Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) is an architectural
paradigm that has gained significant attention within the information
technology (IT) and business communities. The SOA ecosystem described in this
document occupies the area between business and IT. It is neither wholly IT nor
wholly business, but is of both worlds. Neither business nor IT completely own,
govern and manage this SOA ecosystem. Both sets of concerns must be
accommodated for the SOA ecosystem to fulfill its purposes.
The OASIS Reference Model for SOA [SOA-RM] provides a
common language for understanding the important features of SOA but does not
address the issues involved in constructing, using or owning a SOA-based
system. This document focuses on these aspects of SOA.
The intended audiences of this document and expected
benefits to be realized include non-exhaustively:
·
Enterprise Architects - will gain a better understanding when
planning and designing enterprise systems of the principles that underlie
Service Oriented Architecture;
·
Standards Architects and Analysts - will be able to better
position specific specifications in relation to each other in order to support
the goals of SOA;
·
Decision Makers - will be better informed as to the technology
and resource implications of commissioning and living with a SOA-based system;
in particular, the implications following from multiple ownership domains; and
·
Users/Developers - will gain a better understanding of what is
involved in participating in a SOA-based system.
A reference architecture models the abstract architectural
elements in the domain of interest independent of the technologies, protocols,
and products that are used to implement a specific solution for the domain. It
differs from a reference model in that a reference model describes the
important concepts and relationships in the domain focusing on what
distinguishes the elements of the domain; a reference architecture elaborates
further on the model to show a more complete picture that includes showing what
is involved in realizing the modeled entities, while staying independent of any
particular solution but instead applies to a class of solutions.
It is possible to define reference architectures at many
levels of detail or abstraction, and for many different purposes. A reference
architecture is not a concrete architecture; i.e., depending on the
requirements being addressed by the reference architecture, it generally will
not completely specify all the technologies, components and their relationships
in sufficient detail to enable direct implementation.
There is a continuum of architectures, from the most
abstract to the most detailed. This Reference Architecture is an abstract
realization of SOA, focusing on the elements and their relationships needed to
enable SOA-based systems to be used, realized and owned while avoiding reliance
on specific concrete technologies. This positions the work at the more abstract
end of the continuum, and constitutes what is described in [TOGAF v9] as a
“foundation architecture”. It is nonetheless a reference architecture as
it remains solution-independent and is therefore characterized as a Reference
Architecture Foundation because it takes a first principles approach to
architectural modeling of SOA-based systems.
While requirements are addressed more fully in Section 0, the SOA-RAF makes key assumptions that SOA-based systems involve:
·
Use of resources that are distributed across ownership
boundaries;
·
people and systems interacting with each other, also across
ownership boundaries;
·
security, management and governance that are similarly
distributed across ownership boundaries; and
·
interaction between people and systems that is primarily through
the exchange of messages with reliability that is appropriate for the intended
uses and purposes.
Even in apparently homogenous structures, such as within a
single organization, different groups and departments nonetheless often have
ownership boundaries between them. This reflects organizational reality as well
as the real motivations and desires of the people running those organizations.
Such an environment as described above is an ecosystem
and, specifically in the context of SOA-based systems, is a SOA ecosystem.
This concept of an ecosystem perspective of SOA is elaborated further in
Section 1.2.
This SOA-RAF shows how Service Oriented Architecture fits
into the life of users and stakeholders, how SOA-based systems may be realized
effectively, and what is involved in owning and managing them. This serves two
purposes: to ensure that SOA-based systems take account of the specific
constraints of a SOA ecosystem, and to allow the audience to focus on the
high-level issues without becoming over-burdened with details of a particular
implementation technology.
The OASIS Reference Model for Service Oriented Architecture
identifies the key characteristics of SOA and defines many of the important
concepts needed to understand what SOA is and what makes it important. The
Reference Architecture Foundation takes the Reference Model as its starting
point, in particular the vocabulary and definition of important terms and
concepts.
The SOA-RAF goes further in that it shows how SOA-based
systems can be realized – albeit in an abstract way. As noted above, SOA-based
systems are better thought of as dynamic systems rather than stand-alone
software products. Consequently, how they are used and managed is at least as
important architecturally as how they are constructed.
Other SOA reference architectures have emerged in the
industry, both from the analyst community and the vendor/solution provider
community. Some of these reference architectures are quite abstract in
relation to specific implementation technologies, while others are based on a
solution or technology stack. Still others use middleware technology such as
an Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) as their architectural foundation.
As with the Reference Model, this Reference Architecture is
primarily focused on large-scale distributed IT systems where the participants
may be legally separate entities. It is quite possible for many aspects of this
Reference Architecture to be realized on quite different platforms.
In addition, this Reference Architecture Foundation, as the
title illustrates, is intended to provide foundational models on which to build
other reference architectures and eventual concrete architectures. The
relationship to several other industry reference architectures for SOA and
related SOA open standards is described in Appendix E.
1.1.5 Expectations set by
this Reference Architecture Foundation
This Reference Architecture Foundation is not a complete
blueprint for realizing SOA-based systems. Nor is it a technology map
identifying all the technologies needed to realize SOA-based systems. It does
identify many of the key aspects and components that will be present in any
well designed SOA-based system. In order to actually use, construct and manage
SOA-based systems, many additional design decisions and technology choices will
need to be made.
Many systems cannot be completely understood by a simple
decomposition into parts and subsystems – in particular when many autonomous
parts of the system are governing interactions. We need also to understand the
context within which the system functions and the participants involved in
making it function. This is the ecosystem. For example, a
biological ecosystem is a self-sustaining and dynamic association of plants,
animals, and the physical environment in which they live. Understanding an
ecosystem often requires a holistic perspective that considers the
relationships between the elements of the system and their environment at least
as important as the individual parts of the system.
This Reference Architecture Foundation views the SOA
architectural paradigm from an ecosystems perspective: whereas a system will be
a capability developed to fulfill a defined set of needs, a SOA ecosystem is a
space in which people, processes and machines act together to deliver those
capabilities as services.
Viewed as whole, a SOA ecosystem is a network of discrete
processes and machines that, together with a community of people, creates,
uses, and governs specific services as well as external suppliers of resources
required by those services.
In a SOA ecosystem there may not be any single person or organization
that is really "in control" or "in charge" of the whole
although there are identifiable stakeholders who have influence within the
community and control over aspects of the overall system.
The three key principles that inform our approach to a SOA
ecosystem are:
·
a SOA is a paradigm for exchange of value between
independently acting participants;
·
participants (and stakeholders in general) have legitimate claims
to ownership of resources that are made available via the SOA; and
·
the behavior and performance of the participants are subject to rules
of engagement which are captured in a series of policies and contracts.
1. The
SOA-RAF uses and follows the IEEE “Recommended Practice for Architectural
Description of Software-Intensive Systems” [ANSI/IEEE 1471]
and [ISO/IEC 42010]. An architectural description conforming to this
standard must include the following six (6) elements:
2. Architectural
description identification, version, and overview information
3. Identification
of the system stakeholders and their concerns judged
to be relevant to the architecture
4. Specifications
of each viewpoint that has been selected to organize the representation of the
architecture and the rationale for those selections
5. One or
more architectural views
6. A record
of all known inconsistencies among the architectural description’s required
constituents
7. A
rationale for selection of the architecture (in particular, showing how the
architecture supports the identified stakeholders’ concerns).
The standard defines the following terms:
Architecture
The fundamental organization of a system embodied in its
components, their relationships to each other, and to the environment, and the principles
guiding its design and evolution.
Architectural Description
A collection of products that document the architecture.
System
A collection of components organized to accomplish a
specific function or set of functions.
System Stakeholder
A system stakeholder is an individual, team, or
organization (or classes thereof) with interests in, or concerns relative to, a
system.
A stakeholder’s concern should not be confused with either a
need or a formal requirement. A concern, as understood here, is an area or
topic of interest. Within that concern, system stakeholders may have many
different requirements. In other words, something that is of interest or
importance is not the same as something that is obligatory or of necessity [TOGAF
v9].
When describing architectures, it is important to identify
stakeholder concerns and associate them with viewpoints to insure that those
concerns are addressed in some manner by the models that comprise the views on
the architecture. The standard defines views and viewpoints as follows:
View
A representation of the whole system from the perspective
of a related set of concerns.
Viewpoint
A specification of the conventions for constructing and
using a view. A pattern or template from which to develop individual views by
establishing the purposes and audience for a view and the techniques for its
creation and analysis.
In other words, a view is what the stakeholders see whereas
the viewpoint defines the perspective from which the view is taken and the
methods for, and constraints upon, modeling that view.
It is important to note that viewpoints are independent of a
particular system (or solutions). In this way, the architect can select a set
of candidate viewpoints first, or create new viewpoints, and then use those
viewpoints to construct specific views that will be used to organize the
architectural description. A view, on the other hand, is specific to a
particular system. Therefore, the practice of creating an architectural
description involves first selecting the viewpoints and then using those
viewpoints to construct specific views for a particular system or subsystem.
Note that the standard requires that each view corresponds to exactly one
viewpoint. This helps maintain consistency among architectural views which is a
normative requirement of the standard.
A view is comprised of one or more architectural models,
where model is defined as:
Model
An abstraction or representation of some aspect of a thing
(in this case, a system)
All architectural models used in a particular view are
developed using the methods established by the architectural viewpoint
associated with that view. An architectural model may participate in more than
one view but a view must conform to a single viewpoint.
An open standard modeling language is used to help visualize
structural and behavioral architectural concepts. Although many architecture
description languages exist, we have adopted the Unified Modeling Language™ 2
(UML® 2) [UML 2] as the main viewpoint modeling language.
Normative UML is used unless otherwise stated but it should be noted that it
can only partially describe the concepts in each model – it is important to
read the text in order to gain a more complete understanding of the concepts
being described in each section..
Appendix The Unified Modeling Language, UML introduces the
UML notation that is used in this document.
The RAF uses three views that conform to three viewpoints: Participation
in a SOA Ecosystem, Realization of a SOA Ecosystem, and Ownership
in a SOA Ecosystem. There is a one-to-one correspondence between viewpoints
and views (see Table 1).
|
Viewpoint Element
|
Viewpoint
|
|
Participation in a SOA Ecosystem
|
Realization of a SOA Ecosystem
|
Ownership in a SOA Ecosystem
|
|
Main concepts covered
|
Captures what is meant for people to participate in a SOA
ecosystem.
|
Captures what is meant to realize a SOA-based system in a
SOA ecosystem.
|
Captures what is meant to own a SOA-based system in a SOA
ecosystem
|
|
Stakeholders addressed
|
All participants in the SOA ecosystem
|
Those involved in the design, development and deployment
of SOA-based systems
|
Those involved in governing, managing, securing, and
testing SOA-based systems
|
|
Concerns addressed
|
Understanding ecosystem constraints and contexts in which
business can be conducted predictably and effectively.
|
Effective construction of SOA-based systems.
|
Processes to ensure governance, management, security, and
testing of SOA-based systems.
|
|
Modeling Techniques used
|
UML class diagrams
|
UML class, sequence, component, activity, communication,
and composite structure diagrams
|
UML class and communication diagrams
|
Table 1 - Viewpoint
specifications for the OASIS Reference Architecture Foundation for SOA
This viewpoint captures a SOA ecosystem as an environment
for people to conduct their business. We do not limit the applicability of
such an ecosystem to commercial and enterprise systems. We use the term
business to include any transactional activity between multiple users.
All stakeholders in the ecosystem have concerns addressed by
this viewpoint. The primary concern for people is to ensure that they
can conduct their business effectively and safely in accordance with the SOA
paradigm. The primary concern of decision makers is the relationships between
people and organizations using systems for which they, as decision makers, are
responsible but which they may not entirely own, and for which they may not own
all of the components of the system.
Given SOA’s value in allowing people to access, manage and
provide services across ownership boundaries,
we must explicitly identify those boundaries and the implications of crossing
them.
This viewpoint focuses on the infrastructure elements that
are needed to support the construction of SOA-based systems. From this
viewpoint, we are concerned with the application of well-understood
technologies available to system architects to realize the SOA vision of
managing systems and services that cross ownership
boundaries.
The stakeholders are essentially anyone involved in
designing, constructing and deploying a SOA-based system.
This viewpoint addresses the concerns involved in owning and
managing SOA-based systems within the SOA ecosystem. Many of these concerns
are not easily addressed by automation; instead, they often involve
people-oriented processes such as governance bodies.
Owning a SOA-based system implies being able to manage an
evolving system. It involves playing an active role in a wider ecosystem. This
viewpoint is concerned with how systems are managed effectively, how decisions
are made and promulgated to the required end points; how to ensure that people
may use the system effectively; and how the system can be protected against,
and recover from consequences of, malicious intent.
The keywords “MUST”, “MUST NOT”, “REQUIRED”, “SHALL”, “SHALL
NOT”, “SHOULD”, “SHOULD NOT”, “RECOMMENDED”, “MAY”, and “OPTIONAL” in this
document are to be interpreted as described in [RFC2119].
References are surrounded with [square brackets and are in
bold text].
The terms “SOA-RAF”, “this Reference Architecture” and “Reference
Architecture Foundation” refer to this document, while “the Reference Model”
refers to the OASIS Reference Model for Service Oriented Architecture”. [SOA-RM].
Certain terms used in this document to denote concepts with
formal definitions and are used with specific meanings. Where reference is made
to a formally defined concept and the prescribed meaning is intended, we use a bold
font. The first time these terms are used, they are also hyperlinked to
their definition in the body of the text. Where a more colloquial or informal
meaning is intended, these words are used without special emphasis.
[ANSI/IEEE 1471] IEEE Recommended Practice for Architectural
Description of Software-Intensive Systems, American National Standards
Institute/Institute for Electrical and Electronics Engineers, September 21,
2000.
[ISO/IEC 42010] International Organization for Standardization and
International Electrotechnical Commission, System and software engineering — Recommended
practice for architectural description of software-intensive systems, July 15, 2007.
[RFC2119] S. Bradner, Key
words for use in RFCs to Indicate Requirement Levels, http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2119.txt,
IETF RFC 2119, March 1997.
[SOA-RM] OASIS Standard, "Reference Model
for Service Oriented Architecture 1.0, 12 October 2006. http://docs.oasis-open.org/soa-rm/v1.0/soa-rm.pdf
[UML 2] Unified Modeling Language:
Superstructure, Ver. 2.1.1, OMG Adopted Specification, OMG document
formal/2007-02-05, Object Management Group, Needham, MA, February 5, 2007.
[WA] Architecture of the World Wide
Web, W3C, 2004. http://www.w3.org/TR/webarch.
[WSA] David Booth,
et al., ''Web Services Architecture'', W3C Working Group Note, World Wide Web
Consortium (W3C) (Massachusetts Institute of Technology, European Research
Consortium for Informatics and Mathematics, Keio University), February, 2004. http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/NOTE-ws-arch-20040211/
[BLOOMBERG/SCHMELZER] Jason Bloomberg and Ronald
Schmelzer, Service Orient or Be Doomed!, John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken,
NJ, 2006.
[COX] D. E. Cox and H.
Kreger, “Management of the service-oriented architecture life cycle,” ''IBM
Systems Journal'' '''44''', No. 4, 709-726, 2005
[DCMI] Dublin Core
reference
[ERA] A. Fattah, “Enterprise Reference Architecture,” paper presented at 22nd
Enterprise Architecture Practitioners Conference, London, UK, April 2009.
[IEEE-829] IEEE Standard for Software Test
Documentation, Institute
for Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 16 September 1998
[ISO 11179] ISO 11179 reference
[ITU-T Rec. X.700 | ISO/IEC 10746-3:1996(E)]
Information processing systems—Open
Systems Interconnection—Basic Reference Model—Part 4: Management Framework'',
International Telecommunication Union, International Organization for Standardization
and International Electrotechnical Commission, Geneva, Switzerland, 1989.
[NEWCOMER/LOMOW]
Eric Newcomer and Greg Lomow, Understanding
SOA with Web Services, Addison-Wesley: Upper Saddle River, NJ, 2005.
[OECD] Organization
for Economic Cooperation and Development, Directorate for Financial, Fiscal and
Enterprise Affairs, OECD Principles of Corporate Governance, SG/CG(99) 5 and
219, April 1999.
[TOGAF v9] The Open Group Architecture Framework
(TOGAF) Version 9 Enterprise Edition, The Open Group, Doc Number: G091,
February 2009.
[WEILL] Harvard
Business School Press, IT Governance: How Top Performers Manage IT Decision
Rights for Superior Results, Peter Weill and Jeanne W. Ross, 2004
[DAMIANOU] Nicodemos C. Damianou , Thesis -
A Policy Framework for Management of Distributed Systems, University of London,
Department of Computing, 2002.
[LEVESON] Nancy G. Leveson, Safeware:
System Safety and Computers, Addison-Wesley Professional, Addison-Wesley
Publishing Company, Inc.: Boston, pg. 181, 1995.
[STEEL/NAGAPPAN/LAI]
Christopher Steel and Ramesh Nagappan and Ray Lai, core
Security Patterns:Best Practices and Strategies for J2EE, Web Services and
Identity Management, Prentice Hall: 2005
[ISO/IEC 27002] International Organization for
Standardization and International Electrotechnical Commission, Information
technology –- Security techniques – Code of practice for information security
management, 2007
[SOA NAV] Heather Kreger and Jeff Estefan
(Eds.), “Navigating the SOA Open Standards Landscape Around Architecture,”
Joint Paper, The Open Group, OASIS, and OMG, July 2009. http://www.oasis-open.org/committees/download.php/32911/wp_soa_harmonize_d1.pdf
This section identifies the goals of this Reference
Architecture Foundation and the architectural principles that underpin it.
There are three principal goals:
1. to show
how SOA-based systems can effectively bring participants with needs
(‘consumers’) to interact with participants offering appropriate capabilities
as services (‘producers’);
2. for
participants to have a clearly understood level of confidence as they interact
using SOA-based systems; and
3. for
SOA-based systems to be scaled for small or large systems as needed.
There are four factors critical to the achievement of these
goals:
1. Action:
an account of participants’ action within the ecosystem;
2. Trust:
an account of how participants’ internal perceptions of the reliability of
others guide their behavior (i.e., the trust that participants may or may not
have in others)
3. Interaction:
an account of how participants can interact with each other; and
4. Control:
an account of how the management and governance of the entire SOA ecosystem can
be arranged.

Figure 1 - Critical Factors Analysis of the Reference Architecture
Figure 1 represents a Critical Factors Analysis (CFA)
diagram demonstrating the relationship between the primary goals of this
reference architecture, critical factors that determine the success of the
architecture and individual elements that need to be modeled.
A CFA is a structured way of arriving at the requirements
for a project, especially the quality attribute (non-functional) requirements;
as such, it forms a natural complement to other requirements capture techniques
such as use-case analysis, which are oriented more toward functional
requirements capture. The CFA requirement technique and the diagram notation
are summarized in Appendix B.
2.1.1.1 Effectiveness
A primary purpose of the SOA-RAF is to show how SOA-based
systems ensure that participants can use the facilities of the system to meet
their needs. This does not imply that every need has a SOA solution, but for
those needs that can benefit, we look at what is needed to use the SOA paradigm
effectively.
The key factors that govern effectiveness from a
participant’s perspective are actions undertaken– especially across ownership
boundaries – with other participants in the ecosystem and lead to measurable
results.
2.1.1.2 Confidence
SOA-based systems should enable service providers and
consumers to conduct their business with the appropriate level of confidence in
the interaction. Confidence is especially important in situations that are
high-risk; this includes situations involving multiple ownership domains as
well as situations involving the use of sensitive resources.
Confidence has many dimensions: confidence in the successful
interactions with other participants, confidence in the assessment of trust, as
well as confidence that the ecosystem is properly managed.
2.1.1.3 Scalability
The third goal of this reference architecture is
scalability. In architectural terms, we determine scalability in terms of the smooth
growth of complex systems as the number and complexity of services and
interactions between participants increases. Another measure of scalability is
the ease with which interactions can cross ownership boundaries.
A critical success factor (CSF) is a property of the
intended system, or a sub-goal that directly supports a goal and there is
strong belief that without it the goal is unattainable. CSFs are not
necessarily measurable in themselves. As illustrated in Figure 1, CSFs can be associated with more than one goal.
In many cases, critical success factors are often denoted by
adjectives: reliability, trustworthiness, and so on. In our analysis of the SOA
paradigm, however, it seems more natural to identify four critical concepts
(nouns) that characterize important aspects of SOA:
2.1.2.1 Action
Participants’ principal mode of participation in a SOA
ecosystem is action; typically action in the interest of achieving some desired
real world effect. Understanding how action is
related to SOA is thus critical to the paradigm.
2.1.2.2 Trust
The viability of a SOA ecosystem depends on participants
being able to effectively measure the trustworthiness of the system and of
participants. Trust is a private assessment of a participant’s belief in the
integrity and reliability of the SOA ecosystem (see Section 3.1.4).
Trust can be analyzed in terms of trust in infrastructure
facilities (otherwise known as reliability), trust in the relationships and
effects that are realized by interactions with services, and trust in the
integrity and confidentiality of those interactions particularly with respect
to external factors (otherwise known as security).
Note that there is a distinction between trust in a
SOA-based system and trust in the capabilities accessed via the SOA-based
system. The former focuses on the role of SOA-based systems as a medium
for conducting business, the latter on the trustworthiness of participants in
such systems. This architecture focuses on the former, while trying to
encourage the latter.
2.1.2.3 Interaction
In order for a SOA ecosystem to function, it is essential
that the means for participants to interact with each other is available
throughout the system. Interaction encompasses not only the mechanics and
semantics of communication but also the means for discovering and offering
communication.
2.1.2.4 Control
Given that a large-scale SOA-based system may be populated
with many services, and used by large numbers of people; managing SOA-based
systems properly is a critical factor for engendering confidence in them. This
involves both managing the services themselves and managing the relationships
between people and the SOA-based systems they are utilizing; the latter being
more commonly identified with governance.
The governance of SOA-based systems requires decision makers
to be able to set policies about participants, services, and their
relationships. It requires an ability to ensure that policies are effectively
described and enforced. It also requires an effective means of measuring the
historical and current performances of services and participants.
The scope of management of SOA-based systems is constrained
by the existence of multiple ownership domains.
The following principles serve as core tenets that guided
the evolution of this reference architecture.
Technology Neutrality
Statement: Technology neutrality refers to
independence from particular technologies.
Rationale: We
view technology independence as important for three main reasons: technology
specific approach risks confusing issues that are technology specific with
those that are integrally involved with realizing SOA-based systems; and we
believe that the principles that underlie SOA-based systems have the potential
to outlive any specific technologies that are used to deliver them. Finally, a
great proportion of this architecture is inherently concerned with people,
their relationships to services on SOA-based systems and to each other.
Implications: The
Reference Architecture Foundation must be technology neutral, meaning that we
assume that technology will continue to evolve, and that over the lifetime of
this architecture that multiple, potentially competing technologies will
co-exist. Another immediate implication of technology independence is that
greater effort on the part of architects and other decision makers to construct
systems based on this architecture is needed.
Parsimony
Statement: Parsimony
refers to economy of design, avoiding complexity where possible and minimizing
the number of components and relationships needed.
Rationale: The
hallmark of good design is parsimony, or “less is better.” It promotes better
understandability or comprehension of a domain of discourse by avoiding
gratuitous complexity, while being sufficiently rich to meet requirements.
Implications: Parsimoniously
designed systems tend to have fewer but better targeted features.
Distinction of Concerns
Statement: Distinction
of Concerns refers to the ability to cleanly identify and separate out the
concerns of specific stakeholders in such a way that it is possible to create
architectural models that reflect those stakeholders’ viewpoint. In this way,
an individual stakeholder or a set of stakeholders that share common concerns
only see those models that directly address their respective areas of interest.
Rationale: As
SOA-based systems become more mainstream and increasingly complex, it will be
important for the architecture to be able to scale. Trying to maintain a
single, monolithic architecture description that incorporates all models to
address all possible system stakeholders and their associated concerns will not
only rapidly become unmanageable with rising system complexity, but it will
become unusable as well.
Implications: This
is a core tenet that drives this reference architecture to adopt the notion of
architectural viewpoints and corresponding views. A viewpoint provides the
formalization of the groupings of models representing one set of concerns
relative to an architecture, while a view is the actual representation of a
particular system. The ability to leverage an industry standard that
formalizes this notion of architectural viewpoints and views helps us better
ground these concepts for not only the developers of this reference
architecture but also for its readers. The IEEE Recommended Practice for
Architectural Description of Software-Intensive Systems [ANSI/IEEE
1471-2000::ISO/IEC 42010-2007] is the standard that serves as the basis for
the structure and organization of thisdocument.
Applicability
Statement: Applicability
refers to that which is relevant. Here, an architecture is sought that is
relevant to as many facets and applications of SOA-based systems as possible;
even those yet unforeseen.
Rationale: An
architecture that is not relevant to its domain of discourse will not be
adopted and thus likely to languish.
Implications: The
Reference Architecture Foundation needs to be relevant to the problem of
matching needs and capabilities under disparate domains of ownership; to the
concepts of “Intranet SOA” (SOA within the enterprise) as well as “Internet
SOA” (SOA outside the enterprise); to the concept of “Extranet SOA” (SOA within
the extended enterprise, i.e., SOA with suppliers and trading partners); and finally,
to “net-centric SOA” or “Internet-ready SOA.”
No man is an
island
No man is an
island entire of itself; every man
is a piece
of the continent, a part of the main;
if a clod be
washed away by the sea, Europe
is the less,
as well as if a promontory were, as
well as any
manner of thy friends or of thine
own were;
any man's death diminishes me,
because I am
involved in mankind.
And
therefore never send to know for whom
the bell
tolls; it tolls for thee.
John Donne
The OASIS SOA Reference Model defines Service Oriented
Architecture (SOA) as “a paradigm for organizing and utilizing distributed
capabilities that may be under the control of different ownership domains” and services
as “the mechanism by which needs and capabilities are brought together”. The
central focus of SOA is “the task or business function – getting something
done.”
Together, these ideas describe an environment in which
business functions (realized in the form of services) address business needs.
Service implementations utilize capabilities to produce specific (real world)
effects that fulfill those business needs. Both the people
using the services, and the capabilities themselves, may be distributed across
ownership domains, with different policies and conditions of use in force– this
environment is referred to as a SOA Ecosystem.
The role of a service in the SOA context is to enable
effective business solutions in this environment. Any technology system created
to deliver a service in such an environment is referred to as a SOA-based
system. SOA is thus a paradigm that guides the identification, design,
implementation (i.e., organization), and utilization of such services.
A SOA-based system is concerned with how actors in a system
interact to deliver a specific result - the delivery of a capability or
real-world effect. The SOA ecosystem is concerned with all potential stakeholders
and the roles that they can play; how some stakeholders’ needs are satisfied by
other stakeholders’ solutions; how stakeholders assess risk; how they relate to
each other through policies and contracts; and how they communicate and
establish relationships of trust in the processes leading to the delivery of a
specific result.
The Participation in a SOA Ecosystem view in the
SOA-RAF focuses on the constraints and context in which people conduct business
using a SOA-based system. By business we mean any shared activity entered into
whose objective is to satisfy particular needs of each participant.
The OASIS SOA RM defines SOA as “a paradigm for organizing and utilizing
distributed capabilities that may be under the control of different ownership
domains.” To put it another way, to effectively employ the SOA paradigm, the
architecture must take into account the fact and implications of different
ownership domains, and how best to organize and utilize capabilities that are
distributed across those different ownership domains. These are the main
architectural issues that the Participating in a SOA Ecosystem view tries to
address.
The subsections below expand on the completely abstract
reference model by identifying more fully and with more specificity what challenges
need to be addressed in order to successfully apply the SOA paradigm. Although
this section does not provide a specific recipe, it does identify the important
things that need to be thought about and resolved within an ecosystem context.
The people actively participating in a SOA-based system,
together with others who may potentially benefit from the services delivered by
the system, together constitute the stakeholders. The stakeholders, the
system and the environment (or context) within which they all operate, taken
together forms the SOA ecosystem. That ecosystem may reflect the
SOA-based activities within a particular enterprise or of a wider network of
one or more enterprises and individuals.Although a SOA-based system is
essentailly an IT concern, it is nonetheless a system engineered deliberately
to be able to function in a SOA ecosystem. In this context, a service is the
mechanism that brings a SOA-based system capability together with stakeholder
needs in the wider ecosystem. This is explored in more detail in Section 3.2.2
below.
Furthermore, this Participation in a SOA Ecosystem
view helps us understand the importance of execution context – the set of
technical and business elements that allow interaction to occur in, and thus
business to be conducted using, a SOA-based system.
This view describes how a SOA-based system behaves when
participants may be in different organizations, with different rules and
expectations, and assumes that the primary motivation for participants to interact
with each other is to achieve objectives –to get things done.
The dominant mode of communication within a SOA ecosystem is
electronic, supported by IT resources and artifacts. The stakeholders are
nonetheless people: since there is inherent indirection involved when people
and systems interact using electronic means, we lay the foundations for how communication
can be used to represent and enable action. However,
it is important to understand that these communications are usually a means to
an end and not the primary interest of the participants
of the ecosystem.
Several interdependent concerns are important in our view of
a SOA-ecosystem. The ecosystem includes stakeholders who are participants in
the development, deployment and governance and use of a system and its
services; or who may not participate but are nonetheless are affected by the
system. Actors – whether stakeholder participants or delegates
who act only on behalf of participants (without themselves having any stake in
the actions that they have been tasked to perform) – are engaged in actions
which have an impact on the real world and whose meaning and intent are
determined by implied or agreed-to semantics.
The main models in this view are:
·
the Social Structure in a SOA
Ecosystem Model introduces the key elements that underlie the relationships
between participants and that must be
considered as pre-conditions in order to effectively bring needs and
capabilities together across ownership boundaries;
·
the Action in a SOA Ecosystem Model introduces the key
concepts involved in service actions, and shows how joint action and real-world
effect are what is being aimed for in a SOA ecosystem..

