIX documents, including STIX
Objects, STIX Objects grouped as bundles, etc.
STIX Object - A STIX Domain Object (SDO), STIX Cyber
Observable Object (SCO), STIX Relationship Object (SRO), or STIX Meta Object.
STIX Relationship - A link (an "edge" in a
graph) between two STIX Objects represented by either an SRO or an embedded
relationship
TAXII - An application layer protocol for the
communication of cyber threat information
TLP - Traffic Light Protocol
TTP - Tactic, technique, or procedure; behaviors and
resources that attackers use to carry out their attacks
This section defines the common types
used throughout STIX for all STIX Objects. These types will be referenced by
the “Type” column in other sections. This section defines the names and
permitted values of common types that are used in the STIX information model;
it does not, however, define the meaning of any properties using these types.
These types may be further restricted elsewhere in the document.
The table below lists common STIX data types used within
STIX.
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
binary
|
A sequence of bytes.
|
|
boolean
|
A value of true or false.
|
|
dictionary
|
A set of key/value pairs.
|
|
enum
|
A value from a STIX Enumeration.
|
|
external-reference
|
A non-STIX identifier or reference to
other related external content.
|
|
float
|
An IEEE 754 [IEEE 754-2008] double-precision number.
|
|
hashes
|
One or more cryptographic hashes.
|
|
hex
|
An array of octets as hexadecimal.
|
|
identifier
|
An identifier (ID) is for STIX
Objects.
|
|
integer
|
A whole number.
|
|
kill-chain-phase
|
A name and a phase of a kill chain.
|
|
list
|
A sequence of values ordered based on
how they appear in the list. The phrasing “list of type <type>” is used to
indicate that all values within the list MUST conform to the specified
type.
|
|
observable-container
|
One or more STIX Cyber-observable Objects in the
deprecated Cyber Observable Container.
|
|
open-vocab
|
A value from a STIX open (open-vocab)
or suggested vocabulary.
|
|
string
|
A series of Unicode characters.
|
|
timestamp
|
A time value (date and time).
|
Type Name: binary
The binary data type represents a sequence of bytes. In
order to allow pattern matching on custom objects, for all properties that use
the binary type, the property name MUST end with '_bin'.
The JSON MTI serialization represents this as a
base64-encoded string as specified in
[RFC4648]. Other serializations SHOULD
use a native binary type, if available.
Type Name: boolean
A boolean is a value of either true or
false. Properties with this type MUST have a value of true or false.
The JSON MTI serialization uses the true
and false (boolean) values from the JSON values [RFC8259], which are a literal (unquoted) true or false.
Examples
{
...
"summary": true,
...
}
Type Name: dictionary
A dictionary captures an arbitrary set of key/value
pairs. Dictionary keys MUST be unique in each dictionary, MUST be
in ASCII, and are limited to the characters a-z (lowercase ASCII), A-Z
(uppercase ASCII), numerals 0-9, hyphen (-), and underscore (_). Dictionary
keys MUST be no longer than 250 ASCII characters in length and SHOULD
be lowercase.
dictionary values MUST be valid property base types.
Type Name: enum
The enum type is a hardcoded list of terms that is
represented as a string. For properties that use this type there is a defined
list of values that is identified in the definition for said properties. The
STIX Enumerations are defined in section 10. Terms defined in an enum by
the specification MUST NOT be expanded by implementations.
The JSON MTI serialization uses the JSON String type [RFC8259]
when representing enum.
Type Name: external-reference
External references are used to describe
pointers to information represented outside of STIX. For example, a Malware
object could use an external reference to indicate an ID for that malware in an
external database or a report could use references to represent source
material.
The JSON MTI serialization uses the JSON
Object type [RFC8259]
when representing external-reference.
|
Property Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
source_name (required)
|
string
|
The name of the source that the external-reference is defined within (system, registry,
organization, etc.).
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A human readable description.
|
|
url (optional)
|
string
|
A URL
reference to an external resource [RFC3986].
|
|
hashes
(optional)
|
hashes
|
Specifies a dictionary of hashes for the contents of the url. This SHOULD
be provided when the url property is present.
Dictionary keys MUST come from the hash-algorithm-ov.
As stated in Section 2.7, to ensure interoperability, a
SHA-256 hash SHOULD be included whenever possible.
|
|
external_id (optional)
|
string
|
An identifier for the external reference content.
|
●
In addition to the source_name
property, at least one of the description, url,
or external_id properties MUST
be present.
Examples
An external-reference to a VERIS
Community Database (VCDB) [VERIS]
entry
{
...
"external_references": [
{
"source_name":
"veris",
"external_id":
"0001AA7F-C601-424A-B2B8-BE6C9F5164E7",
"url": "https://github.com/vz-risk/VCDB/blob/125307638178efddd3ecfe2c267ea434667a4eea/
data/json/validated/0001AA7F-C601-424A-B2B8-BE6C9F5164E7.json",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"6db12788c37247f2316052e142f42f4b259d6561751e5f401a1ae2a6df9c674b"
}
}
],
...
}
An external-reference from the CAPEC™ [CAPEC] repository
{
...
"external_references": [
{
"source_name":
"capec",
"external_id":
"CAPEC-550"
}
],
...
}
An external-reference from the CAPEC
repository with URL
{
...
"external_references": [
{
"source_name":
"capec",
"external_id":
"CAPEC-550",
"url": "http://capec.mitre.org/data/definitions/550.html"
}
],
...
}
An external-reference to ACME Threat
Intel's report document
{
...
"external_references": [
{
"source_name":
"ACME Threat Intel",
"description":
"Threat report",
"url": "http://www.example.com/threat-report.pdf"
}
],
...
}
An external-reference to a Bugzilla item
{
...
"external_references": [
{
"source_name":
"ACME Bugzilla",
"external_id":
"1370",
"url": "https://www.example.com/bugs/1370"
}
],
...
}
An external-reference to an offline
threat report (i.e., e-mailed, offline, etc.)
{
...
"external_references": [
{
"source_name":
"ACME Threat Intel",
"description":
"Threat report"
}
],
...
}
Type Name: float
The float data type represents an IEEE
754 [IEEE 754-2008]
double-precision number (e.g., a number with a fractional part). However,
because the values ±Infinity and NaN are not representable in JSON, they are
not valid values in STIX.
In the JSON MTI serialization, floating
point values are represented by the JSON Number type [RFC7493].
Examples
{
...
"distance": 8.321,
...
}
Type Name: hashes
The Hashes type represents one or more cryptographic hashes,
as a special set of key/value pairs. Accordingly, the name of each hashing
algorithm MUST be specified as a key in the dictionary and MUST
identify the name of the hashing algorithm used to generate the corresponding
value. This name SHOULD come from one of the values defined in the hash-algorithm-ov.
Dictionary keys MUST be unique in each hashes
property, MUST be in ASCII, and are limited to the characters a-z
(lowercase ASCII), A-Z (uppercase ASCII), numerals 0-9, hyphen (-), and
underscore (_). Dictionary keys MUST have a minimum length of 3 ASCII
characters and MUST be no longer than 250 ASCII characters in length.
To enhance compatibility, the SHA-256 hash SHOULD be
used whenever possible.
Examples
SHA-256 and User-Defined Hash
{
"SHA-256":
"6db12788c37247f2316052e142f42f4b259d6561751e5f401a1ae2a6df9c674b",
"x_foo_hash":
"aaaabbbbccccddddeeeeffff0123457890"
}
Type Name: hex
The hex data type encodes an array of octets (8-bit
bytes) as hexadecimal. The string MUST consist of an even number of
hexadecimal characters, which are the digits '0' through '9' and the lower-case
letters 'a' through 'f'. In order to allow pattern matching on custom objects,
for all properties that use the hex type, the property name MUST
end with '_hex'.
Examples
...
"src_flags_hex":
"00000002"
...
Type Name: identifier
An identifier uniquely identifies a STIX Object and MAY
do so in a deterministic way. A deterministic identifier means that the identifier
generated by more than one producer for the exact same STIX Object using the
same namespace, "ID Contributing Properties", and UUID method will
have the exact same identifier value.
All identifiers, excluding those used in the deprecated
Cyber Observable Container, MUST follow the form object-type--UUID,
where object-type is the exact value (all type names
are lowercase strings, by definition) from the type property of the object being
identified or referenced and where the UUID MUST
be an RFC 4122-compliant UUID [RFC4122].
The UUID part of the identifier
MUST be unique across all objects produced by a given producer
regardless of the type identified by the object-type
prefix. Meaning, a producer MUST NOT reuse the UUID
portion of the identifier
for objects of different types.
STIX Domain Objects, STIX Relationship Objects, STIX Meta
Objects, and STIX Bundle Object SHOULD use UUIDv4 for the UUID
portion of the identifier.
Producers using something other than UUIDv4 need to be mindful of potential
collisions and should use a namespace that guarantees uniqueness, however, they
MUST NOT use a namespace of 00abedb4-aa42-466c-9c01-fed23315a9b7
if generating a UUIDv5.
STIX Cyber-observable Objects SHOULD use UUIDv5 for
the UUID portion of the identifier and the UUID
portion of the UUIDv5-based identifier SHOULD be generated according to
the following rules:
● The
namespace SHOULD be 00abedb4-aa42-466c-9c01-fed23315a9b7
● The
value of the name portion SHOULD be the list of "ID Contributing
Properties" defined on each SCO and those properties SHOULD be
stringified according to JCS
to ensure a canonical representation of the JSON data.
● Producers
not following these rules MUST NOT use a namespace of 00abedb4-aa42-466c-9c01-fed23315a9b7.
STIX Cyber-observable Objects that are used in the
deprecated Cyber Observable Container MAY use any string
value for the identifier.
For the deprecated Cyber Observable Container, it is common for implementers to
use simple numerical strings for these identifiers (e.g., "0",
"1", "2", etc). See section 2.13 for more information.
● These
identifiers, when used inside the deprecated Cyber-observable Objects Container
specify a local reference to a Cyber-observable Object. These references MUST
be valid within the local scope of the Cyber Observable Container (observable-container)
that holds both the source Cyber-observable Object and the Cyber-observable
Object that it references.
● These
identifiers SHOULD be a non-negative monotonically increasing integer,
incrementing by 1 from a starting value of 0, and represented as a string
within the JSON MTI serialization. However, implementers MAY elect to
use an alternate key format if necessary.
Using Identifiers:
Consumers of STIX Cyber Threat Intelligence that are
processing the objects
property of an Observed-Data
object can assume that the identifier is an old deprecated Cyber Observable
Container identifier.
Consumers can also inspect the identifier to see if it contains an object-type,
if not, they can assume that it is a deprecated Cyber Observable Container identifier.
If it does have an object-type and it matches a SCO,
then chances are it is a UUIDv5 deterministic identifier, but this can be verified
by inspecting the UUID portion of the identifier. RFC 4122
defines how one can distinguish between a UUIDv4 and UUIDv5 value.
The JSON MTI serialization uses the JSON String type [RFC8259]
when representing identifier.
Examples
{
...
"type":
"indicator",
"id":
"indicator--e2e1a340-4415-4ba8-9671-f7343fbf0836",
...
}
{
"type": "ipv4-addr",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--ff26c055-6336-5bc5-b98d-13d6226742dd",
"value": "198.51.100.3"
}
Deprecated Cyber Observable
Container Identifiers
{
"0": {
"type": "ipv4-addr",
"value": "198.51.100.2"
},
"1": {
"type":
"network-traffic",
"dst_ref": "0"
}
}
Type Name: integer
The integer data type represents a whole
number. Unless otherwise specified, all integers MUST be capable of
being represented as a signed 54-bit value ([-(2**53)+1, (2**53)-1]) as defined
in [RFC7493]
. Additional restrictions MAY be placed on the type as described where
it is used. The integer size is limited to a 54-bit value not a 64-bit value as
per the RFC.
In the JSON MTI serialization, integers
are represented by the JSON Number type [RFC7493].
Examples
{
...
"count": 8,
...
}
Type Name: kill-chain-phase
The kill-chain-phase represents a phase in
a kill chain, which describes the various phases an attacker may undertake in
order to achieve their objectives.
The JSON MTI serialization uses the JSON
Object type [RFC8259]
when representing kill-chain-phase.
|
Property Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
kill_chain_name (required)
|
string
|
The name of the kill chain. The value of this property SHOULD be all
lowercase and SHOULD use hyphens instead of spaces or underscores as
word separators.
|
|
phase_name
(required)
|
string
|
The name of the phase in the kill chain. The value of this property SHOULD be all
lowercase and SHOULD use hyphens instead of spaces or underscores as
word separators.
|
When referencing the Lockheed Martin
Cyber Kill Chain™, the kill_chain_name
property MUST be lockheed-martin-cyber-kill-chain.
Examples
Example specifying the “reconnaissance”
phase from the Lockheed Martin Cyber Kill Chain
{
...
"kill_chain_phases": [
{
"kill_chain_name":
"lockheed-martin-cyber-kill-chain",
"phase_name":
"reconnaissance"
}
],
...
}
Example specifying the “pre-attack”
phase from the “foo” kill-chain
{
...
"kill_chain_phases": [
{
"kill_chain_name":
"foo",
"phase_name":
"pre-attack"
}
],
...
}
Type Name: list
The list type defines a sequence of values
ordered based on how they appear in the list. The phrasing “list of
type <type>”
is used to indicate that all values within the list MUST conform to the
specified type. For instance, list of type integer means that all values of the
list must be of the integer type. This specification does not specify the maximum
number of allowed values in a list, however every instance of a list MUST
have at least one value. Specific STIX Object properties may define more
restrictive upper and/or lower bounds for the length of the list.
Empty lists are prohibited in STIX and MUST
NOT be used as a substitute for omitting the property if it is optional. If
the property is required, the list MUST be present and MUST have
at least one value.
The JSON MTI serialization uses the JSON
Array type [RFC8259],
which is an ordered list of zero or more values.
Examples
{
...
"observed_data_refs": [
"observed-data--b67d30ff-02ac-498a-92f9-32f845f448cf",
"observed-data--c96f4120-2b4b-47c3-b61f-eceaa54bd9c6",
"observed-data--787710c9-1988-4a1b-9761-a2de5e19c62f"
],
...
}
Type Name: observable-container
Representing Cyber-observable Objects in an Observable
Container has been deprecated and SHOULD NOT be used when creating new
content. Existing Observable Data objects using Observable Containers may
contain SCOs as defined in this specification, but also may contain
Cyber-observable Objects as described in version 2.0 of STIX (STIX™ Version 2.0. Part
3: STIX Objects).
The Observable Container type can
contain one or more STIX Cyber-observable
Objects as a special set of key/value pairs. The keys in the dictionary are the
references used to refer to an object which is
located in the observable container as a value to some key. The value of this
"key" is a
reference that can be used in the embedded relationship properties in
other objects, which MUST be in the same
container (such as the src_ref property on the Network Traffic object).
Resolving a reference is the
process of identifying all of the objects in an observable container by their
"key" reference value. References resolve
to an object when the value of the property (e.g., src_ref) is an exact match
with the key of another object that resides in
the same container as the object that
specifies the reference. All such references are local to the container
and the referenced object MUST be provided within the same container. This specification does not address the implementation of
reference resolution. Each key in the observable container dictionary is an identifier.
STIX 2.0 Examples
Network Traffic with Source/Destination IPv4 Addresses
and AS
{
"0": {
"type": "ipv4-addr",
"value": "1.2.3.4",
"belongs_to_refs":
["3"]
},
"1": {
"type": "ipv4-addr",
"value": "2.3.4.5"
},
"2": {
"type":
"network-traffic",
"src_ref": "0",
"dst_ref": "1",
}
"3": {
"type": "as"
"number": 42
}
}
{
"0": {
"type": "email-addr",
"value":
"jdoe@example.com",
"display_name": "John
Doe"
},
"1": {
"type": "email-addr",
"value":
"mary@example.com",
"display_name": "Mary
Smith"
},
"2": {
"type":
"email-message",
"from_ref": "0",
"to_refs": ["1"],
"date":
"1997-11-21T15:55:06Z",
"subject": "Saying
Hello"
}
}
Type Name: open-vocab
The open-vocab type is represented as a string.
For properties that use this type there will be a list of suggested values,
known as the suggested vocabulary, that is identified in the definition for
that property. The suggested vocabularies are defined in section 10. The
value of the property SHOULD be chosen from the suggested vocabulary,
but MAY be any other string value. Values that are not from the suggested
vocabulary SHOULD be all lowercase and SHOULD use hyphens instead
of spaces or underscores as word separators.
A consumer that receives STIX content
with one or more open-vocab terms not defined in the suggested vocabulary MAY
ignore those values.
The JSON MTI serialization uses the JSON
String type [RFC8259]
when representing open-vocab.
Examples
Example using value from the suggested
vocabulary. In this example the Threat Actor sophistication
property is an open vocabulary and we are using one of the suggested vocabulary
values.
{
...,
"sophistication": "intermediate",
...
}
Example using a user-defined value. In
this example, for the same Threat Actor sophistication
property, we are not using a value in the suggested vocabulary.
{
...,
"sophistication":
"pbx-advanced-activity",
...
}
Type Name: string
The string data type
represents a finite-length string of valid characters from the Unicode coded
character set [ISO10646].
Unicode incorporates ASCII and the characters of many other international
character sets.
The JSON MTI serialization uses the JSON
String type [RFC8259],
which mandates the UTF-8 encoding for supporting Unicode.
Examples
{
...
"name": "The Black
Vine Cyberespionage Group",
...
}
Type Name: timestamp
The timestamp type defines how dates and
times are represented in STIX.
The JSON MTI serialization uses the JSON
String type [RFC8259]
when representing timestamp.
●
The timestamp
property MUST be a valid RFC 3339-formatted timestamp [RFC3339]
using the format YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss[.s+]Z where
the “s+” represents 1 or more sub-second values. The brackets denote that
sub-second precision is optional, and that if no digits are provided, the
decimal place MUST NOT be present.
●
The timestamp MUST be represented in the UTC timezone and MUST
use the “Z” designation to indicate this.
Examples
{
...
"created":
"2016-01-20T12:31:12.123Z",
...
}
All type names, property names, and literals MUST be
in lowercase, except when referencing canonical names defined in another
standard (e.g., literal values from an IANA registry). Lowercase is defined by
the locality conventions. Words in property names MUST be separated with
an underscore (_), while words in type names and string enumerations MUST
be separated with a hyphen (-). Dictionary key and hash algorithm names MAY
have underscores (_) or hyphens (-). All type names, property names, object
names, and vocabulary terms MUST be between three and 250 characters
long.
Certain names of properties MUST have specific
suffixes.
● If
the value of the property contains an ID reference for embedded relationships
it MUST end in _ref
● If
the value of the property contains a list of embedded relationships it MUST
end in _refs.
● If
the value of the property contains a binary value, it MUST end in _bin.
● If
the value of the property contains a hexadecimal value, it MUST end in _hex.
● A
property might contain a string with an alternative encoding. Some object types
will define an additional optional property to specify this encoding. The name
of the additional property MUST end in _enc.
For example, the name property
might contain text in an alternative encoding, and the name_enc property
would be used to specify which encoding is used. The encoding property MUST
NOT be present when the original property is not present.
In the JSON serialization all property names and string
literals MUST be exactly the same, including case, as the names listed
in the property tables in this specification. For example, the SDO common property
created_by_ref must result in
the JSON key name "created_by_ref". Properties marked required in the
property tables MUST be present in the JSON serialization.
Some properties may be designated as "deprecated".
These properties are in the process of being removed or replaced and
implementers should consider using the newer designs.
This section defines all of the common properties that MAY
exist on a STIX Objects. While some STIX Objects use all of these common
properties, not all object types do. Each type of STIX Object defines which
common properties are required, which are optional, and which are not in use. A
comparison summary table is provided below in this section. This information
can also be found at the start of the properties table for each object.
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type
|
string
|
The type
property identifies the type of STIX Object. The value of the type property MUST be the name
of one of the types of STIX Objects defined in sections 4, 5, 6, and 7 (e.g., indicator)
or the name of a Custom Object as defined by section 11.2.
|
|
spec_version
|
string
|
The version of the STIX specification
used to represent this object.
The value of this property MUST
be 2.1
for STIX Objects defined according to this specification.
If objects are found where this
property is not present, the implicit value for all STIX Objects other than
SCOs is 2.0.
Since SCOs are now top-level objects in STIX 2.1, the default value for SCOs
is 2.1.
|
|
id
|
identifier
|
The id
property uniquely identifies this object.
For objects that support versioning,
all objects with the same id
are considered different versions of the same object and the version of the
object is identified by its modified
property.
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier
|
The created_by_ref
property specifies the id
property of the identity object that describes the entity that created this
object.
If this attribute is omitted, the
source of this information is undefined. This may be used by object creators
who wish to remain anonymous.
|
|
created
|
timestamp
|
The created
property represents the time at which the object was originally created.
The object creator can use the time it
deems most appropriate as the time the object was created, but it MUST be
precise to the nearest millisecond (exactly three digits after the decimal
place in seconds).
The created
property MUST NOT be changed when creating a new version of the
object.
See section 3.6 for further definition of
versioning.
|
|
modified
|
timestamp
|
The modified
property is only used by STIX Objects that support versioning and represents
the time that this particular version of the object was last modified.
The object creator can use the time it
deems most appropriate as the time this version of the object was modified,
but it must be precise to the nearest millisecond (exactly three digits after
the decimal place in seconds).
If the created property is defined, then the value of the modified property for a given object
version MUST be later than or equal to the value of the created property.
Object creators MUST set the modified property when creating a new
version of an object if the created
property was set.
See section 3.6 for further definition of
versioning.
|
|
revoked
|
boolean
|
The revoked
property is only used by STIX Objects that support versioning and indicates
whether the object has been revoked.
Revoked objects are no longer
considered valid by the object creator. Revoking an object is permanent;
future versions of the object with this id
MUST NOT be created.
The default value of this property is false.
See section 3.6 for further definition of
versioning.
|
|
labels
|
list of
type string
|
The labels property specifies a set of terms used to describe this
object. The terms are user-defined or trust-group defined and their meaning
is outside the scope of this specification and MAY be ignored.
Where an
object has a specific property defined in the specification for
characterizing subtypes of that object, the labels property MUST NOT
be used for that purpose.
For example,
the Malware SDO has a property malware_types that contains
a list of Malware subtypes (dropper, RAT, etc.). In this example, the labels
property cannot be used to describe these Malware subtypes.
|
|
confidence
|
integer
|
The confidence
property identifies the confidence that the creator has in the correctness of
their data. The confidence value MUST be a number in the range of
0-100.
Appendix
A contains a table of normative mappings to other confidence
scales that MUST be used when presenting the confidence value in one
of those scales.
If the confidence property is not present, then the
confidence of the content is unspecified.
|
|
lang
|
string
|
The lang property identifies the language of the text
content in this object. When present, it MUST be a language code
conformant to [RFC5646]. If
the property is not present, then the language of the content is en (English).
This property SHOULD
be present if the object type contains translatable text properties (e.g.
name, description).
The language of individual
fields in this object MAY be overridden by the lang property in granular markings (see section 7.2.3).
|
|
external_references
|
list of type
external-reference
|
The external_references property specifies a list of external references which
refers to non-STIX information. This property is used to provide one or more
URLs, descriptions, or IDs to records in other systems.
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list
of type identifier
|
The object_marking_refs
property specifies a list of id
properties of marking-definition objects that apply to this object.
In some cases, though uncommon,
marking definitions themselves may be marked with sharing or handling
guidance. In this case, this property MUST NOT contain any references
to the same Marking Definition object (i.e., it cannot contain any circular
references).
See section 7.2 for further definition of data
markings.
|
|
granular_markings
|
list
of type granular-marking
|
The granular_markings
property specifies a list of granular markings applied to this object.
In some cases, though uncommon,
marking definitions themselves may be marked with sharing or handling
guidance. In this case, this property MUST NOT contain any references
to the same Marking Definition object (i.e., it cannot contain any circular
references).
See section 7.2 for further definition of data
markings.
|
|
defanged
|
boolean
|
This property defines whether or
not the data contained within the object has been defanged.
The default value for this
property is false.
This property MUST
NOT be used on any STIX Objects other than SCOs.
|
|
extensions
|
dictionary
|
Specifies any extensions of the object, as a dictionary.
Dictionary keys MUST identify the extension type by
name.
The corresponding dictionary values MUST contain
the contents of the extension instance.
This property MUST NOT
be used on any STIX Objects other than SCOs.
|
This table lists all common
properties and how they are used for each type of STIX Object. The following
table is informational, and the body of the spec is normative and the
definitive reference.
|
|
STIX Core Objects
|
STIX Helper Objects
|
|
Property Name
|
SDOs
|
SROs
|
SCOs
|
Language
|
Markings
|
Bundle
|
|
type
|
Required
|
Required
|
Required
|
Required
|
Required
|
Required
|
|
spec_version
|
Required
|
Required
|
Optional
|
Required
|
Required
|
N/A
|
|
id
|
Required
|
Required
|
Required
|
Required
|
Required
|
Required
|
|
created_by_ref
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
|
created
|
Required
|
Required
|
N/A
|
Required
|
Required
|
N/A
|
|
modified
|
Required
|
Required
|
N/A
|
Required
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
revoked
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
labels
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
confidence
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
lang
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
external_references
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
|
granular_markings
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
|
defanged
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
extensions
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Optional
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
All STIX Objects and the STIX Bundle
Object have an id property
that uniquely identifies each instance of the object. This id MUST meet the requirements of
the identifier
type (see section 2.9).
The identifier type is also used as an ID
reference to define a relationship to other STIX Objects. Resolving an
ID reference is the process of identifying and obtaining the actual object
referred to by the ID reference property. ID references resolve to an object
when the value of the ID reference property (e.g., created_by_ref) is an exact match with the id property of another object. If a
consumer has access to multiple versions of an object, the consumer SHOULD
interpret any references to that object as referring to the latest version as
defined in section 3.6.
ID references can refer to objects to which the consumer/producer may not
currently have. This specification does not address the implementation of ID
reference resolution.
Some ID references (embedded relationships) may be
restricted to a subset of object types, as specified in the description of the
property that defines the relationship. For example, the object_marking_refs common property
specifies that the only valid target of the relationship is one or more marking-definition
objects.
To enable deterministic IDs for STIX Cyber-observable
Objects (SCOs), each SCO defines a set of one or more properties named “ID
Contributing Properties”. These properties MAY be used in the default
calculation of the id when
creating a SCO. In some cases, additional selection of extension properties
that contribute to the ID may be described in the ID Contributing Properties
section listed on each SCO. The default algorithm that creates the SCO ID based
on those named properties is a UUIDv5 as defined in Section 2.9,
however, other algorithms for creating the SCO ID MAY be used.
Deterministic IDs (UUIDv5) in the example SCOs contained in
this specification were computed using the algorithm defined in section 2.9.
Every attempt was made for these IDs to be accurate. Certain IDs which were
used in reference properties of the examples did not include the actual object,
and therefore it was impossible to accurately compute the appropriate UUIDv5.
In these cases, a UUIDv4 was generated.
The object creator is the entity (e.g.,
system, organization, instance of a tool) that generates the id property for a given object. Object
creators are represented as Identity objects. Some STIX Objects allow this
designation (see Section 3.2). An embedded relationship to the Identity object
representing the object creator SHOULD be captured in the created_by_ref property (or that
property can be omitted, meaning the object creator is anonymous).
Entities that re-publish an object from
another entity without making any changes to the object, and thus maintaining
the original id, are
not considered the object creator and MUST NOT change the created_by_ref property. An entity that
accepts objects and republishes them with modifications, additions, or omissions
MUST create a new id
for the object. They are considered the object creator of the new object for
purposes of versioning.
Versioning is the mechanism that object
creators use to update and revoke the STIX Objects that they create. This section
describes the versioning process and normative rules for performing versioning
and revocation. Some STIX Objects are versioned using the revoked, created, and modified
properties. See the properties table in section 3.2 for full definitions and normative
usage of those properties.
STIX Objects MAY be versioned in
order to update, add, or remove information. A version of a STIX Object is
identified uniquely by the combination of its id
and modified properties. The
first version of the object MUST have the same timestamp for the created and modified properties. More recent values of the modified property indicate later
versions of the object. Implementations MUST consider the version of the
STIX Object with the most recent modified
value to be the most recent state of the object. For every new version of an
object, the modified property MUST
be updated to represent the time that the new version was created. If a
consumer receives two objects that are different, but have the same id and modified timestamp, it is not defined how the consumer
handles the objects. This specification does not address how implementations
should handle versions of the object that are not current.
STIX Objects have a single object
creator, the entity that generates the id
for the object and creates the first version. The object creator MAY
(but not necessarily will) be identified in the created_by_ref property of the object. Only
the object creator is permitted to create new versions of a STIX Object.
Producers other than the object creator MUST NOT create new versions of
that object. If a producer other than the object creator wishes to create a new
version, they MUST instead create a new object with a new id. They SHOULD additionally
create a derived-from
Relationship object to relate their new object to the original object that it
was derived from.
Every representation (each time the
object version is serialized and shared) of a version of an object (identified
by the object's id and modified properties) MUST always
have the same set of properties and the same values for each property. If a
property has the same value as the default, it MAY be omitted from a
representation, and this does not represent a change to the object. In order to
change the value of any property, or to add or remove properties, the modified property MUST be
updated with the time of the change to indicate a new version.
Objects can also be revoked, which means
that they are no longer considered valid by the object creator. As with issuing
a new version, only the object creator is permitted to revoke a STIX Object. A
value of true
in the revoked property
indicates that an object (including the current version and all past versions)
has been revoked. Revocation is permanent: once an object is marked as revoked,
later versions of that object MUST NOT be created. Changing the revoked property to indicate that an
object is revoked is an update to the object, and therefore its modified property MUST be
updated at the same time. This specification does not address how
implementations should handle revoked data.
In STIX 2.1, SCOs do not explicitly have those three
versioning properties. Therefore, a SCO cannot be versioned unless custom
properties (discussed in section 11.1) are used. Producers who do this SHOULD
use the property names created_by_ref,
revoked, created, and modified.
It should be noted that if a producer versions a SCO
(assigns value to these four properties) that no other producer would be
allowed to create or modify the same SCO with an equivalent deterministic id,
as that would conflict with the strict versioning rules defined in STIX2.
Therefore, for interoperability and sharing, producers versioning SCOs MUST
NOT use the default namespace for deterministic ID creation. Otherwise
multiple different producers will conflict with each other if producing the
same SCO intelligence.
There are two timestamp properties used
to indicate when STIX Objects were created and modified: created and modified. The created
property indicates the time the first version of the object was created. The modified property indicates the time
the specific version of the object was created. The modified time MUST NOT be earlier than the created time. This specification does
not address the specifics of how implementations should determine the value of the creation
and modification times for use in the created and modified properties (e.g., one system might use when the object is first
added to the local database as the creation time, while another might use the
time when the object is first distributed as STIX).
Eventually an implementation will
encounter a case where a decision must be made regarding whether a change is a
new version of an existing object or is different enough that it is a new
object. This is generally considered a data quality problem and therefore this
specification does not provide any normative text.
However, to assist implementers and
promote consistency across implementations, some rules of thumb are provided.
Any time a change indicates a material change to the meaning of the
object, a new object with a different id
should be used. A material change is any change that the object creator
believes substantively changes the meaning of the object. As an example, an
object creator might consider changing a Threat Actor from one country to
another is a material change. These decisions are always made by the object
creator. The object creator should also think about relationships to the object
when deciding if a change is material. If the change would invalidate the
usefulness of relationships to the object, then the change is considered
material and a new object id
should be used.
Examples
Example of a new version
One object creator has decided that the
previous name they used for an SDO is incorrect. They consider that change as
an update to the object.
Note: the IDs in the example below
use a simplified format to help illustrate the changing IDs more clearly.
|
Step #
|
STIX Object
|
Object Creator Action
|
|
1
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--1",
"created":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"name":
"attention",
"description": "this is the description"
}
|
Original version of an object is
created.
|
|
2
|
N/A, STIX is not involved in this step
|
Object creator changes the name in
their internal database.
|
|
3
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--1",
"created":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-08T03:43:44.000Z",
"name":
"Attention!",
"description": "this is the description"
}
|
Object creator updates the modified property.
|
Example of derived object
One object creator has decided that the
previous name they used for an SDO is incorrect. They consider that change
fundamental to the meaning of the object and therefore revoke the object and
issue a new one.
|
Step #
|
STIX Object
|
Object Creator Action
|
|
1
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--2",
"created":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"name":
"attention",
"description": "this is the description"
}
|
Original object created (via new id
and setting created and modified to the same value).
|
|
2
|
N/A, STIX is not involved in this step
|
Object creator changes the name in
their internal database.
|
|
3
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--2",
"created":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-08T03:43:44.000Z",
"name":
"attention",
"description": "this is the description",
"revoked":
true
}
|
Object creator revokes the existing
object by setting revoked to true. The modified property is updated.
|
|
4
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--3",
"created":
"2016-05-08T03:43:44.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-08T03:43:44.000Z",
"name":
"Something completely different",
"description": "this is the description"
}
|
Object creator creates a new object
(with a new id and setting created and modified to the same value).
|
|
5
|
{
"type":
"relationship",
"id":
"relationship--4",
"created":
"2016-05-08T03:43:44.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-08T03:43:44.000Z",
"relationship_type": "derived-from",
"source_ref": "example--2",
"target_ref": "example--3"
}
|
(Optional) Object creator creates a
new Relationship indicating that the new object is derived from the old
object.
|
Example of consumer workflow
This section describes an example
workflow where a consumer receives multiple updates to a particular object. (In
this example, the STIX Objects have been truncated for brevity.)
|
Step #
|
Received STIX Object
|
Recipient Action
|
|
1
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--5",
"created":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z"
}
|
Consumer stores example object because
this is the first time they have seen the object.
|
|
2
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--5",
"created":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-08T03:43:44.000Z"
}
|
Consumer updates example object
because the received modified
property is later than the object that is currently stored.
|
|
3
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--5",
"created":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-06T06:23:45.000Z"
}
|
Consumer ignores this object because
they already have a newer version of the object.
Note: consumer might choose to store
meta-information about received objects, including versions that were
received out-of-order. The consumer also may choose to store a copy for
reference.
|
|
4
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--5",
"created":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-11T06:41:21.000Z",
"revoked":
true
}
|
Consumer receives revoked version and decides
to delete example object but keeps some metadata regarding the object.
|
|
5
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--5",
"created":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-10T17:28:54.000Z"
}
|
Consumer ignores this object because
they already have a newer version of the object (the revoked version).
|
Example of object creator workflow
This section describes an example
workflow where an object creator publishes multiple updates to a particular
object. This scenario assumes a human using a STIX implementation. (In this
example, the STIX Objects have been truncated for brevity.)
|
Step #
|
STIX Object
|
User Action
|
|
1
|
N/A –
STIX is not involved in this scenario.
(Tools could
choose to create and track STIX versions for internal changes, but it is
not required by the specification.)
|
User clicks a create button in the
user interface, creates an SDO, then clicks save. This action causes
information to be stored in the product’s database.
|
|
2
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--6",
"created":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z"
}
|
The user clicks the “share” button,
delivering the intelligence to sharing partners.
|
|
3
|
N/A –
STIX is not involved in this scenario.
(Tools could
choose to create and track STIX versions for internal changes, but it is
not required by the specification.)
|
The user performs additional analysis
within the STIX implementation, performing multiple modifications and saving
their work multiple times.
|
|
4
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--6",
"created":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-03T16:33:51.000Z"
}
|
The user, happy with the status of
their work, decides to provide an update to some properties of the previously
published object (not shown).
|
|
5
|
{
"type":
"example",
"id":
"example--6",
"created":
"2016-05-01T06:13:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-08T13:35:12.000Z",
"revoked":
true
}
|
The user receives lots of negative
feedback regarding the quality of their work and decides to retract the object
by pressing the “revoke” button.
|
Each SDO and SCO has its own set of
relationship types that are specified in the definition of that SDO or SCO. The
following common relationship types are defined for all SDOs and SCOs. See
section 1.6.4
for more information about relationships.
|
Relationship
Type
|
Source
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
derived-from
|
<SDO or SCO of same type as target>
|
<SDO or SCO of same type as source>
|
The information in the target object
is based on information from the source object.
derived-from is an explicit
relationship between two separate objects and MUST NOT be used as a
substitute for the versioning process defined in section 3.6.
|
|
duplicate-of
|
<SDO or SCO of same type as target>
|
<SDO or SCO of same type as source>
|
The referenced source and target
objects are semantically duplicates of each other.
This specification does not address
whether the source or the target object is the duplicate object or what
action, if any, a consumer should take when receiving an instance of this
relationship.
As an example, a Campaign object from
one organization could be marked as a duplicate-of a Campaign object from
another organization if they both described the same campaign.
|
|
related-to
|
<SDO or SCO of any type>
|
<SDO or SCO of any type>
|
Asserts a non-specific relationship
between two SDOs. This relationship can be used when none of the other
predefined relationships are appropriate, and a user-defined one is not
needed.
As an example, a Malware object
describing a piece of malware could be marked as a related-to a Tool if they
are commonly used together. That relationship is not common enough to
standardize but may be useful to some analysts.
|
This section defines property names that
are reserved for future revisions of this document. The property names defined
in this section and any property name that is marked as RESERVED MUST NOT be
used for the name of any Custom Property or be present in any STIX content
conforming to this version of the specification.
Properties that are currently reserved
across all STIX Objects are:
●
severity
●
usernames
●
phone_numbers
In addition, the following object type
names are reserved:
●
incident
●
action
Capturing the observed encoding of a particular STIX
Cyber-observable Object (SCO) string is useful for attribution, the creation of
indicators, and related use cases.
Certain string properties in STIX Cyber-observable Objects
may contain an additional sibling property with the same base name and a suffix
of _enc that captures the name
of the original observed encoding of the property value. All _enc properties MUST specify
their encoding using the corresponding name from the IANA character set
registry [Character Sets] . If the preferred MIME
name for a character set is defined, this value MUST be used; if it is
not defined, then the Name value from the registry MUST be used instead.
Examples
File with Unicode representation of the filename and a
corresponding encoding specification
{
"type": "file",
"id": "file-1389b98d-a3d3-5190-a996-716fd444059a",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"effb46bba03f6c8aea5c653f9cf984f170dcdd3bbbe2ff6843c3e5da0e698766"
},
"name": "quêry.dll",
"name_enc":
"windows-1252"
}
Predefined Object Extensions have a specific purpose in STIX
Cyber-observable Objects (SCOs): defining coherent sets of properties beyond
the base, e.g., HTTP request information for a Network Traffic object.
Accordingly, each SCO may include one or more Predefined Object Extensions.
Each Predefined Object Extension can be defined at most once
on a given SCO. In an Observable Object instance, each extension is specified
under the extensions property,
which is of type dictionary. Note that this means that each extension is
specified through a corresponding key in the extensions property. For example, when
specified in a File object instance, the NTFS extension would be specified
using the key value of ntfs-ext.
Examples
Basic File with NTFS Extension
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--1b40e321-ae73-5637-bd97-33c35a86b80d",
"hashes": {
"MD5":
"3773a88f65a5e780c8dff9cdc3a056f3"
},
"size": 25537,
"extensions": {
"ntfs-ext": {
"sid": "1234567"
}
}
}
This specification defines the set of
STIX Domain Objects (SDOs), each of which corresponds to a unique concept
commonly represented in CTI. Using SDOs, STIX Cyber-observable Objects (SCOs),
and STIX Relationship Objects (SROs) as building blocks, individuals can create
and share broad and comprehensive cyber threat intelligence.
Property information, relationship
information, and examples are provided for each SDO defined below. Property
information includes common properties as well as properties that are specific
to each SDO. Relationship information includes embedded relationships (e.g., created_by_ref), common relationships
(e.g., related-to),
and SDO-specific relationships. Forward relationships (i.e., relationships from
the SDO to other SDOs or SCOs) are fully defined, while reverse
relationships (i.e., relationships to the SDO from other SDOs or SCOs)
are duplicated for convenience.
Some SDOs are similar and can be grouped
together into categories. Attack Pattern, Malware, and Tool can all be
considered types of tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs): they describe
behaviors and resources that attackers use to carry out their attacks.
Similarly, Campaign, Intrusion Set, and Threat Actor all describe information
about why adversaries carry out attacks and how they organize themselves.
4.1 Attack Pattern
Type Name: attack-pattern
Attack Patterns are a type of TTP that
describe ways that adversaries attempt to compromise targets. Attack Patterns
are used to help categorize attacks, generalize specific attacks to the
patterns that they follow, and provide detailed information about how attacks
are performed. An example of an attack pattern is "spear phishing": a
common type of attack where an attacker sends a carefully crafted e-mail
message to a party with the intent of getting them to click a link or open an
attachment to deliver malware. Attack Patterns can also be more specific; spear
phishing as practiced by a particular threat actor (e.g., they might generally
say that the target won a contest) can also be an Attack Pattern.
The Attack Pattern SDO contains textual
descriptions of the pattern along with references to externally-defined
taxonomies of attacks such as CAPEC [CAPEC].
4.1.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Attack
Pattern Specific Properties
|
|
name,
description, aliases, kill_chain_phases
|
|
Property Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type
(required)
|
string
|
The value of this property MUST be attack-pattern.
|
|
external_references
(optional)
|
list of type
external-reference
|
A list of
external references which refer to non-STIX information. This property MAY
be used to provide one or more Attack Pattern identifiers, such as a
CAPEC ID. When specifying a CAPEC ID, the source_name
property of the external reference MUST be set to capec and the external_id property MUST
be formatted as CAPEC-[id].
|
|
name
(required)
|
string
|
A name used
to identify the Attack Pattern.
|
|
description
(optional)
|
string
|
A
description that provides more details and context about the Attack Pattern,
potentially including its purpose and its key characteristics.
|
|
aliases (optional)
|
list of type string
|
Alternative names used to identify this Attack Pattern.
|
|
kill_chain_phases (optional)
|
list of type kill-chain-phase
|
The list of
Kill Chain Phases for which this Attack Pattern is used.
|
4.1.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
Attack Pattern object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the
embedded relationships by property name along with their corresponding target.
The rest of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this
object type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The
reverse relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this object
type from another object type. They are included here for convenience. For
their definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
Common
Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from,
related-to
|
|
Source
|
Relationship
Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
attack-pattern
|
delivers
|
malware
|
This Relationship describes that this
Attack Pattern is used to deliver this malware instance (or family).
|
|
attack-pattern
|
targets
|
identity, location, vulnerability
|
This Relationship describes that this
Attack Pattern typically targets the type of victim, location, or
vulnerability represented by the related Identity, Location, or Vulnerability
object.
For example, a targets Relationship
linking an Attack Pattern for SQL injection to an Identity object
representing domain administrators means that the form of SQL injection
characterized by the Attack Pattern targets domain administrators in order to
achieve its objectives.
Another example is a Relationship
linking an Attack Pattern for SQL injection to a Vulnerability in blogging
software means that the particular SQL injection attack exploits that
vulnerability.
|
|
attack-pattern
|
uses
|
malware, tool
|
This Relationship describes that the
related Malware or Tool is used to perform the behavior identified in the
Attack Pattern.
For example, a uses Relationship linking
an Attack Pattern for a distributed denial of service (DDoS) to a Tool for
Low Orbit Ion Cannon (LOIC) indicates that the tool can be used to perform
those DDoS attacks.
|
|
Reverse
Relationships
|
|
indicator
|
indicates
|
attack-pattern
|
See forward relationship for
definition.
|
|
course-of-action
|
mitigates
|
attack-pattern
|
See forward relationship for
definition.
|
|
campaign, intrusion-set,
malware, threat-actor
|
uses
|
attack-pattern
|
See forward relationship for
definition.
|
Examples
A generic attack pattern for spear
phishing, referencing CAPEC
{
"type":
"attack-pattern",
"spec_version":
"2.1",
"id":
"attack-pattern--0c7b5b88-8ff7-4a4d-aa9d-feb398cd0061",
"created":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"name": "Spear
Phishing",
"description":
"...",
"external_references": [
{
"source_name":
"capec",
"external_id":
"CAPEC-163"
}
]
}
A specific attack pattern for a
particular form of spear phishing, referencing CAPEC
[
{
"type":
"attack-pattern",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"attack-pattern--7e33a43e-e34b-40ec-89da-36c9bb2cacd5",
"created":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"name": "Spear
Phishing as Practiced by Adversary X",
"description": "A
particular form of spear phishing where the attacker claims that the target had
won a contest, including personal details, to get them to click on a
link.",
"external_references": [
{
"source_name":
"capec",
"external_id":
"CAPEC-163"
}
]
},
{
"type":
"relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--57b56a43-b8b0-4cba-9deb-34e3e1faed9e",
"created":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"uses",
"source_ref":
"intrusion-set--0c7e22ad-b099-4dc3-b0df-2ea3f49ae2e6",
"target_ref":
"attack-pattern--7e33a43e-e34b-40ec-89da-36c9bb2cacd5"
},
{
"type":
"intrusion-set",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"intrusion-set--0c7e22ad-b099-4dc3-b0df-2ea3f49ae2e6",
"created":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"name": "Adversary
X"
}
]
4.2 Campaign
Type Name: campaign
A Campaign is a grouping of adversarial
behaviors that describes a set of malicious activities or attacks (sometimes
called waves) that occur over a period of time against a specific set of
targets. Campaigns usually have well defined objectives and may be part of an Intrusion
Set.
Campaigns are often attributed to an
intrusion set and threat actors. The threat actors may reuse known
infrastructure from the intrusion set or may set up new infrastructure specific
for conducting that campaign.