Figure 2 - Model elements
described in the Participation in a SOA Ecosystem view
The actions undertaken by participants
in a SOA ecosystem are performed in a social context that defines the
relationships between the participants. That context
is the social structure. In order to achieve
success in applying the SOA paradigm, the overall social structure in which the
SOA effort is to be undertaken must be taken into consideration. Ownership
boundaries and their implications can only be understood and addressed within
the context of the larger social structure within which they exist and the
nature of the relationships between the different participants in that
structure.
The primary function of the Social Structure Model is to
explain the relationships between an individual participant
and the social context of that participant. The
model also helps in defining and understanding the implications of crossing ownership boundaries. It is, for example, the
foundation for understanding security, governance and management in the SOA
ecosystem.

Figure 3 - Social Structure
Social Structure
A social structure
is a nexus of relationships amongst participants
brought together for a specific purpose.
A social structure represents a collection of participants and is established with an implied or
explicitly defined purpose. The purpose is usually reflected in specific goals
laid down in the social structure’s constitution or
other ‘charter’.
A social structure may have any number of participants and a
large number of different relationships may exist among participants. The
organizing principle for these relationships is the social structure’s purpose.
In addition, a given participant can be a member of multiple social structures.
Thus, there may be interaction among social structures, sometimes resulting in
disagreements when the premises of the social structures do not align.
A social structure can take different forms. For example, an
enterprise is a common kind of social structure that
embodies a form of hierarchic organization; an online chat room represents a
social structure of peers that is very loose. A market represents a social
structure of buyers and sellers. The legal frameworks of entire countries and
regions also count as social structures.
The RAF is concerned primarily with social structures that
reflect relationships amongst participants in SOA ecosystems, notably:
·
the enterprise social structure which
is composed internally of many participants but that has sufficient cohesiveness to be
considered as a potential stakeholder in its own
right; and
·
the peer group
which governs relationship between participants within an ecosystem..
Enterprise
An enterprise is a social
structure with an identifiable leadership structure, and that has
internally established goals that reflect a defined purpose. It can act as a participant within other social
structures, including other enterprises and is represented by members of
its leadership structure.
Peer Group
A peer group is a social
structure with no discernable leadership structure, that may or may not have
internally established goals, but is identiable as the locus of interaction
between participants with individual goals seeking common outcomes and who are
considered peers of one another.
Many interactions between participants take place within social structures. Depending on the scale and
internal structure of an enterprise social structure, these interactions may or
may not cross ownership boundaries (an enterprise can itself be composed of
sub-enterprises). However, interactions between participants within a peer social structure
inherently cross ownership boundaries.
The nature and extent of the interactions that take place
will reflect, often implicitly, degrees of trust between participants and the
very specific circumstances of each participant at the time, and over the
course, of the interactions. It is in the nature of a SOA ecosystem that these
relationships are rendered more explicit and are formalized and form a central
part of what the SOA-RM refers to as Execution Context.
Social structures involved in a particular interaction are
not always explicitly identified. For example, when a customer buys a book over
the Internet, the social structure that determines the validity of the
transaction is often the legal framework of the region associated with the book
vendor. Such legal jurisdiction qualification is typically buried in the fine
print of the service description.
Constitution
A constitution is a set of rules, written or unwritten,
that spell out the purpose, goals, scope, and functioning of a social structure.
Every social structure functions according to rules by which
participants interact with each other within the
structure. In some cases, this is based on an explicit agreement, in other
cases participants behave as though they agree to the constitution
without a formal agreement. In still other cases, participants abide by the
rules with some degree of reluctance, such as governance of SOA-based systems,
covered below. In all cases, the constitution may change over time, in those
cases of implicit agreement the change can occur quickly.
Social structures have Stakeholders
– people – some of whom may be enterprises. They interact within the broad SOA
ecosystem. Actors on the other hand operate strictly within a SOA-based
system.
There is also the concept of Participant which is
particularly important as it reflects the hybrid role of a person who is both a
Stakeholder in the ecosystem (and thus primarily concerned with expressing
needs and seeing those needs fulfilled) and an Actor in the System (and
thus directly involved with system-level activity.
A stakeholder can be either a participant (and thus also an
actor with a specific functional role in a SOA-based system); or a
non-participant – someone who, without participating, nonetheless has something
at stake within the ecosystem.
An actor can be either a participant (and thus also a
stakeholder with a stake in the ecosystem); or a delegate – a human
actor with no stake in the specific action delegated or some automated agent – acting
on behalf of a participant.
The hybrid role of Participant provides a bridge between the
wider (real-world) ecosystem – the world of the stakeholder – and the more
specific (usually technology-focused) system – the world of the actor.

Figure 4 - Actors, Participants
and Delegates
Stakeholder
A stakeholder in the SOA ecosystem is a person with an
interest – a ‘stake’ – in the ecosystem.
Note: Not all stakeholders
necessarily participate in the SOA ecosystem; indeed, the interest of non-participant
stakeholders may be in realizing the benefits of a well-functioning ecosystem
and not suffering unwanted consequences. They can not all or always be
identified in advance but due account is often taken of such stakeholder types,
including potential customers, beneficiaries, affected third parties, as well
as potential “negative stakeholders” who might deliberately seek a negative
impact on the ecosystem (such as hackers or criminals).
Actor
An actor is a human or non-human agent capable of action within a SOA-based system.
Participant
A participant is a person
who is both a stakeholder in the SOA ecosystem and an
actor in the SOA-based system.
Delegate
A delegate is an actor that is acting
on behalf of a participant.
A delegate can be a person or an automated or semi-automated
agent.
Many stakeholders and actors operate in a SOA ecosystem,
including software agents that permit people to offer, and interact with,
services; delegates that represent the interests of
other participants; or security agents charged with managing the security of
the ecosystem. Note that automated agents are always delegates, in that they
act on behalf of a stakeholder.
In the different models of the RAF, actor is used when it is not important whether the entity
is a delegate or a participant.
If the actor is acting on behalf of a stakeholder, then we
use delegate. This underlines the importance of
delegation in SOA-based systems, whether the delegation is of work procedures
carried out by human agents who have no stake in the actions with which they
are tasked but act on behalf of a participant who does; or whether the
delegation is performed by technology (automation). If the actor
is also a stakeholder in the ecosystem, then we use participant.
In order for a delegate to act on behalf of another person,
they must be able to act and have the authority to do
so.
Social structures are
abstractions: a social structure cannot directly
perform actions – only people or automated processes
following the instructions of people can actually do things. However, an actor may act on behalf of a social
structure and certainly acts within a social
structure depending on the roles that the actor assumes and the nature of the relationships between the
concerned parties or stakeholders.

Figure 5 - Role in Social
Structures
Role
A role is a type of relationship between a participant and the actions that the participant may
perform (or is allowed to perform) within a social
structure.
A role is not immutable and is often time-bound. A participant can have one or more roles concurrently and may change them over
time and in different contexts, even over the course of a particular
interaction.
One participant with appropriate authority in the social structure may formally designate a role
for another participant, with associated rights and responsibilities, and that authority may even qualify a period during
which the designated role may be valid. In addition, while many roles
are clearly identified, with appropriate names and definitions of responsibilities, it is also possible to separately
bestow rights, bestow or assume responsibilities
and so on, often in a temporary fashion. For example, when a company president
delegates certain responsibilities on another person, this does not imply that
the other person has become company president. Likewise, a company president
may bestow on someone else her role during a period of time that she is on
vacation or otherwise unreachable, with the understanding that she will
re-assume the role when she returns from vacation.
Conversely, someone who exhibits qualification
and skill may assume a role without any formal
designation. For example, an office administrator who has demonstrated facility
with personal computers may be known as (and thus assumed to role of) the
‘goto’ person for people who need help with their computers.
Authority
Authority is the right to act on behalf of an organization or another
person.
Right
A right is a predetermined permission conferred upon an actor to
perform some action or assume a role
in relation to the social structure.
Rights can be constrained. For example,
sellers might have a general right to refuse service to potential customers but
this right could be constrained so as to be exercised only when certain
criteria are met.
Responsibility
A responsibility is a predetermined obligation
on a participant to perform some action or assume a role
in relation to other participants.
Responsibility implies human agency, which is
why only participants, as opposed to all actors (who can be non-human agents)
are concerned. This applies even if the consequences of such responsibility can
impact other (human and non-human) actors. Having authority often implies
having responsibility.
Rights, authorities,
responsibilities and roles
form the foundation for the security model as well as contributing to the
governance model in the ‘Ownership in a SOA Ecosystem’ View of the RAF.
People will assume and perform roles according to their
actual or perceived rights and responsibilities, with or without explicit
authority. In the context of a SOA ecosystem, human abilities and skills are
relevant as they equip individuals with knowledge, information and tools that
may be necessary to have meaningful and productive interactions with a view to
achieving a desired outcome. For example, a person who needs a particular book,
and has both the right and responsibility of purchasing the book from a given
bookseller, will not have that need met from the online delegate of that
bookstore if he does not know how to use a web browser. Equally, just because
someone does have the requisite knowledge or skills does not entitle them per
se to interact with a specific system.
Two important types of constraints that are relevant to a
SOA ecosystem are Permission and Obligation.
Permission
A permission is a constraint that identifies actions
that an actor is (or is not) allowed to perform and/or the
states in which the actor is (or is not) permitted.
Note that permissions are distinct
from ability and from authority. Authority refers to the legitimate nature of
an action as performed by an actor
on behalf of a social structure. Ability refers to whether an actor has the capacity
to perform the action. Permission does not always
involve acting on behalf of anyone, nor does it imply or require the capacity
to perform the action.
Obligation
An obligation is a constraint that prescribes the actions that an actor must (or must
not) perform and/or the states the actor
must (or must not) attain or maintain.
An example of obligations is the case where the service consumer and provider have entered into an
agreement to provide and consume a service such that the consumer is obligated
to pay for the service and the provider is obligated to provide the service –
based on the terms of the contract.
An obligation can also be a
requirement to to maintain a given state. This may range from a requirement to maintain a
minimum balance on an account to a requirement that a service provider
‘remember’ that a particular service consumer is
logged in.
Both permissions and obligations can be identified ahead of
time, but only Permissions can be validated a priori:
before the intended action or before entering the
constrained state. Obligations
can only be validated a posteriori through some form
of auditing or verification process.
3.1.2.1 Service Roles
As in roles generically, a participant can play one or more
of those roles inherent to the SOA paradigm in the SOA ecosystem, depending on
the context. A participant may be playing a role of a service provider in one
relationship while simultaneously playing the role of a consumer in another.
Roles inherent to the SOA paradigm include Consumer, Provider, Owner, and
Mediator.

Figure 6 - Participant Roles in
a Service
Provider
A provider is a role assumed by a participant
who is offering a service.
Consumer
A consumer is a role assumed by a participant
who is interacting with a service in order to fulfill a need.
Mediator
A mediator is a role assumed by a participant
to facilitate interaction and connectivity in the offering and use of services.
Owner
An owner is a role assumed by a participant who is claiming
and exercising ownership over a service.
It is a common understanding that service interactions are
typically initiated by service consumers, although this is not necessarily true
in all situations. Additionally, as with service providers, several stakeholders may be involved in a service interaction
supporting a given consumer.
The roles of service provider and service consumer are often
seen as symmetrical, which is also not entirely correct. A consumer tends to
express a ‘Need’ in non-formal terms: “I want to buy that book”. The type of
‘Need’ that a service is intended to fulfill has to be formalized and
encapsulated by designers and developers as a ‘Requirement’. This Requirement
should then be reflected in the target service, as a ‘Capability’that, when
accessed via a service, delivers a ‘Real World Effect’ to an arbitrary user:
“The chosen book is ordered for the user.” It thus satisfies the need that has
been defined for an archetypal user. Specific and particular users may not
experience a need exactly as captured by the service: “I don’t want to pay that
much for the book”, “I wanted an eBook version”, etc. There can therefore be a
process of implicit and explicit negotiation between the user and the service,
aimed at finding a ‘best fit’ between the user’s specific need and the
capabilities of the service that are available and consistent with the service
provider’s offering. This process may continue up until the point that the user
is able to accept what is on offer as being the best fit and finally ‘invokes’
the service. ‘Execution context’ has thus been established. This is explored in
more detail later on. Service mediation by a participant can take many forms
and may invoke and use other services in order to fulfill such mediation. For
example, it might use a service registry in order to identify possible service
partners; or, in our book-buying example, it might provide a price comparison
service, suggest alternative suppliers, different language editions or delivery
options.
A resource is generally
understood as an asset: it has value to someone. Key to this concept in a SOA ecosystem is that a resource needs to be
identifiable.

Figure 7 - Resources
Resource
A resource is any identifiable entity that has value to a stakeholder.
A resource
may be identifiable by different methods but within a SOA ecosystem a
resource must have at least one well-formed identifier that may be
unambiguously resolved to the intended resource.
Codified (but not implied) contracts,
policies, obligations, and permissions are all examples of resources, as are
capabilities, services, service descriptions, and SOA-based systems. An implied
policy, contract, obligation or permission would not be a resource, even though
it may have value to a stakeholder, because it is not an identifiable entity.
Identifier
An identifier is any sequence of characters that may be
unambiguously resolved to identifying a particular resource.
Identifiers typically require a context in order to
establish the connection with the resource. In a SOA
ecosystem, it is good practice to use globally unique identifiers; for
example globally unique Internationalized Resource Identifiers (IRIs).
A given resource may have multiple identifiers, with different value
for different contexts.
The ability to identify a resource is important in
interactions to determine such things as rights and authorizations, to
understand what functions are being performed and what the results mean, and to
ensure repeatability or characterize differences with future interactions. Many
interactions within a SOA ecosystem take place across ownership boundaries and
the combination of interactions can be unpredictable. Identifiers provide the
means for all resources important to a given SOA system to be unambiguously
identifiable at any moment and in any interaction.
3.1.3.2 Ownership
Ownership is defined as a relationship
between a stakeholder and a resource,
where some stakeholder (in a role as owner) has certain claims with
respect to the resource.
Typically, the ownership
relationship is one of control: the owner of a resource can control some
aspect of the resource.
Ownership
Ownership is a particular set of claims, expressed as rights and responsibilities, that
a stakeholder has in relation to a resource; It may include the right to transfer that ownership, or some subset of rights and responsibilities,
to another entity.
To own a resource implies taking
responsibility for creating, maintaining and, if it is to be available to
others, provisioning the resource. More than one stakeholder may own different rights
or responsibilities associated with a given service, such as one stakeholder having the responsibility
to deploy a capability as a service, another owning the rights
to the profits that result from charging consumers for using the service, and
yet another owning the right to use the service. . There
may also be joint ownership of a resource,
where the rights and responsibilities are shared.
A stakeholder who owns a resource
may delegate some or all of these rights and
responsibilities to others, but typically retains the responsibility to see
that the delegated rights and responsibilities
are exercised as intended
A crucial property that distinguishes ownership
from a more limited right to use is the right
to transfer rights and responsibilities totally and
irrevocably to another stakeholder. When a stakeholder uses a resource but does not own the resource, that stakeholder
may not transfer the right to use the resource to a third stakeholder. The
owner of the resource maintains the rights and responsibilities of being able
to authorize other stakeholders to use the owned resource.
Ownership is defined in relation to
the social structure relative to which the given
rights and responsibilities
are exercised. For example, there may be constraints on how ownership
may be transferred, such as a government may not permit a corporation to
transfer assets to a subsidiary in a different jurisdiction.
Ownership Boundary
An ownership boundary is the extent of ownership asserted
by a stakeholder over a set of resources and for which rights and
responsibilities are claimed and (usually) recognized by other stakeholders.
In a SOA ecosystem, providers and consumers of services may
be, or may be acting on behalf of, different owners, and thus the interaction
between the provider and the consumer of a given service will necessarily cross
an ownership boundary. It is important to identify these ownership boundaries
in a SOA ecosystem, as successfully crossing them requires the elements
identified in the following sections be addressed. Addressing the elements
identified in the following sections is referred to in the OASIS SOA RM as
establishing the execution context.
For an interaction to occur each actor must be able and willing
to participate.

Figure 8 - Willingness and
Trust
Willingness
Willingness is the internal commitment of a human actor to carry out its part of an interaction.
Willingness to interact is not the same as a willingness to
perform requested actions, however. For example, a service provider that
rejects all attempts to perform a particular action may still be fully willing
and engaged in interacting with the consumer. Important considerations in
establishing willingness are both trust and risk.
Trust
Trust is a private assessment or internal perception of one
actor that another actor will perform actions in accordance with an assertion
regarding a desired real world effect.
Risk
Risk is a private assessment or internal perception of the
likelihood that certain undesirable real world
effects will result from actions taken and the consequences or implications
of such.
Trust is involved in all interactions – it is necessary for all
participants (consumers, providers, mediators) involved in a given interaction
to trust all involved actors, at least to the extent required for continuance
of the interaction. The degree and nature of that trust is likely to be
different for each actor, most especially when those
actors are in different ownership boundaries.
An actor perceiving risk may take
actions to mitigate that risk. At one extreme this will result in a refusal to
interact. Alternately, it may involve adding protection – for example by using
encrypted communication and/or anonymization – to reduce the perception of
risk. Often, standard procedures are put in place to increase trust and to
mitigate risk.
3.1.4.1 Assessing Trust and Risk
The assessments of trust and risk are based on evidence
available to the trusting participant. In general, participants will seek evidence directly from the trusted
actor (e.g., via documentation provided via the service
description) as well as evidence of the reputation of the trusted actor (e.g.,
third-party annotations such as consumer feedback).
Trust is based on the confidence that the trusting
participant has accurately and sufficiently gathered and assessed evidence to
the degree appropriate for the situation being assessed.
Assessment of trust is rarely binary. An actor
is not completely trusted or untrusted because there is typically some degree
of uncertainty in the accuracy or completeness of the evidence or the
assessment. Similarly, there may be uncertainty in the amount and potential
consequences of risk.
The relevance of trust to interaction depends on the
assessment of risk. If there is little or no perceived risk, or the risk can be
covered by another party who accepts responsibility for it, then the degree of
trust may be less or not relevant in assessing possible actions. For example,
most people consider there to be an acceptable level of risk to privacy when
using search engines, and submit queries without any sense of trust being
considered.
As perceived risk increases, the issue of trust becomes more
of a consideration. For interactions with a high degree of risk, the trusting
participant will typically require stronger or additional evidence when
evaluating the balance between risk and trust. An example of high-risk is where
a consumer’s business is dependent on the provider’s service meeting certain
availability and security requirements. If the service fails to meet those
requirements, the service consumer will go out of business. In this example,
the consumer will look for evidence that the likelihood of the service not
meeting the performance and security requirements is extremely low.
As noted in the Reference Model, a policy
represents some commitment and/or constraint advertised and enforced by a stakeholder and that
stakeholder alone. A contract, on the other hand, represents an
agreement by two or more participants. Enforcement
of contracts may or may not be the responsibility of
the parties to the agreement but is usually performed by a stakeholder in the
ecosystem (public authority, legal system, etc.).