Campaigns can be characterized by their
objectives and the incidents they cause, people or resources they target, and
the resources (infrastructure, intelligence, Malware, Tools, etc.) they use.
For example, a Campaign could be used to
describe a crime syndicate's attack using a specific variant of malware and new
C2 servers against the executives of ACME Bank during the summer of 2016 in
order to gain secret information about an upcoming merger with another bank.
4.2.1 Properties
|
Required
Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Campaign Specific
Properties
|
|
name,
description, aliases, first_seen, last_seen,
objective
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be campaign.
|
|
name (required)
|
string
|
A name used
to identify the Campaign.
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A
description that provides more details and context about the Campaign,
potentially including its purpose and its key characteristics.
|
|
aliases
(optional)
|
list of type string
|
Alternative names used to identify
this Campaign
|
|
first_seen (optional)
|
timestamp
|
The time
that this Campaign was first seen.
This
property is a summary property of data from sightings and other data that may
or may not be available in STIX. If new sightings are received that are
earlier than the first seen timestamp, the object may be updated to account
for the new data.
|
|
last_seen (optional)
|
timestamp
|
The time
that this Campaign was last seen.
This
property is a summary property of data from sightings and other data that may
or may not be available in STIX. If new sightings are received that are later
than the last seen timestamp, the object may be updated to account for the
new data.
This MUST be greater than
or equal to the timestamp in the first_seen property.
|
|
objective (optional)
|
string
|
This
property defines the Campaign’s primary goal, objective, desired outcome, or
intended effect — what the Threat Actor or Intrusion Set hopes to accomplish
with this Campaign.
|
4.2.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
Campaign object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the embedded
relationships by property name along with their corresponding target. The rest
of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this object
type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The reverse
relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this object type
from another object type. They are included here for convenience. For their
definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
Common
Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Relationship
Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
campaign
|
attributed-to
|
intrusion-set, threat-actor
|
This Relationship describes that the
Intrusion Set or Threat Actor that is involved in carrying out the Campaign.
For example, an attributed-to
Relationship from the Glass Gazelle Campaign to the Urban Fowl Threat Actor
means that the actor carried out or was involved in some of the activity
described by the Campaign.
|
|
campaign
|
compromises
|
infrastructure
|
This Relationship describes that the
Campaign compromises the related Infrastructure.
|
|
campaign
|
originates-from
|
location
|
This Relationship describes that the Campaign originates
from the related Location.
For example, an originates-from relationship from
the Glass Gazelle Campaign to a Location representing North America means
that Glass Gazelle appears to originate from or is located in North America.
|
|
campaign
|
targets
|
identity, location, vulnerability
|
This Relationship describes that the
Campaign uses exploits of the related Vulnerability or targets the type of
victims described by the related Identity or Location.
For example, a targets Relationship from
the Glass Gazelle Campaign to a Vulnerability in a blogging platform
indicates that attacks performed as part of Glass Gazelle often exploit that
Vulnerability.
Similarly, a targets Relationship from
the Glass Gazelle Campaign to an Identity describing the energy sector in the
United States means that the Campaign typically carries out attacks against
targets in that sector.
|
|
campaign
|
uses
|
attack-pattern, infrastructure,
malware,
tool
|
This Relationship describes that
attacks carried out as part of the Campaign typically use the related Attack
Pattern, Infrastructure, Malware, or Tool.
For example, a uses Relationship from the
Glass Gazelle Campaign to the xInject Malware indicates that xInject is often
used during attacks attributed to that Campaign.
A campaign, threat actor, intrusion
set, malware, or tool takes infrastructure and compromises and/or uses it for
their own.
|
|
Reverse
Relationships
|
|
indicator
|
indicates
|
campaign
|
See forward relationship for
definition.
|
Examples
{
"type":
"campaign",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"campaign--8e2e2d2b-17d4-4cbf-938f-98ee46b3cd3f",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:03:00.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:03:00.000Z",
"name": "Green Group
Attacks Against Finance",
"description":
"Campaign by Green Group against a series of targets in the financial
services sector."
}
4.3 Course of Action
Type Name: course-of-action
A Course of Action (CoA) is a recommendation from a producer
of intelligence to a consumer on the actions that they might take in response
to that intelligence. The CoA may be preventative to deter exploitation or
corrective to counter its potential impact. The CoA may describe automatable
actions (applying patches, configuring firewalls, etc.), manual processes, or a
combination of the two. For example, a CoA that describes how to remediate a
vulnerability could describe how to apply the patch that removes that
vulnerability.
The CoA includes the encoded content of an action or a
reference to an externally defined action identified by the action_type
property.
4.3.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Course of
Action Specific Properties
|
|
name, description, action_type, os_execution_envs, action_bin, action_reference
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be course-of-action.
|
|
name (required)
|
string
|
A name used
to identify the Course of Action.
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A
description that provides more details and context about the Course of
Action, potentially including its purpose and its key characteristics. In
some cases, this property may contain the actual course of action in prose
text.
|
|
action_type
(optional)
|
open-vocab
|
The type of
action that is included in either the action_bin property or the
dereferenced content from the action_reference property.
For example: textual:text/plain
This is an open vocabulary and
values SHOULD come from the course-of-action-type-ov vocabulary.
|
|
os_execution_envs (optional)
|
list of type string
|
A recommendation on the
operating system(s) that this course of action can be applied to.
If no os_execution_envs
are defined, the operating systems for the action specified by the action_type property are undefined, or the specific
operating system has no impact on the execution of the course of action
(e.g., power off system).
Each string value for this
property SHOULD be a CPE v2.3 entry from the official NVD CPE
Dictionary [NVD].
This property MAY include custom values including values taken from
other standards such as SWID [SWID].
Example:
[
cpe:2.3:o:microsoft:windows_10:*:*:*:*:*:*:x86:*,
cpe:2.3:o:microsoft:windows_10:*:*:*:*:*:*:x64:*
]
This example
means that any version of the Windows 10 operating system is able to process
and use the course of action defined in the action_bin or action_reference properties.
|
|
action_bin (optional)
|
binary
|
This property contains the
base64 encoded "commands" that represent the action for this Course
of Action.
This property MUST NOT be
present if action_reference is provided.
|
|
action_reference (optional)
|
external-reference
|
The value of this property MUST
be a valid external reference that resolves to the action content as defined
by the action_type property.
This property MUST NOT be
present if action_bin is provided.
|
4.3.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the Course
of Action object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the embedded
relationships by property name along with their corresponding target. The rest
of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this object
type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The reverse
relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this object type
from another object type. They are included here for convenience. For their
definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
Common
Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Relationship
Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
course-of-action
|
investigates
|
indicator
|
This Relationship describes that the Course of Action can
be used to investigate the Indicator.
|
|
course-of-action
|
mitigates
|
attack-pattern,
indicator, malware,
tool,
vulnerability
|
This Relationship describes that the Course of Action can mitigate
(e.g. respond to a threat) the related Attack Pattern, Indicator, Malware,
Vulnerability, or Tool.
For example, a mitigates Relationship from a Course
of Action object to a Malware object indicates that the course of action
mitigates the malware.
|
|
course-of-action
|
remediates
|
malware, vulnerability
|
This Relationship describes that the Course of Action can
be used to remediate (e.g. clean up) the malware or vulnerability
|
|
Reverse
Relationships
|
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
Examples
[
{
"type":
"course-of-action",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"course-of-action--8e2e2d2b-17d4-4cbf-938f-98ee46b3cd3f",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:03:48.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:03:48.000Z",
"name":
"mitigation-poison-ivy-firewall",
"description": "This action
points to a recommended set of steps to respond to the Poison Ivy malware on a
Cisco firewall device",
"action_type":
"cisco:ios",
"action_reference":
{ "source_name":
"internet",
"url":
"hxxps://www.stopthebad.com/poisonivyresponse.asa"
}
},
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id": "relationship--44298a74-ba52-4f0c-87a3-1824e67d7fad",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:07:10.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:07:10.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"mitigates",
"source_ref":
"course-of-action--8e2e2d2b-17d4-4cbf-938f-98ee46b3cd3f",
"target_ref":
"malware--31b940d4-6f7f-459a-80ea-9c1f17b5891b"
},
{
"type": "malware",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"malware--31b940d4-6f7f-459a-80ea-9c1f17b5891b",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:07:09.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:07:09.000Z",
"name": "Poison Ivy",
"malware_types":
["trojan"]
}
]
4.4 Grouping
Type Name: grouping
A Grouping object explicitly asserts that the referenced
STIX Objects have a shared context, unlike a STIX Bundle (which explicitly
conveys no context). A Grouping object should not be confused with an
intelligence product, which should be conveyed via a STIX Report.
A STIX Grouping object might represent a set of data that,
in time, given sufficient analysis, would mature to convey an incident or
threat report as a STIX Report object. For example, a Grouping could be used to
characterize an ongoing investigation into a security event or incident. A
Grouping object could also be used to assert that the referenced STIX Objects
are related to an ongoing analysis process, such as when a threat analyst is
collaborating with others in their trust community to examine a series of
Campaigns and Indicators. The Grouping SDO contains a list of references to
SDOs, SCOs, and SROs, along with an explicit statement of the context shared by
the content, a textual description, and the name of the grouping.
4.4.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Grouping Specific Properties
|
|
name, description, context, object_refs
|
|
Property Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of this property MUST
be grouping.
|
|
name (optional)
|
string
|
A name used to identify the Grouping.
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A description that provides more
details and context about the Grouping, potentially including its purpose and
its key characteristics.
|
|
context (required)
|
open-vocab
|
A short descriptor of the
particular context shared by the content referenced by the Grouping.
This is an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come from the grouping-context-ov vocabulary.
|
|
object_refs
(required)
|
list of
type identifier
|
Specifies the STIX Objects that are referred to by this
Grouping.
|
4.4.2 Relationships
There are no relationships explicitly defined between the
Grouping object and other STIX Objects, other than those defined as common
relationships. The first section lists the embedded relationships by property
name along with their corresponding target.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
object_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type STIX Object)
|
|
Common Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Name
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
Examples
A standalone Grouping; the consumer may or may not already
have access to the referenced STIX Objects.
{
"type": "grouping",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"grouping--84e4d88f-44ea-4bcd-bbf3-b2c1c320bcb3",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--a463ffb3-1bd9-4d94-b02d-74e4f1658283",
"created":
"2015-12-21T19:59:11.000Z",
"modified":
"2015-12-21T19:59:11.000Z",
"name": "The Black Vine
Cyberespionage Group",
"description": "A simple
collection of Black Vine Cyberespionage Group attributed intel",
"context":
"suspicious-activity",
"object_refs": [
"indicator--26ffb872-1dd9-446e-b6f5-d58527e5b5d2",
"campaign--83422c77-904c-4dc1-aff5-5c38f3a2c55c",
"relationship--f82356ae-fe6c-437c-9c24-6b64314ae68a",
"file--0203b5c8-f8b6-4ddb-9ad0-527d727f968b"
]
}
4.5 Identity
Type Name: identity
Identities can represent actual
individuals, organizations, or groups (e.g., ACME, Inc.) as well as classes of
individuals, organizations, systems or groups (e.g., the finance sector).
The Identity SDO can capture basic
identifying information, contact information, and the sectors that the Identity
belongs to. Identity is used in STIX to represent, among other things, targets
of attacks, information sources, object creators, and threat actor identities.
4.5.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Identity
Specific Properties
|
|
name,
description, roles, identity_class, sectors,
contact_information
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be identity.
|
|
name (required)
|
string
|
The name of
this Identity. When referring to a specific entity (e.g., an individual or
organization), this property SHOULD contain the canonical name of the
specific entity.
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A
description that provides more details and context about the Identity,
potentially including its purpose and its key characteristics.
|
|
roles (optional)
|
list of type string
|
The list of roles that this
Identity performs (e.g., CEO, Domain Administrators, Doctors, Hospital, or
Retailer). No open vocabulary is yet defined for this property.
|
|
identity_class
(required)
|
open-vocab
|
The type of entity that this Identity
describes, e.g., an individual or organization.
This is an open vocabulary and the
values SHOULD come from the identity-class-ov vocabulary.
|
|
sectors
(optional)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
The list of industry sectors that this
Identity belongs to.
This is
an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come from the industry-sector-ov
vocabulary.
|
|
contact_information
(optional)
|
string
|
The contact information (e-mail, phone
number, etc.) for this Identity. No format for this information is currently
defined by this specification.
|
4.5.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
Identity object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the embedded
relationships by property name along with their corresponding target. The rest
of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this object
type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The reverse
relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this object type
from another object type. They are included here for convenience. For their
definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
Common
Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Relationship
Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
identity
|
located-at
|
location
|
This Relationship describes that the Identity is located
at or in the related Location.
For example, a located-at relationship from the
ACME Corporation to a Location representing the United States means that ACME
Corporation is located in the United States.
|
|
Reverse
Relationships
|
|
attack-pattern, campaign,
intrusion-set,
malware,
threat-actor,
tool
|
targets
|
identity
|
See forward relationship for
definition.
|
|
threat-actor
|
attributed-to, impersonates
|
identity
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
Examples
An Identity for an individual named John
Smith
{
"type":
"identity",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"identity--023d105b-752e-4e3c-941c-7d3f3cb15e9e",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:03:00.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:03:00.000Z",
"name": "John
Smith",
"identity_class":
"individual"
}
An Identity for a company named ACME
Widget, Inc.
{
"type": "identity",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"identity--e5f1b90a-d9b6-40ab-81a9-8a29df4b6b65",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:03:00.000Z",
"modified": "2016-04-06T20:03:00.000Z",
"name": "ACME Widget,
Inc.",
"identity_class":
"organization"
}
4.6 Indicator
Type Name: indicator
Indicators contain a pattern that can be
used to detect suspicious or malicious cyber activity. For example, an
Indicator may be used to represent a set of malicious domains and use the STIX
Patterning Language (see section
9) to specify these domains.
The Indicator SDO contains a simple
textual description, the Kill Chain Phases that it detects behavior in, a time
window for when the Indicator is valid or useful, and a required pattern property to capture a structured
detection pattern. Conforming STIX implementations MUST support the STIX
Patterning Language as defined in section 9.
Relationships from the Indicator can
describe the malicious or suspicious behavior that it directly detects
(Malware, Tool, and Attack Pattern). In addition, it may also imply the
presence of a Campaigns, Intrusion Sets, and Threat Actors, etc.
4.6.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Indicator
Specific Properties
|
|
name,
description, indicator_types, pattern, valid_from, valid_until,
kill_chain_phases
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be indicator.
|
|
name (optional)
|
string
|
A name used
to identify the Indicator.
Producers SHOULD
provide this property to help products and analysts understand what this
Indicator actually does.
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A
description that provides more details and context about the Indicator,
potentially including its purpose and its key characteristics.
Producers SHOULD provide
this property to help products and analysts understand what this Indicator
actually does.
|
|
indicator_types
(required)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
This property is an open vocabulary that specifies a set
of categorizations for this indicator.
This is an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come
from the indicator-type-ov
vocabulary.
|
|
pattern
(required)
|
string
|
The detection pattern for this
Indicator is a STIX Pattern as specified in section 9.
|
|
pattern_type
(required)
|
open-vocab
|
The type of pattern used in this
indicator. The property is an open vocabulary and currently has the values of
stix,
snort,
and yara.
|
|
pattern_version
(optional)
|
string
|
The version of the pattern that is
used. For patterns that do not have a formal specification, the build or code
version that the pattern is known to work with SHOULD be used.
|
|
valid_from
(required)
|
timestamp
|
The time from which this Indicator is considered
a valid indicator of the behaviors it is related or represents.
|
|
valid_until
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
The time at which this Indicator
should no longer considered a valid indicator of the behaviors it is related
to or represents.
If the valid_until property is omitted, then there is no
constraint on the latest time for which the Indicator is valid.
This MUST be greater than the timestamp in the valid_from property.
|
|
kill_chain_phases
(optional)
|
list of type kill-chain-phase
|
The kill chain phase(s) to which this
Indicator corresponds.
|
4.6.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
Indicator object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the embedded
relationships by property name along with their corresponding target. The rest
of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this object
type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The reverse
relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this object type
from another object type. They are included here for convenience. For their
definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
Common
Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Relationship
Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
indicator
|
indicates
|
attack-pattern, campaign,
infrastructure,
intrusion-set,
malware,
threat-actor, tool
|
This Relationship describes that the
Indicator can detect evidence of the related Attack Pattern, Campaign,
Infrastructure, Intrusion Set, Malware, Threat Actor, or Tool. This evidence
may not be direct: for example, the Indicator may detect secondary evidence
of the Campaign, such as malware or behavior commonly used by that Campaign.
For example, an indicates
Relationship from an Indicator to a Campaign object representing Glass
Gazelle means that the Indicator is capable of detecting evidence of Glass
Gazelle, such as command and control IPs commonly used by that Campaign.
|
|
indicator
|
based-on
|
observed-data
|
This relationship describes that the
indicator was created based on information from an observed-data object.
For example, an indicator may be
created based upon the observation of a spearphishing email or created based
upon analysis performed on a piece of malware or adversary infrastructure.
|
|
Reverse
Relationships
|
|
course-of-action
|
investigates
|
indicator
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
course-of-action
|
mitigates
|
indicator
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
Examples
Indicator itself, with context
[
{
"type":
"indicator",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"indicator--8e2e2d2b-17d4-4cbf-938f-98ee46b3cd3f",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:03:48.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:03:48.000Z",
"indicator_types":
["malicious-activity"],
"name": "Poison Ivy
Malware",
"description":
"This file is part of Poison Ivy",
"pattern": "[
file:hashes.'SHA-256' = '4bac27393bdd9777ce02453256c5577cd02275510b2227f473d03f533924f877'
]",
"valid_from":
"2016-01-01T00:00:00Z"
},
{
"type":
"relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--44298a74-ba52-4f0c-87a3-1824e67d7fad",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:06:37.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:06:37.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"indicates",
"source_ref":
"indicator--8e2e2d2b-17d4-4cbf-938f-98ee46b3cd3f",
"target_ref":
"malware--31b940d4-6f7f-459a-80ea-9c1f17b5891b"
},
{
"type":
"malware",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"malware--31b940d4-6f7f-459a-80ea-9c1f17b5891b",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:07:09.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:07:09.000Z",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"name": "Poison
Ivy",
"malware_types":
["trojan"]
}
]
4.7
Infrastructure
Type Name: infrastructure
The Infrastructure SDO represents a type of TTP and
describes any systems, software services and any associated physical or virtual
resources intended to support some purpose (e.g., C2 servers used as part of an
attack, device or server that are part of defence, database servers targeted by
an attack, etc.). While elements of an attack can be represented by other SDOs
or SCOs, the Infrastructure SDO represents a named group of related data that
constitutes the infrastructure.
4.7.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Attack Pattern Specific
Properties
|
|
name, description, infrastructure_types, aliases, kill_chain_phases, first_seen,
last_seen
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be infrastructure.
|
|
name (required)
|
string
|
A name or characterizing text
used to identify the Infrastructure.
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A description that provides more
details and context about the Infrastructure, potentially including its
purpose, how it is being used, how it relates to other intelligence
activities captured in related objects, and its key characteristics.
|
|
infrastructure_types (required)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
The type of infrastructure being
described.
This is an open vocabulary and
values SHOULD come from the infrastructure-type-ov vocabulary.
|
|
aliases (optional)
|
list of type string
|
Alternative names used to identify this Infrastructure.
|
|
kill_chain_phases (optional)
|
list
of type kill-chain-phase
|
The list of Kill Chain Phases
for which this Infrastructure is used.
|
|
first_seen
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
The time that this
Infrastructure was first seen performing malicious activities.
|
|
last_seen
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
The time that this
Infrastructure was last seen performing malicious activities.
If this property and the first_seen property are both defined, then this property MUST
be greater than or equal to the timestamp in the first_seen property.
|
4.7.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
Infrastructure object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the
embedded relationships by property name along with their corresponding target.
The rest of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this
object type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The
reverse relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this
object type from another object type. They are included here for convenience.
For their definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
Common Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Relationship Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
infrastructure
|
communicates-with
|
infrastructure, ipv4-addr, ipv6-addr, domain-name,
url
|
This Relationship documents that this infrastructure
instance communicates with the defined network addressable resource.
For example, a botnet could communicate with a
crypto-currency mining pool. This does not mean that the pool is a part of
this infrastructure.
|
|
infrastructure
|
consists-of
|
infrastructure, observed-data, <All STIX
Cyber-observable Objects>
|
This Relationship documents the objects that are used to
make up an infrastructure instance, such as ipv4-addr, ipv6-addr, domain-name,
url.
An infrastructure instance consists of zero or more objects.
While not all SCO types will make sense as infrastructure,
allowing any type of SCO prevents artificially restricting what could be
used.
|
|
infrastructure
|
controls
|
infrastructure, malware
|
This Relationship describes that this infrastructure
controls some other infrastructure or a malware instance (or family).
|
|
infrastructure
|
delivers
|
malware
|
This Relationship describes that this infrastructure is
used to actively deliver a malware instance (or family).
|
|
infrastructure
|
has
|
vulnerability
|
This Relationship describes that this specific Infrastructure
has this specific Vulnerability.
For example, a web server may not have been patched and
currently is impacted by a CVE.
|
|
infrastructure
|
hosts
|
tool, malware
|
This Relationship describes that this infrastructure has a
tool running on it or is used to passively host the tool / malware.
For example, an SSH server may be hosted on a piece of
infrastructure.
|
|
infrastructure
|
located-at
|
location
|
This Relationship describes that the infrastructure
originates from the related location.
For example, a located-at relationship from the Red
Orca C2 infrastructure to a Location representing North America means that
the Red Orca C2 Infrastructure appears to originate from or is located in
North America.
|
|
infrastructure
|
uses
|
infrastructure
|
This Relationship describes that this infrastructure uses
this other infrastructure to achieve its objectives.
|
|
Reverse Relationships
|
|
campaign, intrusion-set,
threat-actor
|
compromises
|
infrastructure
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
malware
|
beacons-to, exfiltrates-to
|
infrastructure
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
intrusion-set, threat-actor
|
hosts
|
infrastructure
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
indicator
|
indicates
|
infrastructure
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
intrusion-set,
threat-actor
|
owns
|
infrastructure
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
malware,
tool
|
targets
|
infrastructure
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
campaign, intrusion-set,
malware,
threat-actor, tool
|
uses
|
infrastructure
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
Examples (additional examples can be found in Appendix C)
Malware C2
Infrastructure
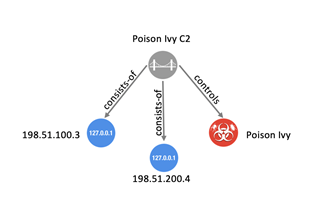
{
"type":"infrastructure",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":"infrastructure--38c47d93-d984-4fd9-b87b-d69d0841628d",
"created":"2016-05-07T11:22:30.000Z",
"modified":"2016-05-07T11:22:30.000Z",
"name":"Poison Ivy
C2",
"infrastructure_types":
["command-and-control"]
}
{
"type":
"relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--7aebe2f0-28d6-48a2-9c3e-b0aaa60266ed",
"created":
"2016-05-09T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-09T08:17:27.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"controls",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--38c47d93-d984-4fd9-b87b-d69d0841628d",
"target_ref":
"malware--16f4f3f9-1b68-4abb-bb66-7639d49f1e30"
}
{
"type":
"malware",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"malware--16f4f3f9-1b68-4abb-bb66-7639d49f1e30",
"created":
"2016-05-08T14:31:09.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-08T14:31:09.000Z",
"is_family": true,
"malware_types":[
"remote-access-trojan"
],
"name": "Poison
Ivy"
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--7aebe2f0-28d6-48a2-9c3e-b0aaa60266ef",
"created":
"2016-05-09T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-09T08:17:27.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"consists-of",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--38c47d93-d984-4fd9-b87b-d69d0841628d",
"target_ref":
"ipv4-addr--b4e29b62-2053-47c4-bab4-bbce39e5ed67"
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--7aebe2f0-28d6-48a2-9c3e-b0aaa60266ef",
"created":
"2016-05-09T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-09T08:17:27.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"consists-of",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--38c47d93-d984-4fd9-b87b-d69d0841628d",
"target_ref":
"ipv4-addr--84445275-e371-444b-baea-ac7d07a180fd"
}
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--b4e29b62-2053-47c4-bab4-bbce39e5ed67",
"value":
"198.51.100.3"
}
{
"type": "ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--84445275-e371-444b-baea-ac7d07a180fd",
"value": "198.52.200.4"
}
4.8 Intrusion Set
Type Name: intrusion-set
An Intrusion Set is a grouped set of
adversarial behaviors and resources with common properties that is believed to
be orchestrated by a single organization. An Intrusion Set may capture multiple
Campaigns or other activities that are all tied together by shared attributes
indicating a common known or unknown Threat Actor. New activity can be
attributed to an Intrusion Set even if the Threat Actors behind the attack are
not known. Threat Actors can move from supporting one Intrusion Set to
supporting another, or they may support multiple Intrusion Sets.
Where a Campaign is a set of attacks
over a period of time against a specific set of targets to achieve some
objective, an Intrusion Set is the entire attack package and may be used over a
very long period of time in multiple Campaigns to achieve potentially multiple
purposes.
While sometimes an Intrusion Set is not
active, or changes focus, it is usually difficult to know if it has truly
disappeared or ended. Analysts may have varying level of fidelity on
attributing an Intrusion Set back to Threat Actors and may be able to only
attribute it back to a nation state or perhaps back to an organization within
that nation state.
4.8.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Intrusion
Set Specific Properties
|
|
name,
description, aliases, first_seen, last_seen,
goals, resource_level, primary_motivation, secondary_motivations
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be intrusion-set.
|
|
name (required)
|
string
|
A name used
to identify this Intrusion Set.
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A
description that provides more details and context about the Intrusion Set,
potentially including its purpose and its key characteristics.
|
|
aliases
(optional)
|
list of type string
|
Alternative names used to identify
this Intrusion Set.
|
|
first_seen (optional)
|
timestamp
|
The time
that this Intrusion Set was first seen.
This
property is a summary property of data from sightings and other data that may
or may not be available in STIX. If new sightings are received that are
earlier than the first seen timestamp, the object may be updated to account
for the new data.
|
|
last_seen (optional)
|
timestamp
|
The time
that this Intrusion Set was last seen.
This
property is a summary property of data from sightings and other data that may
or may not be available in STIX. If new sightings are received that are later
than the last seen timestamp, the object may be updated to account for the
new data.
This MUST be greater than
or equal to the timestamp in the first_seen property.
|
|
goals (optional)
|
list of
type string
|
The
high-level goals of this Intrusion Set, namely, what are they trying
to do. For example, they may be motivated by personal gain, but their goal is
to steal credit card numbers. To do this, they may execute specific Campaigns
that have detailed objectives like compromising point of sale systems at a
large retailer.
Another
example: to gain information about latest merger and IPO information from
ACME Bank.
|
|
resource_level (optional)
|
open-vocab
|
This defines
the organizational level at which this Intrusion Set typically works, which
in turn determines the resources available to this Intrusion Set for use in
an attack.
This is an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come from the attack-resource-level-ov vocabulary.
|
|
primary_motivation
(optional)
|
open-vocab
|
The primary reason, motivation, or
purpose behind this Intrusion Set. The motivation is why the Intrusion
Set wishes to achieve the goal (what they are trying to achieve).
For example, an Intrusion Set with a
goal to disrupt the finance sector in a country might be motivated by
ideological hatred of capitalism.
This is
an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come from the attack-motivation-ov
vocabulary.
|
|
secondary_motivations
(optional)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
The secondary reasons, motivations, or
purposes behind this Intrusion Set. These motivations can exist as an equal
or near-equal cause to the primary motivation. However, it does not replace
or necessarily magnify the primary motivation, but it might indicate
additional context. The position in the list has no significance.
This is
an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come from the attack-motivation-ov
vocabulary.
|
4.8.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
Intrusion Set object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the
embedded relationships by property name along with their corresponding target.
The rest of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this
object type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The
reverse relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this
object type from another object type. They are included here for convenience.
For their definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
Common
Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Relationship
Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
intrusion-set
|
attributed-to
|
threat-actor
|
This Relationship describes that the
related Threat Actor is involved in carrying out the Intrusion Set.
For example, an attributed-to
Relationship from the Red Orca Intrusion Set to the Urban Fowl Threat Actor
means that the actor carried out or was involved in some of the activity
described by the Intrusion Set.
|
|
intrusion-set
|
compromises
|
infrastructure
|
This Relationship describes that the Intrusion Set
compromises the related Infrastructure.
|
|
intrusion-set
|
hosts, owns
|
infrastructure
|
This Relationship describes that the Intrusion Set hosts
or owns the related Infrastructure (e.g. an actor that rents botnets to other
threat actors).
|
|
intrusion-set
|
originates-from
|
location
|
This Relationship describes that the Intrusion Set
originates from the related location and SHOULD NOT be used to define
attribution.
For example, an originates-from relationship from
the Red Orca Intrusion Set to a Location representing North America means
that the Red Orca Intrusion Set appears to originate from or is located in
North America.
|
|
intrusion-set
|
targets
|
identity, location, vulnerability
|
This Relationship describes that the
Intrusion Set uses exploits of the related Vulnerability or targets the type
of victims described by the related Identity or Location.
For example, a targets Relationship from
the Red Orca Intrusion Set to a Vulnerability in a blogging platform
indicates that attacks performed as part of Red Orca often exploit that
Vulnerability.
Similarly, a targets Relationship from
the Red Orca Intrusion Set to an Identity describing the energy sector in the
United States means that the Intrusion Set typically carries out attacks
against targets in that sector.
|
|
intrusion-set
|
uses
|
attack-pattern, infrastructure,
malware,
tool
|
This Relationship describes that
attacks carried out as part of the Intrusion Set typically use the related
Attack Pattern, Infrastructure, Malware, or Tool.
For example, a uses Relationship from the
Red Orca Intrusion Set to the xInject Malware indicates that xInject is often
used during attacks attributed to that Intrusion Set.
|
|
Reverse
Relationships
|
|
campaign
|
attributed-to
|
intrusion-set
|
See forward relationship for
definition.
|
|
malware
|
authored-by
|
intrusion-set
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
indicator
|
indicates
|
intrusion-set
|
See forward relationship for
definition.
|
Examples
{
"type":
"intrusion-set",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"intrusion-set--4e78f46f-a023-4e5f-bc24-71b3ca22ec29",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:03:48.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:03:48.000Z",
"name": "Bobcat
Breakin",
"description":
"Incidents usually feature a shared TTP of a bobcat being released within
the building containing network access, scaring users to leave their computers
without locking them first. Still determining where the threat actors are
getting the bobcats.",
"aliases":
["Zookeeper"],
"goals":
["acquisition-theft", "harassment", "damage"]
}
4.9 Location
Type Name: location
A Location represents a geographic location. The location
may be described as any, some or all of the following: region (e.g., North
America), civic address (e.g. New York, US), latitude and longitude.
Locations are primarily used to give context to other SDOs.
For example, a Location could be used in a relationship to describe that the
Bourgeois Swallow intrusion set originates from Eastern Europe.
The Location SDO can be related to an Identity or Intrusion
Set to indicate that the identity or intrusion set is located in that location.
It can also be related from a malware or attack pattern to indicate that they
target victims in that location. The Location object describes geographic areas,
not governments, even in cases where that area might have a government. For
example, a Location representing the United States describes the United States
as a geographic area, not the federal government of the United States.
At least one of the following properties/sets of properties MUST
be provided:
●
region
●
country
●
latitude and longitude
When a combination of properties is provided (e.g. a region and a latitude and longitude)
the more precise properties are what the location describes. In other words, if
a location contains both a region of northern-america and a country of us, then
the location describes the United States, not all of North America. In cases
where a latitude and longitude are specified without a precision, the location
describes the most precise other value.
If precision is specified, then the datum for latitude and longitude MUST be WGS 84 [WGS84].
Organizations specifying a designated location using latitude and longitude
SHOULD specify the precision which is appropriate for the scope of the
location being identified. The scope is defined by the boundary as outlined by
the precision around the coordinates.
4.9.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Location Specific Properties
|
|
name, description, latitude, longitude, precision,
region, country, administrative_area, city,
street_address, postal_code
|
|
Property Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of this property MUST
be location.
|
|
name
(optional)
|
string
|
A name used to identify the Location.
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A textual description of the
Location.
|
|
latitude
(optional)
|
float
|
The latitude of the Location in
decimal degrees. Positive numbers describe latitudes north of the equator,
and negative numbers describe latitudes south of the equator. The value of
this property MUST be between -90.0 and 90.0, inclusive.
If the longitude property is present, this property MUST be
present.
|
|
longitude
(optional)
|
float
|
The longitude of the Location in
decimal degrees. Positive numbers describe longitudes east of the prime
meridian and negative numbers describe longitudes west of the prime meridian.
The value of this property MUST be between -180.0 and 180.0,
inclusive.
If the latitude property is present, this property MUST be
present.
|
|
precision
(optional)
|
float
|
Defines the precision of the
coordinates specified by the latitude and longitude properties. This is measured in meters. The actual
Location may be anywhere up to precision meters from the
defined point.
If this property is not present,
then the precision is unspecified.
If this property is present, the
latitude and longitude properties MUST
be present.
|
|
region (optional)
|
open-vocab
|
The region that this Location
describes. This property SHOULD contain a value from region-ov.
|
|
country (optional)
|
string
|
The country that this Location
describes. This property SHOULD contain a valid ISO 3166-1 ALPHA-2
Code [ISO3166-1].
|
|
administrative_area (optional)
|
string
|
The state, province, or other
sub-national administrative area that this Location describes.
|
|
city (optional)
|
string
|
The city that this Location
describes.
|
|
street_address
(optional)
|
string
|
The street address that this
Location describes. This property includes all aspects or parts of the street
address. For example, some addresses may have multiple lines including a
mailstop or apartment number.
|
|
postal_code
(optional)
|
string
|
The postal code for this
Location.
|
4.9.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the Location
object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the embedded
relationships by property name along with their corresponding target. The rest
of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this object
type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The reverse
relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this object type
from another object type. They are included here for convenience. For their
definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
Common Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Relationship Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
|
Reverse Relationships
|
|
identity,
infrastructure, threat-actor
|
located-at
|
location
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
campaign, intrusion-set, malware
|
originates-from
|
location
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
attack-pattern, campaign, intrusion-set, malware,
threat-actor,
tool
|
targets
|
location
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
Examples
{
"type": "location",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"location--a6e9345f-5a15-4c29-8bb3-7dcc5d168d64",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:03:00.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:03:00.000Z",
"region":
"northern-america"
}
{
"type": "location",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"location--a6e9345f-5a15-4c29-8bb3-7dcc5d168d64",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:03:00.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:03:00.000Z",
"region":
"south-eastern-asia",
"country": "th",
"administrative_area":
"Tak",
"postal_code": "63170"
}
{
"type": "location",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"location--a6e9345f-5a15-4c29-8bb3-7dcc5d168d64",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:03:00.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:03:00.000Z",
"latitude": "48.8566",
"longitude": "2.3522"
}
4.10 Malware
Type Name: malware
Malware is a type of TTP that represents malicious code. It
generally refers to a program that is inserted into a system, usually covertly.
The intent is to compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of
the victim's data, applications, or operating system (OS) or otherwise annoy or
disrupt the victim.
The Malware SDO characterizes, identifies, and categorizes
malware instances and families from data that may be derived from analysis.
This SDO captures detailed information about how the malware works and what it
does. This SDO captures contextual data relevant to sharing Malware data without
requiring the full analysis provided by the Malware Analysis SDO.
The Indicator SDO provides intelligence producers with the
ability to define, using the STIX Pattern Grammar in a standard way to identify
and detect behaviors associated with malicious activities. Although the Malware
SDO provides vital intelligence on a specific instance or malware family, it
does not provide a standard grammar that the Indicator SDO provides to identify
those properties in security detection systems designed to process the STIX
Pattern grammar. We strongly encourage the use of STIX Indicators for the
detection of actual malware, due to its use of the STIX Patterning language and
the clear semantics that it provides.
To minimize the risk of a consumer compromising their system
in parsing malware samples, producers SHOULD consider sharing defanged
content (archive and password-protected samples) instead of raw, base64-encoded
malware samples.
4.10.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Malware Specific Properties
|
|
name, description, malware_types, is_family, aliases, kill_chain_phases,
first_seen, last_seen, os_execution_envs, architecture_execution_envs,
implementation_languages, capabilities, sample_refs
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be malware.
|
|
name (optional)
|
string
|
A name used to identify the
malware instance or family, as specified by the producer of the SDO. For a
malware family the name MUST be defined. If a name for a malware
instance is not available, the SHA-256 hash value or sample’s filename MAY
be used instead.
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A description that provides more
details and context about the malware instance or family, potentially
including its purpose and its key characteristics.
|
|
malware_types
(required)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
This property is an open vocabulary that specifies a set
of categorizations for the malware being described.
This is an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come
from the malware-type-ov
vocabulary.
|
|
is_family
(required)
|
boolean
|
Whether the object represents a malware family (if true) or
a malware instance (if false).
|
|
aliases (optional)
|
list of type string
|
Alternative names used to identify this malware or malware
family.
|
|
kill_chain_phases (optional)
|
list
of type kill-chain-phase
|
The list of Kill Chain Phases
for which this malware can be used.
|
|
first_seen
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
The time that the malware
instance or family was first seen.
This property is a summary property
of data from sightings and other data that may or may not be available in
STIX. If new sightings are received that are earlier than the first seen
timestamp, the object may be updated to account for the new data.
|
|
last_seen
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
The time that the malware family
or malware instance was last seen.
This property is a summary
property of data from sightings and other data that may or may not be
available in STIX. If new sightings are received that are later than the last_seen timestamp, the object may be updated to account for the
new data.
This MUST be greater than
or equal to the timestamp in the first_seen property.
|
|
os_execution_envs (optional)
|
list of type string
|
The operating systems that the
malware family or malware instance is executable on.
Each string value for this
property SHOULD be a CPE v2.3 entry from the official NVD CPE
Dictionary [NVD]
. This property MAY include custom values including values taken from
other standards such as SWID [SWID].
|
|
architecture_execution_envs (optional)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
The processor architectures
(e.g., x86, ARM, etc.) that the malware instance or family is executable on.
This is an open vocabulary and
values SHOULD come from the processor-architecture-ov vocabulary.
|
|
implementation_languages
(optional)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
The programming language(s) used
to implement the malware instance or family.
This is an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come from the implementation-language-ov vocabulary.
|
|
capabilities
(optional)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
Specifies any capabilities
identified for the malware instance or family.
This is an open vocabulary and
values SHOULD come from the malware-capabilities-ov vocabulary.
|
|
sample_refs (optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
The sample_refs property specifies a list of identifiers of the SCO file or artifact objects associated with this malware instance(s) or
family.
If is_family is false, then all samples
listed in sample_refs MUST refer to the same binary data.
|
4.10.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
Malware object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the embedded
relationships by property name along with their corresponding target. The rest
of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this object
type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The reverse
relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this object type
from another object type. They are included here for convenience. For their
definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
sample_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type file or artifact)
|
|
Common Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Relationship Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
malware
|
authored-by
|
threat-actor, intrusion-set
|
This Relationship describes that the malware instance or
family was developed by the related threat actor or intrusion set.
|
|
malware
|
beacons-to, exfiltrates-to
|
infrastructure
|
This Relationship describes that the malware instance or
family beacons to or exfiltrates data to the related Infrastructure.
|
|
malware
|
communicates-with
|
ipv4-addr, ipv6-addr, domain-name, url
|
This Relationship documents that this malware instance (or
family) communicates with (beacons to, connects to, or exfiltrated data to)
the defined network addressable resource.
|
|
malware
|
controls
|
malware
|
This Relationship documents that this malware instance (or
family) can control other malware which may be resident on the same system on
which it is executing.
Note that this is not meant to imply or state that the
malware instance or family drops other malware (which is covered by the drops
relationship). Rather, it is meant to state that the malware instance or
family is able to subvert or control other malware to achieve its goals.
|
|
malware
|
downloads, drops
|
malware, tool, file
|
These Relationships document that this malware instance
(or family) downloads or drops another malware instance, tool or file. This
is especially common with “first-stage” malware instances such as downloaders
and droppers.
|
|
malware
|
exploits
|
vulnerability
|
This Relationship documents that this malware instance or
family exploits or attempts to exploit a particular vulnerability.
For example, an exploits Relationship linking a
malware instance or family representing a downloader to a Vulnerability for
CVE-2016-0001 means that the malware instance or family exploits that
vulnerability.
|
|
malware
|
originates-from
|
location
|
This Relationship documents that this malware instance or
family originates from a particular location.
|
|
malware
|
targets
|
identity, infrastructure,
location, vulnerability
|
This Relationship documents that a malware instance or
family is being used to target an Identity, Infrastructure, or Location. For
malware families, this can be used to capture the full set of identities,
infrastructures, or locations targeted by the family.
Similarly, a targets Relationship linking a malware instance or
family representing a downloader to an Identity representing the energy
sector means that downloader is typically used against targets in the energy
sector.
|
|
malware
|
uses
|
attack-pattern, infrastructure, malware,
tool
|
This Relationship documents that this malware instance or family
uses the attack pattern, infrastructure, malware, or tool to achieve its
objectives.
For example, a uses Relationship from the jay-sm17h
Threat Actor to the xInject Malware indicates that xInject is often used by
jay-sm17h.
|
|
malware
|
variant-of
|
malware
|
This Relationship is used to document that one malware
instance or family is a variant of another malware instance or family.
Only the following uses of this relationship are valid:
Malware instance → Malware family: a Malware
instance is a variant of a Malware family. For example, a particular Zeus
version 2 sample is a variant of the broader Zeus family.
Malware family → Malware family: a Malware family is
a variant of another Malware family. For example, the Gameover Zeus family is
a variant of the broader Zeus family.
Malware instance → Malware instance: a Malware
instance is a variant of another Malware instance. For example, a particular
Cryptolocker instance that is based on an another Cryptolocker instance with
minor changes.
Malware family → Malware instance: this relationship
MUST NOT be used as it is not semantically valid.
|
|
Reverse Relationships
|
|
attack-pattern, infrastructure, tool
|
delivers
|
malware
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
indicator
|
indicates
|
malware
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
course-of-action
|
mitigates, remediates
|
malware
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
attack-pattern, campaign, intrusion-set, threat-actor
|
uses
|
malware
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
tool
|
drops
|
malware
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
infrastructure
|
controls
|
malware
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
malware-analysis
|
characterizes,
av-analysis-of,
static-analysis-of,
dynamic-analysis-of
|
malware
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
Examples
{
"type": "malware",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"malware--0c7b5b88-8ff7-4a4d-aa9d-feb398cd0061",
"created":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"name": "Cryptolocker",
"description": "A variant of
the cryptolocker family",
"malware_types":
["ransomware"],
"is_family": false
}
4.11 Malware Analysis
Type Name: malware-analysis
Malware Analysis captures the metadata and results of a
particular static or dynamic analysis performed on a malware instance or
family. One of av_result or analysis_sco_refs MUST be
provided.
4.11.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Malware Analysis Specific
Properties
|
|
product, version, host_vm_ref, operating_system_ref,
installed_software_ref, configuration_version, module, analysis_engine_version, analysis_definition_version, submitted, analysis_started,
analysis_ended, av_result, analysis_sco_refs
|
|
Property Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be malware-analysis.
|
|
product (required)
|
string
|
The name of the analysis engine or product that was used.
Product names SHOULD be all lowercase with words separated by a dash
"-".
For cases where the name of a product cannot be specified,
a value of "anonymized" MUST be used.
|
|
version
(optional)
|
string
|
The version of the analysis product that was used to
perform the analysis.
|
|
host_vm_ref (optional)
|
identifier
|
A description of the virtual machine environment used to
host the guest operating system (if applicable) that was used for the dynamic
analysis of the malware instance or family.
If this value is not included in conjunction with the operating_system_ref property, this
means that the dynamic analysis may have been performed on bare metal (i.e.
without virtualization) or the information was redacted.
The value of this property MUST be the identifier
for a SCO software
object.
|
|
operating_system_ref (optional)
|
identifier
|
The operating system used for the dynamic analysis of the
malware instance or family. This applies to virtualized operating systems as
well as those running on bare metal.
The value of this property MUST be the identifier
for a SCO software
object.
|
|
installed_software_refs (optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
Any non-standard software installed on the operating
system (specified through the operating-system value) used for the dynamic
analysis of the malware instance or family.
The value of this property MUST be the identifier
for a SCO software
object.
|
|
configuration_version
(optional)
|
string
|
This property captures the named configuration of
additional product configuration parameters for this analysis run.
For example, when a product is configured to do full depth
analysis of Window™ PE files. This configuration may have a named version and
that named version can be captured in this property. This will ensure
additional runs can be configured in the same way.
|
|
modules
(optional)
|
list of type
string
|
This property captures the specific analysis modules that
were used and configured in the product during this analysis run.
For example, configuring a product to support analysis of
Dridex.
|
|
analysis_engine_version (optional)
|
string
|
The version of the analysis engine or product (including
AV engines) that was used to perform the analysis.
|
|
analysis_definition_version (optional)
|
string
|
The version of the analysis definitions used by the
analysis tool (including AV tools).
|
|
submitted (optional)
|
timestamp
|
The date and time that the malware was first submitted for
scanning or analysis. This value will stay constant while the scanned date
can change. For example, when Malware was submitted to a virus analysis tool.
|
|
analysis_started (optional)
|
timestamp
|
The date and time that the malware analysis was initiated.
|
|
analysis_ended (optional)
|
timestamp
|
The date and time that the malware analysis ended.
|
|
av_result (optional)
|
string
|
The classification result or name assigned to the malware instance
by the AV scanner tool.