Figure 9 - Policies and
Contracts
Policy
A policy is an assertion made by a
stakeholder which the stakeholder commits to uphold
and, if possible and necessary, enforce through stated constraints.
Policies can often be said to be about something – they have
an object. For example, there may be policies about the use of a service.
Policies have an owner – the stakeholder who asserts and takes
responsibility for the policy. Note that the policy owner may or may not be the
owner of the object of the policy. Thirdly, policies represent constraints –
some measurable limitation on the state or behavior of the object of the
policy, or of the behavior of the stakeholders owning the policy.
Contract
A contract represents an agreement made by two or more participants (the contracting parties) on a set of conditions
(or contractual terms) together with a set of constraints that govern their
behavior and/or state in fulfilling those conditions.
A service provider’s policy may become a service
provider/consumer contract when a service consumer agrees to the provider’s
policy. That agreement may be formal, or may be informal. If a consumer’s
policy and a provider’s policy are mutually exclusive, then some form of
negotiation (involving human interactions) or mediation must resolve the mutual
exclusion before the service consumer/provider interaction can occur. Note,
this also applies if the policy is introduced by the consumer instead of the
provider.
Both policies and contracts
imply a desire to see constraints respected and enforced. Policies
are owned by service providers – individual (or aggregate) stakeholders – and contracts are owned by both service
providers and consumers – the parties to the contract; these stakeholders are responsible for ensuring that any
constraints in the policy or contract are enforced,
although the actual enforcement may be delegated to a different mechanism. A
contract does not necessarily oblige the contracting parties to act (for
example to use a service) but it does constrain how they act if and when the
condition covered by the contract occurs (for example, when a service is
invoked and used).
Communication
A communication is a process of reaching mutual
understanding, in which participants not only exchange information as messages
but share the meaning of this information.
A communication involves at
least one actor in the role of sender and at least one other actor in the
role of recipient.All actors must perform their role in order for the
communication to occur.
A given communication may involve any number of recipients.
In some situations, the sender may not be aware of the recipient. However,
without both a sender and a recipient there is no communication. A given
communication does not necessarily involve interaction between the actors; it
can be a simple one-way transmission requiring no further action by the
recipient. However, interaction does, necessarily, involve communication.
A communication involves a message, which an actor
receiving must be able to correctly interpret. The extent of that correct
interpretation depends on the role of the actor
and the purpose of the communication.
A communication is not effective unless the recipient can
correctly interpret the message (or at least, that part of it which is relevant
to the participant). However, interpretation can itself be characterized in
terms of semantic engagement: the proper
understanding of a message in a given context.
We can characterize the necessary modes of interpretation in
terms of a shared understanding of a common vocabulary (or mediation among vocabularies) and of the purpose
of the communication. More formally, we can say that a communication has a
combination of message and purpose.
Interactions between service
consumers and providers do not need to resemble human speech.
Machine-machine communication is typically highly stylized in form, it may have
particular forms and it may involve particular terms not found in everyday
human communication.
A SOA ecosystem is a space in which actors
need to share understanding
as well as sharing actions. Indeed, such shared understanding is a
pre-requisite to a joint action being carried out as intended. It is vital to a
trusted and effective ecosystem. Semantics are therefore pervasive throughout
SOA ecosystems and important in communicative actions described above, as well
as a driver for policies and other aspects of the
ecosystem.
In order to arrive at shared understanding, an actor must
effectively process and understand assertions in a manner appropriate to the
particular context. An assertion, in general, is a measurable and explicit
statement made by an actor. In a SOA ecosystem, in particular, assertions are
concerned with the ‘what’ and the ‘why’ of the state of the ecosystem and its
actors.
Understanding and interpreting those assertions allows other
actors to know what may be expected of them in any particular joint action. An
actor can potentially ‘understand’ an assertion in a number of ways, but it is
specifically the process of arriving at a shared understanding that is
important in the ecosystem. This process is semantic engagement among the actors
in the SOA ecosystem. It can be instantaneous or progressively achieved. It is
important that there is a level of engagement appropriate to the particular
context.
Semantic Engagement
Semantic engagement is the process by which an actor
engages with a set of assertions based on that actor’s interpretation and
understanding of those assertions.
Different actors have differing
capabilities and requirements for understanding assertions.
This is true for both human and non-human actors. For
example, a purchase order process does not require that a message forwarding
agent ‘understand’ the purchase order, but a processing agent does need to
‘understand’ the purchase order in order to know what to with the order once
received.
The impact of any assertion can
only be fully understood in terms of specific social contexts that necessarily
include the actors that are involved. For example, a policy statement that governs the actions relating to a particular
resource may have a different impact or purpose for the participant that owns
the resource than for the actor that is trying to access it: the former
understands the purpose of the policy as a statement of
enforcement - the latter understands it as a statement of constraint.
Participants cannot always achieve desired results by leveraging
resources in their own ownership domain. This unfulfilled need leads them to
seek and leverage services provided by other participants and using resources
beyond their ownership and control. The participants identify service providers
with which they think they can interact to achieve their objective and engage
in joint action with those other actors (service providers) in order to bring
about the desired outcome. The SOA ecosystem provides the environment in which
this happens.
An action model is put forth a-priori by the service
provider, and is effectively an undertaking by the service provider that the
actions – identified in the action model and invoked consistent with the
process model – will result in the described real world effect. The action
model describes the actions leading to a real-world effect. A potential service
consumer – who is interested in a particular outcome to satisfy their need –
must understand those actions as capable of achieving that desired outcome.
When the consumer “invokes” a service, a joint action is
started as identified in the action model, consistent with the temporal
sequence as defined by the process model, and where the consumer and the
provider are the two parties of the joint action. Additionally, the consumer
can be assured that the identified real-world effects will be accomplished
through evidence provided via the service description.
Since the service provider does not know about all potential
service consumers, the service provider may also describe what additional
constraints are necessary in order for the service consumer to invoke
particular actions, and thus participate in the joint action. These additional
constraints, along with others that might not be listed, are preconditions for
the joint action to occur and/or continue (as per the process model), and are
referred to in the SOA RM as execution context. Execution context goes all the
way from human beings involved in aligning policies, semantics, network
connectivity and communication protocols, to the automated negotiation of
security protocols and end-points as the individual actions proceed through the
process model.
Also, it is important to note that both actions and RWE are
‘fractal’ in nature, in the sense that they can often be broken down into more
and more granularity depending on how they are examined and what level of
detail is important.
All of these things are important to getting to the core of participants’ concern
in a SOA ecosystem: the ability to leverage resources or capabilities to
achieve a desired outcome, and in particular where those resources or capabilities do not belong to
them or are beyond their direct control. i.e., that are outside of their
ownership boundary.
In order to use such resources, participants must be able to
identify their own needs in the form of requirements, identify and compose into
a business solution those resources or capabilities that will meet their needs,
and engage in joint action
– the coordinated set of actions that participants pursue in order to achieve
measurable results in furtherance of their goals.
In order to act in a way that is appropriate and consistent,
participants must communicate with each other about their own goals, objectives
and policies, and those of others. This is the main concern of Semantic
Engagement.
A key aspect of joint action revolves around the trust that
both parties must exhibit in order to participate in the joint action. The
willingness to act and a mutual understanding of both the information exchanged
and the expected results is the particular focus of Sections 3.1.4 and 3.1.7.
Participants in a SOA ecosystem often need other
participants to do something, leveraging a capability that they do not
themselves possess. For example, a customer requiring a book may call upon a
service provider to deliver the book. Likewise, the service provider needs the
customer to pay for it.
There is a reason that participants are
engaged in this activity: different participants
have different needs and have or apply different capabilities for
satisfying them.These are core to the concept of a service. The SOA-RM defines
a service as “the mechanism by which needs and capabilities are brought
together”. This idea of services being a mechanism “between” needs and
capabilities was introduced in order to emphasize capability as the notional or
existing business functionality that would address a well-defined need. Service
is therefore the implementation of such business functionality such
that it is accessible through a well-defined interface. A capability that
is isolated (i.e., it is inaccessible to potential consumers) is emphatically
not a service.
Business functionality
Business functionality is a defined set of business-aligned
tasks that provide recognizable business value to ‘consumer’ stakeholders and
possibly others in the SOA ecosystem.
The idea of a service in a SOA ecosystem combines business
functionality with implementation, including the artifacts needed and made
available as IT resources. From the perspective of software developers, a SOA
service enables the use of capabilities in an IT context. For the consumer, the
service (combining business functionality and implementation) generates
intended real world effects. The consumer is not concerned with the underlying
artifacts which make that delivery possible.
In a SOA context, the consumer (as a stakeholder) expresses
a need (“I want to buy a book”) and looks to an appropriate service to fulfill
that need and assesses issues such as the trustworthiness, intent and
willingness of a particular provider. This ecosystem communication continues up
to the point when the consumer is ready to act. The consumer (as an actor now)
will then interact with a provider by invoking a service (for example, ordering
the book using an online bookseller) and engaging in relevant actions
(validating the purchase, submitting billing and delivery details) within the
system with a view to achieving the desired Real World Effect (having the book
delivered).
Need
A need is a general statement expressed by a stakeholder of
something deemed necessary. It may be formalized as one or more requirements
that must be fulfilled in order to achieve a stated goal.
Requirement
A requirement is a formal statement of a desired result (a
real world effect) that, if achieved, will satisfy a need.
This requirement can then be used to create a capability
that in turn can be brought to bear to satisfy that need. Both the requirement
and the capability to fulfill it are expressed in terms of desired real world
effect.
Capability
A capability is an ability to deliver a real world effect.
The Reference Model makes a distinction between a capability
(as a potential to deliver the real world effect) and the ability of
bringing that capability to bear (via a realized service) as the realization of
the real world effect.
The SOA paradigm often emphasizes the interface through
which service interaction is accomplished. While this enables predictable
integration in the sense of traditional software development, the prescribed
interface alone does not guarantee that services will be composable into
business solutions.
Business solution
A business solution is a set of defined
interactions that combine implemented or notional business functionality in
order to address a set of business needs.
Composability
Composability is the ability to combine individual
services, each providing defined business functionality, so as to provide more
complex business solutions.
To achieve composability, capabilities must be identified
that serve as building blocks for business solutions. In a SOA ecosystem, these
building blocks are captured as services representing well-defined business
functions, operating under well-defined policies and other constraints, and
generating well-defined real world effects. These service building blocks
should be relatively stable so as not to force repeated changes in the
compositions that utilize them, but should also embody SOA attributes that
readily support creating compositions that can be varied to reflect changing
circumstances.
The SOA paradigm emphasizes both composition of services and
opacity of how a given service is implemented. With respect to opacity, the
SOA-RM states that the service could carry out its described functionality
through one or more automated and/or manual processes that in turn could invoke
other available services.
Any composition can itself be made available as a service
and the details of the business functionality, conditions of use, and effects
are among the information documented in its service description.
Composability is important because many of the benefits of a
SOA approach assume multiple uses for services, and multiple use requires that
the service deliver a business function that is reusable in multiple business
solutions. Simply providing a Web Service interface for an existing IT
artifact does not, in general, create opportunities for sharing business
functions. Furthermore, the use of tools to auto-generate service software
interfaces will not guarantee services than can effectively be used within
compositions if the underlying code represents programming constructs rather
than business functions. In such cases, services that directly expose the
software details will be as brittle to change as the underlying code and will
not exhibit the characteristic of loose coupling.
In general terms, entities act in order to achieve their
goals. However, the form of action that is of most
interest within a SOA ecosystem is that involving interaction across ownership
boundaries (between more than one actor) – joint
action.
Action
An action is the application of
intent to cause an effect.
The aspect of action that distinguishes it from mere force
or accident is that someone intends that the action achieves a desired
objective or effect. This definition of action is very general. In the case of
SOA, we are mostly concerned with actions that take place within a system and
have specific effects on the SOA ecosystem – what we call Real World Effects. The actual real world
effect of an action, however, may go beyond the intended effect.
Objectives refer to real world
effects that participants believe are achievable by a specific action or set of actions that deliver appropriate changes in shared state. In
contrast, a goal is not expressed in terms of specific action but rather in terms of desired end state.
For example, someone may wish to have enough light to read a
book. In order to satisfy that goal, the reader walks over to flip a light
switch. The objective is to change the state of the light bulb, by
turning on the lamp, whereas the goal is to be able to read. The real
world effect is more light being available to enable the person to read.
While an effect is any measurable change resulting from an
action, a SOA ecosystem is concerned more specifically with real world effects.
Real World Effect
A real world effect is a measurable change to the shared state of pertinent
entities, relevant to and experienced by specific stakeholders of an ecosystem.
This
implies measurable change in the overall state of the SOA ecosystem. In
practice, however, it is specific state changes of certain entities that are
relevant to particular participants that constitute the real world effect as
experienced by those participants.
In this Reference Architecture Foundation, we are concerned
with two levels of activity: as communication and as participants engaged in
joint actions to use and offer services.
In order for multiple actors to
participate in a joint action, they must each act
according to their role within the joint action. This is
achieved through communication and messaging.
Communication – the formulation, transmission, receipt and
interpretation of messages – is the foundation of all joint actions within the
SOA ecosystem, given the inherent separation – often across ownership
boundaries – of actors in the system.
Communication between actors requires
that they play the roles of ‘sender’ or ‘receiver’ of messages as appropriate
to a particular action – although it is not necessarily required that they both
be active simultaneously.
An actor sends a message in order to communicate with other actors. The
communication itself is often not intended as part of the desired real world
effect but rather includes messages that seek to establish, manage, monitor,
report on, and guide the joint action throughout its execution.
Like communication, joint
action usually involves different actors. However, joint action – resulting
from the deliberate actions undertaken by different actors – intentionally
impacts shared state within the system leading to real world effects.
Joint Action
Joint action is the coordinated set of actions involving
the efforts of two or more actors to achieve an effect.
Note that the effect of a joint action is not always
equivalent to one or more effects of the individual actions of the
participating actors, i.e., it may be more than the sum of
the parts.
Different viewpoints lead to either communication or joint
action as being considered most important. For example, from the viewpoint of
ecosystem security, the integrity of the communications may be dominant; from
the viewpoint of ecosystem governance, the integrity of the joint action may be
dominant.
3.2.4 State,
Shared State and Real-World Effect
State
State is the condition of an entity at a particular time.
State is characterized by a set of facts that is true of the entity. In principle, the total state of an entity (or the world as a whole) is unbounded. In
practice, we are concerned only with a subset of the State of an entity that is
measurable and useful in a given context.
For example, the total state of a lightbulb includes the
temperature of the filament of the bulb. It also includes a great deal of other
state – the composition of the glass, the dirt that is on the bulb’s surface
and so on. However, an actor may be primarily interested
in whether the bulb is ‘on’ or ‘off’ and not on the amount of dirt accumulated.
That actor’s characterization of the state of the bulb reduces to the fact:
‘bulb is now on’.
In a SOA ecosystem, there is a distinction between the set
of facts about an entity that only that entity can access – the so-called
Private State – and the set of facts that may be accessible to other actors in
the SOA-based system – the public or Shared State.
Private State
The private state is that part of of an entity’s state that is knowable by, and accessible to, only that
entity.
Shared State
Shared state is that part of an entity’s state
that is knowable by, and may be accessible to, other actors.
Note that shared state does not imply that the state is
accessible to all actors. It simply refers to that subset of state that may
be accessed by other actors. Generally this will be the case when actors
need to participate in joint actions.
It is the aggregation of the shared states of pertinent
entities that constitutes the desired effect of a joint action. Thus the change
to this shared state is what is experienced in the wider ecosystem as a real
world effect
A SOA ecosystem’s participants
are organized into various forms of social structure.
Not all social structures are hierarchical: a
SOA ecosystem should be able to incorporate peer-to-peer forms of organization
as well as hierarchic structures. In addition, it should be possible to
identify and manage any constitutional agreements that define the social structures present in a SOA ecosystem.
·
Different social structures have
different rules of engagement but predictable behavior is one of the
underpinnings of trust. This therefore requires mechanisms to:
o
express constitutions and other organizing principles of
participants;
o
inherit rules of engagement from parent to child social
structures.
·
Social structures have roles and members and this impacts who may be authorized to
act and in what circumstances. This requires mechanisms to:
o
identify and manage members of social
structures
o
Identify and manage attributes of the members
o
describe roles and role
adoption
·
Social structures overlap and interact, giving rise to situations
in which rules of engagement may conflict. In addition, a given actor may be member of multiple social
structures and the social structures may be associated with different
jurisdictions. This requires mechanisms to:
o
identify the social structures that are active during a series of
joint actions;
o
identify and resolve conflicts and inconsistencies.
Communication about and between, visibility into, and
leveraging of resources requires the unambiguous identification of those
resources. Ensuring unambiguous identities implies
·
Mechanism for assigning and guaranteeing uniqueness of globally
unique identifiers
·
Identifying the extent of the enterprise over which the
identifier needs to be understandable and unique
·
Mechanism and framework for ensuring the long-livedness of
identifiers (i.e., they cannot just change arbitrarily)
·
Policies are constraints
o
Policies MUST be expressed
o
Constraints MUST be enforceable
o
Manage,emt of potentially large numbers of policies MUST be
achievable
·
Policies have owners
o
Policies SHOULD be established by social structures.
·
Policies may not be consistent with one another
o
Policy conflict resolution techniques MUST
exist and be in place
·
Agreements are constraints agreed to
o
Contracts SHOULD be enforced by mechanisms of the social
structure
Using message exchange for mediating action
implies
·
Ensuring correct identification of the structure of messages:
o
Identifying the syntax of the message;
o
Identifying the vocabularies used in the communication
o
Identifying the higher-level structure of the communication, such
as policy assertion, contract enforcement, etc.
·
A principal objective of communication is to mediate action
o
Messages convey actions and events
o
Receiving a message is an action, but is
not the same action as the action conveyed by the
message
o
Actions are associated with objectives of the actors
involved
§
Explicit representation of objectives may facilitate automated
processing of messages
o
An actor agreeing to adopt an objective
becomes responsible for that objective
Semantics is pervasive in a SOA ecosystem. There are many
forms of utterance that are relevant to the ecosystem: apart from communicated
content there are policy statements, goals, purposes, descriptions, and
agreements which are all forms of utterance.
The operation of the SOA ecosystem is significantly enhanced
if
·
A careful distinction is made between public semantics and
private semantics. In particular, it MUST be possible for actors to process
content such as communications, descriptions and policies solely on the basis
of the public semantics of those utterances.
·
A well founded semantics ensures that any assertions that are
essential to the operator of the ecosystem (such as policy statements, and
descriptions) have carefully chosen written expressions and associated decision
procedures.
·
The role of vocabularies as a focal point for multiple actors to
be able to understand each other is critical. While no two actors can fully
share their interpretation of elements of vocabularies, ensuring that they do
understand the public meaning of vocabularies’ elements is essential.
In traditional systems, the balance between trust and risk
is achieved by severely restricting interactions and by controlling the participants of a system.
It is important that actors are able to
explicitly reason about both trust and risk in order to effectively participate
in a SOA ecosystem. The more open and public the SOA ecosystem is, the more
important it is for actors to be able to reason about
their participation.
In the process of capturing needs as requirements, and the
subsequent requirements decomposition and allocation processes need to be
informed by capabilities that already exist.
·
Architecture needs to
o
Take into account existing capabilities available as services
Participants participate in a SOA
ecosystem in order to get their needs met. This involves action;
both individual actions and joint actions.
Any architectural realization of a SOA ecosystem should
address:
·
How actions are modeled:
o
Identifying the performer or agent of the action;
o
the target of the action; and the
o
verb of the action.
Any explicit models of joint action should take into account
·
The choreography that defines the joint action.
·
The potential for multiple joint actions to be layered on top of
each other
Make
everything as simple as possible but no simpler.
Albert Einstein
The Realization of a SOA Ecosystem view focuses on
elements that are needed to support the discovery of and interaction with
services. The key questions asked are "What are services, what support is
needed and how are they realized?"
The models in this view include the Service Description Model,
the Service Visibility Model, the Interacting with Services Model, and the
Policies and Contracts Model.

Figure 10 - Model Elements Described in the Realization
of a SOA Ecosystem view
The Service Description Model informs the participants of what services exist and the
conditions under which they can be used. Some of those conditions follow from
policies and agreements on policy that flow from the Policies and Contracts
Model. The information in the service description as augmented by details of policy provides the basis for visibility as
defined in the SOA Reference Model and captured in the Service Visibility
Model. Finally, the process by which services as described are used under the
defined conditions and agreements is described in the Interacting with Services
Model.
A service description is an artifact, often document-based,
that defines or references the information needed to use, deploy, manage and
otherwise control a service. This includes not only the information and
behavior models associated with a service that define the service interface but
also includes information needed to decide whether the service is appropriate
for the current needs of the service consumer. Thus, the service
description should also include information such as service reachability,
service functionality, and the policies associated with a service.
A service description artifact may be a single document or
it may be an interlinked set of documents. For the purposes of this model,
differences in representation are to be ignored, but the implications of a “web
of documents” are discussed later in this section.
There are several points to note regarding service
description:
·
The Reference Model states that
one of the hallmarks of SOA is the large amount of associated description. The
model presented below focuses on the description of services but it is equally
important to consider the descriptions of the consumer, other participants, and needed resources other than services.
·
Descriptions are inherently
incomplete but may be determined as sufficient when it is possible for
the participants to access and use the
described services based only on the descriptions provided. This means that, at
one end of the spectrum, a description along the lines of “That service on that
machine” may be sufficient for the intended audience. On the other extreme, a
service description with a machine-process-able description of the semantics of
its operations and real world effects may be required for
services accessed via automated service discovery and planning systems.
·
Descriptions come with context, i.e. a given description
comprises information needed to adequately support the context. For example, a
list of items can define a version of a service, but for many contexts an
indicated version number is sufficient without the detailed list. The current
model focuses on the description needed by a service consumer to understand what the
service does, under what conditions he service will do it, how well the service
does it, and what steps are needed by the consumer to initiate and complete a
service interaction. Such information also enables the service provider to
clearly specify what is being provided and the intended conditions of use.
·
Descriptions change over time as, for example, the ingredients
and nutrition information for food labeling continues to evolve. A requirement
for transparency of transactions may require additional description for those
associated contexts.
·
Description always proceeds from a basis of what is considered
"common knowledge". This may be social conventions that are commonly
expected or possibly codified in law. It is impossible to describe everything
and it can be expected that a mechanism as far reaching as SOA will also
connect entities where there is inconsistent "common" knowledge.
·
Descriptions become the collection point of information related
to a service or any other resource, but it is not necessarily the
originating point or the motivation for generating this information. In
particular, given a SOA service as the access to an underlying capability, the
service may point to some of the capability’s previously generated description,
e.g. a service providing access to a data store may also have access to
information indicating the freshness of the data.
These points emphasize that there is no one “right”
description for all contexts and for all time. Several descriptions for the
same subject may exist at the same time, and this emphasizes the importance of
the description referencing source material maintained by that material’s owner
rather than having multiple copies that become out of synch and inconsistent.
It may also prove useful for a description assembled for one
context to cross-reference description assembled for another context as a way
of referencing ancillary information without overburdening any single
description. Rather than a single artifact, description can be thought of as a
web of documents that enhance the total available description.
This Reference Architecture Foundation uses the term service
description for consistency with the concept defined in the Reference Model.
Some SOA literature treats the idea of a “service contract” as equivalent to
service description. In the SOA-RAF, the term service description is
preferred. Replacing the term “service description” with the term “service
contract” implies that just one side of the interaction is governing and misses
the point that a single set of policies identified by a service description may
lead to numerous contracts, i.e. service level agreements,
leveraging the same description.
Figure 11 shows Service Description as a subclass of the
general Description class, where Description is a subclass of the resource class as defined in Section 3.1.3.1. In addition, each resource is assumed to have a description.
The following section discusses the relationships among elements of general
description and the subsequent sections focus on service description. Other
descriptions, such as those of participants, are important to SOA but are not
individually elaborated in this document.
The general Description class is composed of a number of
elements that are expected to be common among all descriptions supporting a
service oriented architecture. A registry often contains a subset of the
description instance, where the chosen subset is identified as that which
facilitates discovery. Additional information contained in a more complete
description may be needed to initiate and continue interaction.

Figure 11 - General Description
While the resource Identifier provides the means to
know which subject and subject description are being considered, Provenance as
related to the Description class provides information that reflects on the
quality or usability of the subject. Provenance specifically identifies the
stakeholder (human, defined role, organization, ...) that assumes
responsibility for the resource being described and tracks
historic information that establishes a context for understanding what the resource provides and how it has changed
over time. Responsibilities may be directly assumed by
the stakeholder who owns a resource or the Owner may designate
Responsible Parties for the various aspects of maintaining the resource and provisioning it for use by
others. There may be more than one stakeholder identified under Responsible
Parties; for example, one stakeholder may be responsible for code maintenance while
another is responsible for provisioning of the executable code.
4.1.1.1.2 Keywords and Classification Terms
A traditional element of description has been to associate
the resource being described with predefined
keywords or classification taxonomies that derive from referenceable formal
definitions and vocabularies. This Reference Architecture Foundation does not
prescribe which vocabularies or taxonomies may be referenced, nor does it limit
the number of keywords or classifications that may be associated with the resource. It does, however, state that a
normative definition of any terms or keywords SHOULD be referenced, whether
that be a representation in a formal ontology language, a pointer to an online
dictionary, or any other accessible source. See Section 4.1.1.2 for further discussion on associating semantics with assigned values.
The general description instance may also reference
associated documentation that is in addition to that considered necessary in
this model. For example, the owner of a service may have documentation on best
practices for using the service. Alternately, a third party may certify a
service based on their own criteria and certification process; this may be
vital information to other prospective consumers if they were willing to accept
the certification in lieu of having to perform another certification
themselves. Note, while the examples of Associated Documentation presented
here are related to services, the concept applies equally to description of
other entities.

Figure 12 - Representation of a Description
Figure 11 shows the template for a general description, but
individual description instances depend on the ability to associate meaningful
values with the identified elements. Figure 12 shows a model for a collection
of information that provides for value assignment and traceability for both the
meaning and the source of a value. The model is not meant to replace existing
or future schema or other structures that have or will be defined for specific
implementations, but it is meant as guidance for the information such
structures need to capture to generate sufficient description. It is expected
that tools will be developed to assist the user in populating description and
auto-filling many of these fields, and in that context, this model provides
guidance to the tool developers.
In Figure 12, each class has an associated value specifier
or is made up of components that eventually resolve to a value specifier. For
example, Description has several components, one of which is Categorization,
which would have an associated value specifier.
A value specifier consists of
·
a collection of value sets with associated property-value pairs,
pointers to such value sets, or pointers to descriptions that eventually
resolve to value sets that describe the component; and
·
attributes that qualify the value specifier and the value sets it
contains.
The qualifying attributes for the value specifier include
·
an optional identifier that would allow the value set to be
defined, accessed, and reused elsewhere;
·
provenance information that identifies the party (individual, role, or organization) that has
responsibility for assigning the value sets to any description component;
·
an optional source of the value set, if appropriate and
meaningful, e.g. if a particular data source is mandated.
If the value specifier is contained within a higher-level
component (such as Service Description containing Service Functionality), the
component may assume values from the attributes of its container.
Note, provenance as a qualifying attribute of a value
specifier is different from provenance as part of an instance of Description.
Provenance for a service identifies those who own and are responsible for the
service, as described in Section 3.1.3. Provenance for a value specifier
identifies who is responsible for choosing and assigning values to the value
sets that comprise the value specifier. It is assumed that granularity at the
value specifier level is sufficient and provenance is not required for each
value set.
The value set also has attributes that define its structure
and semantics.
·
The semantics of the value set property should be associated with
a semantic context conveying the meaning of the property within the execution
context, where the semantic context could vary from a free text definition to a
formal ontology.
·
For numeric values, the structure would provide the numeric
format of the value and the “semantics” would be conveyed by a dimensional unit
with an identifier to an authoritative source defining the dimensional unit and
preferred mechanisms for its conversion to other dimensional units of like
type.
·
For nonnumeric values, the structure would provide the data
structure for the value representation and the semantics would be an associated
semantic model.
·
For pointers, architectural guidelines would define the preferred
addressing scheme.
The value specifier may indicate a default semantic model
for its component value sets and the individual value sets may provide an
override.
The property-value pair construct is introduced for the
value set to emphasize the need to identify unambiguously both what is being
specified and what is a consistent associated value. The further qualifying of
Structure and Semantics in the Set Attributes allows for flexibility in
defining the form of the associated values.
4.1.1.3 Model Elements Specific to Service Description

Figure 13 - Service Description
The major elements for the Service Description subclass
follow directly from the areas discussed in the Reference Model. Here, we
discuss the detail shown in Figure 13 and the purpose served by each element of
service description.
Note, the intent in the subsections that follow is to
describe how a particular element, such as the service interface, is reflected
in the service description, not to elaborate on the details of that element.
4.1.1.3.1 Service Interface
As noted in the Reference Model, the service interface is
the means for interacting with a service. For the SOA-RAF and as shown in
Section 4.3 the service interface supports an exchange of messages, where
·
the message conforms to a referenceable message exchange pattern
(MEP),
·
the message payload conforms to the structure and semantics of
the indicated information model,
·
the messages are used to denote events or actions against the service,
where the actions are specified in the action model and any required sequencing of
actions is specified in the process model.

Figure 14 - Service Interface
Note we distinguish the structure and semantics of the
message from that of the underlying protocol that conveys the message. The
message structure may include nested structures that are independently defined,
such as an enclosing envelope structure and an enclosed data structure.
These aspects of messages are discussed in more detail in
Section 4.3.2.
4.1.1.3.2 Service Reachability
Service reachability, as modeled in Section 4.2.2.3 enables service participants to locate and interact with
one another. To support service reachability, the service description should
indicate the endpoints to which a service consumer can direct messages to
invoke actions and the protocol to be used for message exchange using that
endpoint.
As generally applied to an action, the endpoint is the conceptual
location where one applies an action; with respect to service
description, it is the actual address where a message is sent.
While the service interface and service reachability are
concerned with the mechanics of using a service, service functionality and
performance metrics (discussed in Section 4.1.1.3.4) describe what can be
expected as a result of interacting with a service. Service Functionality,
shown in Figure 13 as part of the overall Service Description model and
extended in Figure 15, is a clear expression of service function(s) and the real world effects of invoking the
function. The Functions represent business activities in some domain that
produce the desired real world effects.

Figure 15 - Service Functionality
The Service Functionality may also be limited by technical
assumptions/constraints that underlie the effects that can result. Technical
constraints are defined as domain specific restrictions and may express underlying
physical limitations, such as flow speeds must be below sonic velocity or disk
access that cannot be faster than the maximum for its host drive. Technical
constraints are related to the underlying capability accessed by the service.
In any case, the real world effects must be consistent with
the technical assumptions/constraints.
In Figure 13 and Figure 15, we specifically refer to Service
Level and Action Level real world effects.
Service Level Real World Effect
A service level real world effect is a specific change in
the state or the information returned as a result of interacting with a
service.
Action Level Real World Effect
An action level real world effect is a specific change in the
state or the information returned as a result of interacting through a specific
action.
Service description describes the service as a whole while
the component aspects should contribute to that whole. Thus, while individual
Actions may contribute to the real world effects to be realized from
interaction with the service, there would be a serious disconnect for Actions
to contribute real world effects that could not
consistently be reflected in the Service Level Real World Effects and thus the
Service Functionality. The relationship to Action Level Real World Effects and
the implications on defining the scope of a service are discussed in Section 4.1.2.1.
Elements of Service Functionality may be expressed as
natural language text, reference an existing taxonomy of functions or other
formal model.
Policies prescribe the conditions and constraints for
interacting with a service and impact the willingness to continue visibility
with the other participants. Whereas technical constraints
are statements of “physical” fact, policies are subjective assertions made by
the service provider (sometimes as passed on from higher authorities).
The service description provides a central location for
identifying what policies have been asserted by the service provider. The
specific representation of the policy, e.g. in some formal policy language, is outside of the service
description. The service description would reference the normative definition
of the policy.
Policies may also be asserted by other service participants, as illustrated by the model
shown in Figure 16. Policies that are generally applicable to any interaction
with the service are asserted by the service provider and included in the
Service Policies section of the service description.

Figure 16 - Model for Policies and Contracts as
related to Service Participants
In Figure 16, we specifically refer to policies at the
service level. In a similar manner to that discussed for Service Level vs.
Action Level Real World Effects in Section 4.1.1.3.3, individual Actions may
have associated policies stating conditions for performing the action, but these must be reflected in and
be consistent with the policies made visible at the service level and thus the
description of the service as a whole. The relationship to Action Level
Policies and the implications on defining the scope of a service are discussed
in Section 4.1.2.1.
As noted in Figure 16, the policies asserted may be
reflected as Technical Constraints that available services or their underlying
capabilities must be capable of meeting; it may similarly affect the semantics
that can be used. For example of the former, there may be a policy that specifies the surge capacity to
be accommodated by a server, but a service that is not designed to make use of
the larger server capacity would not satisfy the intent of the policy and
would not be appropriate to use. For the latter, a policy may require that only services that
support interaction via a community-sponsored vocabulary can be used.
Contracts are agreements among the service participants. The contract may reconcile
inconsistent policies asserted by the participants or may specify details of the
interaction. Service level agreements (SLAs) are one commonly used category of
contracts.
The definition and later enforcement of policies and contracts are predicated on the potential
for measurement; the relationships among the relevant concepts are shown in the
model in Figure 17. Performance Metrics identify quantities that characterize
the speed and quality of realizing the real world effects produced using the SOA
service; in addition, policies and contracts may depend on nonperformance
metrics, such as whether a license is in place to use the service. Some of
these metrics reflect the underlying capability, e.g. a SOA service cannot
respond in two seconds if the underlying capability is expected to take five
seconds to do its processing; some metrics reflect the SOA service, e.g. the
additional overhead introduced when making data access requests across the
network.
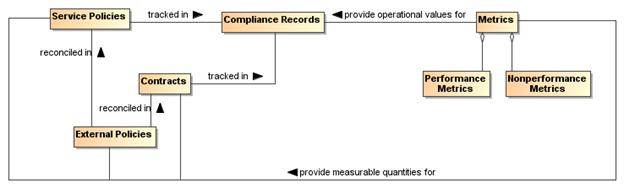
Figure 17 - Policies and Contracts, Metrics, and Compliance Records
As with many quantities, the metrics associated with a
service are not themselves defined by this Service Description Model because it
is not known a priori which metrics are being collected or otherwise
checked by the services, the SOA infrastructure, or other resources that
participate in the SOA interactions. However, the service description SHOULD
provide a placeholder (possibly through a link to an externally compiled list)
for identifying which metrics are available and how these can be accessed.
The use of metrics to evaluate compliance is discussed in
Section 4.1.1.3.4. The results of compliance evaluation SHOULD be maintained in
compliance records and the means to access the compliance records MAY be
included in the Service Policies portion of the service description. For
example, the description may be in the form of static information (e.g. over
the first year of operation, this service had a 91% availability), a link to a
dynamically generated metric (e.g. over the past 30 days, the service has had a
93.3% availability), or access to a dynamic means to check the service for
current availability (e.g., a ping). The relationship between service presence
and the presence of the individual actions that can be invoked is discussed
under Reachability in Section 4.2.2.3.
Note, even when policies relate to the perspective of a
single participant, policy compliance can be measured and
policies may be enforceable without contractual agreement with other participants. While certain elements of
contracts and contract compliance are likely private, public aspects of
compliance should be reflected in the compliance record information referenced
in the service description.
If we assume we have awareness, the service participants must still establish
willingness and presence to ensure full visibility (See Section 4.2) and to interact with the service. Service description provides necessary
information for many aspects of preparing for and carrying through with
interaction. Recall the fundamental definition of service is a mechanism to
access an underlying capability; the service description describes this
mechanism and its use. It lays the groundwork for what can occur, whereas
service interaction comprises the specifics through which real-world effects
are realized.