If no resulting context-specific classification value or
name is provided by the AV scanner tool or cannot be specified, then the
result value SHOULD come from the malware-av-result-ov open
vocabulary.
|
|
analysis_sco_refs (optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
This property contains the references to the STIX
Cyber-observable Objects that were captured during the analysis process.
|
4.11.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
Malware Analysis object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the
embedded relationships by property name along with their corresponding target.
The rest of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this
object type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The
reverse relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this
object type from another object type. They are included here for convenience.
For their definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_markings_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
host_vm_ref
|
identifier (of type software)
|
|
operating_system_ref
|
identifier (of type software)
|
|
installed_software_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type software)
|
|
analysis_sco_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type STIX Object)
|
|
Common Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Name
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
malware-analysis
|
characterizes
|
malware
|
This Relationship describes that the malware analysis is
describes the related malware.
|
|
malware-analysis
|
av-analysis-of
|
malware
|
This Relationship describes that the malware analysis is
AV scan results for the related malware.
|
|
malware-analysis
|
static-analysis-of
|
malware
|
This Relationship describes that the malware analysis is
static analysis results for the related malware.
|
|
malware-analysis
|
dynamic-analysis-of
|
malware
|
This Relationship describes that the malware analysis is
dynamic analysis results for the related malware.
|
|
Reverse Relationships
|
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
4.12 Note
Type Name: note
A Note is intended to convey informative text to provide
further context and/or to provide additional analysis not contained in the STIX
Objects, Marking Definition objects, or Language Content objects which the Note
relates to. Notes can be created by anyone (not just the original object
creator).
For example, an analyst may add a Note to a Campaign object
created by another organization indicating that they've seen posts related to
that Campaign on a hacker forum.
Because Notes are typically (though not always) created by
human analysts and are comprised of human-oriented text, they contain an
additional property to capture the analyst(s) that created the Note. This is
distinct from the created_by_ref
property, which is meant to capture the organization that created the object.
4.12.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Note
Specific Properties
|
|
abstract, content,
authors, object_refs
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type
(required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be note
|
|
abstract (optional)
|
string
|
A brief
summary of the note content.
|
|
content
(required)
|
string
|
The content of the note.
|
|
authors
(optional)
|
list of type string
|
The name of the author(s) of
this note (e.g., the analyst(s) that created it).
|
|
object_refs (required)
|
list of type identifier
|
The STIX Objects that the note
is being applied to.
|
4.12.2 Relationships
There are no relationships explicitly defined between the
Note object and other STIX Objects, other than the embedded relationships
listed below. These embedded relationships are listed by property name along
with their corresponding target.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identity
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
object_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type STIX Object)
|
Examples
A generic Note defining additional context and shows an
optional external reference to a ticketing system.
{
"type": "note",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"note--0c7b5b88-8ff7-4a4d-aa9d-feb398cd0061",
"created":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"external_references": [
{
"source_name":
"job-tracker",
"id": "job-id-1234"
}
],
"abstract": "Tracking Team
Note#1",
"content": "This note
indicates the various steps taken by the threat analyst team to investigate
this specific campaign. Step 1) Do a scan 2) Review scanned results for
identified hosts not known by external intel….etc",
"authors": ["John Doe"],
"object_refs":
["campaign--8e2e2d2b-17d4-4cbf-938f-98ee46b3cd3f"]
}
4.13 Observed Data
Type Name: observed-data
Observed Data conveys information about
cyber security related entities such as files, systems, and networks using the
STIX Cyber-observable Objects (SCOs). For example, Observed Data can capture
information about an IP address, a network connection, a file, or a registry
key. Observed Data is not an intelligence assertion, it is simply the raw
information without any context for what it means.
Observed Data can capture that a piece
of information was seen one or more times. Meaning, it can capture both a
single observation of a single entity (file, network connection) as well as the
aggregation of multiple observations of an entity. When the number_observed property is 1 the
Observed Data represents a single entity. When the number_observed property is greater than 1, the
Observed Data represents several instances of an entity potentially collected
over a period of time. If a time window is known, that can be captured using
the first_observed and last_observed properties. When used to
collect aggregate data, it is likely that some properties in the SCO (e.g.,
timestamp properties) will be omitted because they would differ for each of the
individual observations.
Observed Data may be used by itself
(without relationships) to convey raw data collected from any source including
analyst reports, sandboxes, and network and host-based detection tools. An
intelligence producer conveying Observed Data SHOULD include as much
context (e.g. SCOs) as possible that supports the use of the observed data set
in systems expecting to utilize the Observed Data for improved security. This
includes all SCOs that matched on an Indicator pattern and are represented in the
collected observed event (or events) being conveyed in the Observed Data
object. For example, a firewall could emit a single Observed Data instance
containing a single Network Traffic object for each connection it sees. The
firewall could also aggregate data and instead send out an Observed Data
instance every ten minutes with an IP address and an appropriate number_observed value to indicate the
number of times that IP address was observed in that window. A sandbox could
emit an Observed Data instance containing a file hash that it discovered.
Observed Data may also be related to
other SDOs to represent raw data that is relevant to those objects. For
example, the Sighting Relationship object, can relate an Indicator, Malware, or
other SDO to a specific Observed Data to represent the raw information that led
to the creation of the Sighting (e.g., what was actually seen that suggested
that a particular instance of malware was active).
To support backwards compatibility, related SCOs can still
be specified using the objects
properties, Either the objects
property or the object_refs
property MUST be provided, but both MUST NOT be present at the
same time.
4.13.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Observed
Data Specific Properties
|
|
first_observed,
last_observed, number_observed, objects, object_refs
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be observed-data.
|
|
first_observed
(required)
|
timestamp
|
The beginning of the time window
during which the data was seen.
|
|
last_observed
(required)
|
timestamp
|
The end of the time window during
which the data was seen.
This MUST be greater than or equal to the timestamp
in the first_observed
property.
|
|
number_observed
(required)
|
integer
|
The number of times that each
Cyber-observable object represented in the objects
or object_ref property was seen. If present, this MUST be an
integer between 1 and 999,999,999 inclusive.
If the number_observed property is greater than 1, the
data contained in the objects
or object_refs property was
seen multiple times. In these cases, object creators MAY omit
properties of the SCO (such as timestamps) that are specific to a single
instance of that observed data.
|
|
objects
(optional - deprecated)
|
observable-container
|
A dictionary of SCO representing the observation. The
dictionary MUST contain at least one object.
The cyber observable content MAY include multiple
objects if those objects are related as part of a single observation.
Multiple objects not related to each other via cyber observable Relationships
MUST NOT be contained within the same Observed Data instance.
This property MUST NOT be present if object_refs is provided.
For example, a Network Traffic object and two IPv4 Address
objects related via the src_ref
and dst_ref properties can
be contained in the same Observed Data because they are all related and used
to characterize that single entity.
NOTE: this property is now deprecated in favor of
object_refs and will be removed in a future version.
|
|
object_refs
(optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
A list of SCOs and SROs representing
the observation. The object_refs
MUST contain at least one SCO reference if defined.
The object_refs
MAY include multiple SCOs and their corresponding SROs, if those SCOs are
related as part of a single observation.
For example, a Network Traffic object
and two IPv4 Address objects related via the src_ref and dst_ref
properties can be contained in the same Observed Data because they are all
related and used to characterize that single entity.
This property MUST NOT be present if objects is provided.
|
4.13.2 Relationships
There are no forward relationships explicitly
defined between the Observed Data object and other STIX Objects, other than
those defined as common relationships. The first section lists the embedded
relationships by property name along with their corresponding target. The
reverse relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this
object type from another object type. They are included here for convenience.
For their definitions, please see the "Source" object.
In addition to the relationships created
using the generic Relationship object, Observed Data is also a direct target of
the Sighting SRO. Sightings represent a relationship between some intelligence
entity that was seen (e.g., an Indicator or Malware instance), where it was
seen, and what evidence was actually seen. The evidence (or raw data) in that
relationship is captured as Observed Data.
Relationships are not restricted to
those listed below. Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
object_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type SCO or SRO)
|
|
Common
Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Name
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
|
Reverse Relationships
|
|
indicator
|
based-on
|
observed-data
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
infrastructure
|
consists-of
|
observed-data
|
See forward relationship for definition
|
Examples
Observed Data that references two SCOs
{
"type":
"observed-data",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"observed-data--b67d30ff-02ac-498a-92f9-32f845f448cf",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T19:58:16.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T19:58:16.000Z",
"first_observed":
"2015-12-21T19:00:00Z",
"last_observed":
"2015-12-21T19:00:00Z",
"number_observed": 50,
"object_refs": [
"ipv4-address--efcd5e80-570d-4131-b213-62cb18eaa6a8",
"domain-name--ecb120bf-2694-4902-a737-62b74539a41b"
]
}
{
"type": "domain-name",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"domain-name--ecb120bf-2694-4902-a737-62b74539a41b",
"value": "example.com",
"resolves_to_refs":
["ipv4-addr--efcd5e80-570d-4131-b213-62cb18eaa6a8"]
}
{
"type": "ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--efcd5e80-570d-4131-b213-62cb18eaa6a8",
"value": "198.51.100.3"
}
4.14 Opinion
Type Name: opinion
An Opinion is an assessment of the correctness of the
information in a STIX Object produced by a different entity. The primary
property is the opinion
property, which captures the level of agreement or disagreement using a fixed
scale. That fixed scale also supports a numeric mapping to allow for consistent
statistical operations across opinions.
For example, an analyst from a consuming organization might
say that they "strongly disagree" with a Campaign object and provide
an explanation about why. In a more automated workflow, a SOC operator might
give an Indicator "one star" in their TIP (expressing "strongly
disagree") because it is considered to be a false positive within their
environment. Opinions are subjective, and the specification does not address
how best to interpret them. Sharing communities are encouraged to provide clear
guidelines to their constituents regarding best practice for the use of Opinion
objects within the community.
Because Opinions are typically (though not always) created
by human analysts and are comprised of human-oriented text, they contain an
additional property to capture the analyst(s) that created the Opinion. This is
distinct from the created_by_ref
property, which is meant to capture the organization that created
the object.
4.14.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Opinion
Specific Properties
|
|
explanation,
authors, opinion, object_refs
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type
(required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be opinion
|
|
explanation
(optional)
|
string
|
An explanation of why the
producer has this Opinion. For example, if an Opinion of strongly-disagree is
given, the explanation can contain an explanation of why the Opinion producer
disagrees and what evidence they have for their disagreement.
|
|
authors
(optional)
|
list of type string
|
The name of the author(s) of
this Opinion (e.g., the analyst(s) that created it).
|
|
opinion (required)
|
enum
|
The opinion that the producer
has about all of the STIX Object(s) listed in the object_refs property.
The values of this property MUST
come from the opinion-enum
enumeration.
|
|
object_refs
(required)
|
list of type identifier
|
The STIX Objects that the
Opinion is being applied to.
|
4.14.2 Relationships
There are no relationships explicitly defined between the Opinion
object and other STIX Objects, other than those defined as common
relationships. The first section lists the embedded relationships by property
name along with their corresponding target.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below. Relationships
can be created between any objects using the related-to relationship name or, as
with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identity
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
object_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type any STIX Object
type)
|
|
Common
Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Name
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
Examples
[
{
"type": "opinion",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id": "opinion--b01efc25-77b4-4003-b18b-f6e24b5cd9f7",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"object_refs":
["relationship--16d2358f-3b0d-4c88-b047-0da2f7ed4471"],
"opinion":
"strongly-disagree",
"explanation": "This doesn't
seem like it is feasible. We've seen how PandaCat has attacked Spanish
infrastructure over the last 3 years, so this change in targeting seems too
great to be viable. The methods used are more commonly associated with the
FlameDragonCrew."
}
]
4.15 Report
Type Name: report
Reports are collections of threat
intelligence focused on one or more topics, such as a description of a threat
actor, malware, or attack technique, including context and related details.
They are used to group related threat intelligence together so that it can be
published as a comprehensive cyber threat story.
The Report SDO contains a list of
references to STIX Objects (the CTI objects included in the report) along with
a textual description and the name of the report.
For example, a threat report produced by
ACME Defense Corp. discussing the Glass Gazelle campaign should be represented
using Report. The Report itself would contain the narrative of the report while
the Campaign SDO and any related SDOs (e.g., Indicators for the Campaign, Malware
it uses, and the associated Relationships) would be referenced in the report
contents.
4.15.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Report
Specific Properties
|
|
name,
description, report_types, published, object_refs
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be report.
|
|
name (required)
|
string
|
A name used
to identify the Report.
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A
description that provides more details and context about the Report,
potentially including its purpose and its key characteristics.
|
|
report_types
(required)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
This property is an open vocabulary that specifies the
primary subject(s) of this report.
This is an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come
from the report-type-ov
vocabulary.
|
|
published (required)
|
timestamp
|
The date
that this Report object was officially published by the creator of this
report.
The
publication date (public release, legal release, etc.) may be different than
the date the report was created or shared internally (the date in the created property).
|
|
object_refs
(required)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies the STIX Objects that are referred
to by this Report.
|
4.15.2 Relationships
There are no relationships explicitly
defined between the Report object and other STIX Objects, other than those
defined as common relationships. The first section lists the embedded
relationships by property name along with their corresponding target.
Relationships are not restricted to
those listed below. Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship name or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
object_refs
|
list of type identifier (of STIX Objects
type)
|
|
Common
Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Name
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
Examples
A standalone Report; the consumer may or
may not already have access to the referenced STIX Objects.
{
"type":
"report",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"report--84e4d88f-44ea-4bcd-bbf3-b2c1c320bcb3",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--a463ffb3-1bd9-4d94-b02d-74e4f1658283",
"created":
"2015-12-21T19:59:11.000Z",
"modified":
"2015-12-21T19:59:11.000Z",
"name": "The Black
Vine Cyberespionage Group",
"description": "A
simple report with an indicator and campaign",
"published":
"2016-01-20T17:00:00.000Z",
"report_types":
["campaign"],
"object_refs": [
"indicator--26ffb872-1dd9-446e-b6f5-d58527e5b5d2",
"campaign--83422c77-904c-4dc1-aff5-5c38f3a2c55c",
"relationship--f82356ae-fe6c-437c-9c24-6b64314ae68a"
]
}
A Bundle with a Report and the STIX
Objects that are referred to by the Report
{
"type":
"bundle",
"id":
"bundle--44af6c39-c09b-49c5-9de2-394224b04982",
"objects": [
{
"type":
"identity",
"spec_version":
"2.1",
"id":
"identity--a463ffb3-1bd9-4d94-b02d-74e4f1658283",
...,
"name": "Acme
Cybersecurity Solutions"
},
{
"type":
"report",
"spec_version":
"2.1",
"id":
"report--84e4d88f-44ea-4bcd-bbf3-b2c1c320bcbd",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--a463ffb3-1bd9-4d94-b02d-74e4f1658283",
"created":
"2015-12-21T19:59:11.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-21T19:59:11.000Z",
"name": "The
Black Vine Cyberespionage Group",
"description": "A
simple report with an indicator and campaign",
"published":
"2016-01-201T17:00:00Z",
"report_types":
["campaign"],
"object_refs": [
"indicator--26ffb872-1dd9-446e-b6f5-d58527e5b5d2",
"campaign--83422c77-904c-4dc1-aff5-5c38f3a2c55c",
"relationship--f82356ae-fe6c-437c-9c24-6b64314ae68a"
]
},
{
"type":
"indicator",
"spec_version":
"2.1",
"id":
"indicator--26ffb872-1dd9-446e-b6f5-d58527e5b5d2",
"created":
"2015-12-21T19:59:17.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-21T19:59:17.000Z",
"name": "Some
indicator",
"indicator_types":
["malicious-activity"],
"pattern": "[
file:hashes.MD5 = '3773a88f65a5e780c8dff9cdc3a056f3' ]",
"valid_from":
"2015-12-21T19:59:17Z",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--a463ffb3-1bd9-4d94-b02d-74e4f1658283"
},
{
"type":
"campaign",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"campaign--83422c77-904c-4dc1-aff5-5c38f3a2c55c",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--a463ffb3-1bd9-4d94-b02d-74e4f1658283",
"created":
"2015-12-21T19:59:17.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-21T19:59:17.000Z",
"name": "Some
Campaign"
},
{
"type":
"relationship",
"spec_version":
"2.1",
"id":
"relationship--f82356ae-fe6c-437c-9c24-6b64314ae68a",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--a463ffb3-1bd9-4d94-b02d-74e4f1658283",
"created":
"2015-12-21T19:59:17.000Z",
"modified":
"2015-12-21T19:59:17.000Z",
"source_ref":
"indicator--26ffb872-1dd9-446e-b6f5-d58527e5b5d2",
"target_ref":
"campaign--26ffb872-1dd9-446e-b6f5-d58527e5b5d2",
"relationship_type":
"indicates"
}
]
}
4.16 Threat Actor
Type Name: threat-actor
Threat Actors are actual individuals,
groups, or organizations believed to be operating with malicious intent. A
Threat Actor is not an Intrusion Set but may support or be affiliated with
various Intrusion Sets, groups, or organizations over time.
Threat Actors leverage their resources,
and possibly the resources of an Intrusion Set, to conduct attacks and run
Campaigns against targets.
Threat Actors can be characterized by
their motives, capabilities, goals, sophistication level, past activities,
resources they have access to, and their role in the organization.
4.16.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Threat
Actor Specific Properties
|
|
name,
description, threat_actor_types, aliases, first_seen, last_seen,
roles, goals, sophistication, resource_level,
primary_motivation, secondary_motivations, personal_motivations
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be
threat-actor.
|
|
name (required)
|
string
|
A name used
to identify this Threat Actor or Threat Actor group.
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A
description that provides more details and context about the Threat Actor, potentially
including its purpose and its key characteristics.
|
|
threat_actor_types
(required)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
This property specifies the type(s) of this threat actor.
This is an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come
from the threat-actor-type-ov
vocabulary.
|
|
aliases
(optional)
|
list of type string
|
A list of other names that this Threat
Actor is believed to use.
|
|
first_seen (optional)
|
timestamp
|
The time that this Threat Actor
was first seen.
This property is a summary property
of data from sightings and other data that may or may not be available in
STIX. If new sightings are received that are earlier than the first seen
timestamp, the object may be updated to account for the new data.
|
|
last_seen (optional)
|
timestamp
|
The time that this Threat Actor
was last seen.
This property is a summary
property of data from sightings and other data that may or may not be
available in STIX. If new sightings are received that are later than the last
seen timestamp, the object may be updated to account for the new data.
This MUST be greater than
or equal to the timestamp in the first_seen property.
|
|
roles
(optional)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
A list of roles the Threat Actor
plays.
This is an open vocabulary and the
values SHOULD come from the threat-actor-role-ov vocabulary.
|
|
goals (optional)
|
list of
type string
|
The
high-level goals of this Threat Actor, namely, what are they trying to
do. For example, they may be motivated by personal gain, but their goal is to
steal credit card numbers. To do this, they may execute specific Campaigns
that have detailed objectives like compromising point of sale systems at a
large retailer.
|
|
sophistication (optional)
|
open-vocab
|
The skill,
specific knowledge, special training, or expertise a Threat Actor must have
to perform the attack.
This is an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come from the threat-actor-sophistication-ov vocabulary.
|
|
resource_level (optional)
|
open-vocab
|
This defines
the organizational level at which this Threat Actor typically works, which in
turn determines the resources available to this Threat Actor for use in an
attack. This attribute is linked to the sophistication
property — a specific resource level implies that the Threat Actor has access
to at least a specific sophistication level.
This is an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come from the attack-resource-level-ov vocabulary.
|
|
primary_motivation
(optional)
|
open-vocab
|
The primary reason, motivation, or
purpose behind this Threat Actor. The motivation is why the Threat
Actor wishes to achieve the goal (what they are trying to achieve).
For example, a Threat Actor with a
goal to disrupt the finance sector in a country might be motivated by
ideological hatred of capitalism.
This is
an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come from the attack-motivation-ov
vocabulary.
|
|
secondary_motivations
(optional)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
The secondary reasons, motivations, or
purposes behind this Threat Actor.
These motivations can exist as an
equal or near-equal cause to the primary motivation. However, it does not
replace or necessarily magnify the primary motivation, but it might indicate
additional context. The position in the list has no significance.
This is
an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come from the attack-motivation-ov
vocabulary.
|
|
personal_motivations
(optional)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
The personal reasons, motivations, or
purposes of the Threat Actor regardless of organizational goals.
Personal motivation, which is
independent of the organization’s goals, describes what impels an individual
to carry out an attack. Personal motivation may align with the organization’s
motivation—as is common with activists—but more often it supports personal
goals. For example, an individual analyst may join a Data Miner corporation
because his or her skills may align with the corporation’s objectives. But
the analyst most likely performs his or her daily work toward those
objectives for personal reward in the form of a paycheck. The motivation of
personal reward may be even stronger for Threat Actors who commit illegal
acts, as it is more difficult for someone to cross that line purely for
altruistic reasons. The position in the list has no significance.
This is
an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come from the attack-motivation-ov
vocabulary.
|
4.16.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the Threat
Actor object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the embedded
relationships by property name along with their corresponding target. The rest
of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this object
type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The reverse
relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this object type
from another object type. They are included here for convenience. For their
definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
Common
Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Relationship
Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
threat-actor
|
attributed-to
|
identity
|
This Relationship describes that the
Threat Actor's real identity is the related Identity.
For example, an attributed-to
Relationship from the jay-sm17h Threat Actor to the John Smith Identity means
that the actor known as jay-sm17h is John Smith.
|
|
threat-actor
|
compromises
|
infrastructure
|
This Relationship describes that the Threat Actor
compromises the related Infrastructure.
|
|
threat-actor
|
hosts, owns
|
infrastructure
|
This Relationship describes that the Threat Actor hosts or
owns the related Infrastructure (e.g. an actor that rents botnets to other
threat actors).
|
|
threat-actor
|
impersonates
|
identity
|
This Relationship describes that the
Threat Actor impersonates the related Identity.
For example, an impersonates
Relationship from the gh0st Threat Actor to the ACME Corp. Identity means
that the actor known as gh0st impersonates ACME Corp.
|
|
threat-actor
|
located-at
|
location
|
This Relationship describes that the Threat Actor is
located at or in the related Location.
For example, a located-at relationship from the
gh0st Threat Actor to a Location representing the United States means that
ACME Corporation is located in the United States.
|
|
threat-actor
|
targets
|
identity, location, vulnerability
|
This Relationship describes that the
Threat Actor uses exploits of the related Vulnerability or targets the type
of victims described by the related Identity or Location.
For example, a targets Relationship from
the jay-sm17h Threat Actor to a Vulnerability in a blogging platform
indicates that attacks performed by John Smith often exploit that
Vulnerability.
Similarly, a targets Relationship from
the jay-sm17h Threat Actor to an Identity describing the energy sector in the
United States means that John Smith often carries out attacks against targets
in that sector.
|
|
threat-actor
|
uses
|
attack-pattern, infrastructure,
malware,
tool
|
This Relationship describes that
attacks carried out as part of the Threat Actor typically use the related
Attack Pattern, Infrastructure, Malware, or Tool.
For example, a uses Relationship from the
jay-sm17h Threat Actor to the xInject Malware indicates that xInject is often
used by John Smith.
A campaign, threat actor, intrusion set, malware, or tool
takes infrastructure and compromises and/or uses it for their own.
|
|
Reverse
Relationships
|
|
campaign, intrusion-set
|
attributed-to
|
threat-actor
|
See forward relationship for
definition.
|
|
malware
|
authored-by
|
threat-actor
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
indicator
|
indicates
|
threat-actor
|
See forward relationship for
definition.
|
Examples
{
"type":
"threat-actor",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"threat-actor--8e2e2d2b-17d4-4cbf-938f-98ee46b3cd3f",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:03:48.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:03:48.000Z",
"threat_actor_types": [
"crime-syndicate"],
"name": "Evil
Org",
"description": "The
Evil Org threat actor group",
"aliases":
["Syndicate 1", "Evil Syndicate 99"],
"roles":
"director",
"goals": ["Steal bank
money", "Steal credit cards"],
"sophistication": "advanced",
"resource_level":
"team",
"primary_motivation":
"organizational-gain"
}
4.17 Tool
Type Name: tool
Tools are legitimate software that can
be used by threat actors to perform attacks. Knowing how and when threat actors
use such tools can be important for understanding how campaigns are executed.
Unlike malware, these tools or software packages are often found on a system
and have legitimate purposes for power users, system administrators, network
administrators, or even normal users. Remote access tools (e.g., RDP) and
network scanning tools (e.g., Nmap) are examples of Tools that may be used by a
Threat Actor during an attack.
The Tool SDO characterizes the
properties of these software tools and can be used as a basis for making an
assertion about how a Threat Actor uses them during an attack. It contains
properties to name and describe the tool, a list of Kill Chain Phases the tool
can be used to carry out, and the version of the tool.
This SDO MUST NOT be used to
characterize malware. Further, Tool MUST NOT be used to characterise
tools used as part of a course of action in response to an attack.
4.17.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Tool
Specific Properties
|
|
name,
description, tool_types, aliases, kill_chain_phases, tool_version
|
|
Property Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of this property MUST be tool.
|
|
name
(required)
|
string
|
The name
used to identify the Tool.
|
|
description
(optional)
|
string
|
A
description that provides more details and context about the Tool,
potentially including its purpose and its key characteristics.
|
|
tool_types
(required)
|
list of type open-vocab
|
The kind(s) of tool(s) being described.
This is an open vocabulary and values SHOULD come
from the tool-type-ov
vocabulary.
|
|
aliases (optional)
|
list of type string
|
Alternative names used to identify this Tool.
|
|
kill_chain_phases (optional)
|
list of
type kill-chain-phase
|
The list of
kill chain phases for which this Tool can be used.
|
|
tool_version (optional)
|
string
|
The version
identifier associated with the Tool.
|
4.17.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
Tool object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the embedded
relationships by property name along with their corresponding target. The rest
of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this object
type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The reverse
relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this object type
from another object type. They are included here for convenience. For their
definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
Common
Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Relationship
Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
tool
|
delivers
|
malware
|
This Relationship describes that this Tool is used to
deliver a malware instance (or family).
|
|
tool
|
drops
|
malware
|
This Relationship documents that this
Tool drops a malware instance (or family).
|
|
tool
|
has
|
vulnerability
|
This Relationship describes that this specific Tool has
this specific Vulnerability.
For example, a tool may not have been patched and
currently is impacted by a CVE.
|
|
tool
|
targets
|
identity, infrastructure, location,
vulnerability
|
This Relationship documents that this
Tool is being used to target this Identity, Infrastructure, Location, or
exploit the Vulnerability.
For example, a targets Relationship
linking an exploit Tool to a Vulnerability for CVE-2016-0001 means that the
tool exploits that vulnerability.
Similarly, a targets Relationship
linking a DDoS Tool to an Identity representing the energy sector means that
Tool is typically used against targets in the energy sector.
|
|
tool
|
uses
|
infrastructure
|
This Relationship describes that this Tool uses the
related Infrastructure.
|
|
Reverse Relationships
|
|
infrastructure
|
hosts
|
tool
|
See forward relationship for definition
|
|
malware
|
downloads, drops
|
tool
|
See forward relationship for definition
|
|
indicator
|
indicates
|
tool
|
See forward relationship for
definition
|
|
course-of-action
|
mitigates
|
tool
|
See forward relationship for
definition
|
|
attack-pattern, campaign,
intrusion-set,
malware,
threat-actor
|
uses
|
tool
|
See forward relationship for
definition
|
Examples
{
"type": "tool",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"tool--8e2e2d2b-17d4-4cbf-938f-98ee46b3cd3f",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:03:48.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:03:48.000Z",
"tool_types": [
"remote-access"],
"name": "VNC"
}
4.18 Vulnerability
Type Name: vulnerability
A Vulnerability is "a mistake in
software that can be directly used by a hacker to gain access to a system or
network" . For example, if a piece of malware exploits CVE-2015-12345, a
Malware object could be linked to a Vulnerability object that references
CVE-2015-12345. CVE is a list of information security vulnerabilities and
exposures that provides common names for publicly known problems [CVE].
The Vulnerability SDO is primarily used
to link to external definitions of vulnerabilities or to describe 0-day
vulnerabilities that do not yet have an external definition. Typically, other
SDOs assert relationships to Vulnerability objects when a specific
vulnerability is targeted and exploited as part of malicious cyber activity. As
such, Vulnerability objects can be used as a linkage to the asset management
and compliance process.
4.18.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Vulnerability
Specific Properties
|
|
name,
description
|
|
Property Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type
(required)
|
string
|
The value of this property MUST be vulnerability.
|
|
external_references
(optional)
|
list of type
external-reference
|
A list of
external references which refer to non-STIX information. This property MAY
be used to provide one or more Vulnerability identifiers, such as a CVE
ID [CVE].
When specifying a CVE ID, the source_name property of the
external reference MUST be set to cve
and the external_id property MUST be the exact CVE identifier.
|
|
name
(required)
|
string
|
A name used
to identify the Vulnerability.
|
|
description
(optional)
|
string
|
A
description that provides more details and context about the Vulnerability,
potentially including its purpose and its key characteristics.
|
4.18.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
Vulnerability object and other STIX Objects. The first section lists the embedded
relationships by property name along with their corresponding target. The rest
of the table identifies the relationships that can be made from this object
type to another object type by way of the Relationship object. The reverse
relationships section illustrates the relationships targeting this object type
from another object type. They are included here for convenience. For their
definitions, please see the "Source" object.
Relationships are not restricted to those listed below.
Relationships can be created between any objects using the related-to
relationship type or, as with open vocabularies, user-defined names.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
Common
Relationships
|
|
duplicate-of, derived-from, related-to
|
|
Source
|
Relationship
Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
|
Reverse
Relationships
|
|
attack-pattern, campaign,
intrusion-set,
malware,
threat-actor,
tool
|
targets
|
vulnerability
|
See forward relationship for
definition.
|
|
malware
|
exploits
|
vulnerability
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
|
course-of-action
|
mitigates, remediates
|
vulnerability
|
See forward relationship for
definition.
|
|
infrastructure
|
has
|
vulnerability
|
See forward relationship for definition.
|
Examples
{
"type":
"vulnerability",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"vulnerability--0c7b5b88-8ff7-4a4d-aa9d-feb398cd0061",
"created":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"name":
"CVE-2016-1234",
"external_references": [
{
"source_name":
"cve",
"external_id":
"CVE-2016-1234"
}
]
}
5
STIX™ Relationship Objects
STIX Relationship Objects (SROs)
represent types of relationships used to describe CTI. The Generic Relationship
SRO is used to describe many varied types of relationships, while the specific
Sighting SRO contains additional properties to represent Sighting
relationships.
Property information, relationship
information, and examples are provided for each SRO defined below. Property
information includes common properties as well as properties that are specific
to each SRO. Because SROs cannot be the source or target of other SROs,
relationship information is included but only to describe embedded
relationships (e.g., created_by_ref).
5.1 Relationship
Type Name: relationship
The Relationship object is used to link
together two SDOs or SCOs in order to describe how they are related to each
other. If SDOs and SCOs are considered "nodes" or
"vertices" in the graph, the Relationship Objects (SROs) represent "edges".
STIX defines many relationship types to
link together SDOs and SCOs. These relationships are contained in the
"Relationships" table under each SDO and SCO definition. Relationship
types defined in the specification SHOULD be used to ensure consistency.
An example of a specification-defined relationship is that an indicator indicates
a campaign.
That relationship type is listed in the Relationships section of the Indicator
SDO definition.
STIX also allows relationships from any
SDO or SCO to any SDO or SCO that have not been defined in this specification.
These relationships MAY use the related-to relationship type or MAY
use a user-defined relationship type. As an example, a user might want to
link malware
directly to a tool.
They can do so using related-to to say that the Malware is related to the
Tool but not describe how, or they could use delivered-by (a user-defined name they
determined) to indicate more detail.
Note that some relationships in STIX may
seem like "shortcuts". For example, an Indicator doesn't really
detect a Campaign: it detects activity (Attack Patterns, Malware,
Infrastructure, etc.) that are often used by that campaign. While some analysts
might want all of the source data and think that shortcuts are misleading, in
many cases it's helpful to provide just the key points (shortcuts) and leave
out the low-level details. In other cases, the low-level analysis may not be
known or sharable, while the high-level analysis is. For these reasons,
relationships that might appear to be "shortcuts" are not excluded
from STIX.
5.1.1 Specification-Defined
Relationships Summary
A relationship summary table for all
specification-defined relationships can be found In Appendix B of this document
The relationship summary table is provided as a convenience. If there is a
discrepancy between the table and the relationships defined with each of the
SDOs, then the relationships defined with the SDOs MUST be viewed as
authoritative.
5.1.2 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Relationship
Specific Properties
|
|
relationship_type,
description, source_ref, target_ref, start_time, stop_time
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be relationship.
|
|
relationship_type
(required)
|
string
|
The name
used to identify the type of Relationship. This value SHOULD be an
exact value listed in the relationships for the source and target SDO, but MAY
be any string. The value of this property MUST be in ASCII and is
limited to characters a–z (lowercase ASCII), 0–9, and hyphen (-).
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A description
that provides more details and context about the Relationship, potentially
including its purpose and its key characteristics.
|
|
source_ref
(required)
|
identifier
|
The id
of the source (from) object. The value MUST be an ID reference to an
SDO or SCO (i.e., it cannot point to an SRO, Bundle, Language Content,or
Marking Definition).
|
|
target_ref
(required)
|
identifier
|
The id
of the target (to) object. The value MUST be an ID reference to an SDO
or SCO (i.e., it cannot point to an SRO, Bundle, Language Content, or Marking
Definition).
|
|
start_time
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
This optional timestamp represents the
earliest time at which the Relationship between the objects exists. If this
property is a future timestamp, at the time the start_time property is defined, then this represents an
estimate by the producer of the intelligence of the earliest time at which
relationship will be asserted to be true.
If it is not specified, then the
earliest time at which the relationship between the objects exists is not
defined.
|
|
stop_time
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
The latest time at which the
Relationship between the objects exists. If this property is a future
timestamp, at the time the stop_time
property is defined, then this represents an estimate by the producer of the
intelligence of the latest time at which relationship will be asserted to be
true.
If start_time
and stop_time are both
defined, then stop_time MUST
be later than the start_time
value.
If stop_time
is not specified, then the latest time at which the relationship between the
objects exists is either not known, not disclosed, or has no defined stop
time.
|
5.1.3 Relationships
There are no relationships explicitly defined between the
Relationship object and other STIX Objects, other than the embedded
relationships listed below. These embedded relationships are listed by property
name along with their corresponding target.
The only type of relationship that can point to a
Relationship Object is the embedded relationship on the Note, Opinion, and
Language Content Objects.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
5.2 Sighting
Type Name: sighting
A Sighting denotes the belief that
something in CTI (e.g., an indicator, malware, tool, threat actor, etc.) was
seen. Sightings are used to track who and what are being targeted, how attacks
are carried out, and to track trends in attack behavior.
The Sighting relationship object is a
special type of SRO; it is a relationship that contains extra properties not
present on the Generic Relationship object. These extra properties are included
to represent data specific to sighting relationships (e.g., count, representing how many times
something was seen), but for other purposes a Sighting can be thought of as a
Relationship with a name of "sighting-of". Sighting is captured as a
relationship because you cannot have a sighting unless you have something that
has been sighted. Sighting does not make sense without the relationship to what
was sighted.
Sighting relationships relate three
aspects of the sighting:
●
What was sighted, such as the Indicator, Malware, Campaign, or other SDO
(sighting_of_ref)
●
Who sighted it and/or where it was sighted, represented as an Identity (where_sighted_refs) and
●
What was actually seen on systems and networks, represented as Observed
Data (observed_data_refs)
What was sighted is required; a sighting
does not make sense unless you say what you saw. Who sighted it, where it was
sighted, and what was actually seen are optional. In many cases it is not
necessary to provide that level of detail in order to provide value.
Sightings are used whenever any SDO has
been "seen". In some cases, the object creator wishes to convey very
little information about the sighting; the details might be sensitive, but the
fact that they saw a malware instance or threat actor could still be very
useful. In other cases, providing the details may be helpful or even necessary;
saying exactly which of the 1000 IP addresses in an indicator were sighted is
helpful when tracking which of those IPs is still malicious.
Sighting is distinct from Observed Data
in that Sighting is an intelligence assertion ("I saw this threat
actor") while Observed Data is simply information ("I saw this
file"). When you combine them by including the linked Observed Data (observed_data_refs) from a Sighting,
you can say "I saw this file, and that makes me think I saw this threat
actor".
5.2.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
defanged, extensions
|
|
Sighting
Specific Properties
|
|
description,
first_seen, last_seen, count, sighting_of_ref,
observed_data_refs, where_sighted_refs, summary
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be sighting.
|
|
description (optional)
|
string
|
A description that provides more
details and context about the Sighting.
|
|
first_seen
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
The beginning of the time window
during which the SDO referenced by the sighting_of_ref property was
sighted.
|
|
last_seen
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
The end of the time window during
which the SDO referenced by the sighting_of_ref property was sighted.
If first_seen
and last_seen are both
defined, then last_seen MUST
be later than the first_seen
value.
|
|
count
(optional)
|
integer
|
If present, this MUST be an
integer between 0 and 999,999,999 inclusive and represents the number of
times the SDO referenced by the sighting_of_ref property was sighted.
Observed Data has a similar property
called number_observed,
which refers to the number of times the data was observed. These counts refer
to different concepts and are distinct.
For example, a single sighting of a
DDoS bot might have many millions of observations of the network traffic that
it generates. Thus, the Sighting count
would be 1 (the bot was observed once) but the Observed Data number_observed would be much higher.
As another example, a sighting with a
count of 0 can be used to express that an indicator was not seen at all.
|
|
sighting_of_ref
(required)
|
identifier
|
An ID reference to the SDO that was
sighted (e.g., Indicator or Malware).
For example, if this is a Sighting of
an Indicator, that Indicator’s ID would be the value of this property.
This property MUST reference
only an SDO or a Custom Object.
|
|
observed_data_refs
(optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
A list of ID references to the
Observed Data objects that contain the raw cyber data for this Sighting.
For example, a Sighting of an
Indicator with an IP address could include the Observed Data for the network
connection that the Indicator was used to detect.
This property MUST reference
only Observed Data SDOs.
|
|
where_sighted_refs
(optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
A list of ID references to the
Identity or Location objects describing the entities or types of entities
that saw the sighting.
Omitting the where_sighted_refs property does not
imply that the sighting was seen by the object creator. To indicate that the
sighting was seen by the object creator, an Identity representing the object
creator should be listed in where_sighted_refs.
This property MUST reference
only Identity or Location SDOs.
|
|
summary
(optional)
|
boolean
|
The summary
property indicates whether the Sighting should be considered summary data.
Summary data is an aggregation of previous Sightings reports and should not
be considered primary source data. Default value is false.
|
5.2.2 Relationships
There are no relationships explicitly defined between the
Sighting object and other STIX Objects, other than the embedded relationships
listed below. These embedded relationships are listed by property name along
with their corresponding target.
The only type of relationship that can point to a Sighting
Object is the embedded relationship on the Note, Opinion, and Language Content
Objects.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identifier (of type identity)
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type marking-definition)
|
|
sighting_of_ref
|
identifier (of type SDO)
|
|
observed_data_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type SCO)
|
|
where_sighted_refs
|
list of type identifier (of type identity)
|
Examples
Sighting of Indicator, without Observed
Data
{
"type":
"sighting",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"sighting--ee20065d-2555-424f-ad9e-0f8428623c75",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:08:31.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:08:31.000Z",
"sighting_of_ref":
"indicator--8e2e2d2b-17d4-4cbf-938f-98ee46b3cd3f"
}
Sighting of Indicator, with Observed
Data (what exactly was seen) and where it was seen
[
{
"type":
"sighting",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"sighting--ee20065d-2555-424f-ad9e-0f8428623c75",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T20:08:31.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T20:08:31.000Z",
"first_seen":
"2015-12-21T19:00:00Z",
"last_seen":
"2015-12-21T19:00:00Z",
"count": 50,
"sighting_of_ref":
"indicator--8e2e2d2b-17d4-4cbf-938f-98ee46b3cd3f",
"observed_data_refs":
["observed-data--b67d30ff-02ac-498a-92f9-32f845f448cf"],
"where_sighted_refs":
["identity--b67d30ff-02ac-498a-92f9-32f845f448ff"]
},
{
"type":
"observed-data",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"observed-data--b67d30ff-02ac-498a-92f9-32f845f448cf",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-06T19:58:16.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-06T19:58:16.000Z",
"first_observed":
"2015-12-21T19:00:00Z",
"last_observed":
"2016-04-06T19:58:16Z",
"number_observed": 50,
"object_refs": [
"file--30038539-3eb6-44bc-a59e-d0d3fe84695a"
]
}
]
Type Name: artifact
The Artifact object permits capturing an
array of bytes (8-bits), as a base64-encoded string, or linking to a file-like
payload.
One of payload_bin
or url MUST be
provided. It is incumbent on object creators to ensure that the URL is
accessible for downstream consumers.
6.1.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
Artifact
Object Specific Properties
|
|
mime_type,
payload_bin, url, hashes, encryption_algorithm,
decryption_key
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
hashes, payload_bin
If the hashes
property is present, include only one hash. The selected hash SHOULD
come from this ordered list (based on the following order of preference) [
MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-512 ].
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be artifact.
|
|
mime_type (optional)
|
string
|
Whenever feasible, this value SHOULD
be one of the values defined in the Template column in the IANA media type
registry [Media
Types]. Maintaining a comprehensive universal catalog of all
extant file types is obviously not possible. When specifying a MIME Type not
included in the IANA registry, implementers should use their best judgement
so as to facilitate interoperability.
|
|
payload_bin
(optional)
|
binary
|
Specifies the binary data contained in
the artifact as a base64-encoded string.
This property MUST NOT be
present if url is provided.
|
|
url
(optional)
|
string
|
The value of this property MUST
be a valid URL that resolves to the unencoded content.
This property MUST NOT be
present if payload_bin is
provided.
|
|
hashes
(optional)
|
hashes
|
Specifies a dictionary of hashes for
the contents of the url or the payload_bin.
This property MUST be present
when the url property is present.
Dictionary keys MUST come from the hash-algorithm-ov.
|
|
encryption_algorithm
(optional)
|
enum
|
If the artifact is encrypted, specifies the type of
encryption algorithm the binary data (either via payload_bin or url) is encoded in.
The value of this property MUST come from the encryption-algorithm-enum
enumeration.
If both mime_type
and encryption_algorithm are
included, this signifies that the artifact represents an encrypted archive.
|
|
decryption_key
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the decryption key for the encrypted binary data
(either via payload_bin or url).
For example, this may be useful in cases of sharing malware samples, which
are often encoded in an encrypted archive.
This property MUST NOT be present when the encryption_algorithm property is
absent.
|
Examples
Basic Image Artifact
{
"type":
"artifact",
"spec_version":
"2.1",
"id":
"artifact--ca17bcf8-9846-5ab4-8662-75c1bf6e63ee",
"mime_type":
"image/jpeg",
"payload_bin":
"VBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAADI== ..."
}
Encrypted Zip Archive Artifact
{
"type": "artifact",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"artifact--6f437177-6e48-5cf8-9d9e-872a2bddd641",
"mime_type":
"application/zip",
"payload_bin": "ZX7HIBWPQA99NSUhEUgAAADI==
...",
"encryption_algorithm": "mime-type-indicated",
"decryption_key": "My voice is
my passport"
}
6.2 AS Object
Type Name: autonomous-system
The AS object represents the properties
of an Autonomous System (AS).
6.2.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
AS Object
Specific Properties
|
|
number,
name, rir
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
number
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be autonomous-system.
|
|
number (required)
|
integer
|
Specifies
the number assigned to the AS. Such assignments are typically performed by a
Regional Internet Registry (RIR).
|
|
name
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the name of the AS.
|
|
rir
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the name of the Regional Internet Registry (RIR) that assigned the number to
the AS.
|
Examples
Basic AS object
{
"type":
"autonomous-system",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"autonomous-system--f720c34b-98ae-597f-ade5-27dc241e8c74",
"number": 15139,
"name": "Slime
Industries",
"rir": "ARIN"
}
6.3 Directory Object
Type Name: directory
The Directory object represents the
properties common to a file system directory.
6.3.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
Directory
Object Specific Properties
|
|
path,
path_enc, ctime, mtime, atime,
contains_refs
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
path
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be directory.
|
|
path (required)
|
string
|
Specifies
the path, as originally observed, to the directory on the file system.
|
|
path_enc
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the observed encoding for
the path. The value MUST be specified if the path is stored in a
non-Unicode encoding. This value MUST be specified using the
corresponding name from the 2013-12-20 revision of the IANA character set registry [Character Sets].
If the preferred MIME name for a character set is defined, this value MUST
be used; if it is not defined, then the Name value from the registry MUST
be used instead.
|
|
ctime
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the date/time the directory
was created.
|
|
mtime
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the date/time the directory
was last written to/modified.
|
|
atime
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the date/time the directory
was last accessed.
|
|
contains_refs
(optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies a list of references to
other File and/or Directory objects contained within the directory.
The objects referenced in this list MUST
be of type file or directory.
|
Examples
Basic directory
{
"type":
"directory",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"directory--93c0a9b0-520d-545d-9094-1a08ddf46b05",
"path":
"C:\\Windows\\System32"
}
6.4 Domain Name Object
Type Name: domain-name
The Domain Name object represents the
properties of a network domain name.
6.4.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
Domain
Name Object Specific Properties
|
|
value,
resolves_to_refs
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
value
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be domain-name.
|
|
value (required)
|
string
|
Specifies
the value of the domain name. The value of this property MUST conform
to [RFC1034],
and each domain and sub-domain contained within the domain name MUST
conform to [RFC5890].
|
|
resolves_to_refs (optional - deprecated)
|
list of
type identifier
|
Specifies a
list of references to one or more IP addresses or domain names that the
domain name resolves to.
The objects
referenced in this list MUST be of type ipv4-addr or ipv6-addr or domain-name (for cases such as CNAME records).
|
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
Domain Name object and other STIX Objects. The table identifies the
relationships that can be made from this object type to another object type by
way of the Relationship object.
|
Source
|
Relationship Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
domain-name
|
resolves-to
|
domain-name, ipv4-addr, ipv6-addr
|
This Relationship describes that this Domain Name resolves
to one or more IP addresses or domain names.
|
Examples
Basic FQDN
{
"type":
"domain-name",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"domain-name--3c10e93f-798e-5a26-a0c1-08156efab7f5",
"value":
"example.com",
}
{
"type": "ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--ff26c055-6336-5bc5-b98d-13d6226742dd",
"value": "198.51.100.3"
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--ecca811f-f6ce-4c46-86c6-1ea1b1d58a0a",
"created": "2018-11-23T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2018-11-23T08:17:27.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"resolves-to",
"source_ref":
"domain-name--3c10e93f-798e-5a26-a0c1-08156efab7f5,
"target_ref":
"ipv4-addr--ff26c055-6336-5bc5-b98d-13d6226742dd"
}
6.5 Email Address Object
Type Name: email-addr
The Email Address object represents a
single email address.
6.5.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
Email
Address Object Specific Properties
|
|
value,
display_name, belongs_to_ref
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
value
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be email-addr.
|
|
value (required)
|
string
|
Specifies
the value of the email address. This MUST NOT include the display
name.
This
property corresponds to the addr-spec construction in section 3.4 of [RFC5322],
for example, jane.smith@example.com.
|
|
display_name
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies a single email display name,
i.e., the name that is displayed to the human user of a mail application.
This property corresponds to
the display-name construction in section 3.4 of [RFC5322],
for example, Jane
Smith.
|
|
belongs_to_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies the user account that the
email address belongs to, as a reference to a User Account object.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type user-account.
|
Examples
Basic Email Address
{
"type":
"email-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"email-addr--2d77a846-6264-5d51-b586-e43822ea1ea3",
"value":
"john@example.com",
"display_name": "John
Doe"
}
6.6 Email Message Object
Type Name: email-message
The Email Message object represents an
instance of an email message, corresponding to the internet message format
described in [RFC5322]
and related RFCs.
Header field values that have been
encoded as described in section 2 of [RFC2047] MUST be decoded before inclusion
in Email Message object properties. For example, this is some text MUST
be used instead of =?iso-8859-1?q?this=20is=20some=20text?=.
Any characters in the encoded value which cannot be decoded into Unicode SHOULD
be replaced with the 'REPLACEMENT CHARACTER' (U+FFFD). If it is necessary
to capture the header value as observed, this can be achieved by referencing an
Artifact object through the raw_email_ref
property.
6.6.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
Email
Message Object Specific Properties
|
|
is_multipart,
date, content_type, from_ref, sender_ref, to_refs,
cc_refs, bcc_refs, subject, received_lines,
additional_header_fields, body, body_multipart, raw_email_ref
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
from_ref,
subject, body
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be email-message.
|
|
is_multipart (required)
|
boolean
|
Indicates
whether the email body contains multiple MIME parts.
|
|
date
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the date/time that the email
message was sent.
|
|
content_type
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the value of the
“Content-Type” header of the email message.
|
|
from_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies the value of the “From:”
header of the email message. The "From:" field specifies the author
of the message, that is, the mailbox(es) of the person or system responsible
for the writing of the message.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type email-address.
|
|
sender_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies the value of the “Sender”
field of the email message. The "Sender:" field specifies the
mailbox of the agent responsible for the actual transmission of the message.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type email-address.
|
|
to_refs
(optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies the mailboxes that are “To:”
recipients of the email message.
The objects referenced in this list MUST
be of type email-address.
|
|
cc_refs
(optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies the mailboxes that are “CC:”
recipients of the email message.
The objects referenced in this list MUST
be of type email-address.
|
|
bcc_refs
(optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies the mailboxes that are
“BCC:” recipients of the email message.
As per [RFC5322], the absence of this property
should not be interpreted as semantically equivalent to an absent BCC header
on the message being characterized.
The objects referenced in this list MUST
be of type email-address.
|
|
message_id
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the Message-ID field of the
email message.
|
|
subject
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the subject of the email
message.
|
|
received_lines
(optional)
|
list of type string
|
Specifies one or more
"Received" header fields that may be included in the email headers.
List values MUST appear in the
same order as present in the email message.
|
|
additional_header_fields
(optional)
|
dictionary
|
Specifies
any other header fields (except for date, received_lines, content_type, from_ref, sender_ref, to_refs, cc_refs, bcc_refs, and subject) found in
the email message, as a dictionary.
Each
key/value pair in the dictionary represents the name/value of a single header
field or names/values of a header field that occurs more than once. Each
dictionary key SHOULD be a case-preserved version of the header field
name. The corresponding value for each dictionary key MUST always be a
list of type string
to support when a header field is repeated.
|
|
body
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies a string containing the email
body. This property MUST NOT be used if is_multipart is true.
|
|
body_multipart
(optional)
|
list of type mime-part-type
|
Specifies a list of the MIME parts
that make up the email body. This property MUST NOT be used if is_multipart is false.
|
|
raw_email_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies the raw binary contents of
the email message, including both the headers and body, as a reference to an
Artifact object.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type artifact.
|
6.6.2 Email
MIME Component Type
Type Name: mime-part-type
Specifies one component of a multi-part
email body.
There is no property to capture the
value of the “Content-Transfer-Encoding” header field, since the body MUST be
decoded before being represented in the body
property.
One of body
OR body_raw_ref MUST be
included.
6.6.2.1 Properties
|
Property Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
body (optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the contents of the MIME part if the content_type is not provided or starts with text/ (e.g., in the case of plain text or HTML email).
For
inclusion in this property, the contents MUST be decoded to Unicode.
Note that the charset provided in content_type is for
informational usage and not for decoding of this property.
|
|
body_raw_ref (optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies
the contents of non-textual MIME parts, that is those whose content_type does not start with text/, as a reference to an Artifact object or File object.
The object
referenced in this property MUST be of type artifact or file. For use cases
where conveying the actual data contained in the MIME part is of primary
importance, artifact SHOULD
be used. Otherwise, for use cases where conveying metadata about the
file-like properties of the MIME part is of primary importance, file SHOULD be used.
|
|
content_type
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the value of the
“Content-Type” header field of the MIME part.
Any additional “Content-Type” header
field parameters such as charset SHOULD be included in this
property.
Example:
text/html; charset=UTF-8
|
|
content_disposition
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the value of the
“Content-Disposition” header field of the MIME part.
|
Examples
Simple Email Message
{
"type": "email-message",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"email-message--72b7698f-10c2-565a-a2a6-b4996a2f2265",
"from_ref":
"email-addr--89f52ea8-d6ef-51e9-8fce-6a29236436ed",
"to_refs":
["email-addr--e4ee5301-b52d-59cd-a8fa-8036738c7194"],
"is_multipart": false,
"date":
"1997-11-21T15:55:06.000Z",
"subject": "Saying Hello"
}
{
"type":
"email-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"email-addr--89f52ea8-d6ef-51e9-8fce-6a29236436ed",
"value":
"jdoe@example.com",
"display_name": "John
Doe"
}
{
"type":
"email-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"email-addr--e4ee5301-b52d-59cd-a8fa-8036738c7194",
"value":
"mary@example.com",
"display_name": "Mary
Smith"
}
Simple Email Message with
Additional Header Properties
{
"type": "email-message",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"email-message--0c57a381-2a17-5e61-8754-5ef96efb286c",
"from_ref":
"email-addr--9b7e29b3-fd8d-562e-b3f0-8fc8134f5dda",
"to_refs":
["email-addr--d1b3bf0c-f02a-51a1-8102-11aba7959868"],
"is_multipart": false,
"date":
"2004-04-19T12:22:23.000Z",
"subject": "Did you see
this?",
"additional_header_fields": {
"Reply-To": [
"steve@example.com",
"jane@example.com"
]
}
}
{
"type":
"email-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"email-addr--9b7e29b3-fd8d-562e-b3f0-8fc8134f5dda",
"value":
"joe@example.com",
"display_name": "Joe
Smith"
}
{
"type":
"email-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"email-addr--d1b3bf0c-f02a-51a1-8102-11aba7959868",
"value":
"bob@example.com",
"display_name": "Bob
Smith"
}
Complex MIME Email Message
{
"type":
"email-message",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"email-message--cf9b4b7f-14c8-5955-8065-020e0316b559",
"is_multipart": true,
"received_lines": [
"from mail.example.com
([198.51.100.3]) by smtp.gmail.com with ESMTPSA id
q23sm23309939wme.17.2016.07.19.07.20.32 (version=TLS1_2
cipher=ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256 bits=128/128); Tue, 19 Jul 2016 07:20:40
-0700 (PDT)"
],
"content_type":
"multipart/mixed",
"date":
"2016-06-19T14:20:40.000Z",
"from_ref": "email-addr--89f52ea8-d6ef-51e9-8fce-6a29236436ed",
"to_refs": ["email-addr--d1b3bf0c-f02a-51a1-8102-11aba7959868"],
"cc_refs": ["email-addr--e4ee5301-b52d-59cd-a8fa-8036738c7194"],
"subject": "Check out
this picture of a cat!",
"additional_header_fields": {
"Content-Disposition":
"inline",
"X-Mailer":
"Mutt/1.5.23",
"X-Originating-IP":
"198.51.100.3"
},
"body_multipart": [
{
"content_type":
"text/plain; charset=utf-8",
"content_disposition":
"inline",
"body": "Cats are
funny!"
},
{
"content_type":
"image/png",
"content_disposition":
"attachment; filename=\"tabby.png\"",
"body_raw_ref": "artifact--4cce66f8-6eaa-53cb-85d5-3a85fca3a6c5"
},
{
"content_type":
"application/zip",
"content_disposition":
"attachment; filename=\"tabby_pics.zip\"",
"body_raw_ref": "file--6ce09d9c-0ad3-5ebf-900c-e3cb288955b5"
}
]
}
{
"type":
"email-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"email-addr--89f52ea8-d6ef-51e9-8fce-6a29236436ed",
"value":
"jdoe@example.com",
"display_name": "John
Doe"
}
{
"type":
"email-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"email-addr--d1b3bf0c-f02a-51a1-8102-11aba7959868",
"value": "bob@example.com",
"display_name": "Bob
Smith"
}
{
"type":
"email-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"email-addr--e4ee5301-b52d-59cd-a8fa-8036738c7194",
"value":
"mary@example.com",
"display_name": "Mary
Smith"
}
{
"type":
"artifact",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"artifact--4cce66f8-6eaa-53cb-85d5-3a85fca3a6c5",
"mime_type":
"image/jpeg",
"payload_bin":
"VBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAADI== ...",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"effb46bba03f6c8aea5c653f9cf984f170dcdd3bbbe2ff6843c3e5da0e698766"
}
}
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--6ce09d9c-0ad3-5ebf-900c-e3cb288955b5",
"name":
"tabby_pics.zip",
"magic_number_hex":
"504B0304",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"fe90a7e910cb3a4739bed9180e807e93fa70c90f25a8915476f5e4bfbac681db"
}
}
6.7 File Object
Type Name: file
The File object represents the
properties of a file. A File object MUST contain at least one of hashes or name.
6.7.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
File
Object Specific Properties
|
|
hashes,
size, name, name_enc, magic_number_hex,
mime_type, ctime, mtime, atime,
parent_directory_ref, contains_refs, content_ref
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
hashes, name, extensions
If the hashes
property is present, include only one hash. The selected hash SHOULD
come from this ordered list (based on the following order of preference) [
MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-512 ].
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be file.
|
|
extensions (optional)
|
dictionary
|
The File
object defines the following extensions. In addition to these, producers MAY
create their own.
ntfs-ext, raster-image-ext, pdf-ext, archive-ext, windows-pebinary-ext
Dictionary
keys MUST identify the extension type by name.
The
corresponding dictionary values MUST contain the contents of the
extension instance.
|
|
hashes
(optional)
|
hashes
|
Specifies a dictionary of hashes for
the file.
(When used with the Archive File Extension, this refers to the hash of the entire
archive file, not its contents.)
Dictionary keys MUST come from
the hash-algorithm-ov.
|
|
size
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the size of the file, in
bytes. The value of this property MUST NOT be negative.
|
|
name
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the name of the file.
|
|
name_enc
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the observed encoding for
the name of the file. This value MUST be specified using the
corresponding name from the 2013-12-20 revision of the IANA character set
registry [Character
Sets]. If the value from the Preferred MIME Name column for a
character set is defined, this value MUST be used; if it is not
defined, then the value from the Name column in the registry MUST be
used instead.
This property allows for the capture
of the original text encoding for the file name, which may be forensically
relevant; for example, a file on an NTFS volume whose name was created using
the windows-1251 encoding, commonly used for languages based on Cyrillic
script.
|
|
magic_number_hex (optional)
|
hex
|
Specifies
the hexadecimal constant (“magic number”) associated with a specific file
format that corresponds to the file, if applicable.
|
|
mime_type
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the MIME type name specified
for the file, e.g., application/msword.
Whenever feasible, this value SHOULD
be one of the values defined in the Template column in the IANA media type
registry [Media
Types].
Maintaining a comprehensive universal
catalog of all extant file types is obviously not possible. When specifying a
MIME Type not included in the IANA registry, implementers should use their
best judgement so as to facilitate interoperability.
|
|
ctime
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the date/time the file was
created.
|
|
mtime
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the date/time the file was
last written to/modified.
|
|
atime
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the date/time the file was
last accessed.
|
|
parent_directory_ref (optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies
the parent directory of the file, as a reference to a Directory object.
The object
referenced in this property MUST be of type directory.
|
|
contains_refs
(optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies a list of references to
other Cyber-observable Objects contained within the file, such as another
file that is appended to the end of the file, or an IP address that is
contained somewhere in the file.
This is intended for use cases other
than those targeted by the Archive extension.
|
|
content_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies the content of the file,
represented as an Artifact object.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type artifact.
|
Examples
Basic file with file system properties
without observed encoding
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--e277603e-1060-5ad4-9937-c26c97f1ca68",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"fe90a7e910cb3a4739bed9180e807e93fa70c90f25a8915476f5e4bfbac681db"
},
"size": 25536,
"name":
"foo.dll"
}
Basic file with file system
properties with observed encoding
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id": "file--90bd400b-89a5-51a5-b17d-55bc7719723b",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"841a8921140aba50671ebb0770fecc4ee308c4952cfeff8de154ab14eeef4649"
},
"name":
"quêry.dll",
"name_enc":
"windows-1252"
}
In this example, the file name would
have originally appeared using the bytes 71 75 ea 72 79 2e 64 6c 6c.
Representing it in UTF-8, as required for JSON, would use the bytes 71 75 c3
aa 72 79 2e 64 6c 6c.
Basic file with parent directory
{
"type":
"directory",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"directory--93c0a9b0-520d-545d-9094-1a08ddf46b05",
"path":
"C:\\Windows\\System32"
}
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--66156fad-2a0d-5237-bba4-ba1912887cfe",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"ceafbfd424be2ca4a5f0402cae090dda2fb0526cf521b60b60077c0f622b285a"
},
"parent_directory_ref":
"directory--93c0a9b0-520d-545d-9094-1a08ddf46b05",
"name":
"qwerty.dll"
}
6.7.2 Archive
File Extension
Type Name: archive-ext
The Archive File extension specifies a
default extension for capturing properties specific to archive files. The key
for this extension when used in the extensions
dictionary MUST be archive-ext.
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
contains_refs (required)
|
list of
type identifier
|
This
property specifies the files that are contained in the archive. It MUST
contain references to one or more File objects.
The objects
referenced in this list MUST be of type file or directory.
|
|
comment
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies a comment included as part
of the archive file.
|
Examples
Basic unencrypted ZIP Archive
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--019fde1c-94ca-5967-8b3c-a906a51d87ac",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"ceafbfd424be2ca4a5f0402cae090dda2fb0526cf521b60b60077c0f622b285a"
}
}
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--94fc2163-dec3-5715-b824-6e689c4de865",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"19c549ec2628b989382f6b280cbd7bb836a0b461332c0fe53511ce7d584b89d3"
}
}
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--d07ff290-d7e0-545b-a2ff-04602a9e0b73",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"0969de02ecf8a5f003e3f6d063d848c8a193aada092623f8ce408c15bcb5f038"
}
}
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id": "file--9a1f834d-2506-5367-baec-7aa63996ac43",
"name":
"foo.zip",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"35a01331e9ad96f751278b891b6ea09699806faedfa237d40513d92ad1b7100f"
},
"mime_type":
"application/zip",
"extensions": {
"archive-ext": {
"contains_refs": [
"file--019fde1c-94ca-5967-8b3c-a906a51d87ac",
"file--94fc2163-dec3-5715-b824-6e689c4de865",
"file--d07ff290-d7e0-545b-a2ff-04602a9e0b73"
]
}
}
}
6.7.3 NTFS
File Extension
Type Name: ntfs-ext
The NTFS file extension specifies a
default extension for capturing properties specific to the storage of the file
on the NTFS file system. The key for this extension when used in the extensions dictionary MUST be ntfs-ext.
An object using the NTFS File Extension MUST contain at least one
property from this extension.
6.7.3.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
sid
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the security ID (SID) value
assigned to the file.
|
|
alternate_data_streams
(optional)
|
list of type alternate-data-stream-type
|
Specifies a list of NTFS alternate
data streams that exist for the file.
|
6.7.3.2 Alternate Data Stream Type
Type Name: alternate-data-stream-type
The Alternate Data Stream type represents
an NTFS alternate data stream.
6.7.3.2.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
name (required)
|
string
|
Specifies
the name of the alternate data stream.
|
|
hashes
(optional)
|
hashes
|
Specifies a dictionary of hashes for
the data contained in the alternate data stream.
Dictionary keys MUST come from the hash-algorithm-ov.
|
|
size
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the size of the alternate
data stream, in bytes. The value of this property MUST NOT be
negative.
|
Examples
NTFS File with a single alternate
data stream
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--73c4cd13-7206-5100-88ef-822c42d3f02c",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"35a01331e9ad96f751278b891b6ea09699806faedfa237d40513d92ad1b7100f"
},
"extensions": {
"ntfs-ext": {
"alternate_data_streams": [
{
"name":
"second.stream",
"size": 25536
}
]
}
}
}
6.7.4 PDF File
Extension
Type Name: pdf-ext
The PDF file extension specifies a
default extension for capturing properties specific to PDF files. The key for
this extension when used in the extensions
dictionary MUST be pdf-ext. An object using the PDF File Extension MUST
contain at least one property from this extension.
6.7.4.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
version
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the decimal version number
of the string from the PDF header that specifies the version of the PDF
specification to which the PDF file conforms. E.g., 1.4.
|
|
is_optimized
(optional)
|
boolean
|
Specifies whether the PDF file has
been optimized.
|
|
document_info_dict
(optional)
|
dictionary
|
Specifies details of the PDF document
information dictionary (DID), which includes properties like the document
creation data and producer, as a dictionary. Each key in the dictionary SHOULD
be a case-preserved version of the corresponding entry in the document
information dictionary without the prepended forward slash, e.g., Title.
The corresponding value for the key MUST be the value specified for
the document information dictionary entry, as a string.
|
|
pdfid0
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the first file identifier
found for the PDF file.
|
|
pdfid1
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the second file identifier
found for the PDF file.
|
Examples
Basic PDF file
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--ec3415cc-5f4f-5ec8-bdb1-6f86996ae66d",
"extensions": {
"pdf-ext": {
"version":
"1.7",
"document_info_dict":
{
"Title":
"Sample document",
"Author":
"Adobe Systems Incorporated",
"Creator":
"Adobe FrameMaker 5.5.3 for Power Macintosh",
"Producer":
"Acrobat Distiller 3.01 for Power Macintosh",
"CreationDate":
"20070412090123-02"
},
"pdfid0":
"DFCE52BD827ECF765649852119D",
"pdfid1":
"57A1E0F9ED2AE523E313C"
}
}
}
6.7.5 Raster
Image File Extension
Type Name: raster-image-ext
The Raster Image file extension
specifies a default extension for capturing properties specific to raster image
files. The key for this extension when used in the extensions dictionary MUST be raster-image-ext.
An object using the Raster Image File Extension MUST contain at least
one property from this extension.
6.7.5.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
image_height
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the height of the image in
the image file, in pixels.
|
|
image_width
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the width of the image in
the image file, in pixels.
|
|
bits_per_pixel
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the sum of bits used for
each color channel in the image file, and thus the total number of pixels
used for expressing the color depth of the image.
|
|
exif_tags
(optional)
|
dictionary
|
Specifies the set of EXIF tags found
in the image file, as a dictionary. Each key/value pair in the dictionary
represents the name/value of a single EXIF tag. Accordingly, each dictionary
key MUST be a case-preserved version of the EXIF tag name, e.g., XResolution.
Each dictionary value MUST be either an integer (for int* EXIF datatypes) or
a string
(for all other EXIF datatypes).
|
Examples
Simple Image File with EXIF Data
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--c7d1e135-8b34-549a-bb47-302f5cf998ed",
"name":
"picture.jpg",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256": "4bac27393bdd9777ce02453256c5577cd02275510b2227f473d03f533924f877"
},
"extensions": {
"raster-image-ext": {
"exif_tags": {
"Make":
"Nikon",
"Model":
"D7000",
"XResolution": 4928,
"YResolution": 3264
}
}
}
}
6.7.6 Windows™
PE Binary File Extension
Type Name: windows-pebinary-ext
The Windows™ PE Binary File
extension specifies a default extension for capturing properties specific to
Windows portable executable (PE) files. The key for this extension when used in
the extensions dictionary MUST
be windows-pebinary-ext.
An object using the Windows™ PE Binary File Extension MUST
contain at least one property other than the required pe_type property from this
extension.
6.7.6.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
pe_type (required)
|
open-vocab
|
Specifies
the type of the PE binary. This is an open vocabulary and values SHOULD
come from the windows-pebinary-type-ov
vocabulary.
|
|
imphash
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the special import hash, or
‘imphash’, calculated for the PE Binary based on its imported libraries and
functions. For more information on the imphash algorithm, see the original
article by Mandiant/FireEye: https://www.fireeye.com/blog/threat-research/2014/01/tracking-malware-import-hashing.html.
|
|
machine_hex (optional)
|
hex
|
Specifies
the type of target machine.
|
|
number_of_sections
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the number of sections in
the PE binary, as a non-negative integer.
|
|
time_date_stamp
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the time when the PE binary
was created. The timestamp value MUST be precise to the second.
|
|
pointer_to_symbol_table_hex
(optional)
|
hex
|
Specifies the file offset of the COFF
symbol table.
|
|
number_of_symbols
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the number of entries in the
symbol table of the PE binary, as a non-negative integer.
|
|
size_of_optional_header
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the size of the optional
header of the PE binary. The value of this property MUST NOT be
negative.
|
|
characteristics_hex
(optional)
|
hex
|
Specifies the flags that indicate the
file’s characteristics.
|
|
file_header_hashes
(optional)
|
hashes
|
Specifies any hashes that were
computed for the file header.
Dictionary keys MUST come from the hash-algorithm-ov.
|
|
optional_header
(optional)
|
windows-pe-optional-header-type
|
Specifies the PE optional header of
the PE binary. When used, at least one property from the
windows-pe-optional-header-type MUST be included.
|
|
sections
(optional)
|
list of type windows-pe-section-type
|
Specifies metadata about the sections
in the PE file.
|
6.7.6.2 Windows™ PE Optional Header Type
Type Name: windows-pe-optional-header-type
The Windows PE Optional Header type
represents the properties of the PE optional header. An object using the
Windows PE Optional Header Type MUST contain at least one property from
this type.
6.7.6.2.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
magic_hex
(optional)
|
hex
|
Specifies the hex value that indicates
the type of the PE binary.
|
|
major_linker_version
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the linker major version
number.
|
|
minor_linker_version
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the linker minor version
number.
|
|
size_of_code
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the size of the code (text)
section. If there are multiple such sections, this refers to the sum of the
sizes of each section. The value of this property MUST NOT be
negative.
|
|
size_of_initialized_data
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the size of the initialized
data section. If there are multiple such sections, this refers to the sum of
the sizes of each section. The value of this property MUST NOT be
negative.
|
|
size_of_uninitialized_data
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the size of the
uninitialized data section. If there are multiple such sections, this refers
to the sum of the sizes of each section. The value of this property MUST
NOT be negative.
|
|
address_of_entry_point
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the address of the entry
point relative to the image base when the executable is loaded into memory.
|
|
base_of_code
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the address that is relative
to the image base of the beginning-of-code section when it is loaded into
memory.
|
|
base_of_data
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the address that is relative
to the image base of the beginning-of-data section when it is loaded into
memory.
|
|
image_base
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the preferred address of the
first byte of the image when loaded into memory.
|
|
section_alignment
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the alignment (in bytes) of
PE sections when they are loaded into memory.
|
|
file_alignment
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the factor (in bytes) that
is used to align the raw data of sections in the image file.
|
|
major_os_version
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the major version number of
the required operating system.
|
|
minor_os_version
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the minor version number of
the required operating system.
|
|
major_image_version
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the major version number of
the image.
|
|
minor_image_version
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the minor version number of
the image.
|
|
major_subsystem_version
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the major version number of
the subsystem.
|
|
minor_subsystem_version
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the minor version number of
the subsystem.
|
|
win32_version_value_hex
(optional)
|
hex
|
Specifies the reserved win32 version
value.
|
|
size_of_image
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the size of the image in
bytes, including all headers, as the image is loaded in memory. The value of
this property MUST NOT be negative.
|
|
size_of_headers
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the combined size of the
MS-DOS, PE header, and section headers, rounded up to a multiple of the value
specified in the file_alignment header. The value of this property MUST
NOT be negative.
|
|
checksum_hex
(optional)
|
hex
|
Specifies the checksum of the PE
binary.
|
|
subsystem_hex
(optional)
|
hex
|
Specifies the subsystem (e.g., GUI,
device driver, etc.) that is required to run this image.
|
|
dll_characteristics_hex
(optional)
|
hex
|
Specifies the flags that characterize
the PE binary.
|
|
size_of_stack_reserve
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the size of the stack to
reserve, in bytes. The value of this property MUST NOT be negative.
|
|
size_of_stack_commit
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the size of the stack to
commit, in bytes. The value of this property MUST NOT be negative.
|
|
size_of_heap_reserve
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the size of the local heap
space to reserve, in bytes. The value of this property MUST NOT be
negative.
|
|
size_of_heap_commit
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the size of the local heap
space to commit, in bytes. The value of this property MUST NOT be
negative.
|
|
loader_flags_hex
(optional)
|
hex
|
Specifies the reserved loader flags.
|
|
number_of_rva_and_sizes
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the number of data-directory
entries in the remainder of the optional header.
|
|
hashes
(optional)
|
hashes
|
Specifies any hashes that were
computed for the optional header.
Dictionary keys MUST come from the hash-algorithm-ov.
|
6.7.6.3 Windows™ PE Section Type
Type Name: windows-pe-section-type
The Windows PE Section type specifies
metadata about a PE file section.
6.7.6.3.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
name (required)
|
string
|
Specifies
the name of the section.
|
|
size
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the size of the section, in
bytes. The value of this property MUST NOT be negative.
|
|
entropy
(optional)
|
float
|
Specifies the calculated entropy for
the section, as calculated using the Shannon algorithm (https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Shannon_entropy).
The size of each input character is defined as a byte, resulting in a
possible range of 0 through 8.
|
|
hashes
(optional)
|
hashes
|
Specifies any hashes computed over the
section.
Dictionary keys MUST come from the hash-algorithm-ov.
|
Examples
Typical EXE File
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--fb0419a8-f09c-57f8-be64-71a80417591c",
"extensions": {
"windows-pebinary-ext":
{
"pe_type":
"exe",
"machine_hex":
"014c",
"number_of_sections":
4,
"time_date_stamp":
"2016-01-22T12:31:12Z",
"pointer_to_symbol_table_hex": "74726144",
"number_of_symbols":
4542568,
"size_of_optional_header": 224,
"characteristics_hex":
"818f",
"optional_header": {
"magic_hex":
"010b",
"major_linker_version": 2,
"minor_linker_version": 25,
"size_of_code": 512,
"size_of_initialized_data": 283648,
"size_of_uninitialized_data": 0,
"address_of_entry_point": 4096,
"base_of_code":
4096,
"base_of_data":
8192,
"image_base":
14548992,
"section_alignment":
4096,
"file_alignment":
4096,
"major_os_version":
1,
"minor_os_version":
0,
"major_image_version": 0,
"minor_image_version": 0,
"major_subsystem_version": 4,
"minor_subsystem_version": 0,
"win32_version_value_hex": "00",
"size_of_image":
299008,
"size_of_headers":
4096,
"checksum_hex":
"00",
"subsystem_hex":
"03",
"dll_characteristics_hex": "00",
"size_of_stack_reserve": 100000,
"size_of_stack_commit": 8192,
"size_of_heap_reserve": 100000,
"size_of_heap_commit":
4096,
"loader_flags_hex":
"abdbffde",
"number_of_rva_and_sizes": 3758087646
},
"sections": [
{
"name":
"CODE",
"entropy":
0.061089
},
{
"name": "DATA",
"entropy":
7.980693
},
{
"name":
"NicolasB",
"entropy":
0.607433
},
{
"name":
".idata",
"entropy":
0.607433
}
]
}
}
}
6.8 IPv4 Address Object
Type Name: ipv4-addr
The IPv4 Address object represents one
or more IPv4 addresses expressed using CIDR notation.
6.8.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
IPv4
Address Object Specific Properties
|
|
value,
resolves_to_refs, belongs_to_refs
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
value
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be ipv4-addr.
|
|
value (required)
|
string
|
Specifies
the values of one or more IPv4 addresses expressed using CIDR notation.
If a given
IPv4 Address object represents a single IPv4 address, the CIDR /32 suffix MAY
be omitted.
Example: 10.2.4.5/24
|
|
resolves_to_refs
(optional - deprecated)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies a list of references to one
or more Layer 2 Media Access Control (MAC) addresses that the IPv4 address
resolves to.
The objects referenced in this list MUST
be of type mac-addr.
|
|
belongs_to_refs
(optional - deprecated)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies a list of references to one
or more autonomous systems (AS) that the IPv4 address belongs to.
The objects referenced in this list MUST
be of type autonomous-system.
|
6.8.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
IPv4 Address object and other STIX Objects. The table identifies the
relationships that can be made from this object type to another object type by
way of the Relationship object.
|
Source
|
Relationship Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
ipv4-addr
|
resolves-to
|
mac-addr
|
This Relationship describes that this IPv4 Address
resolves to one or more Layer 2 Media Access Control (MAC) addresses.
|
|
ipv4-addr
|
belongs-to
|
autonomous-system
|
This Relationship describes that this IPv4 Address belongs
to one or more autonomous systems (AS).
|
Examples
IPv4 Single Address
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--ff26c055-6336-5bc5-b98d-13d6226742dd",
"value":
"198.51.100.3"
}
IPv4 CIDR Block
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--5853f6a4-638f-5b4e-9b0f-ded361ae3812",
"value":
"198.51.100.0/24"
}
6.9 IPv6 Address Object
Type Name: ipv6-addr
The IPv6 Address object represents one
or more IPv6 addresses expressed using CIDR notation.
6.9.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
IPv6 Address
Object Specific Properties
|
|
value,
resolves_to_refs, belongs_to_refs
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
value
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be ipv6-addr.
|
|
value (required)
|
string
|
Specifies
the values of one or more IPv6 addresses expressed using CIDR notation.
If a given
IPv6 Address object represents a single IPv6 address, the CIDR /128 suffix MAY
be omitted.
|
|
resolves_to_refs
(optional - deprecated)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies a list of references to one
or more Layer 2 Media Access Control (MAC) addresses that the IPv6 address
resolves to.
The objects referenced in this list MUST
be of type mac-addr.
|
|
belongs_to_refs
(optional - deprecated)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies a list of references to one
or more autonomous systems (AS) that the IPv6 address belongs to.
The objects referenced in this list MUST
be of type autonomous-system.
|
6.9.2 Relationships
These are the relationships explicitly defined between the
IPv6 Address object and other STIX Objects. The table identifies the
relationships that can be made from this object type to another object type by
way of the Relationship object.
|
Source
|
Relationship Type
|
Target
|
Description
|
|
ipv6-addr
|
resolves-to
|
mac-addr
|
This Relationship describes that this IPv6 Address
resolves to one or more Layer 2 Media Access Control (MAC) addresses.
|
|
ipv6-addr
|
belongs-to
|
autonomous-system
|
This Relationship describes that this IPv6 Address belongs
to one or more autonomous systems (AS).
|
Examples
IPv6 Single Address
{
"type":
"ipv6-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv6-addr--1e61d36c-a16c-53b7-a80f-2a00161c96b1",
"value":
"2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334"
}
IPv6 CIDR block
{
"type":
"ipv6-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv6-addr--5daf7456-8863-5481-9d42-237d477697f4",
"value":
"2001:0db8::/96"
}
6.10 MAC Address Object
Type Name: mac-addr
The MAC Address object represents a
single Media Access Control (MAC) address.
6.10.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
MAC
Address Object Specific Properties
|
|
value
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
value
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be mac-addr.
|
|
value (required)
|
string
|
Specifies the value of a single MAC
address.
The MAC address value MUST be
represented as a single colon-delimited, lowercase MAC-48 address, which MUST
include leading zeros for each octet.
Example: 00:00:ab:cd:ef:01
|
Examples
Typical MAC address
{
"type":
"mac-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"mac-addr--65cfcf98-8a6e-5a1b-8f61-379ac4f92d00",
"value":
"d2:fb:49:24:37:18"
}
6.11 Mutex Object
Type Name: mutex
The Mutex object represents the
properties of a mutual exclusion (mutex) object.
6.11.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
Mutex
Object Specific Properties
|
|
Name
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
name
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be mutex.
|
|
name (required)
|
string
|
Specifies
the name of the mutex object.
|
Examples
Malware mutex
{
"type": "mutex",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"mutex--eba44954-d4e4-5d3b-814c-2b17dd8de300",
"name":
"__CLEANSWEEP__"
}
6.12 Network Traffic Object
Type Name: network-traffic
The Network Traffic object represents
arbitrary network traffic that originates from a source and is addressed to a
destination. The network traffic MAY or MAY NOT constitute a
valid unicast, multicast, or broadcast network connection. This MAY also include traffic that is not
established, such as a SYN flood.
To allow for use cases where a source or
destination address may be sensitive and not suitable for sharing, such as
addresses that are internal to an organization’s network, the source and
destination properties (src_ref
and dst_ref, respectively) are
defined as optional in the properties table below. However, a Network Traffic
object MUST contain the protocols
property and at least one of the src_ref
or dst_ref properties and
SHOULD contain the src_port
and dst_port properties.
6.12.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
Network
Traffic Specific Properties
|
|
start,
end, is_active, src_ref, dst_ref,
src_port, dst_port, protocols, src_byte_count,
dst_byte_count, src_packets, dst_packets, ipfix, src_payload_ref, dst_payload_ref,
encapsulates_refs, encapsulated_by_ref
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
start, src_ref, dst_ref, src_port,
dst_port, protocols
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be network-traffic.
|
|
extensions (optional)
|
dictionary
|
The Network
Traffic object defines the following extensions. In addition to these,
producers MAY create their own.
http-request-ext, tcp-ext, icmp-ext, socket-ext
Dictionary
keys MUST identify the extension type by name.
The
corresponding dictionary values MUST contain the contents of the
extension instance.
|
|
start
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the date/time the network
traffic was initiated, if known.
|
|
end
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the date/time the network
traffic ended, if known.
If the is_active property is true, then the end property MUST NOT
be included.
If start
and end are both defined,
then end MUST be
later than the start value.
|
|
is_active
(optional)
|
boolean
|
Indicates whether the network traffic
is still ongoing.
If the end property is provided, this property MUST
be false.
|
|
src_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies the source of the network
traffic, as a reference to a Cyber-observable Object.
The object referenced MUST be
of type ipv4-addr,
ipv6-addr,
mac-addr,
or domain-name
(for cases where the IP address for a domain name is unknown).
|
|
dst_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies the destination of the
network traffic, as a reference to a Cyber-observable Object.
The object referenced MUST be
of type ipv4-addr,
ipv6-addr,
mac-addr,
or domain-name
(for cases where the IP address for a domain name is unknown).
|
|
src_port
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the source port used in the
network traffic, as an integer. The port value MUST be in the range of
0 - 65535.
|
|
dst_port
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the destination port used in
the network traffic, as an integer. The port value MUST be in the
range of 0 - 65535.
|
|
protocols
(required)
|
list of type string
|
Specifies the protocols observed in
the network traffic, along with their corresponding state.
Protocols MUST be listed in low
to high order, from outer to inner in terms of packet encapsulation. That is,
the protocols in the outer level of the packet, such as IP, MUST be
listed first.
The protocol names SHOULD come
from the service names defined in the Service Name column of the IANA Service
Name and Port Number Registry [Port Numbers]. In cases where there is
variance in the name of a network protocol not included in the IANA Registry,
content producers should exercise their best judgement, and it is recommended
that lowercase names be used for consistency with the IANA registry.
Examples:
ipv4, tcp, http
ipv4, udp
ipv6, tcp, http
ipv6, tcp, ssl, https
|
|
src_byte_count
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the number of bytes, as a
positive integer, sent from the source to the destination.
|
|
dst_byte_count
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the number of bytes, as a
positive integer, sent from the destination to the source.
|
|
src_packets
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the number of packets, as a
positive integer, sent from the source to the destination.
|
|
dst_packets
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the number of packets, as a
positive integer, sent from the destination to the source.
|
|
ipfix
(optional)
|
dictionary
|
Specifies any IP Flow Information
Export [IPFIX]
data for the traffic, as a dictionary. Each key/value pair in the dictionary
represents the name/value of a single IPFIX element. Accordingly, each
dictionary key SHOULD be a case-preserved version of the IPFIX element
name, e.g., octetDeltaCount. Each dictionary value MUST
be either an integer
or a string,
as well as a valid IPFIX property.
|
|
src_payload_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies the bytes sent from the
source to the destination.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type artifact.
|
|
dst_payload_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies the bytes sent from the
destination to the source.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type artifact.
|
|
encapsulates_refs
(optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
Links to other network-traffic objects
encapsulated by this network-traffic object.
The objects referenced in this
property MUST be of type network-traffic.
|
|
encapsulated_by_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Links to another network-traffic
object which encapsulates this object.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type network-traffic.
|
Examples
Basic TCP Network Traffic
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--4d22aae0-2bf9-5427-8819-e4f6abf20a5300",
"value":
"198.51.100.2"
}
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--ff26c055-6336-5bc5-b98d-13d6226742dd",
"value":
"198.51.100.3"
}
{
"type":
"network-traffic",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"network-traffic--2568d22a-8998-58eb-99ec-3c8ca74f527d",
"src_ref": "ipv4-addr--4d22aae0-2bf9-5427-8819-e4f6abf20a53",
"dst_ref": "ipv4-addr--ff26c055-6336-5bc5-b98d-13d6226742dd",
"protocols": [
"tcp"
]
}
Basic HTTP Network Traffic
{
"type":
"domain-name",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"domain-name--3c10e93f-798e-5a26-a0c1-08156efab7f5",
"value":
"example.com"
}
{
"type":
"network-traffic",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id": "network-traffic--15a157a8-26e3-56e0-820b-0c2a8e553a2c",
"dst_ref": "domain-name--3c10e93f-798e-5a26-a0c1-08156efab7f5",
"protocols": [
"ipv4",
"tcp",
"http"
]
}
Network Traffic with Netflow Data
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--e42c19c8-f9fe-5ae9-9fc8-22c398f78fb7",
"value":
"203.0.113.1"
}
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--03b708d9-7761-5523-ab75-5ea096294a68",
"value":
"203.0.113.5"
}
{
"type":
"network-traffic",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"network-traffic--630d7bb1-0bbc-53a6-a6d4-f3c2d35c2734",
"src_ref": "ipv4-addr--e42c19c8-f9fe-5ae9-9fc8-22c398f78fb",
"dst_ref": "ipv4-addr--03b708d9-7761-5523-ab75-5ea096294a68",
"protocols": [
"ipv4",
"tcp"
],
"src_byte_count": 147600,
"src_packets": 100,
"ipfix": {
"minimumIpTotalLength":
32,
"maximumIpTotalLength":
2556
}
}
Basic Tunneled Network Traffic
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--4d22aae0-2bf9-5427-8819-e4f6abf20a53",
"value":
"198.51.100.2"
}
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--e42c19c8-f9fe-5ae9-9fc8-22c398f78fb7",
"value":
"203.0.113.1"
}
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--ffe65ce3-bf2a-577c-bb7e-947d39198637",
"value":
"203.0.113.2"
}
{
"type":
"network-traffic",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"network-traffic--ac267abc-1a41-536d-8e8d-98458d9bf491",
"src_ref": "ipv4-addr--4d22aae0-2bf9-5427-8819-e4f6abf20a53",
"dst_ref": "ipv4-addr--e42c19c8-f9fe-5ae9-9fc8-22c398f78fb7",
"src_port": 2487,
"dst_port": 1723,
"protocols": [
"ipv4",
"pptp"
],
"src_byte_count": 35779,
"dst_byte_count": 935750,
"encapsulates_refs": [
"network-traffic--53e0bf48-2eee-5c03-8bde-ed7049d2c0a3"
]
}
{
"type":
"network-traffic",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"network-traffic--53e0bf48-2eee-5c03-8bde-ed7049d2c0a3",
"src_ref": "ipv4-addr--4d22aae0-2bf9-5427-8819-e4f6abf20a53",
"dst_ref": "ipv4-addr--ffe65ce3-bf2a-577c-bb7e-947d39198637",
"src_port": 24678,
"dst_port": 80,
"protocols": [
"ipv4",
"tcp",
"http"
],
"src_packets": 14356,
"dst_packets": 14356,
"encapsulated_by_ref":
"network-traffic--ac267abc-1a41-536d-8e8d-98458d9bf491"
}
Web traffic tunneled over DNS
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--e42c19c8-f9fe-5ae9-9fc8-22c398f78fb7",
"value":
"203.0.113.1"
}
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--f2d3c796-6c1a-5c4f-8516-d4db54727f89",
"value":
"198.51.100.34"
}
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--bb884ffe-f2e4-56bb-a0c3-21f6711cb649",
"value":
"198.51.100.54"
}
{
"type":
"network-traffic",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"network-traffic--b4a8c150-e214-57a3-9017-e85dfa345f46",
"src_ref": "ipv4-addr--e42c19c8-f9fe-5ae9-9fc8-22c398f78fb7",
"dst_ref": "ipv4-addr--f2d3c796-6c1a-5c4f-8516-d4db54727f89",
"src_port": 2487,
"dst_port": 53,
"protocols": [
"ipv4",
"udp",
"dns"
],
"src_byte_count": 35779,
"dst_byte_count": 935750,
"encapsulates_refs": [
"network-traffic--65a6016d-a91c-5781-baad-178cd55f01d4"
]
}
{
"type":
"network-traffic",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"network-traffic--65a6016d-a91c-5781-baad-178cd55f01d4",
"src_ref": "ipv4-addr--f2d3c796-6c1a-5c4f-8516-d4db54727f89",
"dst_ref": "ipv4-addr--bb884ffe-f2e4-56bb-a0c3-21f6711cb649",
"src_port": 24678,
"dst_port": 443,
"protocols": [
"ipv4",
"tcp",
"ssl",
"http"
],
"src_packets": 14356,
"dst_packets": 14356,
"encapsulated_by_ref":
"network-traffic--b4a8c150-e214-57a3-9017-e85dfa345f46"
}
6.12.2 HTTP
Request Extension
Type Name: http-request-ext
The HTTP request extension specifies a
default extension for capturing network traffic properties specific to HTTP
requests. The key for this extension when used in the extensions dictionary MUST be http-request-ext.
6.12.2.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
request_method (required)
|
string
|
Specifies the HTTP method portion of the HTTP request line, as a
lowercase string.
|
|
request_value (required)
|
string
|
Specifies the value (typically a resource path) portion of the HTTP
request line.
|
|
request_version (optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the HTTP version portion of the HTTP request line, as a
lowercase string.
|
|
request_header
(optional)
|
dictionary
|
Specifies
all of the HTTP header fields that may be found in the HTTP client request,
as a dictionary.