Figure 18 - Relationship between Action and Components of Service Description Modelx
Figure 18 combines the models in the subsections of Section 4.1.1 to concisely relate action and the relevant components of the
Service Description model. The purpose of Figure 18 is to demonstrate that the
components of service description go beyond arbitrary documentation and form
the critical set of information needed to define the what and how of action. In Figure 18, the leaf nodes from Figure 13 are shown in blue.
Action is typically invoked via a Message where the
structure and behavioral details of the message conform to an identified
Protocol and is directed to the address of the identified endpoint, and the
message payload conforms to the service Information Model.
The availability of an action is reflected in the Action Presence
and each Action Presence contributes to the overall Service Presence; this is
discussed further in Section 4.2.2.3. Each action has its own endpoint and also its
own protocols associated with the endpoint[7]
and to some extent, e.g. current or average availability, there is presence for
the action through that endpoint. The endpoint
and service presence are also part of the service description.
An action may have preconditions where a
Precondition is something that needs to be in place before an action can occur, e.g. confirmation of a
precursor action. Whether preconditions are
satisfied is evaluated when an actor tries to perform the action and not before. Presence for an action means an actor can initiate it and
is independent of whether the preconditions are satisfied. However, the
successful completion of the action may depend on whether its
preconditions were satisfied.
Analogous to the relationship between actions and
preconditions, the Process Model may imply Dependencies for succeeding steps in
a process, e.g. that a previous step has successfully completed, or may be
isolated to a given step. An example of the latter would be a dependency that
the host server has scheduled maintenance and access attempts at these times
would fail. Dependencies related to the process model do not affect the
presence of a service although these may affect whether the business function successfully
completes.
The conditions under which an action can be invoked may depend on
policies associated with the action. The Action Level Policies MUST be
reflected in (or subsumed by) the Service Policies because such policies may be
critical to determining whether the conditions for use of the service are
consistent with the policies asserted by the service consumer. The Service Policies are
included in the service description.
Similarly, the result of invoking an action is one or more real world effects, and any Action Level
Real World Effects MUST be reflected in the Service Level Real World Effect
included in the service description. The unambiguous expression of action
level policies and real world effects as service counterparts
is necessary to adequately describe what constitutes the service interaction.
An adequate service description MUST provide a consumer with
information needed to determine if the service policies, the (business)
functions, and service-level real world effects are of interest, and there is
nothing in the technical constraints that preclude use of the service.
Note at the service level, the business functions are not
concerned with the action or process models. These models are detailed
separately.
The service description is not intended to be isolated
documentation but rather an integral part of service use. Changes in service
description SHOULD immediately be made known to consumers and potential
consumers.
4.1.2.1.1 Description and Invoking Actions Against a Service
At this point, let us assume the descriptions were
sufficient to establish willingness; see Section 4.2.2.2. Figure 18 indicates the service endpoint establishes where to actually carry out the interaction.
This is where we start considering the action and process models.
The action model identifies the multiple actions a user can
perform against a service and the user would perform these in the context of
the process model as specified or referenced under the Service Interface
portion of Service Description. For a given business function, there is a
corresponding process model, where any process model may involve multiple
actions. From the above discussion of model elements of description we may conclude
(1) actions have reachability information, including endpoint and presence, (2)
presence of service is some aggregation of presence of its actions, (3) action
preconditions and service dependencies do not affect presence although these
may affect successful completion.
Having established visibility, the interaction can proceed.
Given a business function, the consumer knows what will be accomplished (the
service functionality), the conditions under which interaction will proceed
(service policies and contracts), and the process that must be
followed (the process model). The remaining question is how the description
information for structure and semantics enable interaction.
We have established the importance of the process model in
identifying relevant actions and their sequence. Interaction proceeds through
messages and thus it is the syntax and semantics of the messages with which we
are here concerned. A common approach is to define the structure and semantics
that can appear as part of a message; then assemble the pieces into messages;
and, associate messages with actions. Actions make use of structure and
semantics as defined in the information model to describe its legal messages.
The process model identifies actions to be performed against
a service and the sequence for performing the actions. For a given action, the Reachability portion of
description indicates the protocol bindings that are available, the endpoint
corresponding to a binding, and whether there is presence at that endpoint. An
interaction is through the exchange of messages that conform to the structure
and semantics defined in the information model and the message sequence
conforming to the action’s identified MEP. The result is
some portion of the real world effect that must be assessed
and/or processed (e.g. if an error exists, that part that covers the error
processing would be invoked).
4.1.2.1.2 The Question of Multiple Business Functions
Action level effects and policies MUST be reflected at the
service level for service description to support visibility.
It is assumed that a SOA service represents an identifiable
business function to which policies can be applied and from which desired
business effects can be obtained. While contemporary discussions of SOA
services and supporting standards do not constrain what actions or combinations
of actions can or should be defined for a service, the SOA-RAF considers the
implications of service description in defining the range of actions
appropriate for an individual SOA service.
Consider the situation if a given SOA service is the
mechanism for access to multiple independent (but loosely related) business
functions. These are not multiple effects from a single function but multiple
functions with potentially different sets of effects for each function. A
service can have multiple actions a user may perform against it, and this does
not change with multiple business functions. As an individual business function
corresponds to a process model, so multiple business functions imply multiple
process models. The same action may be used in multiple process
models but the aggregated service presence would be specific to each business
function because the components being aggregated may be different between
process models. In summary, for a service with multiple business functions,
each function has (1) its own process model and dependencies, (2) its own
aggregated presence, and (3) possibly its own list of policies and real world effects.
A common variation on this theme is for a single service to
have multiple endpoints for different levels of quality of service (QoS).
Different QoS imply separate statements of policy, separate endpoints, possibly
separate dependencies, and so on. One could say the QoS variation does not
require this because there can be a single QoS policy that encompasses the
variations, and all other aspects of the service would be the same except for
the endpoint used for each QoS. However, the different aspects of policy at
the service level would need to be mapped to endpoints, and this introduces an
undesirable level of coupling across the elements of description. In addition,
it is obvious that description at the service level can become very complicated
if the number of combinations is allowed to grow.
One could imagine a service description that is basically a
container for action descriptions, where each action
description is self contained; however, this would lead to duplication of
description components across actions. If common description components are
factored, this either is limited to components common across all actions or
requires complicated tagging to capture the components that often but do not
universally apply.
If a provider cannot describe a service as a whole but must
describe every action, this leads to the situation where
it may be extremely difficult to construct a clear and concise service
description that can effectively support discovery and use without tedious
logic to process the description and assemble the available permutations. In
effect, if adequate description of an action begins to look like description of a
service, it may be best to have it as a separate service.
Recall, more than one service can access the same underlying
capability, and this is appropriate if a different real world effect is to be exposed. Along
these lines, one can argue that different QoS are different services because
getting a response in one minute rather than one hour is more than a QoS
difference; it is a fundamental difference in the business function being
provided.
As a best practice, a criteria for whether a service is
appropriately scoped may be the ease or difficulty in creating an unambiguous
service description. A consequence of having tightly-scoped services is there
will likely be a greater reliance on combining services, i.e. more fundamental
business functions, to create more advanced business functions. This is
consistent with the principles of service oriented architecture and is the
basic position of the Reference Architecture, although not an absolute
requirement. Combining services increases the reliance on understanding and
implementing the concepts of orchestration, choreography, and other approaches
yet to be developed; these are discussed in more detail in section 4.4
Interacting with Services.
4.1.2.1.3 Service Description, Execution Context, and Service Interaction
The service description MUST provide sufficient information
to support service visibility, including the willingness of service participants to interact. However, the
corresponding descriptions for providers and consumers may both contain
policies, technical assumptions, constraints on semantics, and other technical
and procedural conditions that must be aligned to define the terms of
willingness. The agreements which encapsulate the necessary alignment form the
basis upon which interactions may proceed – in the Reference Model, this
collection of agreements and the necessary environmental support establish the
execution context.
To illustrate the concept of the execution context, consider
a Web-based system for timecard entry. For an employee onsite at an employer
facility, the execution context requires a computer connected to the local
network and the employee must enter their network ID and password. Relevant
policies include that the employee must maintain the most recent anti-virus
software and virus definitions for any computer connected to the network.
For the same employee connecting from offsite, the execution
context specifies the need for a computer with installed VPN software and a
security token to negotiate the VPN connection. The execution context also
includes proxy settings as needed to connect to the offsite network. The
employee must still comply with the requirements for onsite computers and
access, but the offsite execution context includes additional items before the
employee can access the same underlying capability and realize the same real world effect s, i.e. the timecard
entries.

Figure 19 - Execution Context
Figure 19 shows a few broad categories found in execution
context. These are not meant to be comprehensive. Other items may need to be
included to provide a sufficient description of the interaction conditions.
Any other items not explicitly noted in the model but needed to set the
environment SHOULD be included in the execution context.
While the execution context captures the conditions under
which interaction can occur, it does not capture the specific service
invocations that do occur in a specific interaction. A service interaction as
modeled in Figure 20 introduces the concept of an Interaction Description which
is composed of both the Execution Context and an Interaction Log. The execution
context specifies the set of conditions under which the interaction occurs and
the interaction log captures the sequence of service interactions that occur
within the execution context. This sequence should follow the Process Model
but can include details beyond those specified there. For example, the Process
Model may specify an action that results in identifying a data
source, and the identified source is used in a subsequent action. The Interaction Log would record
the specific data source used.
The execution context can be thought of as a container in
which the interaction occurs and the interaction log captures what happens
inside the container. This combination is needed to support auditability and
repeatability of the interactions.

Figure 20 - Interaction Description
SOA allows flexibility to accomplish both repeatability and
reusability. In facilitating reusability, a service can be updated without
disrupting the user experience of the service. So, Google can improve their
ranking algorithm without notifying the user about the details of the update.
However, it may also be vital for the consumer to be able to
recreate past results or to generate consistent results in the future, and
information such as what conditions, which services, and which versions of
those services were used is indispensible in retracing one’s path. The
interaction log is a critical part of the resulting real world effects because it defines how
the effects were generated and possibly the meaning of observed effects. This
increases in importance as dynamic composability becomes more feasible. In
essence, a result has limited value if one does not know how it was generated.
The interaction log SHOULD be a detailed trace for a
specific interaction, and its reuse is limited to duplicating that
interaction. An execution context can act as a template for identical or
similar interactions. Any given execution context MAY define the conditions of
future interactions.
Such uses of execution context imply (1) a standardized
format for capturing execution context and (2) a subclass of general
description could be defined to support visibility of saved execution
contexts. The specifics of the relevant formats and descriptions are beyond
the scope of this document.
A service description is unlikely to track interaction
descriptions or the constituent execution contexts or interaction logs that
include mention of the service. However, as appropriate, linking to specific
instances of either of these could be done through associated annotations.
While the representation shown in Figure 12 is derived from
considerations related to service description, it is acknowledged that other
metadata standards are relevant and should, as possible, be incorporated into
this work. Two standards of particular relevance are the Dublin Core Metadata
Initiative (DCMI) [DCMI] and ISO 11179 [ISO 11179], especially
Part 5.
When the service description (or even the general
description class) is considered as the DCMI “resource”, Figure 12 aligns
nicely with the DCMI resource model. While some differences exist, these are
mostly in areas where DCMI goes into detail that is considered beyond the scope
of the current Reference Architecture. For example, DCMI defines classes of
“shared semantics” whereas this Reference Architecture Framework considers that
an identification of relevant semantic models is sufficient. Likewise, the
DCMI “description model” goes into the details of possible syntax encodings whereas
for the Reference Architecture Framework it is sufficient to identify the
relevant formats.
With respect to ISO 11179 Part 5, the metadata fields
defined in that reference may be used without prejudice as the properties in Figure 12. Additionally, other defined metadata sets may be used by the service
provider if the other sets are considered more appropriate, i.e. it is
fundamental to this reference architecture to identify the need and the means
to make vocabulary declarations explicit but it is beyond the scope to specify
which vocabularies are to be used. In addition, the identification of domain
of the properties and range of the values has not been included in the current
Reference Architecture discussion, but the text of ISO 11179 Part 5 can be used
consistently with the model prescribed in this document.
Description as defined here considers a wide range of
applicability and support of the principles of service oriented architecture.
Other metadata models can be used in concert with the model presented here
because most of these focus on a finer level of detail that is outside the
present scope, and so provide a level of implementation guidance that can be
applied as appropriate.
The definition of service description indicates numerous
architectural implications on the SOA ecosystem:
·
It changes over time and its contents will reflect changing needs
and context. This requires the existence of:
o
mechanisms to support the storage, referencing, and access to
normative definitions of one or more versioning schemes that may be applied to
identify different aggregations of descriptive information, where the different
schemes may be versions of a versioning scheme itself;
o
configuration management mechanisms to capture the contents of
each aggregation and apply a unique identifier in a manner consistent with an
identified versioning scheme;
o
one or more mechanisms to support the storage, referencing, and
access to conversion relationships between versioning schemes, and the
mechanisms to carry out such conversions.
·
Description makes use of defined semantics, where the semantics
may be used for categorization or providing other property and value
information for description classes. This requires the existence of:
o
semantic models that provide normative descriptions of the
utilized terms, where the models may range from a simple dictionary of terms to
an ontology showing complex relationships and capable of supporting enhanced
reasoning;
o
mechanisms to support the storage, referencing, and access to
these semantic models;
o
configuration management mechanisms to capture the normative
description of each semantic model and to apply a unique identifier in a manner
consistent with an identified versioning scheme;
o
one or more mechanisms to support the storage, referencing, and
access to conversion relationships between semantic models, and the mechanisms
to carry out such conversions.
·
Descriptions include reference to policies defining conditions of
use. In this sense, policies are also resources that need to be visible,
discoverable, and accessible. This requires the existence of (as also
enumerated under governance):
o
description of policies, including a unique identifier for the
policy and a sufficient, and preferably a machine processible, representation
of the meaning of terms used to describe the policy, its functions, and its effects;
o
one or more discovery mechanisms that enable searching for
policies that best meet the search criteria specified by the service participant; where the discovery mechanism
has access to the individual policy descriptions, possibly through some
repository mechanism;
o
accessible storage of policies and policy descriptions, so service participants can access, examine, and use
the policies as defined.
·
Descriptions include references to metrics which describe the
operational characteristics of the subjects being described. This requires the
existence of (as partially enumerated under governance):
o
the infrastructure monitoring and reporting information on SOA
resources;
o
possible interface requirements to make accessible metrics
information generated;
o
mechanisms to catalog and enable discovery of which metrics are
available for a described resources and information on how these metrics can be
accessed;
o
mechanisms to catalog and enable discovery of compliance records
associated with policies and contracts that are based on these metrics.
·
Descriptions of the interactions are important for enabling
auditability and repeatability, thereby establishing a context for results and
support for understanding observed change in performance or results. This
requires the existence of:
o
one or more mechanisms to capture, describe, store, discover, and
retrieve interaction logs, execution contexts, and the combined interaction descriptions;
o
one or more mechanisms for attaching to any results the means to
identify and retrieve the interaction description under which the results were
generated.
·
Descriptions may capture very focused information subsets or can
be an aggregate of numerous component descriptions. Service description is an
example of an aggregate for which manual maintenance of the whole would not be
feasible. This requires the existence of:
o
tools to facilitate identifying description elements that are to
be aggregated to assemble the composite description;
o
tools to facilitate identifying the sources of information to
associate with the description elements;
o
tools to collect the identified description elements and their
associated sources into a standard, referenceable format that can support
general access and understanding;
o
tools to automatically update the composite description as the
component sources change, and to consistently apply versioning schemes to
identify the new description contents and the type and significance of change
that occurred.
·
The description is the source of vital information in
establishing willingness to interact with a resource, reachability to make interaction
possible, and compliance with relevant conditions of use. This requires the
existence of:
o
one or more discovery mechanisms that enable searching for
described resources that best meet the criteria
specified by a service participant;
o
tools to appropriately track users of the descriptions and notify
them when a new version of the description is available.
One of the key requirements for participants interacting with each other in
the context of a SOA is achieving visibility: before services can interoperate,
the participants have to be visible to each
other using whatever means are appropriate. The Reference Model analyzes
visibility in terms of awareness, willingness, and reachability. In this
section, we explore how visibility may be achieved.
The relationship of visibility to the SOA ecosystem
encompasses both human social structures and automated IT
mechanisms. Figure 21 depicts a business setting that is a basis for
visibility as related to the social structure Model in the Participation
in a SOA Ecosystem view (see Section 3.1). Service consumers and service providers may
have direct awareness or mediated awareness where mediated awareness is
achieved through some third party. A consumer’s willingness to use a service is
reflected by the consumer’s presumption of satisfying goals and needs based on
the service description. Service providers offer capabilities that have real world effects that result in a change
in state. Reachability of the service by the consumer may lead to interactions
that change the state of the SOA ecosystem. The consumer can measure the
change of state to determine if the claims made by description and the real world effects of consuming the service
meet the consumer’s needs.

Figure 21 - Visibility to Business
Visibility and interoperability in a SOA ecosystem requires
more than location and interface information. A meta-model for this broader
view of visibility is depicted in Section 4.1. In addition to providing
improved awareness of service capabilities through description of information
such as reachability, behavior models, information models, functionality, and
metrics, the service description may contain policies valuable for
determination of willingness to interact.
A mediator using service descriptions may provide event
notifications to both consumers and providers about information relating to the
descriptions. One example of this capability is a publish/subscribe model
where the mediator allows consumers to subscribe to service description version
changes made by the provider. Likewise, the mediator may provide notifications
to the provider of consumers that have subscribed to service description
updates.
Another important capability in a SOA environment is the
ability to narrow visibility to trusted members within a social structure. Mediators for awareness
may provide policy based access to service descriptions
allowing for the dynamic formation of awareness between trusted members.
Attaining visibility is described in terms of steps that
lead to visibility. Different participant communities can bring different
contexts for visibility within a single social structure, and the same general
steps can be applied to each of the contexts to accomplish visibility.
Attaining SOA visibility requires
·
service description creation and maintenance,
·
processes and mechanisms for achieving awareness of and accessing
descriptions,
·
processes and mechanisms for establishing willingness of participants,
·
processes and mechanisms to determine reachability.
Visibility may occur in stages, i.e. a participant can become aware enough to look
or ask for further description, and with this description, the participant can decide on willingness,
possibly requiring additional description. For example, if a potential consumer
has a need for a tree cutting (business) service, the consumer can use a web
search engine to find web sites of providers. The web search engine (a
mediator) gives the consumer links to relevant web pages and the consumer can
access those descriptions. For those prospective providers that satisfy the
consumer's criteria, the consumer's willingness to interact increases. The
consumer may contact several tree services to get detailed cost information (or
arrange for an estimate) and may ask for references (further description). The
consumer is likely to establish full visibility and proceed with interaction
with the tree service who mutually establishes visibility.
An important means for a service participant to be aware of another participant is to have access to a description
of that participant and for the description to have
sufficient completeness to establish the other requirements of visibility.
Awareness is inherently a function
of a participant; awareness can be established
without any action on the part of the target participant other than the target providing
appropriate descriptions. Awareness is often discussed in terms of consumer
awareness of providers but the concepts are equally valid for provider
awareness of consumers.
Awareness can be decomposed into: creating the descriptions,
making them available, and discovering the descriptions. Discovery can be
initiated or it can be by notification. Initiated discovery for business may
require formalization of the required capabilities and resources to achieve business goals.
Achieving awareness in a SOA can range from word of mouth to
formal service descriptions in a standards-based registry-repository. Some
other examples of achieving awareness in a SOA are the use of a web page
containing description information, email notifications of descriptions, and
document based descriptions.
A mediator for awareness is a third party participant that provides awareness to one
or more consumers of one or more services. Direct awareness is awareness
between a consumer and provider without the use of a third party. A
registry/repository can act as a mediator; a Web page displaying similar
information can also be considered a mediator.
Direct awareness may be the result of having previously
established an execution context, or direct awareness may include determining
the presence of services and then querying the service directly for
description. As an example, a priori visibility of some sensor device may
provide the means for interaction or a query for standardized sensor device
metadata may be broadcast to multiple locations. If acknowledged, the service
interface for the device may directly provide description to a consumer so the
consumer can determine willingness to interact.
The same medium for awareness may be direct in one context
and may be mediated in another context. For example, a service provider may
maintain a web site with links to the provider’s descriptions of services
giving the consumers direct awareness to the provider’s services.
Alternatively, a community may maintain a mediated web site with links to
various provider descriptions of services for any number of consumers. More
than one mediator may be involved, as different mediators may specialize in
different mediation functions.
Descriptions may be formal or informal. Section 4.1, provides a comprehensive model for service description that can be used to
mediate visibility. Using consistent description taxonomies and standards based
mediated awareness helps provide more effective awareness.
4.2.2.1.1 Mediated Awareness
Mediated awareness promotes loose coupling by keeping the
consumers and services from explicitly referring to each other. Mediation lets
interaction vary independently. Rather than all potential service consumers being informed on a
continual basis about all services, there is a known or agreed upon facility or
location that stores and supports discovery and/or notification related to the
service description.

Figure 22 - Mediated Service Awareness
In Figure 22, the potential service consumers perform queries or are
notified in order to locate those services that satisfy their needs. As an
example, the telephone book is a mediating registry where individuals perform
manual searches to locate services (i.e. the yellow pages). The telephone book
is also a mediated registry for solicitors to find and notify potential
customers (i.e. the white pages).
In mediated service awareness for large and dynamic numbers
of service consumers and service providers,
the benefits of utilizing the mediator typically far outweigh the management
issues associated with it. Some of the benefits of mediated service awareness
are
·
Potential service consumers have a known location for
searching thereby eliminating needless and random searches
·
Typically a consortium of interested parties (or a sufficiently
large corporation) signs up to host the mediation facility
·
Standardized tools and methods can be developed and promulgated
to promote interoperability and ease of use.
However, mediated awareness can have some risks associated
with it:
·
A single point of failure. If the mediation service fails then a
large number of service providers and consumers are potentially adversely
affected.
·
A single point of control. If the central mediation service is
owned by, or controlled by, someone other than the service consumers and/or providers then the
latter may be put at a competitive disadvantage based on policies of the
discovery provider.
A common mechanism for mediated awareness is a
registry/repository. The registry stores links or pointers to service
description artifacts. The repository in this example is the storage location
for the service description artifacts. Service descriptions can be pushed
(publish/subscribe for example) or pulled from the registry/repository
mediator.
Registries/repositories may be referred to as federated when
supported functions, such as responding to discovery requests, are distributed
across multiple registry/repository instances.
4.2.2.1.2 Awareness in Complex Social Structures
Awareness applies to one or more communities within one or
more social structures where a community
consists of at least one description provider and one description consumer.
These communities may be part of the same social structure or be part of different ones.
In Figure 23, awareness can be between consumers and
providers within a single community, multiple communities, or all communities
in the social structure. The social structure can encourage or restrict
awareness through its policies, and these policies can affect participant willingness. The information
about policies should be incorporated in the relevant descriptions. The social structure also governs the
conditions for establishing contracts, the results of which are
reflected in the execution context if interaction is to proceed.

Figure 23 - Awareness in a SOA Ecosystem
IT policy/contract mechanisms can be used by
visibility mechanisms to provide awareness between communities. The IT
mechanisms for awareness may incorporate trust mechanisms to enable awareness
between trusted communities. For example, government organizations may want to
limit awareness of an organization’s services to specific communities of
interest.
Another common business model for awareness is maximizing
awareness to communities within the social structure, the traditional market
place business model. A centralized mediator often arises as a provider for
this global visibility, a gatekeeper of visibility so to speak. For example,
Google is a centralized mediator for accessing information on the web. As
another example, television networks have centralized entities providing a
level of awareness to communities that otherwise could not be achieved without
going through the television network.
However, mediators have motivations, and they may be
selective in which information they choose to make available to potential
consumers. For example, in a secure environment, the mediator may enforce
security policies and make information selectively available depending on the
security clearance of the consumers.
Having achieved awareness, participants use descriptions to help
determine their willingness to interact with another participant. Both awareness and
willingness are determined prior to consumer/provider interaction.

Figure 24 - Business, Description and Willingness
Figure 24 relates elements of the Participation in a SOA
Ecosystem view, and elements from the Service Description Model to
willingness. By having a willingness to interact within a particular social structure, the social structure
provides the participant access to capabilities based on
conditions the social structure finds appropriate for its
context. The participant can use these capabilities to
satisfy goals and objectives as specified by the participant’s needs.
In Figure 24, information used to determine willingness is
defined by Description. Information referenced by Description may come from
many sources. For example, a mediator for descriptions may provide 3rd party
annotations for reputation. Another source for reputation may be a participant’s own history of interactions
with another participant.
A participant inspects functionality for
potential satisfaction of needs. Identity is associated with any participant, however, identity may or may
not be verified. If available, participant reputation may be a deciding
factor for willingness to interact. Policies and contracts referenced by the description may
be particularly important to determine the agreements and commitments required for business interactions.
Provenance may be used for verification of authenticity of a resource.
Mechanisms that aid in determining willingness make use of
the artifacts referenced by descriptions of services. Mechanisms for
establishing willingness could be as simple as rendering service description
information for human consumption to automated evaluation of functionality,
policies, and contracts by a rules engine. The rules
engine for determining willingness could operate as a policy decision procedure as defined in Section 4.4.
Reachability involves knowing the endpoint, protocol, and
presence of a service. At a minimum, reachability requires information about
the location of the service and the protocol describing the means of
communication.

Figure 25 - Service
Reachability
Endpoint
An endpoint is a reference-able entity, processor or resource against which an action can be performed.
Protocol
A protocol is a structured means by which details of a service
interaction mechanism are defined.
Presence
Presence is the measurement of reachability of a service at
a particular point in time.
A protocol defines a structured method of communication.
Presence is determined by interaction through a communication protocol.
Presence may not be known in many cases until the interaction begins. To
overcome this problem, IT mechanisms may make use of presence protocols to
provide the current up/down status of a service.
Service reachability enables service participants to locate and interact with
one another. Each action may have its own endpoint and also
its own protocols associated with the endpoint and whether there is presence
for the action through that endpoint. Presence of a
service is an aggregation of the presence of the service’s actions, and the
service level may aggregate to some degraded or restricted presence if some action presence is not confirmed. For
example, if error processing actions are not available, the service can still
provide required functionality if no error processing is needed. This implies
reachability relates to each action as well as applying to the
service/business as a whole.
Visibility in a SOA ecosystem has the following
architectural implications on mechanisms providing support for awareness,
willingness, and reachability:
·
Mechanisms providing support for awareness have the following
minimum capabilities:
o
creation of Description, preferably conforming to a standard
Description format and structure;
o
publishing of Description directly to a consumer or through a
third party mediator;
o
discovery of Description, preferably conforming to a standard for
Description discovery;
o
notification of Description updates or notification of the
addition of new and relevant Descriptions;
o
classification of Description elements according to standardized
classification schemes.
·
In a SOA
ecosystem with complex social structures, awareness may be provided for specific communities of interest.
The architectural mechanisms for providing awareness to communities of interest
require support for:
o
policies that allow dynamic formation of communities of interest;
o
trust that awareness can be provided for and only for specific
communities of interest, the bases of which is typically built on keying and
encryption technology.
·
The architectural mechanisms for
determining willingness to interact require support for:
o
verification of identity and credentials of the provider and/or
consumer;
o
access to and understanding of description;
o
inspection of functionality and capabilities;
o
inspection of policies and/or contracts.
·
The architectural mechanisms for
establishing reachability require support for:
o
the location or address of an endpoint;
o
verification and use of a service interface by means of a
communication protocol;
o
determination of presence with an endpoint which may only be
determined at the point of interaction but may be further aided by the use of a
presence protocol for which the endpoints actively participate.
Interaction is the activity involved in using a service to
access capability in order to achieve a particular desired real world effect, where real world effect
is the actual result of using a service. An interaction can be characterized by
a sequence of communicative actions. Consequently, interacting with a service,
i.e. participating in joint action with the service—usually mediated by a
series of message exchanges—involves individual actions performed by both the
service and the consumer.
Note that a participant (or delegate acting on behalf of the participant) can be the sender of a
message, the receiver of a message, or both.
Recall from the Reference Model that service visibility is
the capacity for those with needs and those with capabilities to be able to
interact with each other, and that the service interface is the means by which
the underlying capabilities of a service are accessed. Ideally, the details of
the underlying service implementation are abstracted away by the service
interface. [Service] interaction therefore has a direct dependency on the
visibility of the service as well as its implementation-neutral interface (see Figure 26). Service visibility is composed of awareness, willingness, and
reachability and service interface is composed of the information and behavior
models. Service visibility is modeled in Section 4.2 while service interface
is modeled in Section 4.1.

Figure 26 - Interaction dependencies
The SOA-RAF uses message exchange between service participants to denote actions performed against and by
the service, and to denote events that report on real world effects that are caused by the service
actions. A visual model of the relationship between these concepts is shown in
Figure 27.

Figure 27 - A ''message'' denotes either an action or an event
Both actions and events, realized by
the SOA services, are denoted by the messages. The Reference Model states that
the action model characterizes the “permissible set of actions that may be
invoked against a service.” We extend that notion here to include events as part of the event model and that messages are
intended for invoking actions or for notification of events.
In Section 3.2.3 we saw that participants
interact with each other in order to participate in joint actions. A joint action is not itself the same thing as the result of the joint
action. When a joint action
is participated in with a service, the real world
effect that results may be reported in the form of an event notification.
Message exchange is the means by which service participants (or their delegates)
interact with each other. There are two primary modes of interaction: joint
actions that cause real world effects and
notification of events that report real world effects.[9]
A message exchange is used to affect an action
when the messages contain the appropriately formatted content, are directed towards
a particular action in accordance with the action model, and the delegates involved interpret the message appropriately.
A message exchange is also used to communicate event notifications. An event is an
occurrence that is of interest to some participant;
in our case when some real world effect has
occurred. Just as action messages have formatting requirements, so do event
notification messages. In this way, the Information Model of a service must
specify the syntax (structure), and semantics (meaning) of the action messages
and event notification messages as part of a service interface. It must also
specify the syntax and semantics of any data that is carried as part of a
payload of the action or event notification message. The Information Model is
described in greater detail in the Service Description Model (see Section 4.1).
In addition to the Information Model that describes the
syntax and semantics of the messages and data payloads, exception conditions
and error handling in the event of faults (e.g., network outages, improper
message formats, etc.) must be specified or referenced as part of the Service
Description.
When a message is used to invoke an action,
the correct interpretation typically requires the receiver to perform an
operation, which itself invokes a set of private, internal actions. These operations
represent the sequence of (private) actions a service must perform in order to
validly participate in a given joint action.
Similarly, the correct consequence of realizing a real world effect may be to initiate the reporting
of that real world effect via an event notification.
Message Exchange
The means by which joint action and event notifications are
coordinated by service participants (or delegates).
Operations
The sequence of actions a service must perform in order to
validly participate in a given joint action.
4.3.3.1 Message Exchange Patterns (MEPs)
The basic temporal aspect of service interaction can be
characterized by two fundamental message exchange patterns (MEPs):
·
Request/response to represent how actions cause a real world effect
·
Event notification to represent how events
report a real world effect
This is by no means a complete list of all possible MEPs
used for inter- or intra-enterprise messaging but it does represent those that
are most commonly used in exchange of information and reporting changes in
state both within organizations and across organizational boundaries.

Figure 28 - Fundamental SOA message exchange patterns (MEPs)
Recall from the Reference Model that the Process Model
characterizes “the temporal relationships between and temporal properties of
actions and events associated with interacting with the
service.” Thus, MEPs are a key element of the Process Model. The meta-level
aspects of the Process Model (just as with the Action Model) are provided as
part of the Service Description Model (see Section 4.1).
In the UML sequence diagram shown in Figure 28 it is assumed
that the service participants (consumer and
provider) have delegated message handling to hardware or software delegates
acting on their behalf. In the case of the service
consumer, this is represented by the Consumer Delegate component.
In the case of the service provider, the delegate is
represented by the Service component. The message interchange model
illustrated represents a logical view of the MEPs and not a physical view. In
other words, specific hosts, network protocols, and underlying messaging system
are not shown as these tend to be implementation specific. Although such implementation-specific
elements are considered outside the scope of this document, they are important
considerations in modeling the SOA execution context. Recall from the Reference
Model that the execution context of a service interaction is “the set of
infrastructure elements, process entities, policy assertions and agreements
that are identified as part of an instantiated service interaction, and thus
forms a path between those with needs and those with capabilities.”
4.3.3.2 Request/Response MEP
In a request/response MEP, the Consumer Delegate component
sends a request message to the Service component. The Service component then
processes the request message. Based on the content of the message, the
Service component performs the service operation and the associated private
actions. Following the completion of these operations, a response message is
returned to the Consumer Delegate component. The response could be that a step
in a process is complete, the initiation of a follow-on operation, or the
return of requested information.
Although the sequence diagram shows a synchronous
interaction (because the sender of the request message, i.e., Consumer
Delegate, is blocked from continued processing until a response is returned
from the Service) other variations of request/response are valid, including asynchronous
(non-blocking) interaction through use of queues, channels, or other messaging
techniques.
What is important to convey here is that the
request/response MEP represents action, which causes a
real world effect, irrespective of the
underlying messaging techniques and messaging infrastructure used to implement
the request/response MEP.
4.3.3.3 Event Notification MEP
An event is made visible to interested
consumers by means of an event notification message exchange that reports a real world effect; specifically, a change in shared
state between service participants. The basic event
notification MEP takes the form of a one-way message sent by a notifier
component (in this case, the Service component) and received by components with
an interest in the event (here, the Consumer Delegate
component).
Often the sending component may not be fully aware of all
the components that wish to receive the notification; particularly in so-called
publish/subscribe (“pub/sub”) situations. In event notification message
exchanges, it is rare to have a tightly-coupled link between the sending and
the receiving component(s) for a number of practical reasons. One of the most
common needs for pub/sub messaging is the potential for network outages or
communication interrupts that can result in loss of notification of events. Therefore, a third-party mediator component is often
used to decouple the sending and receiving components.
Although this is typically an implementation issue, because
this type of third-party decoupling is so common in event-driven systems, it is
warranted for use in modeling this type of message exchange in the SOA-RAF.
This third-party intermediary is shown in Figure 28 as an Event Broker
mediator. As with the request/response MEP, no distinction is made between
synchronous versus asynchronous communication, although asynchronous message
exchange is illustrated in the UML sequence diagram depicted in Figure 28 .
Composition of services is the act of aggregating or
“composing” a single service from one or more other services. A simple model
of service composition is illustrated in Figure 29.

Figure 29 - Simple model of service composition
Here, Service A is a service that has an exposed interface
IServiceA, which is available to the Consumer Delegate and relies on two other
services in its implementation. The Consumer Delegate does not know that
Services B and C are used by Service A, or whether they are used in serial or
parallel, or if their operations succeed or fail. The Consumer Delegate only
cares about the success or failure of Service A. The exposed interfaces of
Services B and C (IService B and IServiceC) are not necessarily hidden from the
Consumer Delegate; only the fact that these services are used as part of the
composition of Service A. In this example, there is no practical reason the
Consumer Delegate could not interact with Service B or Service C in some other
interaction scenario.
It is possible for a service composition to be opaque from
one perspective and transparent from another. For example, a service may appear
to be a single service from the Consumer’s Delegate’s perspective, but is
transparently composed of one or more services from a service management
perspective. A Service Management capability needs to be able to have
visibility into the composition in order to properly manage the dependencies
between the services used in constructing the composite service—including
managing the service’s lifecycle. The subject of services as management
entities is described and modeled in the Ownership in a SOA Ecosystem
View of the SOA-RAF and is not further elaborated in this section. The point
to be made here is that there can be different levels of opaqueness or
transparency when it comes to visibility of service composition.
Services can be composed in a variety of ways including
direct consumer-to-service interaction by using programming techniques, or they
can be aggregated by means of an aggregation engine approach that leverages a
service composition scripting language. Such approaches are further elaborated
in the following sub-sections on service-oriented business processes and
collaborations.
4.3.4.1 Service-Oriented Business Processes
The concepts of business processes and collaborations in the
context of transactions and exchanges across organizational boundaries are
described and modeled as part of the Participation in a SOA Ecosystem
view of this reference architecture (see Section 3). Here, we focus on the
belief that the principle of composition of services can be applied to business
processes and collaborations. Of course, business processes and collaborations
traditionally represent complex, multi-step business functions that may involve
multiple participants, including internal users,
external customers, and trading partners. Therefore, such complexities cannot
simply be ignored when transforming traditional business processes and
collaborations to their service-oriented variants.
Business Processes
Business processes are a set of one or more linked
activities that are performed to achieve a certain business outcome.
Service orientation as applied to business processes (i.e.,
“service-oriented business processes”) means that the aggregation or
composition of all of the abstracted activities, flows, and rules that govern a
business process can themselves be abstracted as a service [BLOOMBERG/SCHMELZER].
When business processes are abstracted in this manner and
accessed through SOA services, all of the concepts used to describe and model
composition of services that were articulated in Section 4.3.4 apply. There are some important differences between a composite service that represents an
abstraction of a business process and a composite service that represents a
single-step business interaction. Business processes have temporal properties
and can range from short-lived processes that execute on the order of minutes
or hours to long-lived processes that can execute for weeks, months, or even
years. Further, these processes may involve many participants.
These are important considerations for the consumer of a service-oriented
business process and these temporal properties must be articulated as part of
the meta-level aspects of the service-oriented business process in its Service
Description, along with the meta-level aspects of any sub-processes that may be
of use or need to be visible to the service consumer.
In addition, a workflow activity represents a unit of work
that some actor acting in a described role (i.e., role player) is asked to perform. Activities can be
broken down into steps with each step representing a task for the role player to perform. A technique that is used to
compose service-oriented business processes that are hierarchical (top-down)
and self-contained in nature is known as orchestration.
Orchestration
A technique used to compose service-oriented business
processes that are executed and coordinated by an actor
acting as “conductor.”
An orchestration is typically implemented using a scripting
approach to compose service-oriented business processes. This typically
involves use of a standards-based orchestration scripting language. In terms
of automation, an orchestration can be mechanized using a business process
orchestration engine, which is a hardware or software component (delegate) responsible for acting in the role of central
conductor/coordinator responsible for executing the flows that comprise the
orchestration.
A simple generic example of such an orchestration is
illustrated in Figure 30.

Figure 30 - Abstract example of orchestration of service-oriented business process
Here, we use a UML activity diagram to model the simple
service-oriented business process as it allows us to capture the major elements
of business processes such as the set of related tasks to be performed, linking
between tasks in a logical flow, data that is passed between tasks, and any
relevant business rules that govern the transitions between tasks. A task is a
unit of work that an individual, system, or organization performs and can be
accomplished in one or more steps or subtasks. While subtasks can be readily
modeled, they are not illustrated in the orchestration model in Figure 30.
This particular example is based on a request/response MEP
and captures how one particular task (Task 2) actually utilizes an
externally-provided service, Service B. The entire service-oriented business
process is exposed as Service A that is accessible via its externally visible
interface, IServiceA.
Although not explicitly shown in the orchestration model
above, it is assumed that there exists a software or hardware component, i.e.,
orchestration engine that executes the process flow. Recall that a central
concept to orchestration is that process flow is coordinated and executed by a
single conductor delegate; hence the name “orchestration.”
4.3.4.2 Service-Oriented Business Collaborations
Business collaborations typically represent the interaction
involved in executing business transactions.
It is important to note that business collaborations
represent “peer”-style interactions; in other words, peers in a business collaboration act as equals. This means
that unlike the orchestration of business processes, there is no single or
central entity that coordinates or “conducts” a business collaboration. These
peer styles of interactions typically occur between trading partners that span
organizational boundaries.
Business collaborations can also be service-enabled. For
purposes of this Reference Architecture Foundation, we refer to these as
“service-oriented business collaborations.” Service-oriented business
collaborations do not necessarily imply exposing the entire peer-style business
collaboration as a service itself but rather the collaboration uses
service-based interchanges.
The technique that is used to compose service-oriented
business collaborations in which multiple parties collaborate in a peer-style
as part of some larger business transaction
by exchanging messages with trading partners and external organizations (e.g.,
suppliers) is known as choreography [NEWCOMER/LOMOW].
Choreography
A technique used to characterize service-oriented business
collaborations based on ordered message exchanges between peer
entities in order to achieve a common business goal.
Choreography differs from orchestration primarily in that
each party in a business collaboration describes its part in the service
interaction. Note that choreography as we have defined it here should not be
confused with the term process choreography, which is defined in the Participation
in a SOA Ecosystem view as “the
description of the possible interactions that may take place between two or
more participants to fulfill an objective.” This is an example
of domain-specific nomenclature that often leads to confusion and why we are
making note of it here.
A simple generic example of a choreography is illustrated in
Figure 31.

Figure 31 - Abstract example of choreography of service-oriented business collaboration
This example, which is a variant of the orchestration
example illustrated earlier in Figure 30 adds trust boundaries between two
organizations; namely, Organization X and Organization Y. It is assumed that
these two organizations are peer entities that have an interest in a business
collaboration, for example, Organization X and Organization Y could be trading
partners. Organization X retains the service-oriented business process Service
A, which is exposed to internal consumers via its provided service interface,
IServiceA. Organization Y also has a business process that is involved in the
business collaboration; however, for this example, it is an internal business
process that is not exposed to potential consumers either within or outside its
organizational boundary.
The scripting language that is used for the choreography
needs to define how and when to pass control from one trading partner to
another, i.e., between Organization X and Organization Y. Defining the
business protocols used in the business collaboration involves precisely
specifying the visible message exchange behavior of each of the parties
involved in the protocol, without revealing internal implementation details [NEWCOMER/LOMOW].
In a peer-style business collaboration, a choreography
scripting language must be capable of describing the coordination of those
service-oriented processes that cross organizational boundaries.
Interacting with Services has the following architectural
implications on mechanisms that facilitate service interaction:
·
A well-defined service Information Model that:
o
describes the syntax and semantics of the messages used to denote
actions and events;
o
describes the syntax and semantics of the data payload(s)
contained within messages;
o
documents exception conditions in the event of faults due to
network outages, improper message/data formats, etc.;
o
is both human readable and machine processable;
o
is referenceable from the Service Description artifact.
·
A well-defined service Behavior Model that:
o
characterizes the knowledge of the actions invokes against the
service and events that report real
world effects as a result of those actions;
o
characterizes the temporal relationships and temporal properties
of actions and events associated in a service interaction;
o
describe activities involved in a workflow activity that
represents a unit of work;
o
describes the role (s) that a role player performs in a service-oriented business
process or service-oriented business collaboration;
o
is both human readable and machine processable;
o
is referenceable from the Service Description artifact.
·
Service composition mechanisms to support orchestration of
service-oriented business processes and choreography of service-oriented
business collaborations such as:
o
Declarative and programmatic compositional languages;
o
Orchestration and/or choreography engines that support multi-step
processes as part of a short-lived or long-lived business
transaction;
o
Orchestration and/or choreography engines that support
compensating transactions in the presences of exception and fault conditions.
·
Infrastructure services that provides mechanisms to support
service interaction, including but not limited to:
o
mediation services such as message and event brokers, providers,
and/or buses that provide message translation/transformation, gateway
capability, message persistence, reliable message delivery, and/or intelligent
routing semantics;
o
binding services that support translation and transformation of
multiple application-level protocols to standard network transport protocols;
o
auditing and logging services that provide a data store and
mechanism to record information related to service interaction activity such as
message traffic patterns, security violations, and service contract and policy violations
o
security services that provide centralized authorization and
authentication support, etc., which provide protection against common security
threats in a SOA ecosystem;
o
monitoring services such as hardware and software mechanisms that
both monitor the performance of systems that host services and network traffic
during service interaction, and are capable of generating regular monitoring
reports.
·
A layered and tiered service component architecture that supports
multiple message exchange patterns (MEPs) in order to:
o
promote the industry best practice of separation of concerns that
facilitates flexibility in the presence of changing business requirements;
o
promote the industry best practice of separation of roles in a service development lifecycle such that subject
matter experts and teams are structured along areas of expertise;
o
support numerous standard interaction patterns, peer-to-peer
interaction patterns, enterprise integration patterns, and business-to-business
integration patterns.
A common phenomenon of many machines and systems is that the
scope of potential behavior is much broader than is actually needed for a
particular circumstance. This is especially true of a system as powerful as a
SOA ecosystem. As a result, the behavior and performance of the system tend to
be under-constrained by the implementation; instead, the actual behavior is
expressed by means of policies of some form. Policies define the choices that stakeholders make; these choices are used to guide the
actual behavior of the system to the desired behavior and performance.
As noted in Section 3.1.5, a policy is a constraint of some form that is promulgated by a
stakeholder who has the responsibility of ensuring
that the constraint is enforced. In contrast, contracts
are agreements between participants. However,
like policies, it is a necessary part of contracts that
they are enforceable.
While responsibility for enforcement may differ, both contracts and policies share a common characteristic –
there is a constraint that must be enforced. In both cases the
mechanisms needed to enforce constraints are likely to be identical; in this
model we focus on the issues involved in representing policies and contracts and on some of the principles behind their
enforcement.
A policy constraint is a specific kind of constraint:
the ontology of policies and contracts includes the
core concepts of permission, obligation,
owner, subject. In addition, it may be necessary to be able combine policy
constraints and to be able to resolve policy conflicts.
4.4.1.1 Policy Framework
Policy Framework
A policy framework is a language in which policy constraints
may be expressed.
A policy framework combines a syntax for expressing policy
constraints together with a decision procedure
for determining if a policy constraint is satisfied.

Figure 32 - Policies and
Contracts
We can characterize (caricature) a policy framework in terms
of a logical framework and an ontology of policies. The policy ontology details
specific kinds of policy constraints that can be expressed; and the logical
framework is a ‘glue’ that allows us to express combinations of policies.
Logical Framework
A logical framework is a linguistic framework consisting of
a syntax – a way of writing expressions – and a semantics – a way of
interpreting the expressions.
Policy Ontology
A policy ontology is a formalization of a set of concepts
that are relevant to forming policy expressions.
For example, a policy ontology that allows to identify
simple constraints – such as the existence of a property, or that a value of a
property should be compared to a fixed value – is often enough to express many
basic constraints.
Included in many policy ontologies are the basic signals of permissions and obligations.
Some policy frameworks are sufficiently constrained that there is not
possibility of representing an obligation; in which
case there is often no need to ‘call out’ the distinction between permissions and obligations.
The logical framework is also a strong determiner of the
expressivity of the policy framework: the richer the logical framework, the
richer the set of policy constraints that can be expressed. However, there is a
strong inverse correlation between expressivity and ease and efficiency of
implementation.
In the discussion that follows we assume the following basic
policy ontology:
Policy Owner
A policy owner is a stakeholder
that asserts and enforces the policy.
Policy Subject
A policy subject is an actor who is
subject to the constraints of a policy or contract.
Policy Constraint
A policy constraint is a measurable and enforceable proposition
that characterizes the constraint that the policy is about.
Policy Object
A policy object is an identifiable state, action or resource that is
potentially constrained by the policy.
The enforcement of policy constraints has to address two
core problems: how to enforce the atomic policy constraints, and how to enforce
combinations of policy constraints. In addition, it is necessary to address the
resolution of policy conflicts.
4.4.2.1 Enforcing Simple Policy Constraints
The two primary kinds of policy constraint – permission and obligation – naturally lead to different
styles of enforcement. A permission constraint must
typically be enforced prior to the policy subject invoking the policy
object. On the hand, an obligation constraint must typically be enforced
post-facto through some form of auditing process and remedial action.
For example, if a communications policy required that all
communication be encrypted, this is enforceable at the point of communication:
any attempt to communicate a message that is not encrypted can be blocked.
Similarly, an obligation to pay for services rendered is
enforced by ensuring that payment arrives within a reasonable period of time.
Invoices are monitored for prompt (or lack of) payment.
The key concepts in enforcing both forms of policy
constraint are the policy decision and the policy enforcement.
Policy Decision
A policy decision is a determination as to whether a given
policy constraint is satisfied or not.
A policy decision is effectively a measurement of some state
– typically a portion of the SOA ecosystem’s shared state. This implies
a certain timeliness in the measuring: a measurement that is too early or
is too late does not actually help in determining if the policy constraint is
satisfied appropriately.
Policy Enforcement
A policy enforcement is the use of a mechanism which limits
the behavior and/or state of policy subjects to comply with a policy decision.
A policy enforcement implies the use of some mechanism to
ensure compliance with a policy decision. The range of mechanisms is completely
dependent on the kinds of atomic policy constraints that the policy framework
may support. As noted above, the two primary styles of constraint – permission and obligation –lead to different
styles of enforcement.
4.4.2.2 Conflict Resolution
Whenever it is possible that more than one policy constraint
applies in a given situation, there is the potential that the policy
constraints themselves are not mutually consistent. For example, a policy
constraint that requires communication to be encrypted and a policy constraint that
requires an administrator to read every communication conflict with each other
– the two policy constraints cannot both be satisfied concurrently.
In general, with sufficiently rich policy frameworks, it is
not possible to always resolve policy conflicts automatically. However, a
reasonable approach is to augment the policy decision process with simple
policy conflict resolution rules; with the potential for escalating a
policy conflict to human adjudication.
Policy Conflict
A policy conflict exists between two or more policy
constraints in a policy decision process if the satisfaction of one or more
policy constraints leads directly to the violation of one or more other policy
constraints.
Policy Conflict Resolution
A policy conflict resolution rule is a way of determining
which policy constraints should prevail if a policy conflict occurs.
The inevitable consequence of policy conflicts is that it is
not possible to guarantee that all policy constraints are satisfied at all
times. This, in turn, implies a certain flexibility in the application
of policy constraints: each individual constraint may not always be honored.
The key choices that must be made in a system of policies
center on the policy framework, policy enforcement, and conflict resolution
·
There SHOULD be a standard policy framework that is adopted
across ownership domains within the SOA
ecosystem:
o
This framework MUST permit the expression of simple policy
constraints
o
The framework MAY allow (to a varying extent) the combination of
policy constraints, including
·
Both positive and negative constraints
·
Conjunctions and disjunctions of constraints
·
The quantification of constraints
o
The framework MUST at least allow the policy subject and the
policy object to be identified as well as the policy constraint.
o
The framework MAY allow further structuring of policies into
modules, inheritance between policies and so on.
·
There SHOULD be mechanisms that facilitate the application of
policies:
o
There SHOULD be mechanisms that allow policy decisions to be
made, consistent with the policy frameworks.
o
There SHOULD be mechanisms to enforce policy decisions
·
There SHOULD be mechanisms to support the measurement of whether
certain policy constraints are satisfied or not, or to what degree they are
satisfied.
·
Such enforcement mechanisms MAY include support for both permission-style constraints and obligation-style
constraints.
·
Enforcement mechanisms MAY support the simultaneous enforcement
of multiple policy constraints across multiple points in the SOA ecosystem.
o
There SHOULD be mechanisms to resolve policy conflicts
·
This MAY involve escalating policy conflicts to human
adjudication.
o
There SHOULD be mechanisms that support the management and
promulgation of policies.
Governments
are instituted among Men,
deriving their just power from the consent of the governed
American
Declaration of Independence
The Ownership in a SOA Ecosystem View focuses on the
issues, requirements and responsibilities
involved in owning a SOA-based system.
Ownership of a SOA-based system in a SOA ecosystem raises
significantly different challenges to owning other complex systems – such as
Enterprise suites – because there are strong limits on the control and authority of any one party when a system spans multiple
ownership domains.
Even when a SOA-based system is deployed internally within
an organization, there are multiple internal stakeholders
involved and there may not be a simple hierarchy of control and management.
Thus, an early consideration of how multiple boundaries affect SOA-based
systems provides a firm foundation for dealing with them in whatever form they
are found rather than debating whether the boundaries should exist.
This view focuses on the governance and management of
SOA-based systems, on the security challenges involved in running a SOA-based
system, and testing challenges.

Figure 33 - Model Elements
Described in the Ownership in a SOA Ecosystem View
The following subsections present models of these functions.
The Reference Model defines Service Oriented Architecture as
an architectural paradigm for organizing and utilizing distributed capabilities
that may be under the control of different ownership domains [SOA-RM].
Consequently, it is important that organizations that plan to engage in service
interactions adopt governance policies and procedures sufficient to ensure that
there is standardization across both internal and external organizational
boundaries to promote the effective creation and use of SOA-based services.
5.1.1.1 Terminology
Governance is about making decisions that are aligned with
the overall organizational strategy and culture of the enterprise. [Gartner]
It specifies the decision rights and accountability framework to encourage
desirable behaviors [Weill/Ross-MIT Sloan School] towards realizing the
strategy and defines incentives (positive or negative) towards that end. It is
less about overt control and strict adherence to rules, and more about guidance
and effective and equitable usage of resources to ensure sustainability of an
organization’s strategic objectives. [TOGAF v8.1]
To accomplish this, governance requires organizational
structure and processes and must identify who has authority to define and carry
out its mandates. It must address the following questions:
1. what
decisions must be made to ensure effective management and use?,
2. who should
make these decisions?,
3. how will
these decisions be made and monitored? , and
4. how will
these decisions be communicated?
The intent is to achieve goals, add value, and reduce risk.
Within a single ownership domain such as an enterprise,
generally there is a hierarchy of governance structures. Some of the more
common enterprise governance structures include corporate governance,
technology governance, IT governance, and architecture governance [TOGAF
v8.1]. These governance structures can exist at multiple levels (global,
regional, and local) within the overall enterprise.
It is often asserted that SOA governance is a specialization
of IT governance as there is a natural hierarchy of these types of governance
structures; however, the focus of SOA governance is less on decisions to ensure
effective management and use of IT as it is to ensure effective management and
use of SOA-based systems. Certainly, SOA governance must still answer the
basic questions also associated with IT governance, i.e., who should make the
decisions, and how these decisions will be made and monitored.
5.1.1.2 Relationship to Management
There is often confusion centered on the relationship
between governance and management. As described earlier, governance is
concerned with decision making. Management, on the other hand, is concerned
with execution. Put another way, governance describes the world as leadership
wants it to be; management executes activities that intends to make the
leadership’s desired world a reality. Where governance determines who has the
authority and responsibility for making decisions and the establishment of
guidelines for how those decisions should be made, management is the actual
process of making, implementing, and measuring the impact of those decisions [Loeb].
Consequently, governance and management work in concert to ensure a
well-balanced and functioning organization as well as an ecosystem of
inter-related organizations. In the sections that follow, we elaborate further
on the relationship between governance and management in terms of setting and
enforcing service policies, contracts, and standards as
well as addressing issues surrounding regulatory compliance.
5.1.1.3 Why is SOA Governance Important?
One of the hallmarks of SOA that distinguishes it from other
architectural paradigms for distributed computing is the ability to provide a
uniform means to offer, discover, interact with and use capabilities (as well
the ability to compose new capabilities from existing ones) all in an
environment that transcends domains of ownership.
Consequently, ownership, and issues surrounding it,
such as obtaining acceptable terms and conditions (T&Cs) in a contract, is
one of the primary topics for SOA governance. Generally, IT governance does
not include T&Cs, for example, as a condition of use as its primary
concern.
Just as other architectural paradigms, technologies, and
approaches to IT are subject to change and evolution, so too is SOA. Setting
policies that allow change management and evolution, establishing strategies
for change, resolving disputes that arise, and ensuring that SOA-based systems
continue to fulfill the goals of the business are all reasons why governance is
important to SOA.
5.1.1.4 Governance Stakeholders and Concerns
As noted in Section 3.1.1 the participants
in a service interaction include the service provider, the service consumer, and other interested or
unintentional third parties. Depending on the circumstances, it may also
include the owners of the underlying capabilities that the SOA services
access. Governance must establish the policies and rules under which duties
and responsibilities are defined and the
expectations of participants are grounded. The
expectations include transparency in aspects where transparency is mandated,
trust in the impartial and consistent application of governance, and assurance
of reliable and robust behavior throughout the SOA ecosystem.
Governance
Governance is the prescribing of conditions and constraints
consistent with satisfying common goals and the structures and processes needed
to define and respond to actions taken towards realizing those goals.
The following is a generic model of governance represented
by segmented models that begin with motivation and proceed through measuring
compliance. It is not all-encompassing but a focused subset that captures the
aspects necessary to describe governance for SOA. It does not imply that
practical application of governance is a single, isolated instance of these
models; in reality, there may be hierarchical and parallel chains of governance
that deal with different aspects or focus on different goals. This is discussed
further in section 5.1.2.5. The defined models are simultaneously applicable to
each of the overlapping instances.
A given enterprise may already
have portions of these models in place. To a large extent, the models shown
here are not specific to SOA; discussions on direct applicability begin in
section 5.1.3.
5.1.2.1 Motivating Governance

Figure 34 - Motivating Governance
An organizational domain such as an enterprise
is made up of participants who may be individuals or
groups of individuals forming smaller organizational units within the enterprise. The overall business strategy should be
consistent with the Goals of the participants;
otherwise, the business strategy would not provide value to the participants and governance towards those ends becomes
difficult if not impossible. This is not to say that an instance of governance
simultaneously satisfies all the goals of all the participants;
rather, the goals of any governance instance must sufficiently satisfy a useful
subset of each participant's goals so as to provide
value and ensure the cooperation of all the participants.
A policy is the formal characterization of the conditions
and constraints that governance deems as necessary to realize the goals which
it is attempting to satisfy. Policy may identify required conditions or
actions or may prescribe limitations or other constraints on permitted
conditions or actions. For example, a policy may prescribe that safeguards
must be in place to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive material. It may
also prohibit use of computers for activities unrelated to the specified work
assignment. Policy is made operational through the promulgation and implemention
of Rules and Regulations (as defined in section 5.1.2.3).
As noted in section 4.4.2, policy may be asserted by any participant or on behalf of the participant
by its organization. Part of the purpose of governance
is to arbitrate among diverse goals of participants
and the diverse policies articulated to realize those goals. The intent is to
form a consistent whole that allows governance to minimize ambiguity about its purpose. While resolving all ambiguity would be an ideal,
it is unlikely that all inconsistencies will be identified and resolved before
governance becomes operational.
For governance to have effective jurisdiction over participants, there must be some degree of agreement by
all participants
that they will abide by the governance mandates. A minimal degree of agreement
often presages participants who “slow-roll” if not
actively rejecting compliance with Policies that express the specifics of
governance.
5.1.2.2 Setting Up Governance

Figure 35 - Setting Up Governance
Leadership
Leadership is the entity who has the responsibility and
authority to generate consistent policies through which the goals of governance
can be expressed and to define and champion the structures and processes
through which governance is realized.
Governance Framework
The Governance Framework is a set of organizational
structures that enable governance to be consistently defined, clarified, and as
needed, modified to respond to changes in its domain of concern.
Governance Processes
Governance Processes are the defined set of activities that
are performed within the Governance Framework to enable the consistent
definition, application, and as needed, modification of Rules that organize and
regulate the activities of participants for the
fulfillment of expressed policies. (See section 5.1.2.3 for elaboration on the relationship of Governance Processes and Rules.)
As noted earlier, governance requires an appropriate
organizational structure and identification of who has authority to make
governance decisions. In Figure 35, the entity with governance authority is designated the Leadership. This is someone,
possibly one or more of the participants, which participants recognize as having authority
for a given purpose or over a given set of issues or
concerns.
The Leadership is responsible for prescribing or delegating
a working group to prescribe the Governance Framework that forms the structure
for Governance Processes which define how governance is to be carried out.
This does not itself define the specifics of how governance is to be applied,
but it does provide an unambiguous set of procedures that should ensure
consistent actions which participants agree are fair
and account for sufficient input on the subjects to which governance is
applied.
The participants may be part of
the working group that codifies the Governance Framework and Processes. When
complete, the participants must acknowledge and
agree to abide by the products generated through application of this structure.
The Governance Framework and Processes are often documented
in the charter of a body created or designated to oversee governance. This is
discussed further in the next section. Note that the Governance Processes
should also include those necessary to modify the Governance Framework itself.
An important function of Leadership is not only to initiate
but also be the consistent champion of governance. Those responsible for
carrying out governance mandates must have Leadership who make it clear to participants that expressed Policies are seen as a
means to realizing established goals and that compliance with governance is
required.