Each
key in the dictionary MUST be the name of the header field and SHOULD
preserve case, e.g., User-Agent. The corresponding value for each dictionary key MUST always
be a list of type string
to support when a header field is repeated.
|
|
message_body_length
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies
the length of the HTTP message body, if included, in bytes.
|
|
message_body_data_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies
the data contained in the HTTP message body, if included.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type artifact.
|
Examples
Basic HTTP Request
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--6da8dad3-4de3-5f8e-ab23-45d0b8f12f16",
"value":
"198.51.100.53"
}
{
"type":
"network-traffic",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"network-traffic--f8ae967a-3dc3-5cdf-8f94-8505abff00c2",
"dst_ref": "ipv4-addr--6da8dad3-4de3-5f8e-ab23-45d0b8f12f16",
"protocols": [
"tcp",
"http"
],
"extensions": {
"http-request-ext": {
"request_method":
"get",
"request_value":
"/download.html",
"request_version":
"http/1.1",
"request_header": {
"Accept-Encoding":
"gzip,deflate",
"User-Agent":
"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US; rv:1.6)
Gecko/20040113",
"Host":
"www.example.com"
}
}
}
}
6.12.3 ICMP
Extension
Type Name: icmp-ext
The ICMP extension specifies a default
extension for capturing network traffic properties specific to ICMP. The key
for this extension when used in the extensions
dictionary MUST be icmp-ext.
6.12.3.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
icmp_type_hex (required)
|
hex
|
Specifies
the ICMP type byte.
|
|
icmp_code_hex (required)
|
hex
|
Specifies
the ICMP code byte.
|
Examples
Basic ICMP Traffic
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--d7177770-fc12-586b-9244-426596a7008e",
"value":
"198.51.100.9"
}
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--03b708d9-7761-5523-ab75-5ea096294a68",
"value":
"203.0.113.5"
}
{
"type":
"network-traffic",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"network-traffic--e7a939ca-78c6-5f27-8ae0-4ad112454626",
"src_ref": "ipv4-addr--d7177770-fc12-586b-9244-426596a7008e",
"dst_ref": "ipv4-addr--03b708d9-7761-5523-ab75-5ea096294a68",
"protocols": [
"icmp"
],
"extensions": {
"icmp-ext": {
"icmp_type_hex":
"08",
"icmp_code_hex":
"00"
}
}
}
6.12.4 Network
Socket Extension
Type Name: socket-ext
The Network Socket extension specifies a
default extension for capturing network traffic properties associated with
network sockets. The key for this extension when used
in the extensions dictionary MUST be socket-ext.
6.12.4.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
address_family (required)
|
enum
|
Specifies
the address family (AF_*) that the socket is configured for.
The values of this property MUST
come from the network-socket-address-family-enum enumeration.
|
|
is_blocking
(optional)
|
boolean
|
Specifies whether the socket is in
blocking mode.
|
|
is_listening
(optional)
|
boolean
|
Specifies whether the socket is in
listening mode.
|
|
options
(optional)
|
dictionary
|
Specifies any options (SO_*) that may be used by the
socket, as a dictionary. Each key in the dictionary SHOULD be a
case-preserved version of the option name, e.g., SO_ACCEPTCONN.
Each key value in the dictionary MUST be the value for the
corresponding options key.
|
|
socket_type
(optional)
|
enum
|
Specifies the type of the socket.
The values of this property MUST come from the network-socket-type-enum
enumeration.
|
|
socket_descriptor
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the socket file descriptor value associated with the socket, as a
non-negative integer.
|
|
socket_handle
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the handle or inode value
associated with the socket.
|
Examples
Basic Stream Socket
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--4d22aae0-2bf9-5427-8819-e4f6abf20a53",
"value":
"198.51.100.2"
}
{
"type":
"network-traffic",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"network-traffic--c95e972a-20a4-5307-b00d-b8393faf02c5",
"src_ref": "ipv4-addr--4d22aae0-2bf9-5427-8819-e4f6abf20a53",
"src_port": 223,
"protocols": [
"ip",
"tcp"
],
"extensions": {
"socket-ext": {
"is_listening": true,
"address_family":
"AF_INET",
"socket_type":
"SOCK_STREAM"
}
}
}
6.12.5 TCP
Extension
Type Name: tcp-ext
The TCP extension specifies a default
extension for capturing network traffic properties specific to TCP. The key for
this extension when used in the extensions
dictionary MUST be tcp-ext. An object using the TCP Extension MUST
contain at least one property from this extension.
6.12.5.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
src_flags_hex
(optional)
|
hex
|
Specifies the source TCP flags, as the
union of all TCP flags observed between the start of the traffic (as defined
by the start property) and the end of the traffic (as defined by the end
property).
If the start and end times of the
traffic are not specified, this property SHOULD be interpreted as the
union of all TCP flags observed over the entirety of the network traffic
being reported upon.
|
|
dst_flags_hex
(optional)
|
hex
|
Specifies the destination TCP flags,
as the union of all TCP flags observed between the start of the traffic (as
defined by the start property) and the end of the traffic (as defined
by the end property).
If the start and end times of the
traffic are not specified, this property SHOULD be interpreted as the
union of all TCP flags observed over the entirety of the network traffic
being reported upon.
|
Examples
Basic TCP Traffic
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--89830c10-2e94-57fa-8ca6-e0537d2719d1",
"value":
"198.51.100.5"
}
{
"type":
"ipv4-addr",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"ipv4-addr--45f4c6fb-2d7d-576a-a571-edc78d899a72",
"value":
"198.51.100.6"
}
{
"type":
"network-traffic",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"network-traffic--09ca55c3-97e5-5966-bad0-1d41d557ae13",
"src_ref": "ipv4-addr--89830c10-2e94-57fa-8ca6-e0537d2719d1",
"dst_ref": "ipv4-addr--45f4c6fb-2d7d-576a-a571-edc78d899a72",
"src_port": 3372,
"dst_port": 80,
"protocols": [
"tcp"
],
"extensions": {
"tcp-ext": {
"src_flags_hex":
"00000002"
}
}
}
6.13 Process Object
Type Name: process
The Process object represents common properties of an
instance of a computer program as executed on an operating system. A Process
object MUST contain at least one property (other than type) from this object (or one of its
extensions).
6.13.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
Process
Object Specific Properties
|
|
is_hidden,
pid, created_time, cwd, command_line, environment_variables,
opened_connection_refs, creator_user_ref, image_ref, parent_ref, child_refs
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
Since all properties
on this object are optional, please use a UUIDv4 for the ID of this object.
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be process.
|
|
extensions (optional)
|
dictionary
|
The Process
object defines the following extensions. In addition to these, producers MAY
create their own.
windows-process-ext, windows-service-ext
Dictionary
keys MUST identify the extension type by name.
The
corresponding dictionary values MUST contain the contents of the
extension instance.
|
|
is_hidden
(optional)
|
boolean
|
Specifies whether the process is
hidden.
|
|
pid
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the Process ID, or PID, of
the process.
|
|
created_time
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the date/time at which the
process was created.
|
|
cwd
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the current working
directory of the process.
|
|
command_line
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the full command line used
in executing the process, including the process name (which may be specified individually via the image_ref.name property)
and any arguments.
|
|
environment_variables
(optional)
|
dictionary
|
Specifies the list of environment
variables associated with the process as a dictionary. Each key in the
dictionary MUST be a case preserved version of the name of the
environment variable, and each corresponding value MUST be the
environment variable value as a string.
|
|
opened_connection_refs
(optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies the list of network
connections opened by the process, as a reference to one or more Network
Traffic objects.
The objects referenced in this list MUST
be of type network-traffic.
|
|
creator_user_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies the user that created the
process, as a reference to a User Account object.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type user-account.
|
|
image_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies the executable binary that
was executed as the process image, as a reference to a File object.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type file.
|
|
parent_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies the other process that
spawned (i.e. is the parent of) this one, as a reference to a Process object.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type process.
|
|
child_refs
(optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies the other processes that
were spawned by (i.e. children of) this process, as a reference to one or
more other Process objects.
The objects referenced in this list MUST
be of type process.
|
Examples
Basic Process
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--e04f22d1-be2c-59de-add8-10f61d15fe20",
"name": "gedit-bin",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256": "aec070645fe53ee3b3763059376134f058cc337247c978add178b6ccdfb0019f"
},
}
{
"type":
"process",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id": "process--f52a906a-0dfc-40bd-92f1-e7778ead38a9",
"pid": 1221,
"created":
"2016-01-20T14:11:25.55Z",
"command_line": "./gedit-bin
--new-window",
"image_ref": "file--e04f22d1-be2c-59de-add8-10f61d15fe20"
}
6.13.2 Windows™
Process Extension
Type Name: windows-process-ext
The Windows Process extension specifies
a default extension for capturing properties specific to Windows processes. The
key for this extension when used in the extensions
dictionary MUST be windows-process-ext. An object using the Windows
Process Extension MUST contain at least one property from this
extension.
6.13.2.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
aslr_enabled
(optional)
|
boolean
|
Specifies whether Address Space Layout
Randomization (ASLR) is enabled for the process.
|
|
dep_enabled
(optional)
|
boolean
|
Specifies whether Data Execution
Prevention (DEP) is enabled for the process.
|
|
priority
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the current priority class
of the process in Windows. This value SHOULD be a string that ends in _CLASS.
|
|
owner_sid
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the Security ID (SID) value
of the owner of the process.
|
|
window_title
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the title of the main window
of the process.
|
|
startup_info
(optional)
|
dictionary
|
Specifies the STARTUP_INFO struct used
by the process, as a dictionary. Each name/value pair in the struct MUST
be represented as a key/value pair in the dictionary, where each key MUST
be a case-preserved version of the original name. For example, given a name
of "lpDesktop" the corresponding key would be lpDesktop.
|
|
integrity_level
(optional)
|
enum
|
Specifies the Windows integrity level,
or trustworthiness, of the process.
The values of this property MUST come from the windows-integrity-level-enum
enumeration.
|
Examples
Basic Windows Process
{
"type":
"process",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"process--07bc30cad-ebc2-4579-881d-b9cdc7f2b33c",
"pid": 314,
"extensions": {
"windows-process-ext": {
"aslr_enabled": true,
"dep_enabled": true,
"priority":
"HIGH_PRIORITY_CLASS",
"owner_sid":
"S-1-5-21-186985262-1144665072-74031268-1309"
}
}
}
6.13.3 Windows™
Service Extension
Type Name: windows-service-ext
The Windows Service extension specifies
a default extension for capturing properties specific to Windows services. The
key for this extension when used in the extensions
dictionary MUST be windows-service-ext. As all properties of this
extension are optional, at least one of the properties defined below MUST
be included when using this extension.
6.13.3.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
service_name (optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the name of the service.
|
|
descriptions
(optional)
|
list of type string
|
Specifies the descriptions defined for
the service.
|
|
display_name
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the display name of the
service in Windows GUI controls.
|
|
group_name
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the name of the load
ordering group of which the service is a member.
|
|
start_type
(optional)
|
enum
|
Specifies the start options defined
for the service.
The values of this property MUST come
from the windows-service-start-type-enum
enumeration.
|
|
service_dll_refs
(optional)
|
list of type identifier
|
Specifies the DLLs loaded by the
service, as a reference to one or more File objects.
The objects referenced in this
property MUST be of type file.
|
|
service_type
(optional)
|
enum
|
Specifies the type of the service.
The values of this property MUST come from the windows-service-type-enum
enumeration.
|
|
service_status
(optional)
|
enum
|
Specifies the current status of the
service.
The values of this property MUST come from the windows-service-status-enum
enumeration.
|
Examples
Basic Windows Service
{
"type": "file",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"file--3916128d-69af-5525-be7a-99fac2383a59",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256": "bf07a7fbb825fc0aae7bf4a1177b2b31fcf8a3feeaf7092761e18c859ee52a9c"
},
"name":
"sirvizio.exe"
}
{
"type":
"process",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"process--99ab297d-4c39-48ea-9d64-052d596864df",
"pid": 2217,
"command_line":
"C:\\Windows\\System32\\sirvizio.exe /s",
"image_ref": "file--3916128d-69af-5525-be7a-99fac2383a59",
"extensions": {
"windows-service-ext": {
"service_name":
"sirvizio",
"display_name":
"Sirvizio",
"start_type":
"SERVICE_AUTO_START",
"service_type":
"SERVICE_WIN32_OWN_PROCESS",
"service_status":
"SERVICE_RUNNING"
}
}
}
6.14 Software Object
Type Name: software
The Software object represents
high-level properties associated with software, including software products.
6.14.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
Software
Object Specific Properties
|
|
name,
cpe, languages, vendor, version
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
name, cpe, vendor, version
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be software.
|
|
name (required)
|
string
|
Specifies
the name of the software.
|
|
cpe (optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the Common Platform Enumeration (CPE) entry for the software, if available.
The value for this property MUST be a CPE v2.3 entry from the official
NVD CPE Dictionary [NVD]
.
While the
CPE dictionary does not contain entries for all software, whenever it does
contain an identifier for a given instance of software, this property SHOULD
be present.
|
|
languages
(optional)
|
list of type string
|
Specifies the languages supported by
the software. The value of each list member MUST be an ISO 639-2
language code [ISO639-2].
|
|
vendor
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the name of the vendor of
the software.
|
|
version
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the version of the software.
|
Examples
Typical Software Instance
{
"type":
"software",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"software--a1827f6d-ca53-5605-9e93-4316cd22a00a",
"name": "Word",
"cpe":
"cpe:2.3:a:microsoft:word:2000:*:*:*:*:*:*:*",
"version":
"2002",
"vendor":
"Microsoft"
}
6.15 URL Object
Type Name: url
The URL object represents the properties
of a uniform resource locator (URL).
6.15.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
URL
Object Specific Properties
|
|
value
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
value
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be url.
|
|
value (required)
|
string
|
Specifies
the value of the URL. The value of this property MUST conform to [RFC3986],
more specifically section 1.1.3 with reference to the definition for
"Uniform Resource Locator".
|
Examples
Typical URL
{
"type": "url",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"url--c1477287-23ac-5971-a010-5c287877fa60",
"value":
"https://example.com/research/index.html"
}
6.16 User Account Object
Type Name: user-account
The User Account object represents an
instance of any type of user account, including but not limited to operating
system, device, messaging service, and social media platform accounts. As all
properties of this object are optional, at least one of the properties defined
below MUST be included when using this object.
6.16.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
User
Account Object Specific Properties
|
|
user_id,
credential, account_login, account_type, display_name, is_service_account, is_privileged, can_escalate_privs, is_disabled, account_created, account_expires, credential_last_changed, account_first_login, account_last_login
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
account_type,
user_id, account_login
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be user-account.
|
|
extensions (optional)
|
dictionary
|
The User
Account object defines the following extensions. In addition to these,
producers MAY create their own.
unix-account-ext
Dictionary
keys MUST identify the extension type by name.
The
corresponding dictionary values MUST contain the contents of the
extension instance.
|
|
user_id (optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the identifier of the account. The format of the identifier depends on the
system the user account is maintained in, and may be a numeric ID, a GUID, an
account name, an email address, etc. The user_id property
should be populated with whatever field is the unique identifier for the
system the account is a member of. For example, on UNIX systems it would be
populated with the UID.
|
|
credential
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies a cleartext credential. This is only
intended to be used in capturing metadata from malware analysis (e.g., a
hard-coded domain administrator password that the malware attempts to use for
lateral movement) and SHOULD NOT be used for sharing of PII.
|
|
account_login
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the account login string,
used in cases where the user_id
property specifies something other than what a user would type when they
login.
For example, in the case of a Unix
account with user_id 0, the account_login might be “root”.
|
|
account_type
(optional)
|
open-vocab
|
Specifies the type of the account.
This is an open vocabulary and values SHOULD
come from the account-type-ov vocabulary.
|
|
display_name
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the display name of the
account, to be shown in user interfaces, if applicable.
On Unix, this is equivalent to the
GECOS field.
|
|
is_service_account
(optional)
|
boolean
|
Indicates that the account is
associated with a network service or system process (daemon), not a specific
individual.
|
|
is_privileged
(optional)
|
boolean
|
Specifies that the account has
elevated privileges (i.e., in the case of root on Unix or the Windows
Administrator account).
|
|
can_escalate_privs
(optional)
|
boolean
|
Specifies that the account has the
ability to escalate privileges (i.e., in the case of sudo on Unix or a
Windows Domain Admin account)
|
|
is_disabled
(optional)
|
boolean
|
Specifies if the account is disabled.
|
|
account_created
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies when the account was
created.
|
|
account_expires
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the expiration date of the
account.
|
|
credential_last_changed
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies when the account credential
was last changed.
|
|
account_first_login
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies when the account was first
accessed.
|
|
account_last_login
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies when the account was last
accessed.
|
Examples
Basic Unix Account
{
"type":
"user-account",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"user-account--0d5b424b-93b8-5cd8-ac36-306e1789d63c",
"user_id":
"1001",
"account_login":
"jdoe",
"account_type":
"unix",
"display_name": "John
Doe",
"is_service_account":
false,
"is_privileged": false,
"can_escalate_privs":
true,
"account_created":
"2016-01-20T12:31:12Z",
"credential_last_changed":
"2016-01-20T14:27:43Z",
"account_first_login":
"2016-01-20T14:26:07Z",
"account_last_login":
"2016-07-22T16:08:28Z"
}
Basic Twitter Account
{
"type":
"user-account",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"user-account--9bd3afcf-deee-54f9-83e2-520653cb6bba",
"user_id":
"thegrugq_ebooks",
"account_login":
"thegrugq_ebooks",
"account_type":
"twitter",
"display_name": "the
grugq"
}
6.16.2 UNIX™
Account Extension
Type Name: unix-account-ext
The UNIX account extension specifies a
default extension for capturing the additional information for an account on a
UNIX system. The key for this extension when used in the extensions dictionary MUST be unix-account-ext.
An object using the UNIX Account Extension MUST contain at least one
property from this extension.
6.16.2.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
gid
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the primary group ID of the
account.
|
|
groups
(optional)
|
list of type string
|
Specifies a list of names of groups
that the account is a member of.
|
|
home_dir
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the home directory of the
account.
|
|
shell
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the account’s command shell.
|
Examples
Basic UNIX Account
{
"type":
"user-account",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"user-account--0d5b424b-93b8-5cd8-ac36-306e1789d63c",
"user_id":
"1001",
"account_login":
"jdoe",
"account_type":
"unix",
"display_name": "John
Doe",
"is_service_account":
false,
"is_privileged": false,
"can_escalate_privs":
true,
"extensions": {
"unix-account-ext": {
"gid": 1001,
"groups":
["wheel"],
"home_dir": "/home/jdoe",
"shell":
"/bin/bash"
}
}
}
6.17 Windows™ Registry Key Object
Type Name: windows-registry-key
The Registry Key object represents the
properties of a Windows registry key. As all properties of this object are
optional, at least one of the properties defined below MUST be included
when using this object.
6.17.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
WindowsTM
Registry Key Object Specific Properties
|
|
key,
values, modified_time, creator_user_ref, number_of_subkeys
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
key, values (all items defined in the values property MUST be
included)
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be windows-registry-key.
|
|
key (optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the full registry key including the hive.
The value of
the key, including the hive portion, SHOULD be case-preserved. The
hive portion of the key MUST be fully expanded and not truncated;
e.g., HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE must be used instead of HKLM.
|
|
values (optional)
|
list of type windows-registry-value-type
|
Specifies the values found under the
registry key.
|
|
modified_time (optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the last date/time that the
registry key was modified.
|
|
creator_user_ref (optional)
|
identifier
|
Specifies a reference to the user
account that created the registry key.
The object referenced in this property
MUST be of type user-account.
|
|
number_of_subkeys (optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the number of subkeys
contained under the registry key.
|
6.17.2 Windows™
Registry Value Type
Type Name: windows-registry-value-type
The Windows Registry Value type captures
the properties of a Windows Registry Key Value. As all properties of this type
are optional, at least one of the properties defined below MUST be
included when using this type.
6.17.2.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
name (optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the name of the registry value. For specifying the default value in a
registry key, an empty string MUST be used.
|
|
data
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the data contained in the
registry value.
|
|
data_type
(optional)
|
enum
|
Specifies the registry (REG_*) data
type used in the registry value.
The values of this property MUST come from the windows-registry-datatype-enum
enumeration.
|
6.17.3 Examples
Simple registry key
{
"type":
"windows-registry-key",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"windows-registry-key"--9d60798d-4e3e-5fe4-af8a-0e4986f0f90b",
"key":
"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\System\\Foo\\Bar"
}
Registry key with values
{
"type":
"windows-registry-key",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"windows-registry-key--2ba37ae7-2745-5082-9dfd-9486dad41016",
"key":
"hkey_local_machine\\system\\bar\\foo",
"values": [
{
"name":
"Foo",
"data":
"qwerty",
"data_type":
"REG_SZ"
},
{
"name":
"Bar",
"data":
"42",
"data_type":
"REG_DWORD"
}
]
}
6.18 X.509 Certificate Object
Type Name: x509-certificate
The X.509 Certificate object represents
the properties of an X.509 certificate, as defined by ITU recommendation X.509 [X.509].
An X.509 Certificate object MUST contain at least one property (other
than type) from this object.
6.18.1 Properties
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, id
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
spec_version, object_marking_refs, granular_markings, defanged, extensions
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, external_references
|
|
X.509
Certificate Object Specific Properties
|
|
is_self_signed,
hashes, version, serial_number, signature_algorithm,
issuer, validity_not_before, validity_not_after, subject, subject_public_key_algorithm, subject_public_key_modulus, subject_public_key_exponent, x509_v3_extensions
|
|
ID Contributing Properties
|
|
hashes, serial_number
If the hashes
property is present, include only one hash. The selected hash SHOULD
come from this ordered list (based on the following order of preference) [
MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-512 ].
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The value of
this property MUST be x509-certificate.
|
|
is_self_signed
(optional)
|
boolean
|
Specifies whether the certificate is
self-signed, i.e., whether it is
signed by the same entity whose identity it certifies.
|
|
hashes
(optional)
|
hashes
|
Specifies any hashes that were
calculated for the entire contents of the certificate.
Dictionary keys MUST come from the hash-algorithm-ov.
|
|
version
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the version of the encoded
certificate.
|
|
serial_number
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the unique identifier for
the certificate, as issued by a specific Certificate Authority.
|
|
signature_algorithm
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the name of the algorithm
used to sign the certificate.
|
|
issuer
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the name of the Certificate
Authority that issued the certificate.
|
|
validity_not_before
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the date on which the
certificate validity period begins.
|
|
validity_not_after
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies the date on which the
certificate validity period ends.
|
|
subject
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the name of the entity
associated with the public key stored in the subject public key field of the
certificate.
|
|
subject_public_key_algorithm
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the name of the algorithm
with which to encrypt data being sent to the subject.
|
|
subject_public_key_modulus
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies the modulus portion of the
subject’s public RSA key.
|
|
subject_public_key_exponent
(optional)
|
integer
|
Specifies the exponent portion of the
subject’s public RSA key, as an integer.
|
|
x509_v3_extensions
(optional)
|
x509-v3-extensions-type
|
Specifies any standard X.509 v3
extensions that may be used in the certificate.
|
6.18.2 X.509
v3 Extensions Type
Type Name: x509-v3-extensions-type
The X.509 v3 Extensions type captures
properties associated with X.509 v3 extensions, which serve as a mechanism for
specifying additional information such as alternative subject names. An object
using the X.509 v3 Extensions type MUST contain at least one property
from this type.
Note that the use of the term
"extensions" in this context refers to the X.509 v3 Extensions type
and is not a STIX Cyber Observables extension. Therefore, it is a type that
describes X.509 extensions.
6.18.2.1 Properties
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
basic_constraints
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies a multi-valued extension which indicates whether a certificate is a CA
certificate. The first (mandatory) name is CA followed by TRUE or FALSE.
If CA is TRUE, then an optional pathlen name followed by a
non-negative value can be included. Also equivalent to the object ID (OID)
value of 2.5.29.19.
|
|
name_constraints
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
a namespace within which all subject names in subsequent certificates in a
certification path MUST be located. Also equivalent to the object ID
(OID) value of 2.5.29.30.
|
|
policy_constraints
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies any constraints on path validation for certificates issued to CAs.
Also equivalent to the object ID (OID) value of 2.5.29.36.
|
|
key_usage
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
a multi-valued extension consisting of a list of names of the permitted key
usages. Also equivalent to the object ID (OID) value of 2.5.29.15.
|
|
extended_key_usage
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
a list of usages indicating purposes for which the certificate public key can
be used for. Also equivalent to the object ID (OID) value of 2.5.29.37.
|
|
subject_key_identifier
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the identifier that provides a means of identifying certificates that contain
a particular public key. Also equivalent to the object ID (OID) value of
2.5.29.14.
|
|
authority_key_identifier
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the identifier that provides a means of identifying the public key
corresponding to the private key used to sign a certificate. Also equivalent
to the object ID (OID) value of 2.5.29.35.
|
|
subject_alternative_name
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the additional identities to be bound to the subject of the certificate. Also
equivalent to the object ID (OID) value of 2.5.29.17.
|
|
issuer_alternative_name
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the additional identities to be bound to the issuer of the certificate. Also
equivalent to the object ID (OID) value of 2.5.29.18.
|
|
subject_directory_attributes
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the identification attributes (e.g., nationality) of the subject. Also
equivalent to the object ID (OID) value of 2.5.29.9.
|
|
crl_distribution_points
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
how CRL information is obtained. Also equivalent to the object ID (OID) value
of 2.5.29.31.
|
|
inhibit_any_policy
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
the number of additional certificates that may appear in the path before
anyPolicy is no longer permitted. Also equivalent to the object ID (OID)
value of 2.5.29.54.
|
|
private_key_usage_period_not_before
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies
the date on which the validity period begins for the private key, if it is
different from the validity period of the certificate.
|
|
private_key_usage_period_not_after
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
Specifies
the date on which the validity period ends for the private key, if it is
different from the validity period of the certificate.
|
|
certificate_policies
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
a sequence of one or more policy information terms, each of which consists of
an object identifier (OID) and optional qualifiers. Also equivalent to the
object ID (OID) value of 2.5.29.32.
|
|
policy_mappings
(optional)
|
string
|
Specifies
one or more pairs of OIDs; each pair includes an issuerDomainPolicy and a
subjectDomainPolicy. The pairing indicates whether the issuing CA considers
its issuerDomainPolicy equivalent to the subject CA's subjectDomainPolicy.
Also equivalent to the object ID (OID) value of 2.5.29.33.
|
Examples
Basic X.509 certificate
{
"type":
"x509-certificate",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"x509-certificate--463d7b2a-8516-5a50-a3d7-6f801465d5de",
"issuer": "C=ZA,
ST=Western Cape, L=Cape Town, O=Thawte Consulting cc, OU=Certification Services
Division, CN=Thawte Server CA/emailAddress=server-certs@thawte.com",
"validity_not_before":
"2016-03-12T12:00:00Z",
"validity_not_after":
"2016-08-21T12:00:00Z",
"subject": "C=US, ST=Maryland,
L=Pasadena, O=Brent Baccala, OU=FreeSoft, CN=www.freesoft.org/emailAddress=baccala@freesoft.org",
"serial_number":
"36:f7:d4:32:f4:ab:70:ea:d3:ce:98:6e:ea:99:93:49:32:0a:b7:06"}
X.509 Certificate w/ V3 Extensions
{
"type":"x509-certificate",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"x509-certificate--b595eaf0-0b28-5dad-9e8e-0fab9c1facc9",
"issuer":"C=ZA, ST=Western
Cape, L=Cape Town, O=Thawte Consulting cc, OU=Certification Services Division,
CN=Thawte Server CA/emailAddress=server-certs@thawte.com",
"validity_not_before":"2016-03-12T12:00:00Z",
"validity_not_after":"2016-08-21T12:00:00Z",
"subject":"C=US, ST=Maryland,
L=Pasadena, O=Brent Baccala, OU=FreeSoft, CN=www.freesoft.org/emailAddress=baccala@freesoft.org",
"serial_number":
"02:08:87:83:f2:13:58:1f:79:52:1e:66:90:0a:02:24:c9:6b:c7:dc",
"x509_v3_extensions":{
"basic_constraints":"critical,CA:TRUE, pathlen:0",
"name_constraints":"permitted;IP:192.168.0.0/255.255.0.0",
"policy_contraints":"requireExplicitPolicy:3",
"key_usage":"critical,
keyCertSign",
"extended_key_usage":"critical,codeSigning,1.2.3.4",
"subject_key_identifier":"hash",
"authority_key_identifier":"keyid,issuer",
"subject_alternative_name":"email:my@other.address,RID:1.2.3.4",
"issuer_alternative_name":"issuer:copy",
"crl_distribution_points":"URI:http://myhost.com/myca.crl",
"inhibit_any_policy":"2",
"private_key_usage_period_not_before":"2016-03-12T12:00:00Z",
"private_key_usage_period_not_after":"2018-03-12T12:00:00Z",
"certificate_policies":"1.2.4.5, 1.1.3.4"
}
}
The Language Content object represents text content for STIX
Objects represented in languages other than that of the original object.
Language content may be a translation of the original object by a third-party,
a first-source translation by the original publisher, or additional official
language content provided at the time of creation. Instead, the relationships
should be related to the STIX Objects that the Language Content object is
providing a translation of using an embedded relationship.
Language Content contains two important sets of properties:
● The object_ref and object_modified properties specify the
target object that the language content applies to.
○ For
example, to provide additional language content for a Campaign, the object_ref property should be set to
the id of the Campaign and the
object_modified property set
to its modified time. Most relationships in STIX are not specific to a
particular version of a STIX object, but because language content provides the
translation of specific text, the object_modified
property is necessary to provide that specificity.
● The content property is a dictionary
which maps to properties in the target object in order to provide a translation
of them.
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created, modified
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, revoked, labels, confidence, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
lang, defanged, extensions
|
|
Language Content Specific
Properties
|
|
object_ref,
object_modified, contents
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The type property identifies the type of object. The value of
this property MUST be language-content.
|
|
object_ref (required)
|
identifier
|
The object_ref
property identifies the id
of the object that this Language Content applies to. It MUST be the
identifier for a STIX Object.
|
|
object_modified
(optional)
|
timestamp
|
The object_modified
property identifies the modified
time of the object that this Language Content applies to. It MUST be
an exact match for the modified
time of the STIX Object being referenced.
|
|
contents (required)
|
dictionary
|
The contents
property contains the actual Language Content (translation).
The keys in the dictionary MUST be RFC 5646
language codes for which language content is being provided [RFC5646].
The values each consist of a dictionary that mirrors the properties in the
target object (identified by object_ref
and object_modified). For
example, to provide a translation of the name
property on the target object the key in the dictionary would be name.
For each key in the nested dictionary:
● If
the original property is a string, the corresponding property in the language
content object MUST contain a string with the content for that
property in the language of the top-level key.
● If
the original property is a list, the corresponding property in the
translation object must also be a list. Each item in this list
recursively maps to the item at the same position in the list contained in
the target object. The lists MUST have the same length.
● In
the event that translations are only provided for some list items, the
untranslated list items MUST be represented by an empty string
(""). This indicates to a consumer of the Language Content object
that they should interpolate the translated list items in the Language
Content object with the corresponding (untranslated) list items from the original
object as indicated by the object_ref
property.
● If
the original property is an object (including dictionaries), the
corresponding location in the translation object must also be an object. Each
key/value field in this object recursively maps to the object with the same
key in the original.
The translation object MAY contain only a subset of
the translatable fields of the original. Keys that point to non-translatable
properties in the target or to properties that do not exist in the target
object MUST be ignored.
|
There are no relationships explicitly defined between the
Language Content object and other STIX Objects, other than the embedded
relationships listed below. These embedded relationships are listed by property
name along with their corresponding target.
Note that the object_ref
relationship has a companion property, object_modified,
that identifies the version of the object that the language content is being
provided for.
|
Embedded Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identity
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
marking-definition
|
|
object_ref
|
identifier
|
Examples
Translation of a campaign
{
"type": "campaign",
"id": "campaign--12a111f0-b824-4baf-a224-83b80237a094",
"lang": "en",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"created": "2017-02-08T21:31:22.007Z",
"modified": "2017-02-08T21:31:22.007Z",
"name": "Bank Attack",
"description": "More information about bank attack"
}
{
"type":
"language-content",
"id":
"language-content--b86bd89f-98bb-4fa9-8cb2-9ad421da981d",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"created":
"2017-02-08T21:31:22.007Z",
"modified": "2017-02-08T21:31:22.007Z",
"object_ref":
"campaign--12a111f0-b824-4baf-a224-83b80237a094",
"object_modified":
"2017-02-08T21:31:22.007Z",
"contents":
{
"de": {
"name": "Bank
Angriff",
"description": "Weitere
Informationen über Banküberfall"
},
"fr": {
"name": "Attaque
Bank",
"description": "Plus
d'informations sur la crise bancaire"
}
}
}
The threat actor defined here, is
from the example in Section 4.16.
{
"type":
"language-content",
"id":
"language-content--0911f616-727f-48cb-a4c5-9420299562a4",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"created":
"2019-06-08T21:31:22.007Z",
"modified": "2019-07-08T21:31:22.007Z",
"object_ref":
"threat-actor--8e2e2d2b-17d4-4cbf-938f-98ee46b3cd3f",
"contents":
{
"de": {
"goals": ["Bankgeld
stehlen", "Kreditkarten stehlen"]
},
"fr": {
"goals": ["Voler de
l'argent en banque", ""]
}
}
Data markings represent restrictions,
permissions, and other guidance for how data can be used and shared. For
example, data may be shared with the restriction that it must not be re-shared,
or that it must be encrypted at rest. In STIX, data markings are specified
using the marking-definition
object. These definitions are applied to complete STIX Objects using object
markings and to individual properties of STIX Objects via granular markings.
Multiple markings can be added to the
same object, including both object and granular markings. Some types of marking
definitions or trust groups have rules about which markings override other
markings or which markings can be additive to other markings. This
specification does not define rules for how multiple markings applied to the
same object or property should be interpreted.
Granular data markings are also used to mark individual
fields on an object with which language their text content is in. For example,
granular markings can be used to indicate that while the rest of the object is
in English, the description
field is in Japanese. This mechanism does not use the marking-definition object
to represent language, rather a separate lang
field that can also be applied via granular markings.
Type Name: marking-definition
The marking-definition object represents a
specific marking. Data markings typically represent handling or sharing
requirements for data and are applied in the object_marking_refs
and granular_markings
properties on STIX Objects, which reference a list of IDs for marking-definition
objects.
Two marking definition types are defined
in this specification: TLP, to capture TLP markings, and Statement, to capture
text marking statements. In addition, it is expected that the FIRST Information
Exchange Policy (IEP) will be included in a future version once a
machine-usable specification for it has been defined.
Unlike other STIX Objects, Marking
Definition objects cannot be versioned because it would allow for indirect
changes to the markings on a STIX Object. For example, if a Statement marking
is changed from "Reuse Allowed" to "Reuse Prohibited", all
STIX Objects marked with that Statement marking would effectively have an
updated marking without being updated themselves. Instead, a new Statement
marking with the new text should be created and the marked objects updated to
point to the new marking.
The JSON MTI serialization uses the JSON
Object type [RFC8259]
when representing marking-definition.
|
Required Common Properties
|
|
type, spec_version, id, created
|
|
Optional Common Properties
|
|
created_by_ref, external_references, object_marking_refs, granular_markings
|
|
Not Applicable Common
Properties
|
|
modified, revoked, labels, confidence, lang, defanged, extensions
|
|
Marking Definition Specific
Properties
|
|
name, definition_type, definition
|
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The type property identifies the type of object. The value of
this property MUST be marking-definition.
|
|
name
(optional)
|
string
|
A name used to identify the Marking Definition.
|
|
definition_type
(required)
|
open-vocab
|
The definition_type
property identifies the type of Marking Definition. The value of the definition_type property SHOULD
be one of the types defined in the subsections below: statement or tlp (see
sections 7.2.1.3
and 7.2.1.4)
|
|
definition
(required)
|
<marking object>
|
The definition
property contains the marking object itself (e.g., the TLP marking as defined
in section 7.2.1.4, the
Statement marking as defined in section 7.2.1.3, or some other marking definition
defined elsewhere).
|
There are no relationships explicitly defined between the
Marking Definition object and other STIX Objects, other than the embedded
relationships listed below. These embedded relationships are listed by property
name along with their corresponding target.
|
Embedded
Relationships
|
|
created_by_ref
|
identity
|
|
object_marking_refs
|
marking-definition
|
The Statement marking type defines the
representation of a textual marking statement (e.g., copyright, terms of use,
etc.) in a definition. The value of the definition_type
property MUST be statement when using this marking type. Statement
markings are generally not machine-readable, and this specification does not
define any behavior or actions based on their values.
Content may be marked with multiple
statements of use. In other words, the same content can be marked both with a
statement saying "Copyright 2019" and a statement saying, "Terms
of use are ..." and both statements apply.
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
statement
(required)
|
string
|
A Statement (e.g., copyright, terms of
use) applied to the content marked by this marking definition.
|
Examples
{
"type":
"marking-definition",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"marking-definition--34098fce-860f-48ae-8e50-ebd3cc5e41da",
"created":
"2016-08-01T00:00:00.000Z",
"definition_type":
"statement",
"definition": {
"statement":
"Copyright 2019, Example Corp"
}
}
The TLP marking type defines how you
would represent a Traffic Light Protocol (TLP) marking in a definition
property. The value of the definition_type
property MUST be tlp when using this marking type.
|
Property
Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
tlp
(required)
|
string
|
The TLP level [TLP] of the content marked by this
marking definition, as defined in this section.
|
The following standard marking
definitions MUST be used to reference or represent TLP markings. Other
instances of tlp-marking
MUST NOT be used or created (the only instances of TLP marking
definitions permitted are those defined here).
|
white
|
{
"type":
"marking-definition",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"marking-definition--613f2e26-407d-48c7-9eca-b8e91df99dc9",
"created":
"2017-01-20T00:00:00.000Z",
"definition_type":
"tlp",
"name": "TLP:WHITE",
"definition": {
"tlp": "white"
}
}
|
|
green
|
{
"type":
"marking-definition",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"marking-definition--34098fce-860f-48ae-8e50-ebd3cc5e41da",
"created":
"2017-01-20T00:00:00.000Z",
"definition_type":
"tlp",
"name": "TLP:GREEN",
"definition": {
"tlp": "green"
}
}
|
|
amber
|
{
"type":
"marking-definition",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"marking-definition--f88d31f6-486f-44da-b317-01333bde0b82",
"created":
"2017-01-20T00:00:00.000Z",
"definition_type":
"tlp",
"name": "TLP:AMBER",
"definition": {
"tlp": "amber"
}
}
|
|
red
|
{
"type":
"marking-definition",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"marking-definition--5e57c739-391a-4eb3-b6be-7d15ca92d5ed",
"created":
"2017-01-20T00:00:00.000Z",
"definition_type":
"tlp",
"name": "TLP:RED",
"definition": {
"tlp": "red"
}
}
|
Object Markings apply data markings to
an entire STIX Object and all of its contents. Object Markings are specified as
embedded relationships in the object_marking_refs
property, which is an optional list of IDs for Marking Definition objects. The
referenced markings apply to that STIX Object or Marking Definition and all of
its contents. Changes to the object_marking_refs
property (and therefore the markings applied to the object) are treated the
same as changes to any other properties on the object and follow the same rules
for versioning.
Examples
This example marks the Indicator and all
its properties with the Marking Definition referenced by the ID.
{
"type": "indicator",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"indicator--b346b4b3-f4b7-4235-b659-f985f65f0009",
...
"object_marking_refs":
["marking-definition--34098fce-860f-48ae-8e50-ebd3cc5e41da"],
...
}
Whereas object markings apply to an entire STIX Object or
Marking Definition and all its properties, granular markings allow both data
markings and language markings to be applied to individual portions of STIX
Objects and Marking Definitions. Granular markings are specified in the granular_markings property, which is a
list of granular-marking
instances. Each of those instances contains a list of selectors to indicate
what is marked and either a reference to the marking-definition object to be
applied or a language code to be applied. Granular markings can be used, for
example, to indicate that the name
property of an indicator
should be handled as TLP:GREEN, the description
property as TLP:AMBER, and the pattern
property as TLP:RED.
The granular_markings
property can also be used for language markings. To support applying both
data markings and language markings to an object, the granular-marking type has a
choice of two properties in addition to the selector: the lang property is used to
apply language markings, and the marking_ref property is used to apply data markings.
Because each granular marking instance applies to either a language or a
marking, one and only one of these properties MUST be present on each
instance of a granular marking.
The granular-marking type defines how the marking-definition
object referenced by the marking_ref
property or a language specified by the lang
property applies to a set of content identified by the list of selectors in the
selectors property.
|
Property Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
lang
(optional)
|
string
|
The lang
property identifies the language of the text identified by this marking. The
value of the lang property,
if present, MUST be an [RFC5646] language code.
If the marking_ref
property is not present, this property MUST be present. If the marking_ref property is present, this
property MUST NOT be present.
|
|
marking_ref
(optional)
|
identifier
|
The marking_ref
property specifies the ID of the marking-definition object that
describes the marking.
If the lang
property is not present, this property MUST be present. If the lang property is present, this
property MUST NOT be present.
|
|
selectors
(required)
|
list of type string
|
The selectors
property specifies a list of selectors for content contained within the STIX
Object in which this property appears. Selectors MUST conform to the
syntax defined below.
The marking-definition referenced in the
marking_ref property is
applied to the content selected by the selectors in this list.
The [RFC5646] language code specified by the lang property is applied
to the content selected by the selectors in this list.
|
Selector Syntax
Selectors contained in the selectors list are strings that consist
of multiple components that MUST be separated by the .
character. Each component MUST be one of:
●
A property name or dictionary key, e.g., description, or;
●
A zero-based list index, specified as a non-negative integer in square
brackets, e.g., [4]
Selectors denote path traversals: the
root of each selector is the STIX Object that the granular_markings property appears in. Starting from that
root, for each component in the selector, properties and list items are
traversed. When the complete list has been traversed, the value of the content
is considered selected.
Selectors MUST refer to
properties or list items that are actually present on the marked object.
As an example, consider the following
STIX Object:
{
"id":
"vulnerability--ee916c28-c7a4-4d0d-ad56-a8d357f89fef",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"created":
"2016-02-14T00:00:00.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-02-14T00:00:00.000Z",
"type":
"vulnerability",
"name":
"CVE-2014-0160",
"description": "The
(1) TLS...",
"external_references": [{
"source_name":
"cve",
"external_id":
"CVE-2014-0160"
}],
"labels":
["heartbleed", "has-logo"]
}
Valid selectors:
●
description
selects the description
property ("The (1) TLS...").
●
external_references.[0].source_name
selects the source_name
property of the first value of the external_references
list ("cve").
●
labels.[0]
selects the first item contained within the labels
list ("heartbleed").
●
labels
selects the list contained in the labels
property. Due to the recursive nature of the selector, that includes all items
in the list (["heartbleed",
"has-logo"]).
●
external_references
selects the list contained in the external_references
property. Due to the recursive nature of the selector, that includes all list
items and all properties of those list items.
Invalid selectors:
●
pattern
and external_references.[3]
are invalid selectors because they refer to content not present in that object.
●
description.[0]
is an invalid selector because the description property is a string and
not a list.
●
labels.name
is an invalid selector because labels property is a list and not an object.
This syntax is inspired by JSONPath [Goessner 2007]
and is in fact a strict subset of allowable JSONPath expressions (with the
exception that the '$' to indicate the root is implicit). Care should be taken
when passing selectors to JSONPath evaluators to ensure that the root of the
query is the individual STIX Object. It is expected, however, that selectors
can be easily evaluated in programming languages that implement list and
key/value mapping types (dictionaries, hashmaps, etc.) without resorting to an
external library.
Examples
This example marks the description and labels properties with the marking-definition
referenced in the granular_markings
property however the name
property uses the object marking.
{
...
"granular_markings": [
{
"marking_ref":
"marking-definition--089a6ecb-cc15-43cc-9494-767639779123",
"selectors":
["description", "labels"]
}
],
"object_marking_ref":
"marking-definition--79e2fa14-02c6-40d7-aa4b-ebf281dd78ef"
"description": "Some
description",
"name": "Some name",
"labels":
["first", "second"]
}
This example marks the
default language for this object as English (in this case, the name property) and the description as German.
{
"type": "campaign",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id": "campaign--12a111f0-b824-4baf-a224-83b80237a094",
"lang": "en",
"created": "2017-02-08T21:31:22.007Z",
"modified": "2017-02-08T21:31:22.007Z",
"name": "Bank Attack",
"description": "Weitere Informationen über Banküberfall",
"granular_markings": [
{
"selectors":
["description"],
"lang": "de"
}
]
}
Type Name: bundle
A Bundle is a collection of arbitrary STIX Objects grouped
together in a single container. A Bundle does not have any semantic meaning and
the objects contained within the Bundle are not considered related by virtue of
being in the same Bundle.
A STIX Bundle Object is not a STIX Object but makes use of
the type and id Common Properties. A Bundle is
transient, and implementations SHOULD NOT assume that other
implementations will treat it as a persistent object or keep any custom
properties found on the bundle itself.
The JSON MTI serialization uses the JSON Object type [RFC8259]
when representing bundle.
|
Property Name
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
type (required)
|
string
|
The type property identifies the type of object. The value of
this property MUST be bundle.
|
|
id (required)
|
identifier
|
An identifier for this Bundle.