Figure 36 - Carrying Out Governance
Rule
A Rule is a prescribed guide for carrying out activities
and processes leading to desired results, e.g. the operational realization of
policies.
Regulation
A Regulation is a mandated process or the specific details
that derive from the interpretation of Rules and lead to measureable quantities
against which compliance can be measured.
To carry out governance, Leadership charters a Governance
Body to promulgate the Rules needed to make the Policies operational. The
Governance Body acts in line with Governance Processes for its rule-making
process and other functions. Whereas Governance is the setting of Policies and
defining the Rules that provide an operational context for Policies, the
operational details of governance may be delegated by the Governance Body to
Management. Management generates Regulations that specify details for Rules
and other procedures to implement both Rules and Regulations. For example,
Leadership could set a Policy that all authorized parties should have access to
data, the Governance Body would promulgate a Rule that PKI certificates are
required to establish identity of authorized parties, and Management can
specify a Regulation of who it deems to be a recognized PKI issuing body. In
summary, Policy is a predicate to be satisfied and Rules prescribe the
activities by which that satisfying occurs. A number of rules may be required
to satisfy a given policy; the carrying out of a rule may contribute to several
policies being realized.
Whereas the Governance Framework and Processes are
fundamental for having participants acknowledge and
commit to compliance with governance, the Rules and Regulations provide
operational constraints which may require resource commitments
or other levies on the participants. It is
important for participants to consider the framework
and processes to be fair, unambiguous, and capable of being carried out in a
consistent manner and to have an opportunity to formally accept or ratify this
situation. Rules and Regulations, however, do not require individual
acceptance by any given participant although some
level of community comment may be part of the Governance Processes. Having
agreed to governance, the participants are bound to
comply or be subject to prescribed mechanisms for enforcement.
5.1.2.4 Ensuring Governance Compliance

Figure 37 - Ensuring Governance
Compliance
Setting Rules and Regulations does not ensure effective
governance unless compliance can be measured and Rules and Regulations can be
enforced. Metrics are those conditions and quantities that can be measured to
characterize actions and results. Rules and Regulations MUST be based on
collected Metrics or there is no means for Management to assess compliance.
The Metrics are available to the participants, the
Leadership, and the Governance Body so what is measured and the results of
measurement are clear to everyone.
The Leadership in its relationship with participants has certain options that can be used for
Enforcement. A common option may be to affect future funding. The Governance
Body defines specific enforcement responses, such as what degree of compliance
is necessary for full funding to be restored. It is up to Management to
identify compliance shortfalls and to initiate the Enforcement process.
Note, enforcement does not strictly need to be negative
consequences. Management can use Metrics to identify exemplars of compliance
and Leadership can provide options for rewarding the participants.
The Governance Body defines awards or other incentives.
As noted in section 5.1.2, instances of the governance model often occur as a tiered arrangement, with governance at some level delegating
specific authority and responsibility to accomplish a
focused portion of the original level’s mandate. For example, a corporation may
encompass several lines of business and each line of business governs its own
affairs in a manner that is consistent with and contributes to the goals of the
parent organization. Within the line of business, an IT group may be given the
mandate to provide and maintain IT resources, giving rise to IT governance.
In addition to tiered governance, there may be multiple
governance chains working in parallel. For example, a company making widgets
has policies intended to ensure they make high quality widgets and make an
impressive profit for their shareholders. On the other hand,
Sarbanes-Oxley is a parallel governance chain in the United States that
specifies how the management must handle its accounting and information that
needs to be given to its shareholders. The parallel chains may just be
additive or may be in conflict and require some harmonization.
Being distributed and representing different ownership
domains, a SOA participant falls under the
jurisdiction of multiple governance domains simultaneously and may individually
need to resolve consequent conflicts. The governance domains may specify
precedence for governance conformance or it may fall to the discretion of the participant to decide on the course of actions they
believe appropriate.
SOA governance is often discussed in terms of IT governance,
but rather than a parent-child relationship, Figure 38 shows the two as
siblings of the general governance described in section 5.1.2. There are obvious dependencies and a need for coordination between the two, but the idea of
aligning IT with business already demonstrates that resource providers and
resource consumers must be working towards common goals if they are to be
productive and efficient. While SOA governance is shown to be active in the
area of infrastructure, it is a specialized concern for having a dependable
platform to support service interaction; a range of traditional IT issues is
therefore out of scope of this document. A SOA governance plan for an enterprise will not of itself resolve shortcomings with
the enterprise’s IT governance.
Governance in the context of SOA is that organization of
services: that promotes their visibility; that facilitates interaction among
service participants; and that directs that the
results of service interactions are those real world
effects as described within the service description and constrained by
policies and contracts as assembled in the execution
context.
SOA governance must specifically account for control across
different ownership domains, i.e. all the participants
may not be under the jurisdiction of a single governance authority. However,
for governance to be effective, the participants
must agree to recognize the authority of the
Governance Body and must operate within the Governance Framework and through
the Governance Processes so defined.
SOA governance must account for interactions across ownership boundaries, which may also imply across
enterprise governance boundaries. For such situations, governance emphasizes
the need for agreement that some Governance Framework and Governance Processes
have jurisdiction, and the governance defined must satisfy the Goals of the participants for cooperation to continue. A standards
development organization such as OASIS is an example of voluntary agreement to
governance over a limited domain to satisfy common goals.
The specifics discussed in the figures in the previous
sections are equally applicable to governance across ownership boundaries as it is within a single
boundary. There is a charter agreed to when participants
become members of the organization, and this charter sets up the structures and
processes to be followed. Leadership may be shared by the leadership of the
overall organization and the leadership of individual groups themselves
chartered per the Governance Processes. There are Rules/Regulations specific
to individual efforts for which participants agree
to local goals, and Enforcement can be loss of voting rights or under extreme
circumstances, expulsion from the group.
Thus, the major difference for SOA governance is an
appreciation for the cooperative nature of the enterprise and its reliance on furthering
common goals if productive participation is to continue.
5.1.3.2 What Must be Governed
An expected benefit of employing SOA principles is the
ability to quickly bring resources to bear to deal with
unexpected and evolving situations. This requires a great deal of confidence
in the underlying capabilities that can be accessed and in the services that
enable the access. It also requires considerable flexibility in the ways these
resources can be employed. Thus, SOA governance
requires establishing confidence and trust while instituting a solid framework
that enables flexibility, indicating a combination of strict control over a
limited set of foundational aspects but minimum constraints beyond those bounds.

Figure 38 - Relationship Among Types of Governance
SOA governance applies to three aspects of service
definition and use:
·
SOA infrastructure – the “plumbing” that provides utility
functions that enable and support the use of the service
·
Service inventory – the requirements on a service to permit it to
be accessed within the infrastructure
·
Participant interaction – the consistent expectations with which
all participants are expected to comply
5.1.3.2.1 Governance of SOA Infrastructure
The SOA infrastructure is likely composed of several
families of SOA services that provide access to fundamental computing business
services. These include, among many others, services such as messaging,
security, storage, discovery, and mediation. The provisioning of an
infrastructure on which these services may be accessed and the general realm of
those contributing as utility functions of the infrastructure are a traditional
IT governance concern. In contrast, the focus of SOA governance is how the
existence and use of the services enables the SOA ecosystem.
By characterizing the environment as containing families of
SOA services, the assumption is that there may be multiple approaches to
providing the business services or variations in the actual business services
provided. For example, discovery could be based on text search, on metadata
search, on approximate matches when exact matches are not available, and
numerous other variations. The underlying implementation of search algorithms
are not the purview of SOA governance, but the access to the resulting service
infrastructure enabling discovery must be stable, reliable, and extremely
robust to all operating conditions. Such access enables other specialized SOA
services to use the infrastructure in dependable and predictable ways, and is
where governance is important.
5.1.3.2.2 Governance of the Service Inventory
Given an infrastructure in which other SOA services can
operate, a key governance issue is which SOA services to allow in the
ecosystem. The major concern SHOULD be a definition of well-behaved services,
where the required behavior will inherit their characteristics from experiences
with distributed computing but also evolve with SOA experience. A major
requirement for ensuring well-behaved services is collecting sufficient metrics
to know how the service affects the SOA infrastructure and whether it complies
with established infrastructure policies.
Another common concern of service approval is whether there
is a possibility of duplication of function by multiple services. Some
governance models talk to a tightly controlled environment where a primary
concern is to avoid any service duplication. Other governance models talk to a
market of services where the consumers have wide choices. For the latter, it
is anticipated that the better services will emerge from market consensus and
the availability of alternatives will drive innovation.
Some combination of control and openness will emerge,
possibly with a different appropriate balance for different categories of use.
For SOA governance, the issue is less which services are approved but rather
ensuring that sufficient description is available to support informed decisions
for appropriate use. Thus, SOA governance SHOULD concentrate on identifying the
required attributes to adequately describe a service, the required target
values of the attributes, and the standards for defining the meaning of the
attributes and their target values. Governance may also specify the processes
by which the attribute values are measured and the corresponding certification
that some realized attribute set may imply.
For example, unlimited access for using a service may
require a degree of life cycle maturity that has demonstrated sufficient testing
over a certain size community. Alternately, the policy may specify that a
service in an earlier phase of its life cycle may be made available to a
smaller, more technically sophisticated group in order to collect the metrics
that would eventually allow the service to advance its life cycle status.
This aspect of governance is tightly connected to
description because, given a well-behaved set of services, it is the
responsibility of the consumer (or policies promulgated by the consumer’s
organization) to decide whether a service is sufficient for that consumer’s
intended use. The goal is to avoid global governance specifying criteria that
are too restrictive or too lax for the local needs of which global governance
has little insight.
Such an approach to specifying governance allows independent
domains to describe services in local terms while still having the services
available for informed use across domains. In addition, changes to the
attribute sets within a domain can be similarly described, thus supporting the
use of newly described resources with the existing ones
without having to update the description of all the legacy content.
5.1.3.2.3 Governance of Participant Interaction
Finally, given a reliable services infrastructure and a
predictable set of services, the third aspect of governance is prescribing what
is required during a service interaction.
Governance would specify adherence to service interface and
service reachability parameters and would require that the result of an
interaction MUST correspond to the real world effects
as contained in the service description. Governance would ensure preconditions
for service use are satisfied, in particular those related to security aspects
such as user authentication, authorization, and non-repudiation. If conflicts
arise, governance would specify resolution processes to ensure appropriate
agreements, policies, and conditions are met.
It would also rely on sufficient monitoring by the SOA
infrastructure to ensure services remain well-behaved during interactions, e.g.
do not use excessive resources or exhibit other prohibited behavior.
Governance would also require that policy agreements as documented in the
execution context for the interaction are observed and that the results and any
after effects are consistent with the agreed policies. Governance focuses on
more contractual and legal aspects rather than the precursor descriptive
aspects. SOA governance may prescribe the processes by which SOA-specific
policies are allowed to change, but there are probably more business-specific
policies that will be governed by processes outside SOA governance.
5.1.3.3 Overarching Governance Concerns
There are numerous governance related concerns whose effects
span the three areas just discussed. One is the area of standards, how these
are mandated, and how the mandates may change. The Web Services standards
stack is an example of relevant standards where a significant number are still
under development. In addition, while there are notional scenarios that guide
what standards are being developed, the fact that many of these standards do
not yet exist precludes operational testing of their adequacy or effectiveness
as a necessary and sufficient set.
That said, standards are critical to creating a SOA
ecosystem where SOA services can be introduced, used singularly, and combined
with other services to deliver complex business functionality. As with other
aspects of SOA governance, the Governance Body should identify the minimum set
felt to be needed and rigorously enforce that that set be used where
appropriate. The Governance Body takes care to expand and evolve the mandated
standards in a predictable manner and with sufficient technical guidance that
new services are able to coexist as much as possible with the old, and changes
to standards do not cause major disruptions.
Another area that may see increasing activity as SOA expands
is additional regulation by governments and associated legal institutions. New
laws may deal with transactions which are service based, possibly including
taxes on the transactions. Disclosure laws may mandate certain elements of
description so both the consumer and provider act in a predictable environment
and are protected from ambiguity in intent or action.
Such laws spawn rules and regulations that will influence the metrics collected
for evaluation of compliance.
The Reference Architecture definition of a loosely coupled system
is one in which the constraints on the interactions between components is
minimal: sufficient to permit interoperation without additional constraints
that may be an artifact of implementation technology. While governance
experience for standalone systems provides useful guides, we must be careful
not to apply constraints that would preclude the flexibility, agility, and
adaptability we expect to realize from a SOA ecosystem.
One of the strengths of SOA is it can make effective use of
diversity rather than requiring monolithic solutions. Heterogeneous
organizations can interact without requiring each conforms to uniform tools,
representation, and processes. However, with this diversity comes the need to
adequately define those elements necessary for consistent interaction among
systems and participants, such as which
communication protocol, what level of security, which vocabulary for payload
content of messages. The solution is not always to lock down these choices but
to standardize alternatives and standardize the representations through which
an unambiguous identification of the alternative chosen can be conveyed. For
example, the URI standard specifies the URI string, including what protocol is
being used, what is the target of the message, and how parameters may be
attached. It does not limit the available protocols, the semantics of the
target address, or the parameters that can be transferred. Thus, as with our
definition of loose coupling, it provides absolute constraints but minimizes
which constraints it imposes.
There is not a one-size-fits-all governance but a need to
understand the types of things governance is called upon to do in the context
of the goals of SOA. Some communities may initially desire and require
very stringent governance policies and procedures while others see need for
very little. Over time, best practices will evolve, resulting in some
consensus on a sensible minimum and, except in extreme cases where it is
demonstrated to be necessary, a loosening of strict governance toward the best
practice mean.
A question of how much governance may center on how much
time governance activities require versus how quickly is the system being
governed expected to respond to changing conditions. For large single
systems that take years to develop, the governance process could move slowly
without having a serious negative impact. For example, if something takes two
years to develop and the steps involved in governance take two months to
navigate, then the governance can go along in parallel and may not have a
significant impact on system response to changes. Situations where it
takes as long to navigate governance requirements as it does to develop a
response are examples where governance may need to be reevaluated as to whether
it facilitates or inhibits the desired results. Thus, the speed at which
services are expected to appear and evolve needs to be considered when deciding
the processes for control. The added weight of governance should be appropriate
for overall goals of the application domain and the service environment.
Governance, as with other aspects of any SOA implementation,
should start small and be conceptualized in a way that keeps it flexible,
scalable, and realistic. A set of useful guidelines would include:
·
Do not hardwire things that will inevitably change. For example,
develop a system that uses the representation of policies rather than code the
policies into the implementations.
·
Avoid setting up processes that demo well for three services
without considering how they may work for 300. Similarly, consider whether the
display of status and activity for a small number of services will also be
effective for an operator in a crisis situation looking at dozens of services,
each with numerous, sometimes overlapping and sometimes differing activities.
·
Maintain consistency and realism. A service solution responding
to a natural disaster cannot be expected to complete a 6-week review cycle but
be effective in a matter of hours.
The description of SOA governance indicates numerous
architectural requirements on the SOA ecosystem:
·
Governance is expressed through policies and assumes multiple use
of focused policy modules that can be employed across many common
circumstances. This requires the existence of:
o
descriptions to enable the policy modules to be visible, where
the description includes a unique identifier for the policy and a sufficient,
and preferably a machine process-able, representation of the meaning of terms
used to describe the policy, its functions, and its effects;
o
one or more discovery mechanisms that enable searching for
policies that best meet the search criteria specified by the service participant; where the discovery mechanism will have
access to the individual policy descriptions, possibly through some repository
mechanism;
o
accessible storage of policies and policy descriptions, so
service participants can access, examine, and use
the policies as defined.
·
Governance requires that the participants
understand the intent of governance, the structures created to define and
implement governance, and the processes to be followed to make governance
operational. This requires the existence of:
o
an information collection site, such as a Web page or portal,
where governance information is stored and from which the information is always
available for access;
o
a mechanism to inform participants of
significant governance events, such as changes in
policies, rules, or regulations;
o
accessible storage of the specifics of Governance Processes;
o
SOA services to access automated implementations of the
Governance Processes
·
Governance policies are made operational through rules and
regulations. This requires the existence of:
o
descriptions to enable the rules and regulations to be visible,
where the description includes a unique identifier and a sufficient, and
preferably a machine process-able, representation of the meaning of terms used
to describe the rules and regulations;
o
one or more discovery mechanisms that enable searching for rules
and regulations that may apply to situations corresponding to the search
criteria specified by the service participant; where
the discovery mechanism will have access to the individual descriptions of
rules and regulations, possibly through some repository mechanism;
o
accessible storage of rules and regulations and their respective
descriptions, so service participants can understand
and prepare for compliance, as defined.
o
SOA services to access automated implementations of the
Governance Processes.
·
Governance implies management to define and enforce rules and
regulations. Management is discussed more specifically in section 5.3, but in a parallel to governance, management requires the existence of:
o
an information collection site, such as a Web page or portal,
where management information is stored and from which the information is always
available for access;
o
a mechanism to inform participants of
significant management events, such as changes in rules or
regulations;
o
accessible storage of the specifics of processes followed by
management.
·
Governance relies on metrics to define and measure compliance.
This requires the existence of:
o
the infrastructure monitoring and reporting information on SOA
resources;
o
possible interface requirements to make accessible metrics
information generated or most easily accessed by the service itself.
Security is one aspect of confidence – the confidence in the
integrity, reliability, and confidentiality of the system. In particular,
security focuses on those aspects of assurance that involve the accidental or
malign intent of other people to damage or compromise trust in the system and
on the availability of SOA-based systems to perform desired capability.
Security
Security concerns the set of mechanisms for ensuring and
enhancing trust and confidence in the SOA ecosystem.
Providing for security for Service Oriented Architecture is
somewhat different than for other contexts; although many of the same
principles apply equally to SOA and to other systems. The fact that SOA
embraces crossing ownership boundaries makes
the issues involved with moving data more visible.
As well as securing the movement of data within and across ownership boundaries, security often revolves
around resources: the need to guard certain
resources against inappropriate access – whether reading, writing or otherwise
manipulating those resources.
Any comprehensive security solution must take into account
the people that are using, maintaining and managing the SOA. Furthermore, the
relationships between them must also be incorporated: any security assertions
that may be associated with particular interactions originate in the people
that are behind the interaction.
We analyze security in terms of the social structures that define the legitimate permissions, obligations and roles of people in relation to the system, and mechanisms that
must be put into place to realize a secure system. The former are typically
captured in a series of security policy statements; the latter in terms of
security guards that ensure that policies are enforced.
How and when to apply these derived security policy
mechanisms is directly associated with the assessment of the threat model
and a security response model. The threat model identifies the kinds of
threats that directly impact the message and/or application of constraints, and
the response model is the proposed mitigation to those threats. Properly
implemented, the result can be an acceptable level of risk to the safety and
integrity of the system.
We can characterize secure interactions in terms of key
security concepts [ISO/IEC 27002]: confidentiality,
integrity, authentication, authorization, non-repudiation, and availability.
The concepts for secure interactions are well defined in other standards and
publications. The security concepts here are not defined but rather related to
the SOA ecosystem perspective of the SOA-RAF.
5.2.1.1 Confidentiality
Confidentiality concerns the protection of privacy of participants in their interactions. Confidentiality
refers to the assurance that unauthorized entities are not able to read
messages or parts of messages that are transmitted.
Note that confidentiality has degrees: in a completely
confidential exchange, third parties would not even be aware that a
confidential exchange has occurred. In a partially confidential exchange, the
identities of the participants
may be known but the content of the exchange obscured.
5.2.1.2 Integrity
Integrity concerns the protection of information that is
exchanged – either from unauthorized writing or inadvertent corruption.
Integrity refers to the assurance that information that has been exchanged has
not been altered.
Integrity is different from confidentiality in that messages
that are sent from one participant
to another may be obscured to a third party, but the third party may still be
able to introduce his own content into the exchange without the knowledge of
the participants.
Section 5.2.4 describes common computing techniques for
providing confidentiality and integrity during message exchanges.
5.2.1.3 Authentication
Authentication concerns the identity of the participants in
an exchange. Authentication refers to the means by which one participant can
be assured of the identity of other participants.
Figure 39 - Authentication
applies authentication to the identity of participants.

Figure 39 - Authentication
5.2.1.4 Authentication
Authorization concerns the legitimacy of the interaction.
Authorization refers to the means by which a stakeholder may be assured that the
information and actions that are exchanged are either explicitly or implicitly
approved.

Figure 40 - Authorization
The roles and attributes which provide a
participant’s credentials are expanded to include
reputation. Reputation often helps determine willingness to interact, for
example, reviews of a service provider will influence the decision to interact
with the service provider. The roles, reputation, and
attributes are represented as assertions measured by authorization decision
points.
The role of policy for security is to permit stakeholders to
express their choices. In Figure 40, a policy is a written constraint and the
role, reputation, and attribute assertions are evaluated according to the
constraints in the authorization policy. A combination of security mechanisms
and their control via explicit policies can form the basis of an authorization
solution.
5.2.1.5 Non-repudiation
Non-repudiation concerns the accountability of participants. To foster trust in the performance of a
system used to conduct shared activities it is important that the participants are not able to later deny their actions:
to repudiate them. Non-repudiation refers to the means by which a participant may not, at a later time, successfully deny
having participated in the interaction or having performed the actions as
reported by other participants.
5.2.1.6 Availability
Availability concerns the ability of systems to use and
offer the services for which they were designed. One of the threats against
availability is the so-called denial of service attack in which attackers
attempt to prevent legitimate access to the system.
We differentiate here between general availability – which
includes aspects such as systems reliability – and availability as a security
concept where we need to respond to active threats to the system.
The core security concepts are fundamental to all social
interactions. The evolution of sharing information using a SOA requires the
flexibility to dynamically secure computing interactions in a computing
ecosystem where the owning social groups, roles, and authority are constantly changing as described in section
5.1.3.1.
SOA policy-based security can be more adaptive for a
computing ecosystem than previous computing technologies allow for, and
typically involves a greater degree of distributed mechanisms.
Standards for security, as is the case with all aspects of
SOA, play a large role in flexible security on a global scale. SOA security
may also involve greater auditing and reporting to adhere to regulatory
compliance established by governance structures.
5.2.3
Security Threats
There are a number of ways in which an attacker may attempt
to compromise the security of a system. The two primary sources of attack are
third parties attempting to subvert interactions between legitimate participants and an entity that is participating but
attempting to subvert its partner(s). The latter is particularly important in a
SOA where there may be multiple ownership
boundaries and trust boundaries.
The threat model lists some common threats that relate to
the core security concepts listed in Section 5.2.1. Each technology choice in the realization of a SOA can potentially have many threats to consider.
Message alteration
If an attacker is able to modify the content (or even the
order) of messages that are exchanged without the legitimate participants being aware of it then the attacker has
successfully compromised the security of the system. In effect, the participants may unwittingly serve the needs of the
attacker rather than their own.
An attacker may not need to completely replace a message
with his own to achieve his objective: replacing the identity of the
beneficiary of a transaction may be enough.
Message interception
If an attacker is able to intercept and understand messages
exchanged between participants, then the attacker
may be able to gain advantage. This is probably the most commonly understood
security threat.
Man in the middle
In a man-in-the-middle attack, the legitimate participants believe that they are interacting with
each other; but are in fact interacting with the attacker. The attacker
attempts to convince each participant that he is
their correspondent; whereas in fact he is not.
In a successful man-in-the-middle attack, legitimate participants do not have anaccurate understanding of
the state of the other participants. The attacker
can use this to subvert the intentions of the participants.
Spoofing
In a spoofing attack, the attacker convinces a participant that he is really someone else – someone
that the participant would normally trust.
Denial of service attack
In a denial of service (DoS) attack, the attacker attempts
to prevent legitimate users from making use of the service. A DoS attack is
easy to mount and can cause considerable harm: by preventing legitimate
interactions, or by slowing them down enough, the attacker may be able to
simultaneously prevent legitimate access to a service and to attack the service
by another means.
A variation of the DoS attack is the Distributed Denial of
Service attack. In a DDoS attack the attacker uses multiple agents to the
attack the target. In some circumstances this can be extremely difficult to
counteract effectively.
One of the features of a DoS attack is that it does not
require valid interactions to be effective: responding to invalid messages also
takes resources and that may be sufficient to cripple the target.
Replay attack
In a replay attack, the attacker captures the message
traffic during a legitimate interaction and then replays part of it to the
target. The target is persuaded that a similar transaction to the previous one
is being repeated and it responds as though it were a legitimate interaction.
A replay attack may not require that the attacker
understand any of the individual communications; the attacker may have
different objectives (for example attempting to predict how the target would
react to a particular request).
False repudiation
In false repudiation, a user completes a normal transaction
and then later attempts to deny that the transaction occurred. For example, a
customer may use a service to buy a book using a credit card; then, when the
book is delivered, refuse to pay the credit card bill claiming that someone
else must have ordered the book.
Security goals are never absolute: it is not possible to
guarantee 100% confidentiality, non-repudiation, etc. However, a well designed
and implemented security response model can ensure acceptable levels of
security risk. For example, using a well-designed cipher to encrypt messages
may make the cost of breaking communications so great and so lengthy that the
information obtained is valueless.
Performing threat assessments, devising mitigation
strategies, and determining acceptable levels of risk are the foundation for an
effective process to mitigating threats in a cost-effective way.
The choice in hardware and software to realize a SOA will be a basis for threat
assessments and mitigation strategies. The stakeholders
of a specific SOA implementation should determine acceptable levels of risk
based on threat assessments and the cost of mitigating those threats.
5.2.4.1 Privacy Enforcement
The most efficient mechanism to assure confidentiality is
the encryption of information. Encryption is particularly important when
messages must cross trust boundaries; especially over the Internet. Note that
encryption need not be limited to the content of messages: it is possible to
obscure even the existence of messages themselves through encryption and ‘white
noise’ generation in the communications channel.
The specifics of encryption are beyond the scope of this
architecture. However, we are concerned about how the connection between
privacy-related policies and their enforcement is made.
A policy enforcement point for enforcing privacy may take
the form of an automatic function to encrypt messages as they leave a trust
boundary; or perhaps simply ensuring that such messages are suitably encrypted.
Any policies relating to the level of encryption being used
would then apply to these centralized messaging functions.
5.2.4.2 Integrity Protection
To protect against message tampering or inadvertent message
alteration, and to allow the receiver of a message to authenticate the sender,
messages may be accompanied by a digital signature. Digital signatures provide
a means to detect if signed data has been altered. This protection can also
extend to authentication and non-repudiation of a sender.
A common way a digital signature is generated is with the
use of a private key that is associated with a public key and a digital
certificate. The private key of some entity in the system is used to create a digital
signature for some set of data. Other entities in the system can check the
integrity of the signed data set via signature verification algorithms. Any
changes to the data that was signed will cause signature verification to fail,
which indicates that integrity of the data set has been compromised.
A party verifying a digital signature must have access to
the public key that corresponds to the private key used to generate the
signature. A digital certificate contains the public key of the owner, and is
itself protected by a digital signature created using the private key of the
issuing Certificate Authority (CA).
5.2.4.3 Message Replay Protection
To protect against replay attacks, messages may contain
information that can be used to detect replayed messages. The simplest
requirement to prevent replay attacks is that each message that is ever sent is
unique. For example, a message may contain a message ID, a timestamp, and the
intended destination.
By storing message IDs, and comparing each new message with
the store, it becomes possible to verify whether a given message has been
received before (and therefore should be discarded).
The timestamp may be included in the message to help check
for message freshness. Messages that arrive after their message ID could have
been cleared (after receiving the same message some time previously) may also
have been replayed. A common means for representing timestamps is a useful part
of an interoperable replay detection mechanism.
The destination information is used to determine if the
message was misdirected or replayed. If the replayed message is sent to a
different endpoint than the destination of the original message, the replay
could go undetected if the message does not contain information about the
intended destination.
In the case of messages that are replies to prior messages,
it is also possible to include seed information in the prior messages that is
randomly and uniquely generated for each message that is sent out. A replay
attack can then be detected if the reply does not embed the random number that
corresponds to the original message.
5.2.4.4 Auditing and Logging
False repudiation involves a participant
denying that it authorized a previous interaction. An effective strategy for
responding to such a denial is to maintain careful and complete logs of
interactions which can be used for auditing purposes.
The more detailed and comprehensive an audit trail is, the less likely it is
that a false repudiation would be successful.
The countermeasures assume that the non-repudiation tactic
(e.g. digital signatures) is not undermined itself. For example, if private
key is stolen and used by an adversary, even extensive logging cannot assist in
rejecting a false repudiation.
Unlike many of the security responses discussed here, it is
likely that the scope for automation in rejecting a repudiation attempt is
limited to careful logging.
5.2.4.5 Graduated engagement
The key to managing and responding to DoS attacks is to be
careful in the use of resources when responding to
interaction. Put simply, a system has a choice to respond to a communication or
to ignore it. In order to avoid vulnerability to DoS attacks a service provider
should be careful not to commit resources beyond those
implied by the current state of interactions; this permits a graduation in
commitment by the service provider that mirrors any commitment
on the part of service consumers and attackers
alike.
Providing SOA security in an ecosystem of governed services
has the following implications on the policy support and the distributed nature
of mechanisms used to assure SOA security:
·
Security expressed through policies have the same architectural
implications as described in Section 4.4.3 for policies and contracts
architectural implications.
·
Security policies require mechanisms to support security
description administration, storage, and distribution.
·
Service descriptions supporting security policies should:
o
have a meta-structure sufficiently rich to support security
policies;
o
be able to reference one or more security policy artifacts;
o
have a framework for resolving conflicts between security
policies.
·
The mechanisms that make-up the execution context in secure
SOA-based systems should:
o
provide protection of the confidentiality and integrity of
message exchanges;
o
be distributed so as to provide centralized or decentralized
policy-based identification, authentication, and authorization;
o
ensure service availability to consumers;
o
be able to scale to support security for a growing ecosystem of
services;
o
be able to support security between different communication
technologies;
·
Common security services include:
o
services that abstract encryption techniques;
o
services for auditing and logging interactions and security
violations;
o
services for identification;
o
services for authentication;
o
services for authorization;
o
services for intrusion detection and prevention;
o
services for availability including support for quality of
service specifications and metrics.
5.3 Management
Model
Management is a process of controlling resources in
accordance with the policies and principles defined by Governance.
There are three separate but linked domains of interest
within the management of SOA ecosystem:
1. the
management and support of the resources that are involved in any complex
structures – of which SOA ecosystems are excellent examples;
2. the
promulgation and enforcement of the policies and service contracts agreed to by
the stakeholders in the SOA ecosystem;
3. the
management of the relationships of the participants – both to each other and to
the services that they use and offer.
There are many artifacts related to management. Historically,
systems management capabilities have been organized by the “FCAPS” functions
(based on ITU-T Rec. M.3400 (02/2000), "TMN Management Functions"):
·
fault management,
·
configuration management,
·
account management,
·
performance and security management.
The primary task of the functional groups is to concentrate
on maintaining systems in a trusted, active, and accessible state.
In the context of the SOA ecosystem, we see many possible
resources that may require management such as services, service descriptions,
service contracts, policies, roles, relationships, security, people and systems
that implement services and infrastructure elements. In addition, given the
ecosystem nature, it is also potentially necessary to manage the business
relationships between participants.
Successful operation of a SOA ecosystem requires trust among
the stakeholders and between them and the SOA-based system elements. In
contrast, regular systems in technology are not necessarily operated or used in
an environment requiring trust before the stakeholders make use of the system.
Indeed, many of these systems exist in hierarchical management structures,
within which use may be mandated by legal requirement, executive decision, or
good business practice in furthering the business’ strategy. The pre-condition
of trust in the SOA ecosystem is rooted both in the principles of service
orientation and in the distributed, authoritative ownership of independent
services. Even for hierarchical management structures applied to a SOA
ecosystem, the service in use should have a contractual basis rather than being
mandated.
Trust may be established through agreements/contracts, policies,
or implicitly through observation of repeated interactions with others.
Explicit trust is usually accompanied by formalized documents suitable for
management. Implicit trust adds fragility to the management of a SOA ecosystem
because failure to maintain consistent and predictable interactions will
undermine the trust between participants and within the ecosystem as a whole.
Management in
a SOA ecosystem is thus concerned with management taking actions that will
establish the condition of trust that must be present before engaging in
service interactions. These concerns should largely be handled within the
governance of the ecosystem. The policies, agreements, and practices defined
through governance provide the boundaries within which management operates and
for which management must provide enforcement and feedback. However,
governance alone cannot foresee all circumstances but must offer sufficient
guidance where agreement between all stakeholders cannot be reached. Management
in these cases must be flexible and adaptable to handle unanticipated
conditions without unnecessarily breaking trust relationships.
Service management is the process – manual, automated, or a
combination – of proactively monitoring and controlling the behavior of a
service or a set of services. Service management operates under constraints
attributed to the business and social context. Specific policies may be used to
govern cross-boundary relationships. Managing solutions based on such policies (and
that may be used across ownership boundaries) raises issues that are not
typically present when managing a service within a single ownership domain. Care
is therefore required in managing a service when the owner of the service, the
provider of the service, the host of the service and mediators to the service
may all belong to different stakeholders.
Cross-boundary service management takes place in, at least,
the following situations:
·
using combinations of services that belong to different ownership
domains
·
using of services that mediate between ownership domains
·
sharing monitoring and reporting means and results.
These situations are particularly important in ecosystems
that are highly decentralized, in which the participants interact as peers as
well as in the “master-servant” mode.
The management model shown in Figure 41 conveys how the SOA
applies to managing services. Services management operates via service
metadata, such as service lifecycles and attributes associated with service
use, which are typically collected in or accessed through the service
description.

Figure 41 - Manageability capabilities in SOA ecosystem
The service metadata of interest is that set of service
properties that is manageable. These manageability properties are generally
identifiable for any service consumed or supplied within the ecosystem. The
necessary existence of these properties within the SOA ecosystem motivates the
following definitions:
Manageability of a resource is the capability
that allows it to be controlled, monitored, and reported on with
respect to some property. Note that manageability is not necessarily a part of
the managed entities themselves and are generally considered to be external to
the managed entities.
Each resource may be managed through a number of aspects of
management, and the resources may be grouped based on similar aspects. For
example, resources may be grouped according to the aspect referred to as
“Configuration Manageability” for the collection of services. Some resources may
not be managed under a particular capability if there are no manageability
aspects with a clear meaning or use. As an example, all resources within a SOA
ecosystem have a lifecycle that is meaningful within the ecosystem. Thus, all
resources are manageable under Lifecycle Manageability. In contrast, not all
resources report or handle events. Thus, Event Manageability is only concerned
with those resources for which events are meaningful.
Life-cycle Manageability of a service typically
refers to how the service is created, how it is destroyed and how service
versions must be managed. This manageability is a feature of the SOA ecosystem
because the service cannot manage its own life cycle.
Another important consideration is that services may have
resource requirements that must be established at various points in the
services’ life cycles. However actual providers of these resources may not be
known at the time of the service creation and, thus, have to be managed at
service run-time.
Combination Manageability of a service addresses management
of service characteristics that allow for creating and changing combinations in
which the service participates or that the service combines itself. Known models
of such combinations are aggregations and compositions. Examples of patterns of
combinations are choreography and orchestration. Combination Manageability drives
implementation of the Service Composability Principle of service orientation.
Service combination manageability resonates with the
methodology of process management. Combination Manageability may be applied at
different phases of service creation and execution and, in some cases, can
utilize Configuration Manageability.
Service combinations typically contribute the most in
delivering business values to the stakeholders. Managing service combinations
is the one of the most important tasks and features of the SOA ecosystem.
Configuration Manageability of a service allows
managing the identity of and the interactions among internal elements of the
service. Also, Configuration Manageability correlates with the management of
service versions and configuration of the deployment of new services into the
ecosystem. Configuration Management differs from the Combination Manageability
in the scope and scale of manageability, and addresses lower level concerns
than the architectural combination of services.
Event Monitoring Manageability allows managing the
categories of events of interest related to services and reporting recognized
events to the interested stakeholders. Such events may be the ones that trigger
service invocations as well as execution of particular functionality provided
by the service.
Event Monitoring Manageability is
a key lower-level manageability aspect that the service provider and
associated stakeholders are interested. Monitored events may be internal or
external to the SOA ecosystem. For example, a disaster in the oil industry,
which is outside the SOA ecosystem of the Insurer, can trigger the service’s
functionality that is responsible for immediate or constant monitoring of oil
prices in the oil trading exchanges and, respectively, modify the premium paid
by the insured oil companies.
Performance Manageability of a service allows
controlling the service results, shared and sharable real world effects against
the business goals and objectives of the service. This manageability assumes
monitoring of the business performance as well as the management of this
monitoring itself. Performance Manageability includes business and technical
performance manageability through a performance criteria set, such as business
key performance indicators (KPI) and service-level agreements (SLA).
The performance business- and technical-level
characteristics of the service should be known from the service contract. The
service provider and consumer must be able to monitor and measure these
characteristics or be informed about the results measured by a third party.
Performance Manageability is the instrument for providing compliance
of the service with its service contracts. Performance Manageability utilizes
Manageability of Quality of Service.
Manageability of Quality of Service deals with
management of service non-functional characteristics that may be of significant
value to the service consumers and other stakeholders in the SOA ecosystem.
Classic examples of this include bandwidth offerings associated with a service.
Manageability of quality of service assumes that the
properties associated with service qualities are monitored during the service
execution. Results of monitoring may be challenged against SLA and even KPI,
which results in the continuous validation of how the service contract is
preserved by the service provider.
Policy Manageability allows additions, changes and
replacements of the policies associated with a resource in the SOA ecosystem.
The ability to manage those policies (such as promulgating policies, retiring
policies and ensuring that policy decision points and enforcement points are
current) enables the ecosystem to apply policies and evaluate the
results.
The capability to manage, i.e. use a particular
manageability, requires policies from governance to be translated into detailed
rules and regulations which are measured and monitored providing corresponding
feedback for enforcement.
Management of SOA ecosystem recognises the manageability
challenge and requires manageability properties to be considered for all
aforementioned manageability cases. In the following sub-sections, we describe
how thses properties are used in the management. Also we describe some
relationships between management and other components of SOA ecosystem.
A minimal set of management issues for the SOA ecosystem is
shown on Figure 42 and elaborated in the following sections.