The id property for the Bundle is designed to help tools that
may need it for processing, but tools are not required to store or track it.
Tools that consume STIX should not rely on the ability to refer to bundles by
ID.
|
|
objects (optional)
|
list of type <STIX Object>
|
Specifies a set of one or more STIX Objects. Objects in
this list MUST be a STIX Object.
|
STIX Bundle Object is not a STIX Object and MUST NOT
have any relationships to or from it.
Examples
{
"type": "bundle",
"id":
"bundle--5d0092c5-5f74-4287-9642-33f4c354e56d",
"objects": [
{
"type": "indicator",
"spec_version":
"2.1",
"id":
"indicator--8e2e2d2b-17d4-4cbf-938f-98ee46b3cd3f",
"created_by_ref":
"identity--f431f809-377b-45e0-aa1c-6a4751cae5ff",
"created":
"2016-04-29T14:09:00.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-04-29T14:09:00.000Z",
"object_marking_refs":
["marking-definition--089a6ecb-cc15-43cc-9494-767639779123"],
"name": "Poison Ivy
Malware",
"description": "This file
is part of Poison Ivy",
"pattern":
"[file:hashes.'SHA-256' =
'aec070645fe53ee3b3763059376134f058cc337247c978add178b6ccdfb0019f']"
}
]
}
The terms defined below are used
throughout this document.
|
Terms
|
Definitions
|
Example
|
|
whitespace
|
Any Unicode code point that has WSpace
set as a property, for example, line feeds, carriage returns, tabs, and
spaces.
|
n/a
|
|
Observation
|
Observations represent data about
systems or networks that is observed at a particular point in time - for
example, information about a file that existed, a process that was observed
running, or network traffic that was transmitted between two IPs. In STIX,
Observations are represented by Observed Data SDOs, with number_observed observations
occurring between their first_observed
and last_observed
timestamps. It is not defined when the observations occur within that time
window.
For additional background, refer to the STIX Observed Data object definition
in section 4.13.
|
n/a
|
|
Comparison Expression
|
Comparison Expressions are the basic
components of Observation Expressions. They consist of an Object Path and a
constant joined by a Comparison Operator (listed in section 9.6.1,
Comparison Operators).
|
user-account:value =
'Peter'
|
|
Comparison Operators
|
Comparison Operators are used within
Comparison Expressions to compare an Object Path against a constant or set of
constants.
|
MATCHES
|
|
Object Path
|
Object Paths define which properties
of STIX Cyber-observable Objects (SCO) should be evaluated as part of a
Comparison Expression. SCOs and their properties are defined in section 6.
|
ipv6-addr:value
|
|
Observation Expression
|
Observation Expressions consist of one
or more Comparison Expressions joined with Boolean Operators and surrounded
by square brackets.
An Observation Expression may consist
of two Observation Expressions joined by an Observation Operator. This may be
applied recursively to compose multiple Observation Expressions into a single
Observation Expression.
Observation Expressions may optionally
be followed by one or more Qualifiers further constraining the result set.
Qualifiers may be applied to all of the Observation Expressions joined with
Observation Operators; in this case, parentheses should be used to group the
set of Observation Expressions, with the Qualifier following the closing
parenthesis.
|
[ipv4-addr:value =
'203.0.113.1' OR ipv4-addr:value = '203.0.113.2']
or (with Observation Operator):
([ipv4-addr:value =
'198.51.100.5'] FOLLOWEDBY [ipv4-addr:value = '198.51.100.10'])
or (with Observation Operator and
Qualifier):
([ipv4-addr:value =
'198.51.100.5' ] AND [ipv4-addr:value = '198.51.100.10']) WITHIN 300 SECONDS
|
|
Boolean Operators
|
Boolean
Operators are used to combine Comparison Expressions within an Observation
Expression.
|
(Comparison Expressions)
user-account:value =
'Peter' OR user-account:value = 'Mary'
|
|
Qualifier
|
Qualifiers provide a restriction on
the Observations that are considered valid for matching the preceding
Observation Expression.
|
[file:name = 'foo.dll']
START t'2016-06-01T00:00:00Z' STOP t'2016-07-01T00:00:00Z'
|
|
Observation Operators
|
Observation Operators are used to
combine two Observation Expressions operating on two different Observed Data
instances into a single pattern.
Note that some Observation Operators
have the same name as Boolean Operators. However, the former connects
Comparison Expressions and the latter connects Observation Expressions, and
therefore each has slightly different semantics.
|
[ipv4-addr:value =
'198.51.100.5'] AND [ ipv4-addr:value = '198.51.100.10']
|
|
Pattern Expression
|
A Pattern Expression represents a
valid instance of a STIX cyber observable pattern. The most basic Pattern
Expression consists of a single Observation Expression containing a single
Comparison Expression.
|
[file:size = 25536]
|
9.2 Constants
The data types enumerated below are
supported as operands within Comparison Expressions. This table is included
here as a handy reference for implementers.
Note that unlike SCOs (which are defined
in terms of the MTI JSON serialization), STIX Patterns are Unicode strings,
regardless of the underlying serialization, hence the data types defined in the
table below in some cases differ from the definitions contained in section 2.
Each constant defined in Patterning has
a limited set of STIX Data types that they are allowed to be compared against.
In some cases, there are multiple STIX Data Types that could be compared
against a STIX Patterning Constant; this is due to the fact that certain STIX
Data Types are semantically indistinguishable because of their JSON
serialization. The STIX Comparable Data Type(s) column in the table below
defines these limitations.
|
STIX
Patterning Constant
|
STIX
Comparable Data Type(s)
|
Description
|
|
boolean
|
boolean
|
A constant
of boolean type encodes truth or falsehood. Boolean truth is
denoted by the literal true and falsehood by
the literal false.
|
|
binary
|
binary
hex
string
|
A constant
of binary type is a base64 encoded array of octets (8-bit bytes)
per [RFC4648].
The base64 string MUST be surrounded by apostrophes (''' U+0027) and
prefixed by a 'b' (U+0062). Line feeds in the base64 encoded data MUST
be supported and ignored but are not required to be inserted.
Example:
b'ABI='
|
|
hex
|
binary
hex
string
|
A constant
of hex type encodes an array of octets (8-bit bytes) as
hexadecimal. The string MUST consist of an even number of hexadecimal
characters, which are the digits '0' through '9' and the letters 'a' through
'f'. The hex string MUST be surrounded by apostrophes (''' U+0027) and
prefixed by an 'h' (U+0068).
Example:
h'ffc3'
|
|
integer
|
integer
float
|
A constant
of integer type encodes a signed decimal number in the usual
fashion (e.g., 123). In the case of positive integers, the integer MUST
be represented as-is, omitting the plus sign ('+' U+002b). Negative integers MUST
be represented by prepending a hyphen-minus ('-' U+002d).
When
compared against a float, the full value
must be compared and must not be truncated. For example, the result of
comparing a STIX Patterning constant integer value of 1 to a float value of 1.5 is not equal.
The valid
range of values is defined in section 2.
|
|
float
|
integer
float
|
A constant
of float type encodes a floating-point number in the usual
fashion (e.g., 123.456). In the case of positive floating-point number, the
floating-point number MUST be represented as-is, omitting the plus
sign' ('+' U+002b). Negative floating-point numbers MUST be represented
by prepending a hyphen-minus ('-' U+002d).
The valid
range of values is defined in 2.
|
|
string
|
string
binary
hex
|
A constant
of string type encodes a string as a list of Unicode code points
surrounded by apostrophes (''' U+0027).
The escape
character is the backslash ('\' U+005c). Only the apostrophe or the backslash
may follow, and in that case, the respective character is used for the
sequence.
If a string
only contains codepoints less than (U+0100), then the string MAY be
converted to a binary type value (if needed for comparison). The mapping is
code point U+0000 to 00 through U+00ff to ff.
|
|
timestamp
|
timestamp
|
A constant
of timestamp type encodes a STIX timestamp (as specified in section 2.16 as a
string. The timestamp string MUST be surrounded by apostrophes ('''
U+0027) and prefixed with a 't' (U+0074).
Example:
t'2014-01-13T07:03:17Z'
|
9.3 STIX™ Patterns
STIX Patterns are composed of multiple
building blocks, ranging from simple key-value comparisons to more complex, context-sensitive
expressions. The most fundamental building block is the Comparison Expression,
which is a comparison between a single property of a SCO and a given constant
using a Comparison Operator. As a simple example, one might use the following Comparison
Expression (contained within an Observation Expression) to match against an
IPv4 address:
[ipv4-addr:value = '198.51.100.1/32']
Moving up a level of complexity, the
next building block of a STIX Pattern is the Observation Expression, which
consists of one or more Comparison Expressions joined by Boolean Operators and
bounded by square brackets. An Observation Expression refines which set of
cyber observable data (i.e., as part of an Observation) will match the pattern,
by selecting the set that has the SCOs specified by the Comparison Expressions.
An Observation Expression consisting of a single Comparison Expression is the
most basic valid STIX Pattern. Building upon the previous example, one might
construct an Observation Expression to match against multiple IPv4 addresses
and an IPv6 address:
[ipv4-addr:value = '198.51.100.1/32'
OR ipv4-addr:value = '203.0.113.33/32' OR ipv6-addr:value =
'2001:0db8:dead:beef:dead:beef:dead:0001/128']
Observation Expressions may be followed
by one or more Qualifiers, which allow for the expression of further
restrictions on the set of data matching the pattern. Continuing with the above
example, one might use a Qualifier to state that the IP addresses must be
observed several times in repetition:
[ipv4-addr:value = '198.51.100.1/32'
OR ipv4-addr:value = '203.0.113.33/32' OR ipv6-addr:value =
'2001:0db8:dead:beef:dead:beef:dead:0001/128'] REPEATS 5 TIMES
The final, highest level building block
of STIX Patterning combines two or more Object Expressions via Observation
Operators, yielding a STIX Pattern capable of matching across multiple STIX
Observed Data SDOs. Building further upon our previous example, one might use
an Observation Operator to specify that an observation of a particular domain
name must follow the observation of the IP addresses (note the use of
parentheses to encapsulate the two Observation Expressions), along with a
different Qualifier to state that both the IP address and domain name must be
observed within a specific time window:
([ipv4-addr:value = '198.51.100.1/32'
OR ipv4-addr:value = '203.0.113.33/32' OR ipv6-addr:value =
'2001:0db8:dead:beef:dead:beef:dead:0001/128'] FOLLOWEDBY [domain-name:value =
'example.com']) WITHIN 600 SECONDS
The diagram below depicts a truncated version
of the various STIX Patterning components in the above example.
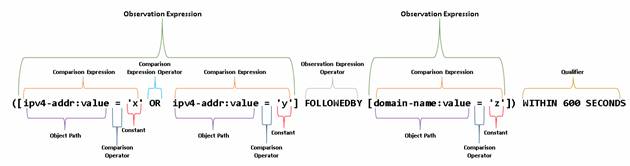
9.4 Pattern Expressions
Pattern Expressions evaluate to true or
false. They comprise one or more Observation Expressions joined by Observation
Operators. Pattern Expressions are evaluated against a set of specific
Observations. If one or more of those Observations match the Pattern
Expression, then it evaluates to true. If no Observations match, the Pattern
Expression evaluates to false.
Pattern Expressions MUST be
encoded as Unicode strings.
Whitespace (i.e., Unicode code points
where WSpace=Y) in the
pattern string is used to delimit parts of the pattern, including keywords,
constants, and field objects. Whitespace characters between operators,
including line feeds and carriage returns, MUST be allowed. Multiple
whitespace characters in a row MUST be treated as a single whitespace
character.
An invalid pattern resulting from
parsing error or invalid constants (e.g., an invalid hex or binary constant) MUST
NOT match any Observations.
9.5 Observation Expressions
Observation Expressions comprise one or
more Comparison Expressions, joined via Boolean Operators.
Observation Expressions MUST be
delimited by square brackets left square bracket ('[' U+005b) and right square
bracket (']' U+005d). One or more Observation Expression Qualifiers MAY
be provided after the closing square bracket or closing parenthesis of an
Observation Expression. Observation Expressions MAY be joined by
Observation Operators.
Individual Observation Expressions
(e.g., [a = b]) match against a single Observation, i.e., a
single STIX Observed Data instance. In cases where matching against multiple
Observations is required, two or more Observation Expressions may be combined
via Observation Operators, indicating that the pattern MUST be evaluated
against two or more distinct Observations; however, in the case of OR, if the
first Observation Expression evaluates to true, then evaluation MUST
terminate and return true.
When matching an Observation against an
Observation Expression, all Comparison Expressions contained within the
Observation Expression MUST match against the same SCO, including
referenced objects. An Observation Expression MAY contain Comparison
Expressions with Object Paths that are based on different object types, but
such Comparison Expressions MUST be joined by OR. The Comparison
Expressions of an Observation Expression that use AND MUST use the same
base Object Path, e.g., file:.
For example, consider the following
Pattern Expression:
[(type-a:property-j = 'W' AND
type-a:property-k = 'X') OR (type-b:property-m = 'Y' AND type-b:property-n =
'Z')]
This expression can match an Observable
with an object of either type-a or type-b, but both
Comparison Expressions for that specific type must evaluate to true for the
same object. Comparison Expressions that are intended to match a single object
type can be joined by either AND or OR. For example:
[type-a:property-j = 'W' AND
type-a:property-k = 'X' OR type-a:property-l = 'Z']
As AND has higher precedence than OR,
the preceding example requires an Observation to have either both property-j
= 'W' AND property-k = 'X' or just property-l = 'Z'.
Observation Expressions, along with
their Observation Operators and optional Qualifiers, MAY be surrounded
with parentheses to delineate which Observation Expressions the Qualifiers
apply to. For example:
([ a ] AND [ b ] REPEATS 5 TIMES)
WITHIN 5 MINUTES
The preceding example results in one a
and 5 b’s that all match in a 5-minute period. As another example:
([ a ] AND [ b ]) REPEATS 5 TIMES
WITHIN 5 MINUTES
The preceding example results in 5 a’s
and 5 b’s (10 Observations) that all match in a 5-minute period.
9.5.1 Observation
Expression Qualifiers
Each Observation Expression MAY
have additional temporal or repetition restrictions using the respective WITHIN, START/STOP, and REPEATS
keywords. An Observation Expression MUST NOT
have more than one Qualifier of a particular type.
|
Qualifiers
|
Description
|
|
a REPEATS x TIMES
|
a MUST be an Observation
Expression or a preceding Qualifier. a MUST match at least x
times, where each match is a different Observation. x MUST be a
positive integer.
This is purely a shorthand way of
writing:
“a” followed by “AND a”, x-1
times.
Example:
[ b ] FOLLOWEDBY [ c ]
REPEATS 5 TIMES
In this example, the REPEATS
applies to c, and it does not apply to b. The results will be b
plus 5 c's where all 5 c's were observed after the b.
Note that there is only a single Qualifier in this example; more complex
patterns may use more than one.
|
|
a WITHIN x SECONDS
|
a MUST be an Observation
Expression or a preceding Qualifier. All Observations matched by a MUST
occur, or have been observed, within the specified time window. x MUST
be a positive floating-point value.
If there is a set of two or more
Observations matched by a, the most recent Observation timestamp
contained within that set MUST NOT be equal to or later than the delta
of the earliest Observation timestamp within the set plus the specified time
window.
Example:
([file:hashes.'SHA-256'
= '13987239847...'] AND [win-registry-key:key = 'hkey']) WITHIN 120 SECONDS
The above Pattern Expression looks for
a file hash and a registry key that were observed within 120 seconds of each
other. The parentheses are needed to apply the WITHIN Qualifier to both Observation
Expressions.
|
|
a START x STOP y
|
a MUST be an Observation
Expression or a preceding Qualifier. All Observations that match a MUST
have an observation time >= x and < y.
x and y MUST be
of type timestamp.
In the event that the Pattern
Expression is being used inside a STIX Indicator pattern property (see
section 4.6)
x SHOULD be greater than or equal to the value contained in the
valid_from
Indicator property, and y SHOULD be less than or equal to the
value contained in the valid_until Indicator property.
|
9.5.2 Observation
Operators
Two or more Observation Expressions MAY
be combined using an Observation Operator in order to further constrain the set
of Observations that match against the Pattern Expression.
|
Observation
Operators
|
Description
|
Associativity
|
|
[ a ] AND [ b ]
|
a and b MUST both
be Observation Expressions and MUST both evaluate to true on different
Observations.
|
Left to right
|
|
[ a ] OR [ b ]
|
a and b MUST both
be Observation Expressions and one of a or b MUST
evaluate to true on different Observations.
|
Left to right
|
|
[ a ] FOLLOWEDBY [ b ]
|
a and b MUST both
be Observation Expressions. Both a and b MUST
both evaluate to true, where the observation timestamp associated with
b is greater than or equal to the observation timestamp
associated with a and MUST evaluate to true on different
Observations.
|
Left to right
|
For example, consider the following
Pattern Expression:
[ a = 'b' ] FOLLOWEDBY [ c = 'd' ]
REPEATS 5 TIMES
The preceding expression says to match
an Observation with a equal to 'b' that precedes 5 occurrences of
Observations that have c equal to ‘d’, for a total of 6 Observations
matched. This interpretation is due to qualifiers not being greedy and is
equivalent to [ a = 'b' ] FOLLOWEDBY ( [ c = 'd' ] REPEATS 5 TIMES).
Alternatively, using parentheses to
group the initial portion, we get the following example:
([ a = 'b' ] FOLLOWEDBY [
c = 'd' ]) REPEATS 5 TIMES
The preceding expression will match 5 pairs of Observations where a
equals 'b' followed by an Observation where c is equal to 'd', for a
total of 10 Observations matched.
9.5.3 Operator
Precedence
Operator associativity and precedence
may be overridden by the use of parentheses. Unless otherwise specified,
operator associativity (including for parentheses) is left-to-right. Precedence
in the below table is from highest to lowest.
|
Operators
|
Associativity
|
Valid
Scope
|
|
()
|
left to right
|
Observation Expression or Pattern
Expression, Observation Expression and Qualifier
|
|
AND
|
left to right
|
Observation Expression, Pattern
Expression
|
|
OR
|
left to right
|
Observation Expression, Pattern
Expression
|
|
FOLLOWEDBY (Observation Operator)
|
left to right
|
Pattern Expression
|
9.6 Comparison Expressions
Comparison Expressions are the most
basic components of STIX Patterning, comprising an Object Path and a constant
joined by a Comparison Operator. Each Comparison Expression is a singleton, and
so they are evaluated from left to right.
A Boolean Operator joins two Comparison
Expressions together. In the following table, a or b is either a
Comparison Expression or a composite expression (which may be composed
recursively) consisting of two or more Comparison Expressions joined with
Boolean Operators and enclosed by parentheses.
|
Boolean
Operator
|
Description
|
Associativity
|
|
a AND b
|
a and b MUST both
be Comparison Expressions or a composite expression (which may be composed
recursively) consisting of two or more Comparison Expressions joined with
Boolean Operators and enclosed by parentheses.
a and b MUST both
evaluate to true on the same Observation.
|
Left to right
|
|
a OR b
|
a and b MUST both
be Comparison Expressions or a composite expression (which may be composed
recursively) consisting of two or more Comparison Expressions joined with
Boolean Operators and enclosed by parentheses.
Either a or b MUST
evaluate to true.
|
Left to right
|
Comparison Expressions may include one
or more Object Path(s) not obtainable within a given Observation, either
because the Object Path(s) are not present within the Observation or because
the evaluating entity does not have access to the data necessary in order to
evaluate the specified Object Path(s). When evaluating a Comparison Expression
against one or more Object Path(s) that are not present or whose data cannot be
obtained, the Comparison Expression MUST evaluate to FALSE,
regardless of the operators included in the expression.
9.6.1 Comparison
Operators
The table below describes the available
Comparison Operators for use in Comparison Expressions; in the table, a MUST
be an Object Path and b MUST be a constant. If the arguments to
the Comparison Operators are of incompatible types (e.g., the Object Path is an
integer and the constant is a string), the results are false; the sole
exception is the != operator in which case the result is true. Some STIX
Patterning constants and STIX data types may be comparable in a Comparison
Expression. For example, the hex and binary types both represent binary
data, and their representative binary data is that which must be compared for
equality. See section 2
for type compatibility between STIX Patterning and STIX types.
A Comparison Operator MAY be
preceded by the modifier NOT, in which case the resultant Comparison
Expression is logically negated.
|
Comparison
Operator
|
Description
|
Example
|
|
a = b
|
a and b MUST be
equal (transitive), where a MUST be an Object Path and b MUST
be a constant of the same data type as the object property specified by a.
|
file:name = 'foo.dll'
|
|
a != b
|
a and b MUST NOT
be equal (transitive), where a MUST be an Object Path and b MUST
be a constant of the same data type as the Object property specified by a.
|
file:size != 4112
|
|
a > b
|
a is numerically or lexically
greater than b, where a MUST be an Object Path and b
MUST be a constant of the same data type as the Object property
specified by a.
|
file:size > 256
|
|
a < b
|
a is numerically or lexically
less than b, where a MUST be an Object Path and b
MUST be a constant of the same data type as the Object property
specified by a.
|
file:size < 1024
|
|
a <= b
|
a is numerically or lexically
less than or equal to b, where a MUST be an Object Path
and b MUST be a constant of the same data type as the Object
property specified by a.
|
file:size <= 25145
|
|
a >= b
|
a is numerically or lexically
greater than or equal to b, where a MUST be an Object
Path and b MUST be a constant of the same data type as the
Object property specified by a.
|
file:size >= 33312
|
|
a IN (x,y,...)
|
a MUST be an Object Path
and MUST evaluate to one of the values enumerated in the set of
x,y,... (transitive). The set values in b MUST be constants of
homogeneous data type and MUST be valid data types for the Object
Property specified by a. The return value is true if a
is equal to one of the values in the list. If a is not equal to any of
the items in the list, then the Comparison Expression evaluates to false.
|
process:name IN
('proccy', 'proximus', 'badproc')
|
|
a LIKE b
|
a MUST be an Object Path
and MUST match the pattern specified in b where any '%' is 0 or
more characters and ‘_' is any one character.
This operator is based upon the SQL LIKE
clause and makes use of the same wildcards.
The string constant b MUST
be NFC normalized [Davis]
prior to evaluation.
|
directory:path LIKE
'C:\\Windows\\%\\foo'
|
|
a MATCHES b
|
a MUST be an Object Path
and MUST be matched by the pattern specified in b, where b
is a string constant containing a PCRE compliant regular expression. a
MUST be NFC normalized [Davis] before comparison if the property
is of string type.
Regular expressions MUST be
conformant to the syntax defined by the Perl-compatible Regular Expression
(PCRE) library (http://www.pcre.org/original/doc/html/pcrepattern.html). The search function MUST be used. The DOTALL option MUST be specified. The standard beginning and end
anchors may be used in the pattern to obtain match behavior.
In the case that the property is binary (e.g., the property name ends in _bin or _hex), then the UNICODE flag MUST NOT be specified.
|
directory:path MATCHES
'^C:\\\\Windows\\w+$'
|
|
Set
Operator
|
Description
|
Example
|
|
a ISSUBSET b
|
When a is a set that is wholly
contained by the set b, the Comparison Expression evaluates to true. a
MUST be an Object Path referring to the value property of an Object of type ipv4-addr
or ipv6-addr.
b MUST be a valid string representation of the corresponding Object
type (as defined in section 6.
For example, if ipv4-addr:value
was 198.51.100.0/27, ISSUBSET '198.51.100.0/24' would
evaluate to true.
In the case that both a and b
evaluate to an identical single IP address or an identical IP subnet, the
Comparison Expression evaluates to true.
|
ipv4-addr:value ISSUBSET
'198.51.100.0/24'
|
|
a ISSUPERSET b
|
When a is a set that wholly
contains the set specified by b, the Comparison Expression evaluates
to true. a MUST be an Object Path referring either an ipv4-addr
or ipv6-addr
Object. b MUST be a valid string representation of the
corresponding Object type (as defined in section 6).
For example, if ipv4-addr:value
was 198.51.100.0/24, ISSUPERSET '198.51.100.0/27' would
evaluate to true.
In the case that both a and b
evaluate to an identical single IP address or an identical IP subnet, the
Comparison Expression evaluates to true.
|
ipv4-addr:value
ISSUPERSET '198.51.100.0/24'
|
|
EXISTS a
|
a MUST be an Object Path which specifies a
single property that MUST exist on the Object specified by the
Observation Expression in order for the Comparison Expression to evaluate to
true.
For example, EXISTS windows-registry-key:values would
evaluate to true on a registry key that contains a 'values' property
(regardless of its contents).
|
EXISTS windows-registry-key:values
|
9.6.2 String
Comparison
For simple string operators, i.e.,
"=",
"!=",
"<",
">",
"<="
and ">=",
as collation languages and methods are unspecifiable, a simple code point
(binary) comparison MUST be used. If one string is longer than the
other, but otherwise equal, the longer string is greater than, but not equal
to, the shorter string. Unicode normalization MUST NOT be performed on
the string. This means that combining marks [Davis] are sorted by their code point, not
the NFC normalized value. E.g. ‘o' U+006f < ‘oz' U+006f U+007a <
‘ò' U+006f U+0300 < ‘z' U+007a < ‘ò' U+00f2. Although Unicode
recommends normalizing strings for comparisons, the use of combining marks may
be significant, and normalizing by default would remove this information.
NFC normalization is, however, required
for other Comparison Operators, e.g., LIKE and MATCHES.
9.6.3 Binary
Type Comparison
When the value of two binary object
properties are compared, they are compared as unsigned octets. That is, 00 is less
than ff.
If one value is longer than the other, but they are otherwise equal, the longer
value is considered greater than, but not equal to, the shorter value.
9.6.4 Native
Format Comparison
The SCO's value MUST be in its
native format when doing the comparison. For example, Cyber-observable Object
properties that use the binary type (defined in section 2.1) must
have their value decoded into its constituent bytes prior to comparison. This
also means that Object Properties which use the hex type must be decoded into raw
octets prior to being evaluated.
In cases where a binary SCO property
(i.e., one ending with _bin or _hex) is evaluated against a
string constant, the string constant MUST be converted into a binary
constant when all of the constituent string code points are less than U+0100.
If this conversion is not possible, the comparison MUST evaluate to
false, unless the comparison operator is !=, in which case it MUST evaluate
to true.
For example, given the following object,
where the payload_bin property is of binary type :
{
"0":{
"type":
"artifact",
"mime_type":
"application/octet-stream",
"payload_bin":
"dGhpcyBpcyBhIHRlc3Q="
}
}
The pattern "artifact:payload_bin
= 'dGhpcyBpcyBhIHRlc3Q='"
would evaluate to false, while the following patterns would all evaluate to
true:
"artifact:payload_bin =
'this is a test'", "artifact:payload_bin =
b'dGhpcyBpcyBhIHRlc3Q='",
and "artifact:payload_bin =
h'7468697320697320612074657374'".
9.7 Object Path Syntax
Defined below is the syntax for
addressing properties of SCOs within a STIX Pattern. The following notation is
used throughout the definitions below:
|
Notation
|
Definition
|
|
<object-type>
|
The type of SCO to match against. This
MUST be the value of the type field specified for a given SCO
in an Observation.
|
|
<property_name>
|
The name of a SCO property to match
against. This MUST be a valid property name as specified in the
definition of the SCO type referenced by the <object-type> notation.
If the <property_name> contains a
hyphen-minus ('-' U+002d) or a full stop ('.' U+002e), the <property_name>
MUST be enclosed in apostrophes (''' U+0027).
Properties that are nested (i.e., are
children of other properties in a SCO) MUST be specified using the
syntax <property_name>.<property_name>,
where the <property_name>
preceding the ‘.' is the name of the parent property and the one following is
the name of the child property.
If the property name is a reference to
another SCO, the referenced Object MUST be dereferenced, so that its
properties function as if they are nested in the Object that it is referenced
by. For example, if the src_ref property of the Network Traffic object
references an IPv4 Address object, the value of this IPv4 address would be
specified by network-traffic:src_ref.value.
|
9.7.1 Basic
Object Properties
Any non-dictionary and non-list
property that is directly specified on a SCO.
Syntax
<object-type>:<property_name>
Example
file:size
9.7.2 List
Object Properties
Any property on a SCO that uses the list data
type.
Syntax
<object-type>:<property_name>[list_index].<property_name>
Where the first property_name MUST be
the name of an Object property of type list and list_index MUST be one
of the following:
●
An integer in the range of 0…N-1, where N is the length of the list. If list_index
is out of range, the result of any operation is false.
●
The literal '*' indicates that all
of the items in the list shall be tried as a value to be evaluated with the
Comparison Operator and other value. If any of these evaluations are true, then
the result is true.
Examples
file:extensions.'windows-pebinary-ext'.sections[*].entropy
network-traffic:protocols[0]
9.7.3 Dictionary
Object Properties
Any property on an SCO that uses the dictionary
data type.
Syntax
<object-type>:<property_name>.<key_name>
Where <property_name> MUST be
the name of an Object property of type dictionary and <key_name> MUST be
the name of key in the dictionary.
Examples
file:hashes.ssdeep
file:extensions.'raster-image-ext'.image_height
9.7.4 Object
Reference Properties
Any property on an SCO that represents
an embedded relationship and uses the identifier data type, either as a
singleton or as a list (i.e., list of type identifier).
Syntax
<object-type>:<property_name>.<dereferenced_object_property>
Where <property_name> MUST be
the name of an Object property that represents an embedded relationships and is
of type identifier
and <dereferenced_object_property>
MUST be the name of a valid property of the dereferenced Object (i.e., the
Object in an Observation that is referenced via <property_name>).
For example, when processing the
Observed Data SDO that uses the object_refs
property instead of the deprecated objects
property, only those SCO's that are listed in the object_refs may be followed. This means that
if the object identifier
is not listed in object_refs
property, then that object is considered not found, and any references to
properties of that object are considered not present.
For cases where <property_name> represents
a list
of embedded relationships and is a list of type identifier, the corresponding
syntax applies:
<object-type>:<property_name>[list_index].<dereferenced_object_property>
Accordingly, the same semantics for list
indices as defined in section 9.7.2 apply in this case.
Examples
email-message:from_ref.value
directory:contains_refs[*].name
9.8 Examples
Note: the
examples below are NOT JSON encoded. This means that some
characters, like double quotes, are not escaped, though they will be when
encoded in a JSON string.
Matching a File with a SHA-256 hash
[file:hashes.'SHA-256' =
'aec070645fe53ee3b3763059376134f058cc337247c978add178b6ccdfb0019f']
Matching an Email Message with a
particular From Email Address and Attachment File Name Using a Regular
Expression
[email-message:from_ref.value MATCHES
'.+\\@example\\.com$' AND email-message:body_multipart[*].body_raw_ref.name
MATCHES '^Final Report.+\\.exe$']
Matching a File with a SHA-256 hash
and a PDF MIME type
[file:hashes.'SHA-256' =
'aec070645fe53ee3b3763059376134f058cc337247c978add178b6ccdfb0019f' AND
file:mime_type = 'application/x-pdf']
Matching a File with SHA-256 or a MD5
hash (e.g., for the case of two different end point tools generating either an
MD5 or a SHA-256), and a different File that has a different SHA-256 hash,
against two different Observations
[file:hashes.'SHA-256' =
'bf07a7fbb825fc0aae7bf4a1177b2b31fcf8a3feeaf7092761e18c859ee52a9c' OR
file:hashes.MD5 = 'cead3f77f6cda6ec00f57d76c9a6879f']
AND [file:hashes.'SHA-256' =
'aec070645fe53ee3b3763059376134f058cc337247c978add178b6ccdfb0019f']
Matching a File with a MD5 hash,
followed by (temporally) a Registry Key object that matches a value, within 5
minutes
([file:hashes.MD5 =
'79054025255fb1a26e4bc422aef54eb4'] FOLLOWEDBY [windows-registry-key:key =
'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\foo\\bar']) WITHIN 300 SECONDS
Matching three different, but
specific Unix User Accounts
[user-account:account_type = 'unix'
AND user-account:user_id = '1007' AND user-account:account_login = 'Peter'] AND
[user-account:account_type = 'unix' AND user-account:user_id = '1008' AND
user-account:account_login = 'Paul'] AND [user-account:account_type = 'unix'
AND user-account:user_id = '1009' AND user-account:account_login = 'Mary']
Matching an Artifact object PCAP
payload header
[artifact:mime_type =
'application/vnd.tcpdump.pcap' AND artifact:payload_bin MATCHES
'\\xd4\\xc3\\xb2\\xa1\\x02\\x00\\x04\\x00']
Matching a File object with a Windows
file path
[file:name = 'foo.dll' AND
file:parent_directory_ref.path = 'C:\\Windows\\System32']
Matching on a Windows PE File with
high section entropy
[file:extensions.'windows-pebinary-ext'.sections[*].entropy
> 7.0]
Matching on a mismatch between a File
object magic number and mime type
[file:mime_type = 'image/bmp' AND
file:magic_number_hex = h'ffd8']
Matching on Network Traffic with a
particular destination
[network-traffic:dst_ref.type =
'ipv4-addr' AND network-traffic:dst_ref.value = '203.0.113.33/32']
Matching on Malware Beaconing to a
Domain Name
[network-traffic:dst_ref.type =
'domain-name' AND network-traffic:dst_ref.value = 'example.com'] REPEATS 5 TIMES
WITHIN 1800 SECONDS
Matching on a Domain Name with IPv4
Resolution
[domain-name:value = 'www.5z8.info'
AND domain-name:resolves_to_refs[*].value = '198.51.100.1/32']
Matching on a URL
[url:value = 'http://example.com/foo'
OR url:value = 'http://example.com/bar']
Matching on an X509 Certificate
[x509-certificate:issuer =
'CN=WEBMAIL' AND x509-certificate:serial_number =
'4c:0b:1d:19:74:86:a7:66:b4:1a:bf:40:27:21:76:28']
Matching on a Windows Registry Key
[windows-registry-key:key =
'HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\CryptoLocker\\Files' OR windows-registry-key:key
=
'HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Microsoft\\CurrentVersion\\Run\\CryptoLocker_0388']
`
Matching on a File with a set of
properties
[(file:name = 'pdf.exe' OR file:size =
371712) AND file:created = t'2014-01-13T07:03:17Z']
Matching on an Email Message with
specific Sender and Subject
[email-message:sender_ref.value =
'jdoe@example.com' AND email-message:subject = 'Conference Info']
Matching on a Custom USB Device
[x-usb-device:usbdrive.serial_number =
'575833314133343231313937']
Matching on Two Processes Launched
with a Specific Set of Command Line Arguments Within a Certain Time Window
[process:command_line MATCHES
'^.+>-add GlobalSign.cer -c -s -r localMachine Root$'] FOLLOWEDBY
[process:command_line MATCHES'^.+>-add GlobalSign.cer -c -s -r
localMachineTrustedPublisher$'] WITHIN 300 SECONDS
Matching on a Network Traffic IP that
is part of a particular Subnet
[network-traffic:dst_ref.value
ISSUBSET '2001:0db8:dead:beef:0000:0000:0000:0000/64']
Matching on several different
combinations of Malware Artifacts. Note the following pattern requires that
both a file and registry key exist, or that one of two processes exist.
([file:name = 'foo.dll'] AND [windows-registry-key:key
= 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\foo\\bar']) OR [process:image_ref.name = 'fooproc' OR
process:image_ref.name = 'procfoo']
The following sections provide object-specific
listings for each of the vocabularies referenced in the object description
sections defined in Sections 4, 5, 6, and 7.
STIX vocabularies that have type names ending in '-ov', are
"open": they provide a listing of common and industry accepted terms
as a guide to the user but do not limit the user to that defined list. These
vocabularies are referenced from the STIX Objects as type open-vocab
and have a statement indicating which vocabulary should be used.
STIX vocabularies that have type names ending in '-enum' are
"closed": the only valid values are those in the vocabulary. These
vocabularies are referenced from the STIX Objects as type enum and
have a statement indicating which enumeration must be used.
10.1 Account Type Vocabulary
Vocabulary Name: account-type-ov
The account type vocabulary is currently used in the following
SCOs:
● User
Account
An open vocabulary of User Account types.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
facebook, ldap, nis, openid, radius, skype, tacacs, twitter,
unix,
windows-local,
windows-domain
|
|
Vocabulary Value
|
Description
|
|
facebook
|
Specifies a Facebook account.
|
|
ldap
|
Specifies an LDAP account.
|
|
nis
|
Specifies a NIS account
|
|
openid
|
Specifies an OpenID
account.
|
|
radius
|
Specifies a RADIUS account.
|
|
skype
|
Specifies a Skype account.
|
|
tacacs
|
Specifies a TACACS account.
|
|
twitter
|
Specifies a Twitter account.
|
|
unix
|
Specifies a POSIX account.
|
|
windows-local
|
Specifies a Windows local
account.
|
|
windows-domain
|
Specifies a Windows domain
account.
|
10.2 Attack Motivation
Vocabulary Name: attack-motivation-ov
The attack motivation vocabulary is currently used in the
following SDOs:
● Intrusion
Set
● Threat
Actor
Knowing a Threat Actor or Intrusion Set's motivation may
allow an analyst or defender to better understand likely targets and behaviors.
Motivation shapes the intensity and the persistence of an
attack. Threat Actors and Intrusion Sets usually act in a manner that reflects
their underlying emotion or situation, and this informs defenders of the manner
of attack. For example, a spy motivated by nationalism (ideology) likely has the
patience to achieve long-term goals and work quietly for years, whereas a
cyber-vandal out for notoriety can create an intense and attention-grabbing
attack but may quickly lose interest and move on. Understanding these
differences allows defenders to implement controls tailored to each type of
attack for greatest efficiency.
This section including vocabulary items and their
descriptions is based on the Threat Agent Motivations publication from
Intel Corp in February 2015 [Casey 2015].
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
accidental, coercion, dominance, ideology,
notoriety,
organizational-gain,
personal-gain,
personal-satisfaction,
revenge,
unpredictable
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
accidental
|
A non-hostile actor whose benevolent or harmless intent
inadvertently causes harm.
For example, a well-meaning and dedicated employee who
through distraction or poor training unintentionally causes harm to his or
her organization.
|
|
coercion
|
Being forced to act on someone else's behalf.
Adversaries who are motivated by coercion are often forced
through intimidation or blackmail to act illegally for someone else’s
benefit. Unlike the other motivations, a coerced person does not act for
personal gain, but out of fear of incurring a loss.
|
|
dominance
|
A desire to assert superiority over someone or something
else.
Adversaries who are seeking dominance over a target are
focused on using their power to force their target into submission or
irrelevance. Dominance may be found with ideology in some state-sponsored
attacks and with notoriety in some cyber vandalism-based attacks.
|
|
ideology
|
A passion to express a set of ideas, beliefs, and values
that may shape and drive harmful and illegal acts.
Adversaries who act for ideological reasons (e.g.,
political, religious, human rights, environmental, desire to cause
chaos/anarchy, etc.) are not usually motivated primarily by the desire for
profit; they are acting on their own sense of morality, justice, or political
loyalty.
For example, an activist group may sabotage a company’s
equipment because they believe the company is harming the environment.
|
|
notoriety
|
Seeking prestige or to become well known through some
activity.
Adversaries motivated by notoriety are often seeking either
personal validation or respect within a community and staying covert is not a
priority. In fact, one of the main goals is to garner the respect of their
target audience.
|
|
organizational-gain
|
Seeking advantage over a competing organization, including
a military organization.
Adversaries motivated by increased profit or other gains
through an unfairly obtained competitive advantage are often seeking theft of
intellectual property, business processes, or supply chain agreements and
thus accelerating their position in a market or capability.
|
|
personal-gain
|
The desire to improve one’s own financial status.
Adversaries motivated by a selfish desire for personal
gain are often out for gains that come from financial fraud, hacking for
hire, or intellectual property theft.
While a Threat Actor or Intrusion Set may be seeking
personal gain, this does not mean they are acting alone. Individuals can band
together solely to maximize their own personal profits.
|
|
personal-satisfaction
|
A desire to satisfy a strictly personal goal, including
curiosity, thrill-seeking, amusement, etc.
Threat Actors or Intrusion Set driven by personal
satisfaction may incidentally receive some other gain from their actions,
such as a profit, but their primary motivation is to gratify a personal,
emotional need. Individuals can band together with others toward a mutual,
but not necessarily organizational, objective.
|
|
revenge
|
A desire to avenge perceived wrongs through harmful
actions such as sabotage, violence, theft, fraud, or embarrassing certain
individuals or the organization.
A disgruntled Threat Actor or Intrusion Set seeking
revenge can include current or former employees, who may have extensive
knowledge to leverage when conducting attacks. Individuals can band together
with others if the individual believes that doing so will enable them to
cause more harm.
|
|
unpredictable
|
Acting without identifiable reason or purpose and creating
unpredictable events.
Unpredictable is not a miscellaneous or default category.
Unpredictable means a truly random and likely bizarre event, which seems to
have no logical purpose to the victims.
|
10.3 Attack Resource Level
Vocabulary Name: attack-resource-level-ov
The attack resource level vocabulary is currently used in
the following SDO(s):
● Intrusion
Set
● Threat
Actor
Attack Resource Level is an open vocabulary that captures
the general level of resources that a threat actor, intrusion set, or campaign
might have access to. It ranges from individual, a person acting alone, to
government, the resources of a national government.
This section including vocabulary items and their
descriptions is based on the Threat Agent Library publication from Intel
Corp in September 2007 [Casey
2007].
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
individual, club, contest, team, organization,
government
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
individual
|
Resources limited to the average individual; Threat Actor
acts independently.
|
|
club
|
Members interact on a social and volunteer basis, often
with little personal interest in the specific target. An example might be a
core group of unrelated activists who regularly exchange tips on a particular
blog. Group persists long term.
|
|
contest
|
A short-lived and perhaps anonymous interaction that
concludes when the participants have achieved a single goal. For example,
people who break into systems just for thrills or prestige may hold a contest
to see who can break into a specific target first. It also includes announced
"operations" to achieve a specific goal, such as the original
"OpIsrael" call for volunteers to disrupt all of Israel's Internet
functions for a day.
|
|
team
|
A formally organized group with a leader, typically
motivated by a specific goal and organized around that goal. Group persists
long term and typically operates within a single geography.
|
|
organization
|
Larger and better resourced than a team; typically, a
company or crime syndicate. Usually operates in multiple geographic areas and
persists long term.
|
|
government
|
Controls public assets and functions within a
jurisdiction; very well resourced and persists long term.
|
10.4 Course of Action Type
Vocabulary Name: course-of-action-type-ov
The course of action type vocabulary is currently used in
the following SDO(s):
● Course
of Action
The Course of Action Type property uses an open vocabulary
to describe the underlying language or structure of the Course of Action that
is being represented.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
textual:text/plain, textual:text/html, textual:text/md,
textual:pdf
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
textual:text/plain
|
Unstructured textual/prose description of a course of
action that does not conform to any standard language
|
|
textual:text/html
|
Prose description of a course of action defined in
structured HTML content
|
|
textual:text/md
|
Prose description of a course of action defined in
structured markdown content
|
|
textual:pdf
|
Prose description of a course of action defined in
structured PDF content
|
10.5 Encryption Algorithm Enumeration
Type Name: encryption-algorithm-enum
The encryption algorithm enumeration is currently used in
the following SCOs:
● Artifact
An enumeration of encryption algorithms for sharing defanged
and/or confidential artifacts.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
AES-256-GCM, ChaCha20-Poly1305, mime-type-indicated
|
|
Vocabulary Value
|
Description
|
|
AES-256-GCM
|
Specifies the AES-256-GCM cipher, as defined in [NIST SP800-38D]
|
|
ChaCha20-Poly1305
|
Specifies the ChaCha20-Poly1305 stream cipher, as defined
in [RFC7539].
|
|
mime-type-indicated
|
The encryption algorithm is self-defined by the artifact's
data. The specified mime-type tells you which format it is, e.g., Word Doc or
GPG. This is intended for formats like Zip files and Word files which take a
simple password, or GPG armored files that contain the key blob along with
the file.
|
10.6 Grouping Context
Vocabulary Name: grouping-context-ov
The Grouping Context open vocabulary is currently used in
the following object:
● Grouping
While the majority of this vocabulary is undefined
(producers may use custom vocabulary entries), it has been added specifically
to capture the suspicious-activity-event
value. That value indicates that the information contained in the Grouping
relates to a suspicious event.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
suspicious-activity, malware-analysis, unspecified
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
suspicious-activity
|
A set of STIX content
related to a particular suspicious activity event.
|
|
malware-analysis
|
A set of STIX content
related to a particular malware instance or family.
|
|
unspecified
|
A set of STIX content
contextually related but without any precise characterization of the
contextual relationship between the objects.
|
10.7 Hashing Algorithm
Vocabulary Name: hash-algorithm-ov
A vocabulary of hashing algorithms.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-512, SHA3-256,
SHA3-512,
SSDEEP
|
|
Vocabulary Value
|
Description
|
|
MD5
|
Specifies the MD5 message digest algorithm. The
corresponding hash string for this value MUST be a valid MD5 message
digest as defined in [RFC1321].
|
|
SHA-1
|
Specifies the SHA-1 (secure-hash algorithm 1)
cryptographic hash function. The corresponding hash string for this value MUST
be a valid SHA-1 message digest as defined in [RFC3174].
|
|
SHA-256
|
Specifies the SHA-256 cryptographic hash function (part
of the SHA2 family). The corresponding hash string for this value MUST
be a valid SHA-256 message digest as defined in [RFC6234].
|
|
SHA-512
|
Specifies the SHA-512 cryptographic hash function (part
of the SHA2 family). The corresponding hash string for this value MUST
be a valid SHA-512 message digest as defined in [RFC6234].
|
|
SHA3-256
|
Specifies the SHA3-256 cryptographic hash function. The
corresponding hash string for this value MUST be a valid SHA3-256
message digest as defined in [FIPS202].
|
|
SHA3-512
|
Specifies the SHA3-512 cryptographic hash function. The
corresponding hash string for this value MUST be a valid SHA3-512
message digest as defined in [FIPS202].
|
|
SSDEEP
|
Specifies the ssdeep fuzzy hashing algorithm. The
corresponding hash string for this value MUST be a valid piecewise
hash as defined in the [SSDEEP] specification.
|
10.8
Identity Class
Vocabulary Name: identity-class-ov
The identity class vocabulary is currently used in the
following SDO(s):
● Identity
This vocabulary describes the type of entity that the
Identity represents: whether it describes an organization, group, individual,
or class.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
individual, group, system, organization, class, unspecified
|
|
Vocabulary Value
|
Description
|
|
individual
|
A single
person.
|
|
group
|
An informal collection of
people, without formal governance, such as a distributed hacker group.
|
|
system
|
A computer system, such as a
SIEM
|
|
organization
|
A formal
organization of people, with governance, such as a company or country.
|
|
class
|
A class of entities,
such as all hospitals, all Europeans, or the Domain Administrators in a
system.
|
|
unspecified
|
It is
unspecified (or unknown) whether the classification is an individual, group,
system, organization, or class.
|
10.9
Implementation Language
Vocabulary Name: implementation-language-ov
The implementation language vocabulary is currently used in
the following SDO(s):
● Malware
This is a non-exhaustive, open vocabulary that covers common
programming languages and is intended to characterize the languages that may
have been used to implement a malware instance or family.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
applescript, bash, c, c++, c#, go, java, javascript, lua, objective-c,
perl,
php,
powershell,
python,
ruby,
scala,
swift,
typescript,
visual-basic,
x86-32,
x86-64
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
applescript
|
Specifies the AppleScript programming language.
|
|
bash
|
Specifies the Bash programming language.
|
|
c
|
Specifies the C programming language.
|
|
c++
|
Specifies the C++ programming language.
|
|
c#
|
Specifies the C# programming language.
|
|
go
|
Specifies the Go (sometimes referred to as golang)
programming language.
|
|
java
|
Specifies the JAVA programming language.
|
|
javascript
|
Specifies the JavaScript programming language.
|
|
lua
|
Specifies the Lua programming language.
|
|
objective-c
|
Specifies the Objective-C programming language.
|
|
perl
|
Specifies the Perl programming language.
|
|
php
|
Specifies the PHP programming language.
|
|
powershell
|
Specifies the Windows Powershell programming language.
|
|
python
|
Specifies the Python programming language.
|
|
ruby
|
Specifies the Ruby programming language.
|
|
scala
|
Specifies the Scala programming language.
|
|
swift
|
Specifies the Swift programming language.
|
|
typescript
|
Specifies the TypeScript programming language.
|
|
visual-basic
|
Specifies the Visual Basic programming language.
|
|
x86-32
|
Specifies the x86 32-bit Assembly programming language.
|
|
x86-64
|
Specifies the x86 64-bit Assembly programming language.
|
10.10 Indicator Type
Vocabulary Name: indicator-type-ov
The indicator type vocabulary is currently used in the
following SDO(s):
● Indicator
Indicator type is an open vocabulary used to categorize
Indicators. It is intended to be high-level to promote consistent practices.
Indicator types should not be used to capture information that can be better
captured via related Malware or Attack Pattern objects. It is better to link an
Indicator to a Malware object describing Poison Ivy rather than simply
providing a type or label of "poison-ivy".
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
anomalous-activity, anonymization, benign, compromised,
malicious-activity,
attribution,
unknown
|
|
Vocabulary Value
|
Description
|
|
anomalous-activity
|
Unexpected,
or unusual activity that may not necessarily be malicious or indicate compromise.
This type of activity may include reconnaissance-like behavior such as port
scans or version identification, network behavior anomalies, and asset and/or
user behavioral anomalies.
|
|
anonymization
|
Suspected
anonymization tools or infrastructure (proxy, TOR, VPN, etc.).
|
|
benign
|
Activity that
is not suspicious or malicious in and of itself, but when combined with other
activity may indicate suspicious or malicious behavior.
|
|
compromised
|
Assets that
are suspected to be compromised.
|
|
malicious-activity
|
Patterns of
suspected malicious objects and/or activity.
|
|
attribution
|
Patterns of
behavior that indicate attribution to a particular Threat Actor or Campaign.
|
|
unknown
|
There is not enough information available to determine the
type of indicator.
|
10.11 Industry
Sector
Vocabulary Name: industry-sector-ov
The industry sector vocabulary is currently used in the
following SDO(s):
● Identity
Industry sector is an open vocabulary that describes
industrial and commercial sectors. It is intended to be holistic; it has been
derived from several other lists and is not limited to "critical
infrastructure" sectors.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
agriculture, aerospace, automotive, communications,
construction,
defence,
education,
energy, entertainment, financial-services, government-national, government-regional,
government-local,
government-public-services,
healthcare,
hospitality-leisure,
infrastructure,
insurance,
manufacturing,
mining,
non-profit,
pharmaceuticals,
retail,
technology,
telecommunications,
transportation,
utilities
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
agriculture
|
|
|
aerospace
|
|
|
automotive
|
|
|
communications
|
|
|
construction
|
|
|
defence
|
|
|
education
|
|
|
energy
|
|
|
entertainment
|
|
|
financial-services
|
|
|
government-national
|
|
|
government-regional
|
|
|
government-local
|
|
|
government-public-services
|
emergency services, sanitation
|
|
healthcare
|
|
|
hospitality-leisure
|
|
|
infrastructure
|
|
|
insurance
|
|
|
manufacturing
|
|
|
mining
|
|
|
non-profit
|
|
|
pharmaceuticals
|
|
|
retail
|
|
|
technology
|
|
|
telecommunications
|
|
|
transportation
|
|
|
utilities
|
|
10.12 Infrastructure Type Vocabulary
Type Name: infrastructure-type-ov
The infrastructure type vocabulary is currently used in the
following SDO(s):
● Infrastructure
A non-exhaustive enumeration of infrastructure types.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
amplification, anonymization, botnet, command-and-control,
exfiltration,
hosting-malware,
hosting-target-lists,
phishing,
reconnaissance,
staging,
undefined
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
amplification
|
Specifies infrastructure used for conducting amplification
attacks.
|
|
anonymization
|
Specific infrastructure used for anonymization, such as a
proxy.
|
|
botnet
|
Specifies the membership/makeup of a botnet, in terms of
the network addresses of the hosts that comprise the botnet.
|
|
command-and-control
|
Specifies infrastructure used for command and control
(C2). This is typically a domain name or IP address.
|
|
exfiltration
|
Specifies infrastructure used as an endpoint for data
exfiltration.
|
|
hosting-malware
|
Specifies infrastructure used for hosting malware.
|
|
hosting-target-lists
|
Specifies infrastructure used for hosting a list of
targets for DDOS attacks, phishing, and other malicious activities. This is
typically a domain name or IP address.
|
|
phishing
|
Specifies infrastructure used for conducting phishing
attacks.
|
|
reconnaissance
|
Specifies infrastructure used for conducting
reconnaissance activities.
|
|
staging
|
Specifies infrastructure used for staging.
|
|
undefined
|
Specifies an infrastructure of some undefined type.
|
10.13 Malware AV Result
Vocabulary Name: malware-av-result-ov
The processor architecture vocabulary is currently used in
the following SDO(s):
● Malware
Analysis
This is a non-exhaustive, open vocabulary that captures
common types of generic malware anti-virus (AV) tool results.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
malicious, suspicious, benign, unknown
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
malicious
|
The AV tool reported the malware binary as malicious.
|
|
suspicious
|
The AV tool reported the malware binary as suspicious but
not definitively malicious.
|
|
benign
|
The AV tool reported the malware binary as benign.
|
|
unknown
|
The AV tool was unable to determine whether the malware
binary is malicious.
|
10.14 Malware Capabilities
Vocabulary Name: malware-capabilities-ov
The malware capabilities vocabulary is currently used in the
following SDO(s):
● Malware
This is an open vocabulary that covers common capabilities
that may be exhibited by a malware instance or family.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
accesses-remote-machines, anti-debugging, anti-disassembly,
anti-emulation,
anti-memory-forensics,
anti-sandbox,
anti-vm,
captures-input-peripherals,
captures-output-peripherals,
captures-system-state-data,
cleans-traces-of-infection,
commits-fraud,
communicates-with-c2,
compromises-data-availability,
compromises-data-integrity,
compromises-system-availability,
controls-local-machine,
degrades-security-software,
degrades-system-updates,
determines-c2-server,
emails-spam,
escalates-privileges,
evades-av,
exfiltrates-data,
fingerprints-host,
hides-artifacts,
hides-executing-code,
infects-files,
infects-remote-machines,
installs-other-components,
persists-after-system-reboot,
prevents-artifact-access,
prevents-artifact-deletion,
probes-network-environment,
self-modifies,
steals-authentication-credentials,
violates-system-operational-integrity
|
|
Vocabulary Value
|
Description
|
|
accesses-remote-machines
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
access one or more remote machines.
|
|
anti-debugging
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
prevent itself from being debugged and/or from being run in a debugger or is
able to make debugging more difficult.
|
|
anti-disassembly
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
prevent itself from being disassembled or make disassembly more difficult.
|
|
anti-emulation
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
prevent its execution inside of an emulator or is able to make emulation more
difficult.
|
|
anti-memory-forensics
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
prevent or make memory forensics more difficult.
|
|
anti-sandbox
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
prevent sandbox-based behavioral analysis or make it more difficult.
|
|
anti-vm
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
prevent virtual machine (VM) based behavioral analysis or make it more
difficult.
|
|
captures-input-peripherals
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
capture data from a system's input peripheral devices, such as a keyboard or
mouse. This includes things like keylogging.
|
|
captures-output-peripherals
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family captures
data sent to a system's output peripherals, such as a display. Examples
include things like screen scraping.
|
|
captures-system-state-data
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
capture information about a system's state (e.g., data currently in its RAM).
|
|
cleans-traces-of-infection
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
clean traces of its infection (e.g., file system artifacts) from a system.
|
|
commits-fraud
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family commits
fraud, such as click fraud (for example).
|
|
communicates-with-c2
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
communicate (i.e., send or receive data) with a command and control (C2)
server.
|
|
compromises-data-availability
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
compromise the availability of data on the local system on which it is
executing and/or one or more remote systems. For example, encrypting data on
disk, as done by ransomware.
|
|
compromises-data-integrity
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
compromise the integrity of some data that resides on (e.g., in the case of
files) or is received/transmitted (e.g., in the case of network traffic) by
the system on which it is executing.
|
|
compromises-system-availability
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
consume system resources for its malicious purposes, such as password
cracking or participating in a DDoS botnet, thereby compromising the
availability of the local system and/or one or more remote systems.
|
|
controls-local-machine
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
control the machine on which it is executing (e.g., RATs).
|
|
degrades-security-software
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
bypass or disable security programs or operating system security features on
a system (including mobile devices), either by stopping them from executing
or by making changes to their code or configuration parameters. For example,
malware that blocks the local machine from accessing the websites of security
vendors.
|
|
degrades-system-updates
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
disable the downloading and installation of system updates and patches.
|
|
determines-c2-server
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
identify one or more command and control (C2) servers with which to
communicate (e.g., DGA).
|
|
emails-spam
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
send spam email messages.
|
|
escalates-privileges
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
escalate the privileges under which it is executing.
|
|
evades-av
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
evade detection by antivirus tools.
|
|
exfiltrates-data
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
gather, prepare, (possibly obfuscate) data and transmit it to exfiltration
points.
|
|
fingerprints-host
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
fingerprint or probe the configuration of the host system on which it is
executing for the purpose of altering its behavior based on this environment.
|
|
hides-artifacts
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
hide its artifacts, such as files and open ports.
|
|
hides-executing-code
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
hide its code by compromising the bootloader, kernel modules, hypervisor,
etc.
|
|
infects-files
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
infect one or more files on the system on which it executes. For example,
malware which injects a malicious payload into all PDFs on a host as a means
of propagation.
|
|
infects-remote-machines
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
self-propagate to a remote machine or infect a remote machine with malware
that is different than itself.
|
|
installs-other-components
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
install additional components. This encompasses the dropping/downloading of
other malicious components such as libraries, other malware, and tools.
|
|
persists-after-system-reboot
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
continue executing after the reboot of the system on which it is resident.
|
|
prevents-artifact-access
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
prevent its artifacts (e.g., files, registry keys, etc.) from being accessed.
|
|
prevents-artifact-deletion
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
prevent its artifacts (e.g., files, registry keys, etc.) from being deleted.
|
|
probes-network-environment
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
probe the properties of its network environment, e.g. to determine whether it
funnels traffic through a proxy.
|
|
self-modifies
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
modify itself.
|
|
steals-authentication-credentials
|
Indicates that the malware instance is able to steal
authentication credentials.
|
|
violates-system-operational-integrity
|
Indicates that the malware instance or family is able to
compromise the operational integrity of the system on which it is executing
and/or one or more remote systems, e.g., by causing them to operate beyond
their set of specified operational parameters. For example, malware that
causes the CPU fan on the machine that it is executing to spin at a higher than
normal speed.
|
10.15 Malware Type
Vocabulary Name: malware-type-ov
The malware type vocabulary is currently used in the
following SDO(s):
● Malware
Malware type is an open vocabulary that represents different
types and functions of malware. Malware types are not mutually exclusive; for
example, a malware instance can be both spyware and a screen capture tool.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
adware, backdoor, bot, bootkit,
ddos,
downloader,
dropper,
exploit-kit,
keylogger,
ransomware,
remote-access-trojan,
resource-exploitation,
rogue-security-software,
rootkit,
screen-capture,
spyware,
trojan,
unknown,
virus,
webshell,
wiper,
worm
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
adware
|
Any software that is funded by advertising. Adware may
also gather sensitive user information from a system.
|
|
backdoor
|
A malicious program that allows an attacker to perform
actions on a remote system, such as transferring files, acquiring passwords,
or executing arbitrary commands [NIST800-83].
|
|
bot
|
A program that resides on an infected system,
communicating with and forming part of a botnet. The bot may be implanted by
a worm or Trojan, which opens a backdoor. The bot then monitors the backdoor
for further instructions.
|
|
bootkit
|
A malicious program which targets the Master Boot Record
of the target computer.
|
|
ddos
|
A program that is used to perform a distributed denial of
service attack.
|
|
downloader
|
A small trojan file programmed to download and execute other files,
usually more complex malware.
|
|
dropper
|
A type of trojan that deposits an enclosed payload
(generally, other malware) onto the target computer.
|
|
exploit-kit
|
A software toolkit to target common vulnerabilities.
|
|
keylogger
|
A type of malware that surreptitiously monitors keystrokes
and either records them for later retrieval or sends them back to a central
collection point.
|
|
ransomware
|
A type of malware that encrypts files on a victim's
system, demanding payment of ransom in return for the access codes required
to unlock files.
|
|
remote-access-trojan
|
A remote access trojan program (or RAT), is a trojan horse
capable of controlling a machine through commands issued by a remote
attacker.
|
|
resource-exploitation
|
A type of malware that steals a system's resources (e.g.,
CPU cycles), such as a malicious bitcoin miner.
|
|
rogue-security-software
|
A fake security product that demands money to clean phony
infections.
|
|
rootkit
|
A type of malware that hides its files or processes from
normal methods of monitoring in order to conceal its presence and activities.
Rootkits can operate at a number of levels, from the application level —
simply replacing or adjusting the settings of system software to prevent the
display of certain information — through hooking certain functions or
inserting modules or drivers into the operating system kernel, to the deeper
level of firmware or virtualization rootkits, which are activated before the
operating system and thus even harder to detect while the system is running.
|
|
screen-capture
|
A type of malware used to capture images from the target
systems screen, used for exfiltration and command and control.
|
|
spyware
|
Software that gathers information on a user's system
without their knowledge and sends it to another party. Spyware is generally
used to track activities for the purpose of delivering advertising.
|
|
trojan
|
Any malicious computer program which is used to hack into
a computer by misleading users of its true intent.
|
|
unknown
|
There is not enough information available to determine the
type of malware.
|
|
virus
|
A malicious computer program that replicates by
reproducing itself or infecting other programs by modifying them.
|
|
webshell
|
A malicious script used by an attacker with the intent to escalate
and maintain persistent access on an already compromised web application.
|
|
wiper
|
A piece of malware whose primary aim is to delete files or
entire disks on a machine.
|
|
worm
|
A self-replicating, self-contained program that usually
executes itself without user intervention.
|
10.16 Network Socket Address Family Enumeration
Vocabulary Name: network-socket-address-family-enum
The network socket address family vocabulary is currently
used in the following SCO(s):
● Network
Traffic (Network Socket extension)
An enumeration of network socket address family types.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
AF_UNSPEC, AF_INET, AF_IPX, AF_APPLETALK,
AF_NETBIOS,
AF_INET6,
AF_IRDA,
AF_BTH
|
|
Vocabulary Value
|
Description
|
|
AF_UNSPEC
|
Specifies an unspecified address family.
|
|
AF_INET
|
Specifies the IPv4 address family.
|
|
AF_IPX
|
Specifies the IPX (Novell
Internet Protocol) address family.
|
|
AF_APPLETALK
|
Specifies the APPLETALK DDP
address family.
|
|
AF_NETBIOS
|
Specifies the NETBIOS address
family.
|
|
AF_INET6
|
Specifies the IPv6 address
family.
|
|
AF_IRDA
|
Specifies IRDA sockets.
|
|
AF_BTH
|
Specifies BTH sockets.
|
10.17 Network Socket Type Enumeration
Vocabulary Name: network-socket-type-enum
The network socket type vocabulary is currently used in the
following SCO(s):
● Network
Traffic (Network Socket extension)
An enumeration of network socket types.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
SOCK_STREAM, AF_ISOCK_DGRAMNET, SOCK_RAW,
SOCK_RDM,
SOCK_SEQPACKET
|
|
Vocabulary Value
|
Description
|
|
SOCK_STREAM
|
Specifies a pipe-like
socket which operates over a connection with a particular remote socket and
transmits data reliably as a stream of bytes.
|
|
SOCK_DGRAM
|
Specifies a socket in which
individually-addressed packets are sent (datagram).
|
|
SOCK_RAW
|
Specifies raw sockets which
allow new IP protocols to be implemented in user space. A raw socket receives
or sends the raw datagram not including link level headers.
|
|
SOCK_RDM
|
Specifies a socket
indicating a reliably-delivered message.
|
|
SOCK_SEQPACKET
|
Specifies a datagram
congestion control protocol socket.
|
10.18 Opinion Enumeration
Vocabulary Name: opinion-enum
The agreement enumeration is currently used in the following
SDOs:
● Opinion
This enumeration captures a degree of agreement with the
information in a STIX Object. It is an ordered enumeration, with the earlier
terms representing disagreement, the middle term neutral, and the later terms
representing agreement.
|
Enumeration
Summary
|
|
strongly-disagree, disagree, neutral, agree, strongly-agree
|
|
Enumeration
Value
|
Description
|
|
strongly-disagree
|
The creator strongly disagrees with the information and
believes it is inaccurate or incorrect.
This MAY be considered equivalent to a 1 in a
numeric scale.
|
|
disagree
|
The creator disagrees with the information and believes it
is inaccurate or incorrect.
This MAY be considered equivalent to a 2 in a
numeric scale.
|
|
neutral
|
The creator is neutral about the accuracy or correctness
of the information.
This MAY be considered equivalent to a 3 in a
numeric scale.
|
|
agree
|
The creator agrees with the information and believes that
it is accurate and correct.
This MAY be considered equivalent to a 4 in a
numeric scale.
|
|
strongly-agree
|
The creator strongly agrees with the information and
believes that it is accurate and correct.
This MAY be considered equivalent to a 5 in a
numeric scale.
|
10.19 Processor Architecture
Vocabulary Name: processor-architecture-ov
The processor architecture vocabulary is currently used in
the following SDO(s):
● Malware
This is a non-exhaustive, open vocabulary that covers common
processor architectures and is intended to characterize the architectures that
a malware instance or family may be able to execute on.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
alpha, arm, ia-64, mips, powerpc,
sparc,
x86,
x86-64
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
alpha
|
Specifies the Alpha architecture.
|
|
arm
|
Specifies the ARM architecture.
|
|
ia-64
|
Specifies the 64-bit IA (Itanium) architecture.
|
|
mips
|
Specifies the MIPS architecture.
|
|
powerpc
|
Specifies the PowerPC architecture.
|
|
sparc
|
Specifies the SPARC architecture.
|
|
x86
|
Specifies the 32-bit x86 architecture.
|
|
x86-64
|
Specifies the 64-bit x86 architecture.
|
10.20 Region Vocabulary
Vocabulary Name: region-ov
The region vocabulary is currently used in the following
SDO(s):
● Location
A list of world regions based on the United Nations
geoscheme [UNSD M49].
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
africa, eastern-africa, middle-africa,
northern-africa,
southern-africa,
western-africa,
americas,
latin-america-caribbean,
south-america,
caribbean,
central-america,
northern-america,
asia,
central-asia,
eastern-asia,
southern-asia,
western-asia,
europe,
eastern-europe,
northern-europe,
southern-europe,
western-europe,
oceania,
australia-new-zealand,
melanesia,
micronesia,
polynesia,
antarctica
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
africa
|
|
|
eastern-africa
|
|
|
middle-africa
|
|
|
northern-africa
|
|
|
southern-africa
|
|
|
western-africa
|
|
|
americas
|
|
|
latin-america-caribbean
|
|
|
south-america
|
|
|
caribbean
|
|
|
central-america
|
|
|
northern-america
|
|
|
asia
|
|
|
central-asia
|
|
|
eastern-asia
|
|
|
southern-asia
|
|
|
south-eastern-asia
|
|
|
western-asia
|
|
|
europe
|
|
|
eastern-europe
|
|
|
northern-europe
|
|
|
southern-europe
|
|
|
western-europe
|
|
|
oceania
|
|
|
antarctica
|
|
|
australia-new-zealand
|
|
|
melanesia
|
|
|
micronesia
|
|
|
polynesia
|
|
10.21 Report Type
Vocabulary Name: report-type-ov
The report type vocabulary is currently used in the following
SDO(s):
● Report
Report type is an open vocabulary to describe the primary
purpose or subject of a report. For example, a report that contains malware and
indicators for that malware should have a report type of malware to
capture that the malware is the primary purpose. Report types are not mutually
exclusive: a Report can be both a malware report and a tool report. Just
because a report contains objects of a type does not mean that the report
should include that type. If the objects are there to simply provide evidence
or context for other objects, it is not necessary to include them in the type.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
attack-pattern, campaign, identity, indicator,
intrusion-set,
malware,
observed-data,
threat-actor,
threat-report,
tool,
vulnerability
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
attack-pattern
|
Report subject is a
characterization of one or more attack patterns and related information.
|
|
campaign
|
Report subject is a
characterization of one or more campaigns and related information.
|
|
identity
|
Report subject is a
characterization of one or more identities and related information.
|
|
indicator
|
Report subject is a
characterization of one or more indicators and related information.
|
|
intrusion-set
|
Report subject is a characterization
of one or more intrusion sets and related information.
|
|
malware
|
Report subject is a
characterization of one or more malware instances and related information.
|
|
observed-data
|
Report subject is a
characterization of observed data and related information.
|
|
threat-actor
|
Report subject is a
characterization of one or more threat actors and related information.
|
|
threat-report
|
Report subject is a broad
characterization of a threat across multiple facets.
|
|
tool
|
Report subject is a
characterization of one or more tools and related information.
|
|
vulnerability
|
Report subject is a
characterization of one or more vulnerabilities and related information.
|
10.22 Threat Actor Type
Vocabulary Name: threat-actor-type-ov
The threat actor type vocabulary is currently used in the
following SDO(s):
● Threat
Actor
Threat actor type is an open vocabulary used to describe
what type of threat actor the individual or group is. For example, some threat
actors are competitors who try to steal information, while others are activists
who act in support of a social or political cause. Actor types are not mutually
exclusive: a threat actor can be both a disgruntled insider and a spy. [Casey 2007])
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
activist, competitor, crime-syndicate, criminal,
hacker,
insider-accidental,
insider-disgruntled,
nation-state,
sensationalist,
spy,
terrorist,
unknown
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
activist
|
Highly motivated, potentially destructive supporter of a
social or political cause (e.g., trade, labor, environment, etc.) that
attempts to disrupt an organization's business model or damage their image.
This category includes actors sometimes referred to as
anarchists, cyber vandals, extremists, and hacktivists.
|
|
competitor
|
An organization that competes in the same economic
marketplace.
The goal of a competitor is to gain an advantage in
business with respect to the rival organization it targets. It usually does
this by copying intellectual property, trade secrets, acquisition strategies,
or other technical or business data from a rival organization with the
intention of using the data to bolster its own assets and market position.
|
|
crime-syndicate
|
An enterprise organized to conduct significant,
large-scale criminal activity for profit.
Crime syndicates, also known as organized crime, are
generally large, well-resourced groups that operate to create profit from all
types of crime.
|
|
criminal
|
Individual who commits computer crimes, often for personal
financial gain and often involves the theft of something valuable.
Intellectual property theft, extortion via ransomware, and
physical destruction are common examples. A criminal as defined here refers
to those acting individually or in very small or informal groups. For
sophisticated organized criminal activity, see the crime syndicate
descriptor.
|
|
hacker
|
An individual that tends to break into networks for the
thrill or the challenge of doing so.
Hackers may use advanced skills or simple attack scripts
they have downloaded.
|
|
insider-accidental
|
A non-hostile insider who unintentionally exposes the
organization to harm.
“Insider” in this context includes any person extended
internal trust, such as regular employees, contractors, consultants, and
temporary workers.
|
|
insider-disgruntled
|
Current or former insiders who seek revengeful and harmful
retaliation for perceived wrongs.
“Insider” in this context includes any person extended
internal trust, such as regular employees, contractors, consultants, and
temporary workers.
Disgruntled threat actors may have extensive knowledge
that can be leveraged when conducting attacks and can take any number of
actions including sabotage, violence, theft, fraud, espionage, or
embarrassing individuals or the organization.
|
|
nation-state
|
Entities who work for the government or military of a
nation state or who work at their direction.
These actors typically have access to significant support,
resources, training, and tools and are capable of designing and executing
very sophisticated and effective Intrusion Sets and Campaigns.
|
|
sensationalist
|
Seeks to cause embarrassment and brand damage by exposing
sensitive information in a manner designed to cause a public relations
crisis.
A sensationalist may be an individual or small group of
people motivated primarily by a need for notoriety. Unlike the activist, the
sensationalist generally has no political goal, and is not using bad PR to
influence the target to change its behavior or business practices.
|
|
spy
|
Secretly collects sensitive information for use,
dissemination, or sale.
Traditional spies (governmental and industrial) are part
of a well-resourced intelligence organization and are capable of very
sophisticated clandestine operations. However, insiders such as employees or
consultants acting as spies can be just as effective and damaging, even when
their activities are largely opportunistic and not part of an overall
campaign.
|
|
terrorist
|
Uses extreme violence to advance a social or political
agenda as well as monetary crimes to support its activities.
In this context a terrorist refers to individuals who
target noncombatants with violence to send a message of fear far beyond the
actual events. They may act independently or as part of a terrorist
organization.
Terrorist organizations must typically raise much of their
operating budget through criminal activity, which often occurs online.
Terrorists are also often adept at using and covertly manipulating social
media for both recruitment and impact.
|
|
unknown
|
There is not enough information available to determine the
type of threat actor.
|
10.23
Threat Actor Role
Vocabulary Name: threat-actor-role-ov
The threat actor role vocabulary is currently used in the
following SDO(s):
● Threat
Actor
Threat actor role is an open vocabulary that is used to
describe the different roles that a threat actor can play. For example, some
threat actors author malware or operate botnets while other actors actually
carry out attacks directly.
Threat actor roles are not mutually exclusive. For example,
an actor can be both a financial backer for attacks and also direct attacks.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
agent, director, independent, infrastructure-architect,
infrastructure-operator,
malware-author,
sponsor
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
agent
|
Threat actor executes attacks either on behalf of
themselves or at the direction of someone else.
|
|
director
|
The threat actor who directs the activities, goals, and
objectives of the malicious activities.
|
|
independent
|
A threat actor acting by themselves.
|
|
infrastructure-architect
|
Someone who designs the battle space.
|
|
infrastructure-operator
|
The threat actor who provides and supports the attack
infrastructure that is used to deliver the attack (botnet providers, cloud
services, etc.).
|
|
malware-author
|
The threat actor who authors malware or other malicious
tools.
|
|
sponsor
|
The threat actor who funds the malicious activities.
|
10.24 Threat Actor Sophistication
Vocabulary Name: threat-actor-sophistication-ov
Threat actor sophistication vocabulary is currently used in
the following SDO(s):
● Threat
Actor
Threat actor sophistication vocabulary captures the skill level
of a threat actor. It ranges from "none", which describes a complete
novice, to "strategic", which describes an attacker who is able to
influence supply chains to introduce vulnerabilities. This vocabulary is
separate from resource level because an innovative, highly-skilled threat actor
may have access to very few resources while a minimal-level actor might have
the resources of an organized crime ring.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
none, minimal, intermediate, advanced,
expert,
innovator,
strategic
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
none
|
Can carry out random acts of disruption or destruction by
running tools they do not understand. Actors in this category have average
computer skills.
Example Roles: Average User
These actors:
● can
not launch targeted attacks
|
|
minimal
|
Can minimally use existing and frequently well known and
easy-to-find techniques and programs or scripts to search for and exploit
weaknesses in other computers. Commonly referred to as a script-kiddie.
These actors rely on others to develop the malicious
tools, delivery mechanisms, and execution strategy and often do not fully
understand the tool they are using or how they work. They also lack the
ability to conduct their own reconnaissance and targeting research.
Example Roles: Script-Kiddie
These actors:
● attack
known weaknesses;
● use
well known scripts and tools; and
● have
minimal knowledge of the tools.
|
|
intermediate
|
Can proficiently use existing attack frameworks and
toolkits to search for and exploit vulnerabilities in computers or systems.
Actors in this category have computer skills equivalent to an IT professional
and typically have a working knowledge of networks, operating systems, and
possibly even defensive techniques and will typically exhibit some
operational security.
These actors rely others to develop the malicious tools
and delivery mechanisms but are able to plan their own execution strategy.
They are proficient in the tools they are using and how they work and can even
make minimal modifications as needed.
Example Roles: Toolkit User
These actors:
● attack
known vulnerabilities;
● use
attack frameworks and toolkits; and
● have
proficient knowledge of the tools.
|
|
advanced
|
Can develop their own tools or scripts from publicly known
vulnerabilities to target systems and users. Actors in this category are very
adept at IT systems and have a background in software development along with
a solid understanding of defensive techniques and operational security.
These actors rely on others to find and identify
weaknesses and vulnerabilities in systems, but are able to create their own
tools, delivery mechanisms, and execution strategies.
Example Roles: Toolkit Developer
These actors:
● attack
known vulnerabilities;
● can
create their own tools; and
● have
proficient knowledge of the tools.
|
|
expert
|
Can focus on the discovery and use of unknown malicious
code, are is adept at installing user and kernel mode rootkits, frequently
use data mining tools, target corporate executives and key users (government
and industry) for the purpose of stealing personal and corporate data. Actors
in this category are very adept at IT systems and software development and
are experts with security systems, defensive techniques, attack methods, and
operational security.
Example Roles: Vulnerability Researcher, Reverse Engineer,
Threat Researcher, Malware Creator
These actors:
● attack
unknown and known vulnerabilities;
● can
create their own tools from scratch; and
● have
proficient knowledge of the tools.
|
|
innovator
|
Typically, criminal or state actors who are organized,
highly technical, proficient, well-funded professionals working in teams to
discover new vulnerabilities and develop exploits.
Demonstrates sophisticated capability. An innovator has
the ability to create and script unique programs and codes targeting
virtually any form of technology. At this level, this actor has a deep
knowledge of networks, operating systems, programming languages, firmware,
and infrastructure topologies and will demonstrate operational security when
conducting his activities. Innovators are largely responsible for the
discovery of 0-day vulnerabilities and the development of new attack
techniques.
Example Roles: Toolkit Innovator, 0-Day Exploit Author
These actors:
● attack
unknown and known vulnerabilities;
● create
attacks against 0-Day exploits from scratch; and
● create
new and innovative attacks and toolkits.
|
|
strategic
|
State actors who create vulnerabilities through an active
program to “influence” commercial products and services during design,
development or manufacturing, or with the ability to impact products while in
the supply chain to enable exploitation of networks and systems of interest.
These actors:
● can
create or use entire supply chains to launch an attack;
● can
create and design attacks for any systems, software package, or device; and
● are
responsible for APT-level attacks.
|
10.25 Tool Type
Vocabulary Name: tool-type-ov
The tool type vocabulary is currently used in the following
SDO(s):
● Tool
Tool types describe the categories of tools that can be used
to perform attacks.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
denial-of-service, exploitation, information-gathering,
network-capture,
credential-exploitation,
remote-access,
vulnerability-scanning,
unknown
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
denial-of-service
|
Tools used to perform denial of service attacks or DDoS
attacks, such as Low Orbit Ion Cannon (LOIC) and DHCPig.
|
|
exploitation
|
Tools used to exploit software and systems, such as sqlmap
and Metasploit.
|
|
information-gathering
|
Tools used to enumerate system and network information,
e.g., NMAP.
|
|
network-capture
|
Tools used to capture network traffic, such as Wireshark
and Kismet.
|
|
credential-exploitation
|
Tools used to crack password databases or otherwise
exploit/discover credentials, either locally or remotely, such as John the
Ripper and NCrack.
|
|
remote-access
|
Tools used to access machines remotely, such as VNC and
Remote Desktop.
|
|
vulnerability-scanning
|
Tools used to scan systems and networks for
vulnerabilities, e.g., Nessus.
|
|
unknown
|
There is not enough information available to determine the
type of tool.
|
10.26 Windows™ Integrity Level Enumeration
Vocabulary Name: windows-integrity-level-enum
The Windows integrity level enumeration is currently used in
the following STIX Cyber-observable Object(s):
● Process
(Windows Process extension)
Windows integrity levels are a security feature and
represent the trustworthiness of an object.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
low, medium, high, system
|
|
Vocabulary
Value
|
Description
|
|
low
|
A low level of integrity.
|
|
medium
|
A medium level of integrity.
|
|
high
|
A high level of integrity.
|
|
system
|
A system level of integrity.
|
10.27 Windows™ PE Binary Vocabulary
Vocabulary Name: windows-pebinary-type-ov
The Windows PE binary vocabulary is currently used in the
following SCO(s):
● File
(Windows PE Binary extension)
An open vocabulary of Windows PE binary types.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
dll, exe, sys
|
|
Value
|
Description
|
|
dll
|
Specifies that the PE
binary is a dynamically linked library (DLL).
|
|
exe
|
Specifies that the PE
binary is an executable image (i.e., not an OBJ or DLL).
|
|
sys
|
Specifies that the PE
binary is a device driver (SYS).
|
10.28 Windows™ Registry Datatype Enumeration
Vocabulary Name: windows-registry-datatype-enum
The Windows registry datatype vocabulary is currently used
in the following SCO(s):
● Windows
Registry Key
An enumeration of Windows registry data types.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
REG_NONE, REG_SZ, REG_EXPAND_SZ, REG_BINARY,
REG_DWORD,
REG_DWORD_BIG_ENDIAN,
REG_DWORD_LITTLE_ENDIAN,
REG_LINK,
REG_MULTI_SZ,
REG_RESOURCE_LIST,
REG_FULL_RESOURCE_DESCRIPTION,
REG_RESOURCE_REQUIREMENTS_LIST,
REG_QWORD,
REG_INVALID_TYPE
|
|
Vocabulary Value
|
Description
|
|
REG_NONE
|
No defined value type.
|
|
REG_SZ
|
A null-terminated string.
This will be either a Unicode or an ANSI string, depending on whether you use
the Unicode or ANSI functions.
|
|
REG_EXPAND_SZ
|
A null-terminated string
that contains unexpanded references to environment variables (for example,
"%PATH%"). It will be a Unicode or ANSI string depending on whether
you use the Unicode or ANSI functions.
|
|
REG_BINARY
|
Binary data in any form.
|
|
REG_DWORD
|
A 32-bit number.
|
|
REG_DWORD_BIG_ENDIAN
|
A 32-bit number in
big-endian format.
|
|
REG_DWORD_LITTLE_ENDIAN
|
A 32-bit number in
little-endian format.
|
|
REG_LINK
|
A null-terminated Unicode
string that contains the target path of a symbolic link.
|
|
REG_MULTI_SZ
|
A sequence of
null-terminated strings, terminated by an empty string (\0).
|
|
REG_RESOURCE_LIST
|
A series of nested lists
designed to store a resource list used by a hardware device driver or one of
the physical devices it controls. This data is detected and written into the
ResourceMap tree by the system and is displayed in Registry Editor in
hexadecimal format as a Binary Value.
|
|
REG_FULL_RESOURCE_DESCRIPTION
|
A series of nested lists
designed to store a resource list used by a physical hardware device. This
data is detected and written into the HardwareDescription tree by the system
and is displayed in Registry Editor in hexadecimal format as a Binary Value.
|
|
REG_RESOURCE_REQUIREMENTS_LIST
|
Device driver list of
hardware resource requirements in Resource Map tree.
|
|
REG_QWORD
|
A 64-bit number.
|
|
REG_INVALID_TYPE
|
Specifies an invalid key.
|
10.29 Windows™ Service Start Type Enumeration
Vocabulary Name: windows-service-start-type-enum
The Windows service start type vocabulary is currently used
in the following SCO(s):
● Process
(Windows Service extension)
An enumeration of Windows service start types.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
SERVICE_AUTO_START, SERVICE_BOOT_START, SERVICE_DEMAND_START,
SERVICE_DISABLED,
SERVICE_SYSTEM_ALERT
|
|
Vocabulary Value
|
Description
|
|
SERVICE_AUTO_START
|
A service started
automatically by the service control manager during system startup.
|
|
SERVICE_BOOT_START
|
A device driver started by
the system loader. This value is valid only for driver services.
|
|
SERVICE_DEMAND_START
|
A service started by the
service control manager when a process calls the StartService function.
|
|
SERVICE_DISABLED
|
A service that cannot be
started. Attempts to start the service result in the error code
ERROR_SERVICE_DISABLED.
|
|
SERVICE_SYSTEM_ALERT
|
A device driver started by
the IoInitSystem function. This value is valid only for driver services.
|
10.30 Windows™ Service Type Enumeration
Vocabulary Name: windows-service-type-enum
The Windows service type vocabulary is currently used in the
following SCO(s):
● Process
(Windows Service extension)
An enumeration of Windows service types.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
SERVICE_KERNEL_DRIVER, SERVICE_FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER,
SERVICE_WIN32_OWN_PROCESS,
SERVICE_WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS
|
|
Vocabulary Value
|
Description
|
|
SERVICE_KERNEL_DRIVER
|
The service is a device driver.
|
|
SERVICE_FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER
|
The service is a file system driver.
|
|
SERVICE_WIN32_OWN_PROCESS
|
The service runs in its own process.
|
|
SERVICE_WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS
|
The service shares a process with other services.
|
10.31 Windows™ Service Status Enumeration
Vocabulary Name: windows-service-status-enum
The Windows service status vocabulary is currently used in
the following SCO(s):
● Process
(Windows Service extension)
An enumeration of Windows service statuses.
|
Vocabulary
Summary
|
|
SERVICE_CONTINUE_PENDING, SERVICE_PAUSE_PENDING, SERVICE_PAUSED,
SERVICE_RUNNING,
SERVICE_START_PENDING,
SERVICE_STOP_PENDING,
SERVICE_STOPPED
|
|
Value
|
Description
|
|
SERVICE_CONTINUE_PENDING
|
The service continue is
pending.
|
|
SERVICE_PAUSE_PENDING
|
The service pause is
pending.
|
|
SERVICE_PAUSED
|
The service is paused.
|
|
SERVICE_RUNNING
|
The service is running.
|
|
SERVICE_START_PENDING
|
The service is starting.
|
|
SERVICE_STOP_PENDING
|
The service is stopping.
|
|
SERVICE_STOPPED
|
The service is not running.
|
There are three primary means to customize STIX:
Custom Properties, Custom Objects and Custom Extensions. Custom Properties
provide a mechanism and requirements for adding properties not defined by this
specification to existing STIX Objects. Custom Objects, on the other hand,
provides a mechanism and requirements to create custom STIX Objects (objects
not defined by this specification). Custom Extensions provide a mechanism and
requirements for the specification of extensions not defined by this
specification on SCOs.
A consumer that receives STIX content
containing Custom Properties, Objects or Extensions it does not understand MAY
refuse to process the content or MAY ignore those properties or objects
and continue processing the content.
Producers of STIX content that contain
Custom Properties, Objects or Extensions should recognize that consumers may
not understand them and may ignore them. Producers should define any Custom
Properties, Objects and Extensions they use, along with any rules for
processing them, and make these definitions and rules accessible to any
potential consumers. This specification does not specify a process for doing
this.
Custom Properties SHOULD be used for cases where it
is necessary to add one or more simple additional properties (i.e. key/value
pairs) on an SCO. On the other hand, Custom Extensions SHOULD be used
for cases where it is necessary to describe more complex additional properties
(i.e., those with potentially multiple levels of hierarchy). As an example, a
vendor-specific property that expresses some custom threat score for a File
object should be added directly to the SCO as a custom property, whereas a set
of properties that represent metadata around a new file system to the File
object should be done as a custom extension.
There will be cases where certain
information exchanges can be improved by adding properties to STIX Objects that
are neither specified nor reserved in this specification; these properties are
called Custom Properties. This section provides guidance and
requirements for how producers can use Custom Properties and how consumers
should interpret them in order to extend STIX in an interoperable manner.
●
A STIX Object MAY have any number of Custom Properties.
●
Custom Property names MUST be in ASCII and MUST only
contain the characters a–z (lowercase ASCII), 0–9, and underscore (_).
●
Custom Property names SHOULD start with “x_” followed by a source
unique identifier (such as a domain name with dots replaced by underscores), an
underscore and then the name. For example, x_example_com_customfield.
●
Custom Property names MUST have a minimum length of 3 ASCII
characters.
●
Custom Property names MUST be no longer than 250 ASCII characters
in length.
●
Custom Property names that do not start with “x_” may be used in a future
version of the specification for a different meaning. If compatibility with
future versions of this specification is required, the “x_” prefix MUST
be used.
●
Custom Properties SHOULD only be used when there are no existing
properties defined by the STIX specification that fulfils that need.
● For
Custom Properties that use the hex type, the property name MUST end with
'_hex'.
● For
Custom Properties that use the binary type, the property name MUST end with
'_bin'.
Examples
{
...,
"x_acme_org_risk_score":
10,
"x_acme_org_scoring": {
"impact":
"high",
"probability":
"low"
},
...
}
There will be cases where certain
information exchanges can be improved by adding objects that are not specified
nor reserved in this specification; these objects are called Custom Objects.
This section provides guidance and requirements for how producers can use
Custom Objects and how consumers should interpret them in order to extend STIX
in an interoperable manner.
●
Producers MAY include any number of Custom Objects in STIX
content.
●
Custom Objects MUST support the Common Properties as defined in
section 3.2.
○
Common property names MUST NOT be reused to represent the custom
properties in the object.
● A
Custom Object MUST have one or more properties.
● The
name of a property of a Custom Object MUST be in ASCII and MUST
only contain the characters a–z (lowercase ASCII), 0–9, and underscore (_). The
"x_" prefix as described in section 11.1.1 MAY be used.
● The
name of a property of a Custom Object MUST have a minimum length of 3
ASCII characters.
● The
name of a property of a Custom Object MUST be no longer than 250 ASCII
characters in length.
●
The type property in a
Custom Object MUST be in ASCII and MUST only contain the
characters a–z (lowercase ASCII), 0–9, and hyphen (-).
●
The type property MUST
NOT contain a hyphen (-) character immediately following another hyphen (-)
character.
●
Custom Object names MUST have a minimum length of 3 ASCII
characters.
●
Custom Object names MUST be no longer than 250 ASCII characters
in length.
●
The value of the type
property in a Custom Object SHOULD start with “x-” followed by a source
unique identifier (like a domain name with dots replaced by hyphens), a hyphen
and then the name. For example, x-example-com-customobject.
●
A Custom Object whose name is not prefixed with “x-” may be used in a
future version of the specification with a different meaning. Therefore, if
compatibility with future versions of this specification is required, the “x-”
prefix MUST be used.
●
The value of the id
property in a Custom Object MUST use the same format as the identifier
type, namely, [object-type]--[UUID].
●
Custom Objects SHOULD only be used when there is no existing STIX
Object defined by the STIX specification that fulfils that need.
Examples
{
"type":
"bundle",
"id":
"bundle--f37aa79d-f5f5-4af7-874b-734d32c08c10",
"objects": [
{
"type":
"x-example-com-customobject",
"id":
"x-example-com-customobject--4527e5de-8572-446a-a57a-706f15467461",
"created":
"2016-08-01T00:00:00.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-08-01T00:00:00.000Z",
"some_custom_stuff":
14,
"other_custom_stuff":
"hello"
}
]
}
In addition to the Predefined Cyber Observable Object
extensions, STIX supports user-defined custom extensions for STIX
Cyber-observable Objects (SCO). As with Predefined Object Extensions, custom
extension data MUST be conveyed under the extensions property. Note,
custom extensions can only be used with SCOs.
● A
SCO MAY have any number of Custom Extensions.
● Custom
Extension names MUST be in ASCII and are limited to characters a-z
(lowercase ASCII), 0-9, and hyphen (-).
● Custom
Extension names SHOULD start with “x-” followed by a source unique
identifier (like a domain name), a hyphen and then the name. For example: x-example-com-customextension.
● Custom
Extension names MUST have a minimum length of 3 ASCII characters.
● Custom
Extension names MUST be no longer than 250 ASCII characters in length.
● Custom
Extension names that are not prefixed with “x-” may be used in a future version
of the specification for a different meaning. If compatibility with future
versions of this specification is required, the “x-” prefix MUST be
used.
● Custom
Extensions SHOULD only be used when there is no existing extension
defined by the STIX 2.1 specification that fulfills that need.
● A
Custom Extension MUST have one or more properties.
Examples
Custom File object extension
{
"type": "file",
"hashes": {
"SHA-256":
"effb46bba03f6c8aea5c653f9cf984f170dcdd3bbbe2ff6843c3e5da0e698766"
},
"extensions": {
"x-example-com-foo": {
"foo_val": "foo",
"bar_val": "bar"
}
}
}
A "STIX 2.1 Producer" is any
software that can create STIX 2.1 content and conforms to the following
normative requirements:
- It MUST be able to create
content encoded as JSON.
- All properties marked required in
the property table for the STIX Object or type MUST be present in
the created content.
- All properties MUST conform
to the data type and normative requirements for that property.
- It MUST support at least one
STIX Object.
- It MUST support all features
listed in section 12,2,
Mandatory Features.
- It MAY support any features
listed in section 12.3,
Optional Features. Software supporting an optional feature MUST comply
with the normative requirements of that feature.
- It MUST support JSON as a serialization
format and MAY support serializations other than JSON.
A "STIX 2.1 Consumer" is any
software that can consume STIX 2.1 content and conforms to the following
normative requirements:
- It MUST support parsing all
required properties for the content that it consumes.
- It MUST support all features
listed in section 12.2,
Mandatory Features.
- It MAY support any features
listed in section 12.3,
Optional Features. Software supporting an optional feature MUST comply
with the normative requirements of that feature.
- It MUST support JSON as a serialization
format and MAY support serializations other than JSON.
A STIX 2.1 Producer or STIX 2.1 Consumer
MUST support versioning by following the normative requirements listed
in section 3.6.
A STIX 2.1 Producer or STIX 2.1 Consumer
MAY support "Object-Level Data Markings". Software claiming to
support "Object-Level Data Markings" MUST follow the normative
requirements listed in sections 7.2.1 and 7.2.2.
A STIX 2.1 Producer or STIX 2.1 Consumer
MAY support "Granular Data Markings". Software claiming to
support "Granular Data Markings" MUST follow the normative
requirements listed in sections 7.2.1 and 7.2.3.
A STIX 2.1 Producer or STIX 2.1 Consumer MAY support
"Custom Properties". Software claiming to support "Custom
Properties" MUST follow the normative requirements listed in
section 11.1.
A STIX 2.1 Producer or STIX Consumer MAY support
"Custom Objects" and/or "Custom Extensions". Software
claiming to support "Custom Objects" MUST follow the normative
requirements listed in section 11.2. Software claiming to support
"Custom Extensions" MUST follow the normative requirements
listed in section 11.3.
Implementers of the STIX Patterning language are not
required to support the full capabilities provided by the language. Rather,
implementers are strongly encouraged to support as much of STIX Patterning as
feasible, given the capabilities of their products, but only required to
support the minimum conformance level (defined below) necessary for their
particular use cases. For example, the vendor of a network intrusion detection
system (NIDS) that looks for malicious network traffic may only need to
implement the Comparison Operators and support basic Observation Expressions to
explicitly match against network traffic and IP addresses.
While the STIX Patterning language specification is tightly
coupled with the STIX Cyber-observable Object data models, it is understood
that in many (or even most) implementations STIX Patterns will be used as an
abstraction layer for transcoding into other proprietary query formats. STIX
Patterns may be evaluated directly against a corpus of STIX Observed Data
instances, but they may also, for example, be translated into some query syntax
for a packet inspection device. In this second case, the STIX Patterns are in
fact evaluated in the context of data passing on the wire, not in the form of
STIX Cyber Observables.
The STIX Patterning language's Observation Operators allow
for the creation of patterns that explicitly match across multiple
Observations; however, the language purposefully does not specify anything
about the source of the underlying data for each Observation. For example,
depending on a particular patterning implementation, the data for a pattern
that matches on network traffic could come from an endpoint or from a NIDS. It
is incumbent upon implementers to ascertain the appropriate data sources (where
applicable) for each Observation within a given pattern.
Software that creates STIX patterns is known as a
"Pattern Producer". Such software MUST support the creation of
patterns that conform to all normative statements and formatting rules in this
document. Pattern Producers MUST specify their conformance in terms of
the conformance levels defined in section 12.7.
Software that consumes STIX patterns is known as a
"Pattern Consumer". Such software MUST support the consumption of
patterns that conform to all normative statements and formatting rules in this
document. Pattern Consumers MUST specify their conformance in terms of
the conformance levels defined in section 12.7.
Software that conforms to the minimum required aspects of
the patterning specification, is known as a “Level 1 STIX Patterning Implementation”.
Such software MUST support the following features by
conforming to all normative statements and behaviors in the referenced
sections:
● Single
Observation Expressions (omitting Qualifiers), as described in section section 9.4
● All
Comparison Operators, as described in section 9.6
This level of conformance is intended primarily for software
that is deployed at endpoints or network boundaries and which is
architecturally unable to maintain state, as would be required in order to
support Qualifiers such as WITHIN.
Software that supports the minimum required aspects of the
patterning specification but can operate on multiple Observations, is known as
a “Level 2 STIX Patterning Implementation”.
Such software MUST support the following features by
conforming to all normative statements and behaviors in the referenced
sections:
● Single
and Compound Observation Expressions (omitting Qualifiers) as described in
section 9.4
● The AND
Observation Operator, as described in section 9.5
● The OR
Observation Operator, as described in section 9.5
●
All Comparison Operators, as described in section 9.6
This level of conformance is intended primarily for software
such as HIDS that can detect patterns across separate Observations but may not
support temporal-based patterning.
Software that is fully conformant with all of the
capabilities of the patterning specification is known as a "Level 3 STIX
Patterning Implementation".
Such software MUST support the following features by
conforming to all normative statements and behaviors in the referenced
sections:
● Section
9.1.
Definitions
● Section
9.3.
STIX Patterns
●
Section 9.4.
Pattern Expressions
● Section
9.5.
Observation Expressions
● Section
9.6.
Comparison Expressions
●
Section 9.7. Object Path Syntax
This level of conformance is intended primarily for software
such as SIEMs that support temporal-based patterning and can also aggregate and
detect patterns across multiple and disparate sources of Observations.
The use of these confidence scales is defined in section 3.2, confidence property. A
value of "Not Specified" in the table below means that the confidence
property is not present.
|
None/Low/Med/High
|
STIX
Confidence Value
|
Range of Values
|
|
Not Specified
|
Not Specified
|
N/A
|
|
None
|
0
|
0
|
|
Low
|
15
|
1-29
|
|
Med
|
50
|
30-69
|
|
High
|
85
|
70-100
|
|
0-10 Scale
|
STIX Confidence
Value
|
Range of Values
|
|
Not Specified
|
Not Specified
|
N/A
|
|
0
|
0
|
0-4
|
|
1
|
10
|
5-14
|
|
2
|
20
|
15-24
|
|
3
|
30
|
25-34
|
|
4
|
40
|
35-44
|
|
5
|
50
|
45-54
|
|
6
|
60
|
55-64
|
|
7
|
70
|
65-74
|
|
8
|
80
|
75-84
|
|
9
|
90
|
85-94
|
|
10
|
100
|
95-100
|
|
Admiralty
Credibility*
|
STIX
Confidence Value
|
Range of Values
|
|
6 - Truth cannot be judged
|
Not Specified
|
N/A
|
|
5 - Improbable
|
10
|
0-19
|
|
4 - Doubtful
|
30
|
20-39
|
|
3 - Possibly True
|
50
|
40-59
|
|
2 - Probably True
|
70
|
60-79
|
|
1 - Confirmed by other sources
|
90
|
80-100
|
*Admiralty Credibility [FM 2-22.3]
|
WEP*
|
STIX
Confidence Value
|
Range of Values
|
|
Not Specified
|
Not Specified
|
N/A
|
|
Impossible
|
0
|
0
|
|
Highly Unlikely/Almost Certainly Not
|
10
|
1-19
|
|
Unlikely/Probably Not
|
30
|
20-39
|
|
Even Chance
|
50
|
40-59
|
|
Likely/Probable
|
70
|
60-79
|
|
Highly likely/Almost Certain
|
90
|
80-99
|
|
Certain
|
100
|
100
|
* Words of Estimative Probability (WEP) [WEP]
|
DNI Scale*
|
STIX
Confidence Value
|
Range of Values
|
|
Not Specified
|
Not Specified
|
N/A
|
|
Almost No Chance / Remote
|
5
|
0-9
|
|
Very Unlikely / Highly Improbable
|
15
|
10-19
|
|
Unlikely / Improbable
|
30
|
20-39
|
|
Roughly Even Chance / Roughly Even Odds
|
50
|
40-59
|
|
Likely / Probable
|
70
|
60-79
|
|
Very Likely / Highly Probable
|
85
|
80-89
|
|
Almost Certain / Nearly
Certain
|
95
|
90-100
|
* DNI Scale [ICD 203]
This following relationship summary table is provided as a
convenience. If there is a discrepancy between this table and the relationships
defined with each of the SDOs, then the relationships defined with the SDOs MUST
be viewed as authoritative.
|
Source
|
Type
|
Target
|
|
attack-pattern
|
delivers
|
malware
|
|
attack-pattern
|
targets
|
identity, location, vulnerability
|
|
attack-pattern
|
uses
|
malware, tool
|
|
campaign
|
attributed-to
|
intrusion-set, threat-actor
|
|
campaign
|
compromises
|
infrastructure
|
|
campaign
|
originates-from
|
location
|
|
campaign
|
targets
|
identity, location, vulnerability
|
|
campaign
|
uses
|
attack-pattern, infrastructure, malware,
tool
|
|
course-of-action
|
investigates
|
indicator
|
|
course-of-action
|
mitigates
|
attack-pattern, indicator, malware, tool, vulnerability
|
|
identity
|
located-at
|
location
|
|
indicator
|
indicates
|
attack-pattern, campaign, infrastructure, intrusion-set,
malware,
threat-actor,
tool
|
|
indicator
|
based-on
|
observed-data
|
|
infrastructure
|
communicates-with
|
infrastructure, ipv4-addr, ipv6-addr, domain-name,
url
|
|
infrastructure
|
consists-of
|
infrastructure, observed-data, <All STIX
Cyber-observable Objects>
|
|
infrastructure
|
controls
|
infrastructure, malware
|
|
infrastructure
|
delivers
|
malware
|
|
infrastructure
|
has
|
vulnerability
|
|
infrastructure
|
hosts
|
tool, malware
|
|
infrastructure
|
located-at
|
location
|
|
infrastructure
|
uses
|
infrastructure
|
|
intrusion-set
|
attributed-to
|
threat-actor
|
|
intrusion-set
|
compromises
|
infrastructure
|
|
intrusion-set
|
hosts, owns
|
infrastructure
|
|
intrusion-set
|
originates-from
|
location
|
|
intrusion-set
|
targets
|
identity, location, vulnerability
|
|
intrusion-set
|
uses
|
attack-pattern, infrastructure, malware,
tool
|
|
malware
|
authored-by
|
threat-actor, intrusion-set
|
|
malware
|
beacons-to, exfiltrate-to
|
infrastructure
|
|
malware
|
communicates-with
|
ipv4-addr, ipv6-addr, domain-name, url
|
|
malware
|
controls
|
malware
|
|
malware
|
downloads, drops
|
malware, tool, file
|
|
malware
|
exploits
|
vulnerability
|
|
malware
|
originates-from
|
location
|
|
malware
|
targets
|
identity, infrastructure, location,
vulnerability
|
|
malware
|
uses
|
attack-pattern, infrastructure, malware,
tool
|
|
malware
|
variant-of
|
malware
|
|
malware-analysis
|
characterizes
|
malware
|
|
malware-analysis
|
av-analysis-of
|
malware
|
|
malware-analysis
|
static-analysis-of
|
malware
|
|
malware-analysis
|
dynamic-analysis-of
|
malware
|
|
threat-actor
|
attributed-to
|
identity
|
|
threat-actor
|
compromises
|
infrastructure
|
|
threat-actor
|
hosts, owns
|
infrastructure
|
|
threat-actor
|
impersonates
|
identity
|
|
threat-actor
|
located-at
|
location
|
|
threat-actor
|
targets
|
identity, location, vulnerability
|
|
threat-actor
|
located-at
|
location
|
|
threat-actor
|
uses
|
attack-pattern, infrastructure, malware,
tool
|
|
tool
|
delivers
|
malware
|
|
tool
|
drops
|
malware
|
|
tool
|
has
|
vulnerability
|
|
tool
|
targets
|
identity, infrastructure, location,
vulnerability
|
C.1
Infrastructure Additional Examples
C.1.1
Malware & Target List Hosting Domain
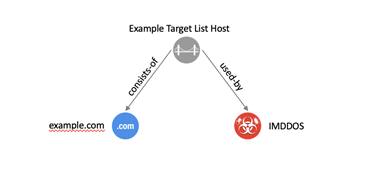
{
"type":"infrastructure",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":"infrastructure--d09c50cf-5bab-465e-9e2d-543912148b73",
"created":"2016-11-22T09:22:30.000Z",
"modified":"2016-11-22T09:22:30.000Z",
"name":"Example Target List
Host",
"infrastructure_types":["hosting-target-lists"]
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--37ac0c8d-f86d-4e56-aee9-914343959a4c",
"created":
"2016-11-23T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-11-23T08:17:27.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"uses",
"source_ref":
"malware--3a41e552-999b-4ad3-bedc-332b6d9ff80c",
"target_ref":
"infrastructure--d09c50cf-5bab-465e-9e2d-543912148b73"
}
{
"type": "malware",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"malware--3a41e552-999b-4ad3-bedc-332b6d9ff80c",
"created":
"2016-11-12T14:31:09.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-11-12T14:31:09.000Z",
"is_family": true,
"malware_types":[
"bot"
],
"name": "IMDDOS"
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--81f12913-1372-4c96-85ec-E9034ac98aba",
"created":
"2016-11-23T10:42:39.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-11-23T10:42:39.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"consists-of",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--d09c50cf-5bab-465e-9e2d-543912148b73",
"target_ref":
"domain-name--3c10e93f-798e-5a26-a0c1-08156efab7f5"
}
{
"id":
"domain-name--3c10e93f-798e-5a26-a0c1-08156efab7f5",
"type": "domain-name",
"value": "example.com"
}
C.1.2
Malware Botnet Infrastructure
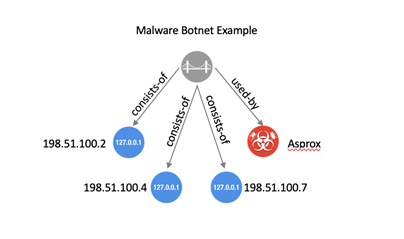
{
"type":"infrastructure",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":"infrastructure--78cc7b4b-c6ab-40d1-82eb-95a3059641da",
"created":"2017-03-15T04:22:30.000Z",
"modified":"2017-03-15T04:22:30.000Z",
"name":"Malware Botnet
Example",
"infrastructure_types":["botnet"]
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--edce6fe8-2ac7-49d6-bd57-3973a4f819b8",
"created":
"2017-03-16T22:17:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2017-03-16T22:17:27.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"uses",
"source_ref":
"malware--496cac0a-77ea-4da0-b913-88e553483c8d",
"target_ref":
"infrastructure--78cc7b4b-c6ab-40d1-82eb-95a3059641da"
}
{
"type": "malware",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"malware--496cac0a-77ea-4da0-b913-88e553483c8d",
"created":
"2017-03-10T07:31:09.000Z",
"modified":
"2017-03-10T07:31:09.000Z",
"is_family": true,
"malware_types":[
"bot"
],
"name": "Asprox"
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--7aebe2f0-28d6-48a2-9c3e-b0aaa60266ef",
"created":
"2017-03-16T10:19:23.000Z",
"modified":
"2017-03-16T10:19:23.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"consists-of",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--78cc7b4b-c6ab-40d1-82eb-95a3059641da",
"target_ref":
"ipv4-addr--4d22aae0-2bf9-5427-8819-e4f6abf20a53"
}
{
"id":
"ipv4-addr--4d22aae0-2bf9-5427-8819-e4f6abf20a53",
"type": "ipv4-addr",
"value": "198.51.100.2"
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--7f5b1a34-c64b-4ad4-8a0f-1ebeffaa2d4",
"created":
"2017-03-16T10:29:55.000Z",
"modified":
"2017-03-16T10:29:55.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"consists-of",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--78cc7b4b-c6ab-40d1-82eb-95a3059641da",
"target_ref":
"ipv4-addr--2ccfc50f-b0f0-5e06-ba9b-2aa51e23af61"
}
{
"id":
"ipv4-addr--2ccfc50f-b0f0-5e06-ba9b-2aa51e23af61",
"type": "ipv4-addr",
"value": "198.51.100.4"
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--2e48e1aa-469d-4473-a110-a128280db964",
"created":
"2017-03-16T10:33:14.000Z",
"modified":
"2017-03-16T10:33:14.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"consists-of",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--78cc7b4b-c6ab-40d1-82eb-95a3059641da",
"target_ref":
"ipv4-addr--3073f2be-0e15-5f42-b81d-495938860cd5"
}
{
"id":
"ipv4-addr--3073f2be-0e15-5f42-b81d-495938860cd5",
"type": "ipv4-addr",
"value": "198.51.100.7"
}
C.1.3
Related/Component Botnet Infrastructure
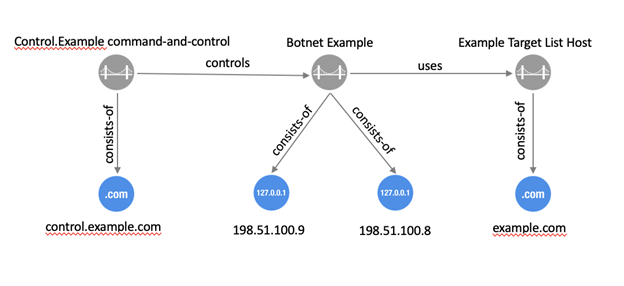
{
"type":"infrastructure",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":"infrastructure--d09c50cf-5bab-465e-9e2d-543912148b73",
"created":"2016-11-22T09:22:30.000Z",
"modified":"2016-11-22T09:22:30.000Z",
"name":"Example Target List
Host",
"infrastructure_types":["hosting-target-lists"]
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--81f12913-1372-4c96-85ec-E9034ac98aba",
"created":
"2016-11-23T10:42:39.000Z",
"modified": "2016-11-23T10:42:39.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"consists-of",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--d09c50cf-5bab-465e-9e2d-543912148b73",
"target_ref":
"domain-name--3c10e93f-798e-5a26-a0c1-08156efab7f5"
}
{
"id":
"domain-name--3c10e93f-798e-5a26-a0c1-08156efab7f5",
"type": "domain-name",
"value": "example.com"
}
{
"type":"infrastructure",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":"infrastructure--e4ed271e-e023-45db-99e6-1f912e79bd06",
"created":"2016-11-22T11:04:18.000Z",
"modified":"2016-11-22T11:04:18.000Z",
"name":"Control.Example
command-and-control",
"infrastructure_types":["command-and-control"]
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--2f340a76-edef-443d-a203-bede067c0bb0",
"created":
"2016-11-25T09:46:09.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-11-25T09:46:09.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"consists-of",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--e4ed271e-e023-45db-99e6-1f912e79bd06",
"target_ref":
"domain-name--a56780a5-93a5-5047-97ab-6900d2441bca"
}
{
"id":
"domain-name--a56780a5-93a5-5047-97ab-6900d2441bca",
"type": "domain-name",
"value":
"control.example.com"
}
{
"type":"infrastructure",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":"infrastructure--a3536537-456a-47b5-84dc-fb7c340959e8",
"created":"2016-11-18T04:22:30.000Z",
"modified":"2016-11-18T04:22:30.000Z",
"name":"Botnet Example",
"infrastructure_types":["botnet"]
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--3263dfe0-6bf4-42eb-bab9-5fc9edc6e443",
"created":
"2016-11-18T08:27:37.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-11-18T08:27:37.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"consists-of",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--a3536537-456a-47b5-84dc-fb7c340959e8",
"target_ref":
"ipv4-addr--182726c7-ba5e-5f77-97ef-378365bd0b79"
}
{
"id":
"ipv4-addr--182726c7-ba5e-5f77-97ef-378365bd0b79",
"type": "ipv4-addr",
"value": "198.51.100.8"
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--80d9ba7d-893b-4286-96f9-32225060a730",
"created":
"2016-11-18T06:22:31.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-11-18T06:22:31.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"consists-of",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--a3536537-456a-47b5-84dc-fb7c340959e8",
"target_ref":
"ipv4-addr--d7177770-fc12-586b-9244-426596a7008e"
}
{
"id":
"ipv4-addr--d7177770-fc12-586b-9244-426596a7008e",
"type": "ipv4-addr",
"value": "198.51.100.9"
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--43f753d8-61e2-472e-918e-d7c58e2463e7",
"created":
"2016-11-25T13:37:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2017-11-25T13:37:27.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"uses",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--a3536537-456a-47b5-84dc-fb7c340959e8",
"target_ref":
"infrastructure--d09c50cf-5bab-465e-9e2d-543912148b73"
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--8386f241-b583-4c59-9056-a3b0db596d93",
"created":
"2016-11-25T13:37:27.000Z",
"modified": "2017-11-25T13:37:27.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"controls",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--e4ed271e-e023-45db-99e6-1f912e79bd06",
"target_ref":
"infrastructure--a3536537-456a-47b5-84dc-fb7c340959e8"
}
C.1.4
Malware Instance Hosted on Compromised Domain
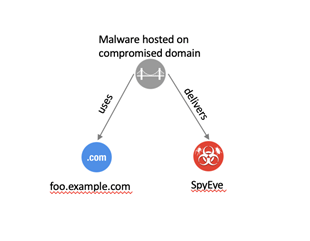
{
"type":"infrastructure",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":"infrastructure--33588e0e-2bab-430e-9073-cacf704ea1e7",
"created":"2017-04-04T13:01:21.000Z",
"modified":"2017-04-04T13:01:21.000Z",
"name":"Malware hosted on
compromised domain",
"infrastructure_types":["hosting-malware"]
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--2f340a76-edef-443d-a203-bede067c0bb0",
"created":
"2016-11-25T09:46:09.000Z",
"modified":
"2016-11-25T09:46:09.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"communicates-with",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--33588e0e-2bab-430e-9073-cacf704ea1e7",
"target_ref":
"domain-name--224dd5a2-d2db-5b8d-91f9-124a0c0c8546"
}
{
"id":
"domain-name--224dd5a2-d2db-5b8d-91f9-124a0c0c8546,
"type": "domain-name",
"value": "foo.example.com"
}
{
"type": "relationship",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":
"relationship--8386f241-b583-4c59-9056-a3b0db596d93",
"created":
"2017-04-05T13:37:27.000Z",
"modified":
"2017-04-05T13:37:27.000Z",
"relationship_type":
"delivers",
"source_ref":
"infrastructure--33588e0e-2bab-430e-9073-cacf704ea1e7",
"target_ref":
"malware--0c7b5b88-8ff7-4a4d-aa9d-feb398cd0061"
}
{
"type":"malware",
"spec_version": "2.1",
"id":"malware--0c7b5b88-8ff7-4a4d-aa9d-feb398cd0061",
"created":"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"modified":"2016-05-12T08:17:27.000Z",
"name":"SpyEye",
"is_family":false,
"malware_types":[
"trojan"
]
}
This appendix contains the required information to register
the STIX media type with IANA. While some of the information here is only for
IANA, implementers of STIX should pay close attention to the security
considerations and privacy considerations outlined in this appendix.
This document defines the "application/stix+json"
media type
Media type name: application
Media subtype name: stix+json
Required parameters: None
Optional parameters: version
This parameter is used to designate
the specification version of STIX that is being used during HTTP content
negotiation. Example: "application/stix+json;version=2.1". The
parameter value is of the form 'n.m', where n is the major version and m the
minor version, both unsigned integer values.
Encoding considerations: binary
Encoding considerations are
identical to those specified for the "application/json" media type.
See [RFC8259].
Security considerations:
Security considerations relating to
the generation and consumption of STIX messages are similar to application/json
and are discussed in section 12 of [RFC8259].
Unicode is used to represent text
such as descriptions in the format. The considerations documented by Unicode
Technical Report #36: Unicode Security Considerations [UnicodeTR#36]
should be taken into account.
The STIX standard does not itself
specify a transport mechanism for STIX documents. It is expected that TAXII is
often used (which uses TLS via HTTPS). As there is no transport mechanism
specified, it is up to the users of this to use an appropriately secured
transport method. For example, TLS, JSON Web Encryption [RFC7516]
and/or JSON Web Signature [RFC7515] can provide such mechanisms.
Documents of
"application/stix+json" are STIX based Cyber Threat Intelligence
(CTI) documents. The documents may contain active or executable content as well
as URLs, IP addresses, and domain names that are known or suspected to be
malicious. Systems should thus take appropriate precautions before decoding any
of this content, either for persistent storage or execution purposes. Such
precautions may include measures such as de-fanging, sandboxing, or other
measures. The samples included in STIX documents are reference samples only,
and there is no provision or expectation in the specification that they will be
loaded and/or executed. There are provisions in the specification to encrypt
these samples so that even if a tool decodes the data, a further active step
must be done before the payload will be "live". It is highly
recommended that all active code be armored in this manner.
STIX specifies the use of hashing
and encryption mechanisms for some data types. A cryptography expert should be
consulted when choosing which hashing or encryption algorithms to use to ensure
that they do not have any security issues.
STIX provides a graph-based data
model. As such, STIX implementations should implement protections against graph
queries that can potentially consume a significant amount of resources and
prevent the implementation from functioning in a normal way.
This specification also describes
"STIX Patterning", a mechanism to describe and evaluate a
search/match for data observed on systems and networks. Patterning is a grammar
itself and includes PCRE regular expressions. Care should be taken when parsing
and evaluating the grammar (particularly when evaluating PCRE from unknown or
untrusted sources) as they can potentially consume a significant amount of
resources.
Privacy considerations:
These considerations are, in part,
derived from Section 10 of the Resource-Oriented Lightweight Information Exchange
[RFC8322].
Documents may include highly
confidential, personal (PII), and/or classified information. There are methods
in the standard for marking elements of the document such that the consumer
knows of these limitations. These markings may not always be used. For example,
an out-of-band agreement may cover and restrict sharing. Just because a
document is not marked as containing information that should not be shared does
not mean that a document is free for sharing. It may be the case that a legal
agreement has been entered into between the parties sharing documents, and that
each party understands and follows their obligations under that agreement as
well as any applicable laws or regulations.
Adoption of the information-sharing
approach described in this document will enable users to more easily perform
correlations across separate, and potentially unrelated, cybersecurity
information providers. A client may succeed in assembling a data set that would
not have been permitted within the context of the authorization policies of
either provider when considered individually. Thus, providers may face a risk
of an attacker obtaining an access that constitutes an undetected separation of
duties (SOD) violation. It is important to note that this risk is not unique to
this specification, and a similar potential for abuse exists with any other
cybersecurity information-sharing protocol.
Interoperability considerations:
The STIX specification specifies
the format of conforming messages and the interpretation thereof. In addition,
the OASIS Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) Technical Committee has defined
interoperability tests to ensure conforming products and solutions can exchange
STIX documents.
Published specification:
STIX Version 2.1 OASIS Committee
Specification 01
http://docs.oasis-open.org/cti/stix/v2.1/cs01/stix-v2.1-cs01.html
Cited in the "OASIS
Standards" document:
https://www.oasis-open.org/standards#oasiscommiteespecs,
from
https://www.oasis-open.org/standards#stix2.1
Applications which use this media:
Structured Threat Information
Expression (STIX) is a language and serialization format used to exchange cyber
threat intelligence (CTI) such as Threat Actors, Campaigns, Intrusion Sets,
Attack Patterns, Indicators of Compromise, etc. STIX enables organizations to
share CTI with one another in a consistent and machine-readable manner,
allowing security communities to better understand what computer-based attacks
they are most likely to see and to anticipate and/or respond to those attacks
faster and more effectively. STIX is designed to improve many different
capabilities, such as collaborative threat analysis, automated threat exchange,
automated detection and response, and more.
Fragment identifier considerations: None
Restrictions on usage: None
Additional information:
1. Deprecated alias names for this
type: application/vnd.oasis.stix+json
2. Magic number(s): n/a [RFC8259]
3. File extension(s): stix
4. Macintosh file type code: TEXT [RFC8259]
5. Object Identifiers: None
Person and email to contact for further information: Chet
Ensign (chet.ensign@oasis-open.org)
Intended usage: COMMON
Author:
OASIS Cyber Threat Intelligence
(CTI) Technical Committee;
URI reference:
http://www.oasis-open.org/committees/cti/.
Change controller: OASIS
Provisional registration: No
STIX
Subcommittee Chairs:
Bret Jordan, Symantec
Corporation
Special
Thanks:
Substantial contributions to this
specification from the following individuals are gratefully acknowledged:
Trey Darley, CCB/CERT.be
Terry MacDonald, Cosive
Jane Ginn, Cyber Threat
Intelligence Network, Inc. (CTIN)
Marlon Taylor, DHS Office of
Cybersecurity and Communications (CS&C)
Chris Ricard, Financial Services
Information Sharing and Analysis Center (FS-ISAC)
Sean Barnum, FireEye
Gary Katz, FireEye, Inc.
Ryusuke Masuoka, Fujitsu Limited
Iain Brown, GDS
Jason Keirstead, IBM
Emily Ratliff, IBM
Tim Casey, Intel
Allan Thomson,
LookingGlass Cyber
Greg Back, MITRE
Corporation
Jon Baker, MITRE Corporation
Sarah Kelley, MITRE Corporation
Ivan Kirillov, MITRE
Corporation
Chris Lenk, Mitre Corporation
Richard Piazza, MITRE Corporation
Richard Struse, MITRE Corporation
Emmanuelle Vargas-Gonzalez, MITRE
Corporation
John Wunder, MITRE
Corporation
John-Mark Gurney, New Context
Services, Inc.
Christian Hunt, New
Context Services, Inc.
Aharon Chernin, Perch
Dave Cridland, Surevine
Bret Jordan, Symantec
Corporation
Jeffrey Mates, US Department of
Defense (DoD)
Participants:
The following individuals were members
of the OASIS CTI Technical Committee during the creation of this specification
and their contributions are gratefully acknowledged:
Kai Li, 360 Enterprise Security
Group
shu li, 360 Enterprise Security
Group
qian yin, 360 Enterprise Security
Group
Xinhua Zheng, 360 Enterprise
Security Group
Robert Coderre, Accenture
Kyle Maxwell, Accenture
David Crawford, Aetna
Marcos Orallo, Airbus Group SAS
Roman Fiedler, AIT Austrian
Institute of Technology
Florian Skopik, AIT Austrian
Institute of Technology
Ryan Clough, Anomali
Nicholas Hayden, Anomali
Wei Huang, Anomali
Russell Matbouli, Anomali
Angela Nichols, Anomali
Hugh Njemanze, Anomali
Katie Pelusi, Anomali
Dean Thompson, Australia and New
Zealand Banking Group (ANZ Bank)
Radu Marian, Bank of America
Sounil Yu, Bank of America
Vicky Laurens, Bank of Montreal
Trey Darley, CCB/CERT.be
Alexandre Dulaunoy, CIRCL
Andras Iklody, CIRCL
Christian Studer, CIRCL
RaphaÎl Vinot, CIRCL
Syam Appala, Cisco Systems
Ted Bedwell, Cisco Systems
Pavan Reddy, Cisco Systems
Omar Santos, Cisco Systems
Sam Taghavi Zargar, Cisco Systems
Jyoti Verma, Cisco Systems
Jart Armin, Cyber Threat Intelligence
Network, Inc. (CTIN)
Doug DePeppe, Cyber Threat
Intelligence Network, Inc. (CTIN)
Jane Ginn, Cyber Threat
Intelligence Network, Inc. (CTIN)
Ben Ottoman, Cyber Threat
Intelligence Network, Inc. (CTIN)
David Powell, Cyber Threat
Intelligence Network, Inc. (CTIN)
Andreas Sfakianakis, Cyber Threat
Intelligence Network, Inc. (CTIN)
Anuj Goel, Cyware Labs
Avkash Kathiriya, Cyware Labs
Jaeden Hampton, DarkLight, Inc.
Ryan Hohimer, DarkLight, Inc.
Ryan Joyce, DarkLight, Inc.
Shawn Riley, DarkLight, Inc.
Ian Roberts, DarkLight, Inc.
Andrew Byrne, Dell
Jeff Odom, Dell
Sreejith Padmajadevi, Dell
Ravi Sharda, Dell
Will Urbanski, Dell
David Ailshire, DHS Office of
Cybersecurity and Communications (CS&C)
Steven Fox, DHS Office of
Cybersecurity and Communications (CS&C)
Taneika Hill, DHS Office of
Cybersecurity and Communications (CS&C)
Evette Maynard-Noel, DHS Office of
Cybersecurity and Communications (CS&C)
Jackie Eun Park, DHS Office of
Cybersecurity and Communications (CS&C)
Sean Sobieraj, DHS Office of
Cybersecurity and Communications (CS&C)
Marlon Taylor, DHS Office of
Cybersecurity and Communications (CS&C)
Preston Werntz, DHS Office of
Cybersecurity and Communications (CS&C)
Jˆrg Abraham, EclecticIQ
wouter bolsterlee, EclecticIQ
Adam Bradbury, EclecticIQ
Marko Dragoljevic, EclecticIQ
Oliver Gheorghe, EclecticIQ
Joep Gommers, EclecticIQ
Caitlin Huey, EclecticIQ
Christopher O'Brien, EclecticIQ
Sergey Polzunov, EclecticIQ
Rutger Prins, EclecticIQ
Aukjan van Belkum, EclecticIQ
Raymon van der Velde, EclecticIQ
Tom Vaughan, EclecticIQ
Joseph Woodruff, EclecticIQ
Ben Sooter, Electric Power Research
Institute (EPRI)
Chris Ricard, Financial Services
Information Sharing and Analysis Center (FS-ISAC)
Sean Barnum, FireEye, Inc.
Phillip Boles, FireEye, Inc.
Prasad Gaikwad, FireEye, Inc.
Haripriya Gajendran, FireEye, Inc.
Will Green, FireEye, Inc.
Rajeev Jha, FireEye, Inc.
Gary Katz, FireEye, Inc.
Anuj Kumar, FireEye, Inc.
James Meck, FireEye, Inc.
Shyamal Pandya, FireEye, Inc.
Paul Patrick, FireEye, Inc.
Remko Weterings, FireEye, Inc.
Tim Jones, ForeScout
Ryusuke Masuoka, Fujitsu Limited
Daisuke Murabayashi, Fujitsu
Limited
Derek Northrope, Fujitsu Limited
Toshitaka Satomi, Fujitsu Limited
Koji Yamada, Fujitsu Limited
Kunihiko Yoshimura, Fujitsu Limited
Robert van Engelen, Genivia
Eric Burger, Georgetown University
Allison Miller, Google Inc.
Mark Risher, Google Inc.
Yoshihide Kawada, Hitachi, Ltd.
Jun Nakanishi, Hitachi, Ltd.
Kazuo Noguchi, Hitachi, Ltd.
Akihito Sawada, Hitachi, Ltd.
Yutaka Takami, Hitachi, Ltd.
Masato Terada, Hitachi, Ltd.
Adrian Bishop, Huntsman Security
Eldan Ben-Haim, IBM
Allen Hadden, IBM
Sandra Hernandez, IBM
Jason Keirstead, IBM
Chenta Lee, IBM
John Morris, IBM
Devesh Parekh, IBM
Emily Ratliff, IBM
Nick Rossmann, IBM
Laura Rusu, IBM
Ron Williams, IBM
Paul Martini, iboss, Inc.
Vasileios Mavroeidis, IFI
Kamer Vishi, IFI
Joerg Eschweiler, Individual
Elysa Jones, Individual
Terry MacDonald, Individual
Tim Casey, Intel Corporation
Julie Modlin, Johns Hopkins
University Applied Physics Laboratory
Mark Moss, Johns Hopkins University
Applied Physics Laboratory
Mark Munoz, Johns Hopkins
University Applied Physics Laboratory
Nathan Reller, Johns Hopkins
University Applied Physics Laboratory
Pamela Smith, Johns Hopkins
University Applied Physics Laboratory
Vivek Jain, JPMorgan Chase Bank,
N.A.
Subodh Kumar, JPMorgan Chase Bank,
N.A.
David Laurance, JPMorgan Chase
Bank, N.A.
Russell Culpepper, Kaiser
Permanente
Beth Pumo, Kaiser Permanente
Michael Slavick, Kaiser Permanente
Daniel Ben-Chitrit, LookingGlass
Wesley Brown, LookingGlass
Dennis Hostetler, LookingGlass
Himanshu Kesar, LookingGlass
Matt Pladna, LookingGlass
Vlad Serban, LookingGlass
Allan Thomson, LookingGlass
Chris Wood, LookingGlass
Kent Landfield, McAfee
Jonathan Baker, Mitre Corporation
Desiree Beck, Mitre Corporation
Michael Chisholm, Mitre Corporation
Sam Cornwell, Mitre Corporation
Sarah Kelley, Mitre Corporation
Ivan Kirillov, Mitre Corporation
Michael Kouremetis, Mitre
Corporation
Chris Lenk, Mitre Corporation
Nicole Parrish, Mitre Corporation
Richard Piazza, Mitre Corporation
Larry Rodrigues, Mitre Corporation
Jon Salwen, Mitre Corporation
Charles Schmidt, Mitre Corporation
Richard Struse, Mitre Corporation
Alex Tweed, Mitre Corporation
Emmanuelle Vargas-Gonzalez, Mitre
Corporation
John Wunder, Mitre Corporation
James Cabral, MTG Management
Consultants, LLC.
Scott Algeier, National Council of
ISACs (NCI)
Denise Anderson, National Council
of ISACs (NCI)
Josh Poster, National Council of
ISACs (NCI)
Mike Boyle, National Security
Agency
Jessica Fitzgerald-McKay, National
Security Agency
David Kemp, National Security
Agency
Shaun McCullough, National Security
Agency
Jason Romano, National Security
Agency
John Anderson, NC4
Michael Butt, NC4
Mark Davidson, NC4
Daniel Dye, NC4
Michael Pepin, NC4
Natalie Suarez, NC4
Benjamin Yates, NC4
Sarah Brown, NCI Agency
Oscar Serrano, NCI Agency
Daichi Hasumi, NEC Corporation
Takahiro Kakumaru, NEC Corporation
Lauri Korts-Parn, NEC Corporation
Kelly Cullinane, New Context
Services, Inc.
John-Mark Gurney, New Context
Services, Inc.
Christian Hunt, New Context
Services, Inc.
Danny Purcell, New Context
Services, Inc.
Daniel Riedel, New Context
Services, Inc.
Andrew Storms, New Context
Services, Inc.
Drew Varner, NineFX, Inc.
Stephen Banghart, NIST
David Darnell, North American
Energy Standards Board
James Crossland, Northrop Grumman
Robert Van Dyk, Northrop Grumman
Cheolho Lee, NSRI
Cory Casanave, Object Management
Group
Joel Myhre, Pacific Disaster Center
Vishaal Hariprasad, Palo Alto
Networks
Brad Bohen, Perch
Aharon Chernin, Perch
Zach Kanzler, Perch
Michael Lane, Perch
Michael Riggs, Perch
Sean O'Brien, Purism SPC
John Tolbert, Queralt Inc.
Forrest Hare, Science Application
International
Duncan Sparrell, sFractal
Consulting LLC
Thomas Schreck, Siemens AG
Adam Wyner, Swansea University
Bret Jordan, Symantec Corp.
Robert Keith, Symantec Corp.
Curtis Kostrosky, Symantec Corp.
Chris Larsen, Symantec Corp.
Michael Mauch, Symantec Corp.
Aubrey Merchant, Symantec Corp.
Efrain Ortiz, Symantec Corp.
Mingliang Pei, Symantec Corp.
Kenneth Schneider, Symantec Corp.
Arnaud Taddei, Symantec Corp.
Brian Witten, Symantec Corp.
Greg Reaume, TELUS
Alan Steer, TELUS
Crystal Hayes, The Boeing Company
Andrew Gidwani, ThreatConnect, Inc.
Cole Iliff, ThreatConnect, Inc.
Andrew Pendergast, ThreatConnect,
Inc.
Jason Spies, ThreatConnect, Inc.
Ryan Trost, ThreatQuotient, Inc.
David Girard, Trend Micro
Brandon Niemczyk, Trend Micro
Eric Shulze, Trend Micro
Patrick Coughlin, TruSTAR
Technology
Chris Roblee, TruSTAR Technology
ADHAM ALBAKRI, University of Kent
Jeffrey Mates, US Department of
Defense (DoD)
Evette Maynard-Noel, US Department
of Homeland Security
Lee Chieffalo, Viasat
Wilson Figueroa, Viasat
Andrew May, Viasat
Ales Cernivec, XLAB
Anthony Rutkowski, Yanna
Technologies LLC
|
Revision
|
Date
|
Editor
|
Changes Made
|
|
01
|
2018-07-20
|
Bret Jordan,
John Wunder,
Rich Piazza,
Ivan Kirillov,
Trey Darley
|
Initial Version
Github Issues: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9,
11, 13, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 25, 26, 27, 31, 33, 35, 36, 37, 38,
39, 40, 41, 42, 54, 55, 57, 68, 71, 78, 88, 89, 91, 98, 99, 121
|
|
02
|
2018-08-10
|
Bret Jordan,
John Wunder,
Rich Piazza,
Ivan Kirillov,
Trey Darley
|
Multiple editorial, style, and grammar
fixes.
Added normative text to ensure that the various ending
timestamp properties are before the first timestamp.
Updates to the "labels" property description to
better describe potential overlap with the specific classification
properties.
Fixed relevant common properties to the definition for
Language Content.
Language Content object: Fixed relevant common property
definitions, expanded the definition of "contents" property to
include handling of lists when not all list items have language content in
that language.
Added a "roles" property to Identity.
Observed Data object: expanded description to broaden its
usage, made "first_observed", "last_observed", and
"number_observed" properties optional, added normative statements
to "first_observed" and "last_observed" properties to
address consistency between the properties.
Option object: renamed "description" property to
"explanation".
Sighting object: updated normative text for the
"where_sighted_refs" property to allow for using Location objects
in addition to Identity objects.
Artifact object: updated normative text for
"encryption_algorithm" from a SHOULD to a MUST use values from the
defined enumeration.
Network Traffic object: added text to indicate that values
for byte and packet counts are positive integers.
Patterning Observation Expression: updated normative text
to clarify the behavior of Observation Expression comparisons with OR is a
short-circuit.
Github Issues: n/a
|
|
03
|
2018-09-05
|
Bret Jordan,
John Wunder,
Rich Piazza,
Ivan Kirillov,
Trey Darley
|
Reverted Observed Data properties back to required.
Github Issues: 90
|
|
04
|
2019-05-29
|
Bret Jordan,
Rich Piazza,
Trey Darley
|
Updated the entire introduction. Merged content down into
a single document.
Merged down the following content sections into the master
document: Introductions, Vocabularies, Customization, Conformance.
Added the following objects and their respective vocabularies:
Infrastructure, Grouping, Malware Analysis.
Updated the following objects: COA, Malware
Github Issues: 8, 10, 12, 14, 24, 32, 64, 72, 76, 79, 81,
87, 92, 93, 94, 101, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 113, 114,
116, 117, 118, 120, 122, 124, 127, 128, 129, 132, 133, 134, 135, 136, 137,
138, 139, 140, 141, 142, 143, 144, 145, 147, 148, 152, 154
|
|
05
|
2019-07-11
|
Bret Jordan,
Rich Piazza,
Trey Darley
|
Some basic formatting cleanup. Renamed conflicting
properties on Directory Object, File Object, Process Object, and Windows
Registry Key Object. Changed Language Content property that allowed version
pinning to be optional. Added relationship from Indicator to Observed Data
called "based-on". Added a description to Sighting. Added a name to
Location. Made some SCO relationships external on Domain-Name, IPv4-Addr, and
IPv6-Addr. Added some text to 3.4 and 3.6.
Relaxed requirements that prevented relationships pointing
to Language Content, Marking Definitions, and Relationships themselves.
Github Issues: 28, 47, 52, 77, 86, 95, 96, 102, 115, 130,
146, 150, 151, 156, 158
|