Figure 42 - Management Means and Relationships in SOA ecosystem
5.3.2.1 Management Policy
The management of resources within the SOA ecosystem may be
governed by management policies. In a deployed SOA-based solution, it may well
be that different aspects of the management of a given service are managed by
different management services. For example, the life-cycle management of
services often involves managing service versions. Managing quality of service
is often very specific to the service itself; for example, quality of service
attributes for a video streaming service are quite different to those for a
banking system.
Additional concepts of management also apply to IT
management.
5.3.2.2 Network Management
Network management deals with the maintenance and
administration of large scale physical networks such as computer networks and
telecommunication networks. Specifics of the networks may affect service
interactions from performance and operational perspectives.
Network and related system management executes a set of
functions required for controlling, planning, deploying, coordinating, and
monitoring the distributed services in the SOA ecosystem. However, while
recognizing their importance, the specifics of systems management or network
management are out of scope for this Reference Architecture Foundation.
5.3.2.3 Security Management
Security Management includes identification of roles,
permissions, access rights, and policy attributes defining security boundaries
and events that may trigger a security response.
Security management within a SOA ecosystem is essential to
maintaining the trust relationships between participants residing in different
ownership domains. Security management must consider not just the internal
properties related to interactions between participants but ecosystem
properties that preserve the integrity of the ecosystem from external threats.
5.3.2.4 Usage Management
Usage Management is concerned with how resources are used,
including:
·
how the resource is accessed, who is using the resource, and the
state of the resource (access properties);
·
controlling or shaping demand for resources to optimize the
overall operation of the ecosystem (demand properties);
·
with assigning costs to the use of resources and distributing
those cost assignments to the participants in an appropriate manner (financial
properties).
The primary role of governance in the context of a SOA
ecosystem is to foster an atmosphere of predictability, trust, and efficiency,
and it accomplishes this by allowing the stakeholders to negotiate and set the
key policies that govern the running of the SOA-based solution. Recall that in
an ecosystems perspective, the goal of governance is less to have complete
fine-grained control but more to enable the individual participants to work
together.
Policies for a SOA ecosystem will tend to focus on the rules
of engagement between participants; for example, what kinds of interactions are
permissible, how disputes are resolved, etc. While governance may primarily
focus on setting policies, management will focus on the realization and
enforcement of policies. Effective management in the SOA ecosystem requires an
ability for governance to understand the consequences of its policies,
guidelines, and principles, and to adjust those as needed when inconsistencies
or ambiguity become evident from the operation of the management functions.
This understanding and adjustment must be facilitated by the results of
management and so the mechanisms for providing feedback from management into
governance must exist.
Governance operates via specialized activities and, thus,
should be managed itself. Governance policies are included in the Governance
Framework and Processes, and driven by the enterprise business model, business
objectives and strategies. Where corporate management policies exist, these are
usually guided and directed by the corporate executives. In peer relationships,
governance policies are set by either an external entity and accepted by the
peers or by the peers themselves. This creates the appropriate authoritative
level for the policies used for the management of the Governance Framework and
Processes. Management to operationalize governance controls the life-cycle of
the governing policies, including procedures and processes, for modifying the
Governance Framework and Processes.
5.3.4.1 Management for Contracts and Policies
As we noted above, management can often be viewed as the
application of contracts and individual policies to ensure the smooth running
of the SOA ecosystem. Policies and service contracts specify the service
characteristics that have to be monitored, analysed and managed and play an
important role as the guiding constraints for management, as well as being artifacts
(e.g., policy and contractual documents) that also need to be managed.
5.3.4.2 Contracts
As described in sections “Participation in a SOA Ecosystem
view” and “Realization of a SOA Ecosystem view”, there are several types
of contractual information in the SOA ecosystem. From the management
perspective, three basic types of the contractual information relate to:
·
relationship between service provider and consumer;
·
communication with the service;
·
control of the quality of the service execution.
When a consumer prepares to interact with a service, the
consumer and the service provider must come to an agreement on the service
features and characteristics that will be provided by the service and made available
to the consumer. This agreement is known as a service contract.
Service Contract
An implicit or explicit documented agreement between the
service consumer and service provider about the use of the service based on
·
the commitment by a service provider to provide service
functionality and results consistent with identified real world
effects and
·
the commitment by a service consumer to interact with the
service per specific means and per specified policies,
where both consumer and provider actions are in the
manner described in the service description.
The service description provides the basis for the service
contract and, in some situations, may be used as an implicit default
service contract. In addition, the service description may set mandatory
aspects of a service contract, e.g. for security services, or may specify
acceptable alternatives. As an example of alternatives, the service
description may identify which versions of a vocabulary will be
recognized, and the specifics of the contract are satisfied when the consumer
uses one of the alternatives. Another alternative
could have a consumer identify a policy they require be satisfied, e.g. a
standard privacy policy on handling personal information, and a provider that
is prepared to accept a policy request would indicate acceptance as part
of the service contract by continuing with the interaction. In each of
these cases, the actions of the participants are consistent with an implicit
service contract without the existence of a formal agreement between the
participants.
In the case of business services, it is anticipated that the
service contract may take an explicit form and the agreement between business
consumer and business service provider is formalized. Formalization requires
up-front interactions between service consumer and service provider. In
many business interactions, especially between business organizations within or
across corporate boundaries, a consumer needs a contractual assurance
from the provider or wants to explicitly indicate choices among
alternatives, e.g., only use a subset of the business functionality offered by
the service and pay a prorated cost.
Figure 43 - Management of the
service interaction
Consequently, an implicit service contract is an
agreement (1) on the consumer side with the terms, conditions,
features and interaction means specified in the service description "as
is" or (2) a selection from alternatives that are made available
through mechanisms included in the service description, and neither of
these require any a priori interactions between the service consumer and
the service provider. An explicit service
contract always requires a form of interaction between the service
consumer and the service provider prior to the service invocation. This
interaction may regard the choice or selection of the subset of the elements of
the service description or other alternatives introduced through
the formal agreement process that would be applicable
to the interaction with the service and affect related joint action.
Any form of explicit contract couples the service consumer and provider.
While explicit contracts may be necessary or desirable in some cases, such
as in supply chain management, commerce often uses a mix of implicit and
explicit contracts, and a service provider may offer (via service description)
a conditional shift from implicit to explicit contract. For example, Twitter
offers an implicit contract on the use of its APIs to any application with the
limit on the amount of service invocations; if the application needs to use
more invocations, one has to enter into the explicit fee-based contract with
the provider. A case where an implicit contract transforms into an explicit
contract may be illustrated when one buys a new computer and it does not work.
The buyer returns the computer for repair under the manufacturer’s warranty as
stated by an implicit purchase contract. However, if the repair does not fix
the problem and the seller offers an upgraded model in replacement, the buyer
may agree to an explicit contract that limits the rights of the buyer to make
the explicit agreement public.
Control of the quality of the service execution, often
represented as a service level agreement (SLA), is performed by service
monitoring systems and includes both technical and operational business
controls. SLA is a part of the service contract and, because of the individual
nature of such contracts, may vary from one service contract to another, even
for the same consumer. Typically, a particular SLA in the service contract is a
concrete instance of the SLA declared in the service description.
Management of the service contracts is based on management
policies that may be mentioned in the service description and in the service
contracts. Management of the service contracts is mandatory for consumer
relationship management. In the case of explicit service contracts, the
contracts have to be created, stored, maintained, reviewed/controlled and
archived/destroyed as needed. All the activities are management concerns.
Explicit service contracts may be stored in specialized repositories that
provide appropriate level of security.
Management of the service interfaces is based on several
management policies that regulate
·
availability of interfaces specified in the service contracts,
·
accessibility of interfaces,
·
procedures for interface changes,
·
interface versions as well as the versions of all parts of the
interfaces,
·
traceability of the interfaces and their versions back to the
service description document.
Management of the SLA is integral to the management of
service monitoring and operational service behavior at run-time. An SLA usually
enumerates service characteristics and expected performances of the service.
Since an SLA carries the connotation of a “promise”, monitoring is needed to
know if the promise is being kept. Existence of an SLA itself does not
guarantee that the consumer will be provided with the service level specified
in the service contract.
The use of an SLA in a SOA ecosystem can be wider than just
an agreement on technical performances. An SLA may contain remedies for
situations where the promised service cannot be maintained, or the real world
effect cannot be achieved due to developments subsequent to the agreement. A
service consumer that acts accordingly to realize the real world effect
may be compensated for the breach of the SLA if the effect is not realized.
Management of the SLA includes, among others, policies to change,
update, and replace the SLA. This aspect concerns service Execution Context
because the business logic associated with a defined interface may differ in
different Execution Contexts and affect the overall performance of the service.
5.3.4.3 Policies
"Although provision of management capabilities enables
a service to become manageable, the extent and degree of permissible management
are defined in management policies that are associated with the services.
Management policies are used to define the obligations for, and permissions
to, managing the service" [WSA]. Management policies, in
essence, are the realization of governing rules and regulations. As such, some
management policies may target services while other policies may target the
management of the services.
In practice, a policy without any means of enforcing it is
vacuous. In the case of management policy, we rely on a management
infrastructure to realize and enforce management policy.
5.3.4.4 Service Description and Management
The service description identifies several management
objects such as a set of service interfaces and related set of SLAs. Service
behavioral characteristics and performances specified in the SLA depend on the
interface type and its Execution Context. In the service description, a service
consumer can find references to management policies, SLA metrics, and the means
of accessing measured values that together increase assurance in the service
quality. At the same time, service description is an artifact that needs to be
managed.
In the SOA ecosystem, the service description is the
assembled information that describes the service but it may be reported or
displayed in different presentations. While each separate version of the
service has one and only one service description, different categories of
service consumers may focus their interests on different aspects of the service
description. Thus, the same service description may be displayed not only in
different languages but also with different cultural and professional accents
in the content.
New service description may be issued to reflect changes and
update in the service. If the change in the service does not affect its service
description, the new service version may have the same service description as
the previous version except for the updated version identifier. For example, a
service description may stay the same if bugs were fixed in the service.
However, if a change in the service influences any aspects of the service
quality that can affect the real world effect resulting from interactions with
the service, the service description must reflect this change even if there are
no changes to the service interface.
Management of service description and related explicit
service contracts is essential for delivery of the service to the consumer
satisfaction. This management can also prevent business problems rooted in poor
communication between the service consumers and the service providers.
Thus, management of service description contains, among
others, management of the service description presentations, the life-cycles of
the service descriptions, service description distribution practices and
storage of the service descriptions and related service contracts. Collections
of service descriptions in the enterprise may manifest a need for specialised
registries and/or repositories. Depending on the enterprise policies, an
allocation of purposes and duties of registries and repositories may vary but
this topic is beyond the current scope.
The successful application of management relies on the
monitoring and reporting aspects of
management to enable the control aspect. Monitoring in the context of management
consists of measuring values of managed aspects and evaluating that measurement in relationship to some expectation. Monitoring in a SOA ecosystem
is enabled through the use of
mechanisms by resources for exposing managed
aspects. In the SOA framework, this
mechanism may be a service for obtaining the measurement. Alternatively, the measurement may be monitored by means of event generation containing updated values of
the managed aspect.
Approaches to monitoring may use a polling strategy in which the measurements are requested from
resources in periodic intervals, in a pull strategy in which the measurements are requested from resources
at random times, or in a push strategy
in which the measurements are
supplied by the resource without
request. The push strategy can be used in a periodic update approach
or in an “update on change”
approach. Management services
must be capable of handling these different approaches to monitoring.
Reporting is the complement to monitoring. Where
monitoring is responsible for obtaining
measurements, reporting is responsible for distributing those measurements to interested stakeholders. The separation between monitoring and reporting is made to include the possibility that data obtained
through monitoring might not be used
until an event impacting the ecosystem occurs or the measurement requires further processing to be useful.
In the SOA framework, reporting is provided using services for
requesting measurement reports. These
reports may consist of raw measurement data, formatted collections of
data, or the results of analysis performed on measurement data from collections
of different managed aspects.
Reporting is also used to support logging and auditing capabilities,
where the reporting mechanisms create
log or audit entries.
All of the properties, policies, interactions, resources,
and management are only possible if a SOA ecosystem infrastructure provides
support for managed capabilities. Each managed capability imposes different requirements on the capabilities supplied by the infrastructure
in SOA ecosystem and requires that those capabilities be usable as services or at the very least be interoperable.
While
not providing a full list of infrastructural elements of a SOA
ecosystem, we list some examples here:
1.
Registries and repositories for services, policies, and related
descriptions and contracts
2.
Synchronous and asynchronous communication channels for service
interactions (e.g., network, e-mail, message routing with ability of mediating
transport protocols, etc.)
3.
Recovery capabilities
4.
Security controls
A SOA ecosystem infrastructure, enabling service management,
should also support:
1.
Management enforcement and control means
2.
Monitoring and SLA validation controls
3.
Testing and Reporting capabilities
The combination of manageability capabilities and infrastructure
elements constitutes a certain level of SOA management maturity. While several
maturity models exist, this topic is out of the scope of the current document.
Testing for SOA combines the typical challenges of software
testing and certification with the additional needs of accommodating the
distributed nature of the resources, the greater access
of a more unbounded consumer population, and the desired flexibility to create
new solutions from existing components over which the solution developer has
little if any control. The purpose of testing is to
demonstrate a required level of reliability, correctness, and effectiveness
that enable prospective consumers to have adequate confidence in using a
service. Adequacy is defined by the consumer based on the consumer's needs and
context of use. Absolute correctness and completeness cannot be proven by
testing; however, for SOA, it is critical for the prospective consumer to know
what testing has been performed, how it has been performed, and what were the
results.
SOA services are largely software artifacts and can leverage
the body of experience that has evolved around software testing. IEEE-829 [IEEE-829]
specifies the basic set of software test documents while allowing flexibility
for tailored use. As such, the document structure can also provide guidance to
SOA testing.
IEEE-829 covers test specification and test reporting
through use of the following document types:
·
Test plan documenting the scope (what is to be tested,
both which entity and what features of the entity), the approach (how it is
tested), and the needed resources (who does the
testing, for how long), with details contained in the:
·
Test design specification: features to be tested, test
conditions (e.g. test cases, test procedures needed) and expected results
(criteria for passing test); entrance and exit criteria
·
Test case specification: test data used for input and
expected output
·
Test procedure specification: steps required to run the
test, including any set-up preconditions
·
Test item transmittal to identify the test items being
transmitted for testing
·
Test log to record what occurred during test, i.e. which
tests run, who ran, what order, what happened
·
Test incident report to capture any event
that happened during test which requires further investigation
·
Test summary as a management report summarizing test run
and results, conclusions
In summary, IEEE-829 captures (1) what was tested, (2) how
it was tested, e.g. the test procedure used, and (3) the results of the test.
5.4.1.1 Types of Testing
There are numerous aspects of testing that, in total, work
to establish that an entity is (1) built as required per policies and related
specifications prescribed by the entity's owner, and (2) delivers the
functionality required by its intended users. This is often referred to as
verification and validation.
Policies, as described in Section 4.4, that are related to testing may prescribe but are not limited to the business processes to be
followed, the standards with which an implementation must comply, and the qualifications of and restrictions on the users. In
addition to the functional requirements prescribing what an entity does, there
may also be non-functional performance and/or quality metrics that state how
well the entity does it. The relation of these policies to SOA testing is
discussed further below.
The identification of policies is the purview of governance
(section 5.1) and the assuring of compliance (including response to
noncompliance) with policies is a matter for management (section 5.3).
5.4.1.2 Range of Test Conditions
Test conditions and expected responses are detailed in the
test case specification. The test conditions should be designed to cover the
areas for which the entity's response must be documented and may include:
·
nominal conditions
·
boundaries and extremes of expected conditions
·
breaking point where the entity has degraded below a certain
level or has otherwise ceased effective functioning
·
random conditions to investigate unidentified dependencies among
combinations of conditions
·
errors conditions to test error handling
The specification of how each of these conditions should be
tested for SOA resources, including the infrastructure elements of the SOA
ecosystem, is beyond the scope of this document but is an area that evolves
along with operational SOA experience.
5.4.1.3 Configuration Management of Test Artifacts
The test item transmittal provides an unambiguous
identification of the entity being tested, thus REQUIRING that the
configuration of the entity is appropriately tracked and documented. In
addition, the test documents (such as those specified by IEEE-829) MUST also be
under a documented and appropriately audited configuration management process,
as should other resources used for testing. The
description of each artifact would follow the general description model as
discussed in section 4.1.1.1; in particular, it would include a version number
for the artifact and reference to the documentation describing the versioning
scheme from which the version number is derived.
Testing of SOA artifacts for use in the SOA ecosystem
differs from traditional software testing for several reasons. First, a highly
touted benefit of SOA is to enable unanticipated consumers to make use of
services for unanticipated purposes. Examples of this could include the
consumer using a service for a result that was not considered the primary one
by the provider, or the service may be used in combination with other services
in a scenario that is different from the one considered when designing for the
initial target consumer community. It is unlikely that a new consumer will
push the services back to anything resembling the initial test phase to test
the new use, and thus additional paradigms for testing are necessary. Some
testing may depend on the availability of test resources made available as a
service outside the initial test community, while some testing is likely to be
done as part of limited use in the operational setting. The potential responsibilities related to such "consumer
testing" is discussed further below.
Secondly, in addition to consumers who interact with a
service to realize the described real world effects,
the developer community is also intended to be a consumer. In the SOA vision
of reuse, the developer composes new solutions using existing services, where
the existing services provides access to some desired real
world effects that are needed by the new solution. The new solution is a
consumer of the existing services, enabling repeated interactions with the
existing services playing the role of reusable components. Note, those
components are used at the locations where they individually reside and are not
typically duplicated for the new solution. The new solution may itself be
offered as a SOA service, and a consumer of the service composition
representing the new solution may be totally unaware of the component services
being used. (See section 4.3.4 for further discussion on service compositions.)
Another difference from traditional testing is that the
distributed, unbounded nature of the SOA ecosystem makes it unlikely to have an
isolated test environment that duplicates the operational environment. A
traditional testing approach often makes use of a test system that is identical
to the eventual operational system but isolated for testing. After testing is
successfully completed, the tested entity would be migrated to the operational
environment, or the test environment may be delivered as part of the system to
become operational. This is not feasible for the SOA ecosystem as a whole.
SOA services must be testable in the environment and under
the conditions that can be encountered in the operational SOA ecosystem. As
the ecosystem is in a state of constant change, so some level of testing is
continuous through the lifetime of the service, leveraging utility services
used by the ecosystem infrastructure to monitor its own health and respond to
situations that could lead to degraded performance. This implies the test
resources must incorporate aspects of the SOA paradigm, and a category of
services may be created to specifically support and enable effective monitoring
and continuous testing for resources participating in
the SOA ecosystem.
While SOA within an enterprise may represent a more
constrained and predictable operational environment, the composability and
unanticipated use aspects are highly touted within the enterprise. The
expanded perspective on testing may not be as demanding within an enterprise
but fuller consideration of the ecosystem enables the enterprise to be more responsive
should conditions change.
IEEE-829 identifies fundamental aspects of testing, and many
of these should carry over to SOA testing: in particular, the identification of
what is to be tested, how it is to be tested, and by whom the testing is to be
done. While IEEE-829 identifies a suggested document tree, the availability of
these documents in the SOA ecosystem is discussed below.
5.4.3.1 What is to be Tested
The focus of this discussion is the SOA service. It is
recognized that the infrastructure components of any SOA environment are likely
to also be SOA services and, as such, falls under the same testing guidance.
Other resources that contribute to a SOA environment may not be SOA services,
but are expected to satisfy the intent if not the letter of guidance presented
here. Specific differences for such resources are as
yet largely undefined and further elaboration is beyond the scope of the
SOA-RAF.
The following discussion often focuses on a singular SOA
service but it is implicit that any service may be a composite of other
services. As such, testing the functionality of a composite service may
effectively be testing an end-to-end business process that is being provided by
the composite service. If new versions are available for the component
services, appropriate end-to-end testing of the composite may be required in
order to verify that the composite functionality is still adequately provided.
The level of required testing of an updated composite depends on policies of
those providing the service, policies of those using the service, and mission
criticality of those depending on the service results.
The SOA service to be tested MUST be unambiguously
identified as specified by its applicable configuration management scheme.
Specifying such a scheme is beyond the scope of the SOA-RAF other than to say
the scheme should be documented and itself under configuration management.
5.4.3.1.1 Origin of Test Requirements
In the Service Description model (Figure 13), the aspects of
a service that need to be described are:
·
the service functionality and technical assumptions that underlie
the functionality;
·
the policies that describe conditions of use;
·
the service interface that defines information exchange with the
service;
·
service reachability that identifies how and where message
exchange is to occur; and
·
metrics access for any participant to
have information on how a service is performing.
Service testing must provide adequate assurance that each of
these aspects is operational as defined.
The information in the service description comes from
different sources. The functionality is defined through whatever process
identifies needs and the community for which these needs are addressed. The
process may be ad hoc as serves the prospective service owner or strictly
governed, but defining the functionality is an essential first step in development.
It is also an early and ongoing focus of testing to ensure the service
accurately reflects the described functionality and the described functionality
accurately addresses the consumer needs.
Policies define the conditions of development and conditions
of use for a service and are typically specified as part of the governance
process. Policies constraining service development, such as coding standards
and best practices, require appropriate testing and auditing during development
to ensure compliance. While the governance process identifies development
policies, these are likely to originate from the technical community
responsible for development activities. Policies that define conditions of use
often define business practices that service owners and providers or those
responsible for the SOA infrastructure want followed. These policies are
initially tested during service development and are continuously monitored
during the operational lifetime of the service.
The testing of the service interface and service
reachability are often related but essentially reflect different motivations
and needs. The service interface is specified as a joint product of the
service owners and providers who define service functionality, the prospective
consumer community, the service developer, and the governance process. The
semantics of the information model must align with the semantics of those who
consume the service in order for there to be meaningful exchange of
information. The structure of the information is influenced by the consumer
semantics and the requirements and constraints of the representation as
interpreted by the service developer. The service process model that defines
actions which can be performed against a service and any temporal dependencies
derive from the defined functionality and may be influenced by the development
process. Any of these constraints may be identified and expressed as policy
through the governance process.
Service reachability conditions are the purview of the
service provider who identifies the service endpoint and the protocols
recognized at the endpoint. These may be constrained by governance decisions
on how endpoint addresses may be allocated and what protocols should be used.
While the considerations for defining the service interface
derive from several sources, testing of the service interface is more
straightforward and isolated in the testing process. At any point where the
interface is modified or exposes a new resource, the
message exchange should be monitored both to ensure the message reaches its
intended destination and it is parsed correctly once received. Once an
interface has been shown to function properly, it is unlikely to fail later
unless something fundamental to the service changes.
The service interface is also tested when the service
endpoint changes. Testing of the endpoint ensures message exchange can occur
at the time of testing and the initial testing shows the interface is being
processed properly at the new endpoint. Functioning of a service endpoint at
one time does not guarantee it is functioning at another time, e.g. the server
with the endpoint address may be down, making testing of service reachability a
continual monitoring function through the life of the service’s use of the
endpoint. Also, while testing of the service endpoint is a necessary and most
commonly noted part of the test regiment, it is not in itself sufficient to
ensure the other aspects of testing discussed in this section.
Finally, governance is impossible without the collection of
metrics against which service behavior can be assessed. Metrics are also a key
indicator for consumers to decide if a service is adequate for their needs.
For instance, the average response time or the recent availability can be
determining factors even if there are no rules or regulations promulgated
through the governance process against which these metrics are assessed. The
available metrics are a combination of those expected by the consumer community
and those mandated through the governance process. The total set of metrics
will evolve over time with SOA experience. Testing of the services that gather
and provide access to the metrics will follow testing as described in this
section, but for an individual service, testing will ensure that the metrics
access indicated in the service description is accurate.
The individual test requirements highlight aspects of the
service that testing must consider but testing must establish more than
isolated behavior. The emphasis is the holistic results of interacting with
the service in the SOA environment. Recall that the execution context is the
set of agreements between a consumer and a provider that define the conditions
under which service interaction occurs. The agreements are expected to be
predominantly the acceptance of the standard conditions as enumerated by the
service provider, but it may include the identification of alternate conditions
that will govern the interaction.
For example, the provider may prefer a policy where it can
sell the contact information of its consumers but will honor the request of a
consumer to keep such information private. The identification of the alternate
privacy policy is part of the execution context, and it is the application of
and compliance with this policy that operational monitoring will attempt to
measure. The collection of metrics showing this condition is indeed met when
chosen is considered part of the ongoing testing of the service.
Other variations in the execution context also require
monitoring to ensure that different combinations of conditions perform together
as desired. For example, if a new privacy policy takes additional resources to apply, this may affect quality of service and
propagate other effects. These could not be tested during the original testing
if the alternate policy did not exist at that time.
5.4.3.1.2 Testing Against Non-Functional Requirements
Testing against non-functional requirements constitutes
testing of business usability of the service. In a marketplace of services,
non-functional characteristics may be the primary differentiator between
services that produce essentially the same real
world effects.
As noted in the previous section, non-functional
characteristics are often associated with policies or other terms of use and
may be collected in service level contracts offered by the service providers.
Non-functional requirements may also reflect the network and hardware infrastructure
that support communication with the service, and changes may impact quality of
service. The service consumer and even the
service provider may not be aware of all such infrastructure changes but the
changes may manifest in shared states that impact the usability of the service.
In general, a change in the non-functional requirements
results in a change to the execution context, but as with any collection of
information that constitutes a description, the execution context is unable to
explicitly capture all non-functional requirements that may apply. A change in
non-functional requirements, whether explicitly part of the execution context
or an implicit contributor, may require retesting of the service even if its functionality
and the implementation of the functionality has not changed. Depending on the
circumstances, retesting may require a formal recertifying of end-to-end
behavior or more likely will be part of the continuous monitoring that applies
throughout the service lifetime.
5.4.3.1.3 Testing Content and the Interests of Consumers
As noted in section 5.4.1.1, testing may involve
verification of conformance with respect to policies and technical
specifications and validation with respect to sufficiency of functionality to
meet some prescribed use. It may also include demonstration of performance and
quality aspects. For some of these items, such as demonstrating the business
processes followed in developing the service or the use of standards in
implementing the service, the testing or relevant auditing is done internal to
the service development process and follows traditional software testing and
quality assurance. If it is believed of value to potential consumers,
information about such testing could be included in the service description.
However, it is not required that all test or compliance artifacts be available
to consumers, as many of the details tested may be part of the opacity of the
service implementation.
Some aspects of the service being tested will reflect
directly on the real world effects realized
through interaction with the service. In these cases, it is more likely that
testing results will be directly relevant to potential consumers. For example,
if the service was designed to correspond to certain elements of a business
process or that a certain workflow is followed, testing should verify that the real world effects reflect that the business
process or workflow were satisfactorily captured.
The testing may also need to demonstrate that specified
conditions of use are satisfied. For example, policies may be asserted that
require certain qualifications of or impose
restrictions on the consumers who may interact with the service. The service
testing must demonstrate that the service independently enforces the policies
or it provides the required information exchanges with the SOA ecosystem so
other resources can ensure the specified conditions.
The completeness of the testing, both in terms of the
features tested and the range of parameters for which response is tested,
depends on the context of expected use: the more critical the use, the more
complete the testing. There are always limits on the resources
available for testing, if nothing else than the service must be available for
use in a finite amount of time.
This again emphasizes the need for adequate documentation to
be available. If the original testing is very thorough, it may be adequate for
less demanding uses in the future. If the original testing was more
constrained, then well-documented test results establish the foundation on which
further testing can be defined and executed.
5.4.3.2 How Testing is to be Done
Testing should follow well-defined methodologies and, if
possible, should reuse test artifacts that have proven generally useful for
past testing. For example, IEEE-829 notes that test cases are separated from
test designs to allow for use in more than one design and to allow for reuse in
other situations. In the SOA ecosystem, description of such artifacts, as with
description of a service, enables awareness of the item and describes how the
artifact may be accessed or used.
As with traditional testing, the specific test procedures
and test case inputs are important so the tests are unambiguously defined and
entities can be retested in the future. Automated testing and regression testing
may be more important in the SOA ecosystem in order to re-verify a service is
still acceptable when incorporated in a new use. For example, if a new use
requires the services to deal with input parameters outside the range of
initial testing, the tests could be rerun with the new parameters. If the
testing resources are available to consumers within the SOA ecosystem, the
testing as designed by test professionals could be consumed through a service
accessed by consumers, and their results could augment those already in place.
This is discussed further in the next section.
5.4.3.3 Who Performs the Testing
As with any software, the first line of testing is unit
testing done by software developers. It is likely that initial testing will be
done by those developing the software but may also be done independently by
other developers. For SOA development, unit testing is likely confined to a
development sandbox isolated from the SOA ecosystem.
SOA testing will differ from traditional software testing in
that testing beyond the development sandbox must incorporate aspects of the SOA
ecosystem, and those doing the testing must be familiar with both the
characteristics and responses of the ecosystem and the tools, especially those
available as services, to facilitate and standardize testing. Test
professionals will know what level of assurance must be established as the
exposure of the service to the ecosystem and ecosystem to the service increases
towards operational status. These test professionals may be internal resources
to an organization or may evolve as a separate discipline provided through
external contracting.
As noted above, it is unlikely that a complete duplicate of
the SOA ecosystem will be available for isolated testing, and thus use of
ecosystem resources will manifest as a transition
process rather than a step change from a test environment to an operational
one. This is especially true for new composite services that incorporate
existing operational services to achieve the new functionality. The test
professionals will need to understand the available resources and the
ramifications of this transition.
As with current software development, a stage beyond work by
test professionals will make use of a select group of typical users, commonly
referred to as beta testers, to report on service response during typical
intended use. This establishes fitness by the consumers, providing final
validation of previously verified processes, requirements, and final
implementation.
In traditional software development, beta testing is the end
of testing for a given version of the software. However, although the initial
test phase can establish an appropriate level of confidence consistent with the
designed use for the initial target consumer community, the operational service
will exist in an evolving ecosystem, and later conditions of use may differ
from those thought to be sufficient during the initial testing. Thus,
operational monitoring becomes an extension of testing through the service
lifetime. This continuous testing will attempt to ensure that a service does
not consume an inordinate amount of ecosystem resources or display other
behavior that degrades the ecosystem, but it will not undercover functional
errors that may surface over time.
As with any software, it is the responsibility of the
consumers to consider the reasonableness of solutions in order to spot errors
in either the software or the way the software is being used. This is
especially important for consumers with unanticipated uses that may go beyond
the original test conditions. It is unlikely the consumers will initiate a new
round of formal testing unless the new use requires a significantly higher
level of confidence in the service. Rather the consumer becomes a new
extension to the testing regiment. Obvious testing would include a sanity
check of results during the new use. However, if the details of legacy testing
are associated with the service through the service description and if testing
resources are available through automated testing services, then the new
consumers can rerun and extend previous testing to include the extended test
conditions. If the test results are acceptable, these can be added to the
documentation of previous results and become the extended basis for future
decisions by prospective consumers on the appropriateness of the service. If
the results are not acceptable or in some way questionable, the responsible
party for the service or testing professionals can be brought in to decide if
remedial action is necessary.
5.4.3.4 How Testing Results are Reported
For any SOA service, an accurate reporting of the testing a
service has undergone and the results of the testing is vital to consumers
deciding whether a service is appropriate for intended use. Appropriateness
may be defined by a consumer organization and require specific test regiments
culminating in a certification; appropriateness could be established by
accepting testing and certifications that have been conferred by others.
The testing and certification information should be
identified in the service description. Referring to the general description
model of Figure 11, tests conducted by or under a request from the service
owner (see ownership in section 3.1.3) would be captured under Annotations from Owners. Testing done by others, such as consumers
with unanticipated uses, could be associated through Annotations from 3rd
Parties. The annotations should clearly indicate what was tested, how the
testing was done, who did the testing, and the testing results. The clear
description of each of these artifacts and of standardized testing protocols
for various levels of sophistication and completeness of testing would enable a
common understanding and comparison of test coverage. It will also make it
more straightforward to conduct and report on future testing, facilitating the
maintenance of the service description.
Consumer testing and the reporting of results raises
additional issues. While stating who did the testing is mandatory, there may
be formal requirements for authentication of the tester to ensure traceability
of the testing claims. In some circumstances, persons or organizations would
not be allowed to state testing claims unless the tester was an approved
entity. In other cases, ensuring the tester had a valid email may be
sufficient. In either case, it would be at the discretion of the potential
consumer to decide what level of authentication was acceptable and which
testers are considered authoritative in the context of their anticipated use.
Finally, in a world of openly shared information, we would
see an ever-expanding set of testing information as new uses and new consumers
interact with a service. In reality, these new uses may represent proprietary
processes or classified use that should only be available to authorized
parties. Testing information, as with other elements of description, may
require special access controls to ensure appropriate access and use.
Testing of SOA services should be consistent with the SOA
paradigm. In particular, testing resources and artifacts should be visible in
support of service interaction between providers and consumers, where here the
interaction is between the testing resource and the tester. In addition, the
idea of opacity of the implementation should limit the details that need to be
available for effective use of the test resources. Testing that requires
knowledge of the internal structure of the service or its underlying capability
should be performed as part of unit testing in the development sandbox, and
should represent a minimum level of confidence before the service begins its
transition to further testing and eventual operation in the SOA ecosystem.
5.4.4.1 Progression of SOA Testing
Software testing is a gradual exercise going from micro
inspection to testing macro effects. The first step in testing is likely the
traditional code reviews. SOA considerations would account for the distributed
nature of SOA, including issues of distributed security and best practices to
ensure secure resources. It would also set the groundwork for opacity of
implementation, hiding programming details and simplifying the use of the
service.
Code review is likely followed by unit testing in a
development sandbox isolated from the operational environment. The unit
testing is done with full knowledge of the service internal structure and
knowledge of resources representing underlying capabilities. It tests the
interface to ensure exchanged messages are as specified in the service description
and the messages can be parsed and interpreted as intended. Unit testing also
verifies intended functionality and that the software has dealt correctly with
internal dependencies, such as structure of a file system or access to other
dedicated resources.
Some aspects of unit testing require external dependencies
be satisfied, and this is often done using mock objects to substitute for the
external resources. In particular, it will likely be necessary to include
mocks of existing operational services, both those provided as part of the SOA
infrastructure and services from other providers.
Service Mock
A service mock is an entity that mimics some aspect of the
performance of an operational service without committing to the real world effects that the operational service
would produce.
Mocks are discussed in detail in sections 5.4.4.3 and 5.4.4.4.
After unit testing has demonstrated an adequate level of
confidence in the service, the testing must transition from the tightly
controlled environment of the development sandbox to an environment that more
clearly resembles the operational SOA ecosystem or, at a minimum, the intended
enterprise. While sandbox testing will use simple mocks of some aspects of the
SOA environment, such as an interface to a security service without the
security service functionality, the dynamic nature of SOA makes a full
simulation infeasible to create or maintain. This is especially true when a
new composite service makes use of operational services provided by others.
Thus, at some point before testing is complete, the service will need to
demonstrate its functionality by using resources and dealing with conditions
that only exist in the full ecosystem or the intended enterprise. Some of
these resources may still provide test interfaces -- more on this below -- but
the interfaces will be accessible using the SOA environment and not just
implemented for the sandbox.
At this stage, the opacity of the service becomes important
as the details of interacting with the service now rely on correct use of the
service interface and not knowledge of the service internals. The workings of
the service will only be observable through the real
world effects realized through service interactions and external indications
that conditions of use, such as user authentication, are satisfied. Monitoring
the behavior of the service will depend on service interfaces that expose
internal monitoring or provide required information to the SOA infrastructure
monitoring function. The monitoring required to test a new service is likely
to have significant overlap with the monitoring the SOA infrastructure includes
to monitor its own health and to identify and isolate behavior outside of
acceptable bounds. This is exactly what is needed as part of service testing,
and it is reasonable to assume that the ecosystem transition includes use of
operational monitoring rather than solely dedicated monitoring for each service
being tested.
Use of SOA monitoring resources during the explicit testing
phase sets the stage for monitoring and a level of continual testing throughout
the service lifetime.
A SOA service is not required to make use of other
operational services beyond what may be required for monitoring by the
ecosystem infrastructure. The service can implement hardcoded dependencies
which have been tested in the development sandbox through the use of dedicated
mocks. While coordination may be required with real data sources during
integration testing, the dependencies can be constrained to things that can be
tested in a more traditional manner. Policies can also be set to restrict
access to pre-approved users, and thus the question of unanticipated users and
unanticipated uses can be eliminated. Operational readiness can be defined in
terms of what can be proven in isolated testing. While all this may provide
more confidence in the service for its designed purpose,
such a service will not fully participate in the benefits or challenges of the
ecosystem. This is akin to filling a swimming pool with sea water and having
someone in the pool say they are swimming in the ocean.
In considering the testing needed for a fully participating
service, consider the example of a new composite service that combines the real world effects and complies with the conditions
of use of five existing operational services. The developer of the composite
service does not own any of the component services and has limited, if any,
ability to get the distributed owners to do any customization. The developer
also is limited by the principle of opacity to information comprising the
service description, and does not know internal details of the component
services. The developer of the composite service must use the component
services as they exist as part of the SOA environment, including what is
provided to support testing by new users. This introduces requirements for
what is needed in the way of service mocks.
Service mocks enables the tested service to respond to
specific features of an operational service that is being used as a component.
It allows service testing to proceed without needing access to or with only
limited engagement with the component service. Mocks can also mimic difficult
to create situations for which it is desired to test the new service response.
For composite services using multiple component services, mocks may be used in
combination to function for any number of the components. Note, when using
service mocks, it is important to remember that it is not the component service
that is being tested (although anomalous behavior may be uncovered during
testing) but the use of the component in the new composite.
Individual service mocks can emphasize different features of
the component service they represent but any given mock does not have to mimic
all features. For example, a mock of the service interface can echo a sent
message and demonstrate the message is reaching its intended destination. A
mock could go further and parse the sent message to demonstrate the message not
only reached its destination but was understood. As a final step, the mock
could report back what actions would have been taken by the component service
and what real world effects would result. If
the response mimicked the operational response, functional testing could
proceed as if the real world effect actually
occurred.
There are numerous ways to provide mock functionality. The
service mock could be a simulation of the operational service and return
simulated results in a realistic response message or event notification. It is
also possible for the operational service to act as its own mock and simply not
execute the commit stage of its functionality. The service mock could use a
combination of simulation and service action without commit to generate a
report of what would have occurred during the defined interaction with the
operational service.
As the service proceeds through testing, mocks should be
systematically replaced by the component resources accessed through their
operational interfaces. Before beta testing begins, end-to-end testing, i.e.
proceeding from the beginning of the service interaction to the resulting real
world results, should be accomplished using component resources via their
operational interfaces.
In traditional testing, it is often the test professionals
who design and develop the mocks, but in the distributed world of SOA, this may
not be efficient or desirable.
In the development sandbox, it is likely the new service
developer or test professionals working with the developer will create mocks
adequate for unit testing. Given that most of this testing is to verify the new
service is performing as designed, it is not necessary to have high fidelity
models of other resources being accessed. In addition, given opacity of SOA
implementation, the developer of the new service may not have sufficient
detailed knowledge of a component service to build a detailed mock of the
component service functionality. Sharing existing mocks at this stage may be
possible but the mocks would need to be implemented in the sandbox, and for
simple models it is likely easier to build the mock from scratch.
As testing begins its transition to the wider SOA
environment, mocks may be available as services. For existing resources, it is
possible that an Open Source model could evolve where service mocks of
available functions can be catalogued and used during initial interaction of
the tested service and the operational environment. Widely used functions may
have numerous service mocks, some mimicking detailed conditions within the SOA
infrastructure. However, the Open Source model is less likely to be sufficient
for specialty services that are not widely used by a large consumer community.
The service developer is probably best qualified for also
developing more detailed service mocks or for mock modes of operational
services. This implies that in addition to their operational interfaces,
services will routinely provide test interfaces to enable service mocks to be
used as services. As noted above, a new service developer wanting to build a
mock of component services is limited to the description provided by the
component service developer or owner. The description typically will detail real world effects and conditions of use but will
not provide implementation details, some of which may be proprietary. Just as
important in the SOA ecosystem, if it becomes standard protocol for developers
to create service mocks of their own services, a new service developer is only
responsible for building his own mocks and can expect other mocks to be
available from other developers. This reduces duplication of effort where
multiple developers would be trying to build the same mocks from the same
insufficient information. Finally, a service developer is probably best
qualified to know when and how a service mock should be updated to reflect
modified functionality or message exchange.
It is also possible that testing organizations will evolve
to provide high-fidelity test harnesses for new services. The harnesses would
allow new services to plug into a test environment and would facilitate
accessing mocks of component services. However, it will remain a constant
challenge for such organizations to capture evolving uses and characteristics
of service interactions in the real SOA environment and maintain the fidelity
and accuracy of the test systems.
5.4.4.5 Fundamental Questions for SOA Testing
In order for the transition to the SOA operational
environment to proceed, it is necessary to answer two fundamental questions:
·
Who provides what testing resources for the SOA operational
environment, e.g. mocks of interfaces, mocks of functionality, monitoring
tools?
·
What testing needs to be accomplished before operational
environment resources can be accessed for further testing?
The discussion in section 5.4.4.4 notes various levels of sophistication of service mocks and different communities are likely to be responsible
for different levels. Section 5.4.4.4 advocates a significant role for service
developers, but there needs to be community consensus that such mocks are
needed and that service developers will agree to fulfilling this role.
There is also a need for consensus as to what tools should be available as
services from the SOA infrastructure.
As for use of the service mocks and SOA environment
monitoring services, practical experience is needed upon which guidelines can
be established for when a new service has been adequately tested to proceed
with a greater level of exposure with the SOA environment. Malfunctioning services
could cause serious problems if they cannot be identified and isolated. On the
other hand, without adequate testing under SOA operational conditions, it is
unlikely that problems can be uncovered and corrected before they reach an
operational stage.
As noted in section 5.4.4.2, some of these questions can be avoided by restricting services to more traditional use scenarios. However, such
restriction will limit the effectiveness of SOA use and the result will
resemble the constraints of traditional integration activities we are trying to
move beyond.
The discussion of SOA Testing indicates numerous architectural
implications on the SOA ecosystem:
·
The distributed, boundary-less nature of the SOA ecosystem makes
it infeasible to create and maintain a single mock of the entire ecosystem to
support testing activities.
·
A standard suite of monitoring services needs to be defined,
developed, and maintained. This should be done in a manner consistent with the
evolving nature of the ecosystem.
·
Services should provide interfaces that support access in a test
mode.
·
Testing resources must be described and their descriptions must
be catalogued in a manner that enables their discovery and access.
·
Guidelines for testing and ecosystem access need to be
established and the ecosystem must be able to enforce those guidelines asserted
as policies.
·
Services should be available to support automated testing and
regression testing.
·
Services should be available to facilitate updating service
description by anyone who has performed testing of a service.
This Reference Architecture Framework is an abstract
architectural description of Service Oriented Architecture, which means that it
is especially difficult to construct tests for conformance to the architecture.
In addition, conformance to an architectural specification does not, by itself,
guarantee any form of interoperability between multiple implementations.
However, it is possible to decide whether or not a
given architecture is conformant to an architectural description such as this
one. In discussions of conformance we use the term target architecture
to identify the (typically concrete) architecture that may be viewable as
conforming to the abstract principles outlined in this document.
Target Architecture
A target architecture is an architectural description of a
system that is intended to be viewed as conforming to the SOA-RAF.
While we cannot guarantee interoperability between target
architectures (or more specifically between applications and systems residing
within the ecosystems of those target architectures), interoperability between
target architectures is promoted by conformance to this Reference Architecture
Framework as it reduces the semantic impedance mismatch between the different
ecosystems.
The primary measure of conformance is whether given concepts
as described in document have corresponding concepts in the target
architecture. Such a correspondence MUST honor the relationships identified
within this document for the target architecture to be considered conforming.
For example, in Section 3.1.3.1 we identify resource as a key concept. A resource is associated with an owner and a number of
identifiers. For a target architecture to conform to the SOA-RAF, it must be
possible to find corresponding concepts of resource,
identifier and owner within the target architecture: say entity,
token and user . Furthermore, the relationships between entity,
token and user MUST mirror the relationships between resource, identifier and owner appropriately.
Clearly, such correspondence is simpler if the terminology
within the target architecture is identical to that in the SOA-RAF. But so long
as the ‘graph’ of concepts and relationships is consistent, that is all that is
required for the target architecture to conform to this Reference Architecture
Framework.
[EDITOR’S NOTE: The conformance section is not complete]
The following individuals have participated in the work of
the technical committee responsible for creation of this specification and are
gratefully acknowledged:
Participants:
Chris Bashioum, MITRE Corporation
Rex Brooks, Individual Member
Peter Brown, Individual Member
Scott Came, Search Group Inc.
Joseph Chiusano, Booz Allen Hamilton
Robert Ellinger, Northrop Grumman Corporation
David Ellis, Sandia National Laboratories
Jeff A. Estefan, Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Don Flinn, Individual Member
Anil John, Johns Hopkins University
Ken Laskey, MITRE Corporation
Boris Lublinsky, Nokia Corporation
Francis G. McCabe, Individual Member
Christopher McDaniels, USSTRATCOM
Tom Merkle, Lockheed Martin Corporation
Jyoti Namjoshi, Patni Computer Systems Ltd.
Duane Nickull, Adobe Inc.
James Odell, Associate
Michael Poulin, Fidelity Investments
Michael Stiefel, Associate
Danny Thornton, Northrop Grumman
Timothy Vibbert, Lockheed Martin Corporation
Robert Vitello, New York Dept. of Labor
The committee would particularly like to underline the
significant contributions made by Rex Brooks, Jeff Estefan, Ken Laskey, Boris
Lublinsky, Frank McCabe, Michael Poulin and Danny Thornton
The first page number refers to the first use of the term.
The second, where necessary, refers to the page where the term is formally
defined.
Action
Action Level Real World Effect
Actor
Architecture
Architectural Description
Authority
Business Processes
Capability
Choreography
Commitment
Communicative Action
Constitution
Contract
Delegate
Description
Endpoint
Enterprise
Governance
Governance Framework
Governance Processes
Identifier
Identity
Joint Action
Leadership
Life-cycle manageability
Logical Framework
Management
Management Policy
Management Service
Manageability Capability
Message Exchange
Model
Obligation
Objective
Operations
Orchestration
Ownership
Ownership Boundary
Participant
Peer
Permission
Policy
Policy Conflict
Policy Conflict Resolution
Policy Constraint
Policy Decision
Policy Enforcement
Policy Framework
Policy Object
Policy Ontology
Policy Owner
Policy Subject
Presence
Private State
Protocol
Public Semantics
Qualification
Real World Effect
Regulation
Resource
Responsibility
Right
Risk
Role
Rule
Security
Semantic Engagement
Service Action
Service Consumer
Service Level Real World Effect
Service Mediator
Service Provider
Shared State
Skill
Social Structure
Stakeholder
State
System
System Stakeholder
Trust
View
Viewpoint
Figure 44 illustrates an annotated example of a UML class
diagram that is used to represent a visual model depiction of the Resources
Model in the Participation in a SOA Ecosystem view.

Figure 44 - Example UML class diagram—Resources
Lines connecting boxes (classifiers) represent associations
between things. An association has two roles (one in each direction). A role
can have cardinality, for example, one or more (“1..*”) stakeholders
own zero or more (“0..*) resources. The role from
classifier A to B is labeled closest to B, and vice versa, for example, the
role between resource to
Identity can be read as resource embodies Identity, and Identity denotes a resource.
Mostly, we use named associations, which are denoted with a
verb or verb phrase associated with an arrowhead. A named association reads
from classifier A to B, for example, one or more stakeholders
owns zero or more resources.
Named associations are a very effective way to model relationships between
concepts.
An open diamond (at the end of an association line) denotes
an aggregation, which is a part-of relationship, for example, Identifiers are
part of Identity (or conversely, Identity is made up of Identifiers).
A stronger form of aggregation is known as composition,
which involves using a filled-in diamond at the end of an association line (not
shown in above diagram). For example, if the association between Identity and
Identifier were a composition rather than an aggregation as shown, deleting
Identity would also delete any owned Identifiers. There is also an element of
exclusive ownership in a composition relationship between classifiers, but this
usually refers to specific instances of the owned classes (objects).
This is by no means a complete description of the semantics
of all diagram elements that comprise a UML class diagram, but rather is
intended to serve as an illustrative example for the reader. It should be
noted that the SOA-RAF utilizes additional class diagram elements as well as
other UML diagram types such as sequence diagrams and component diagrams. The
reader who is unfamiliar with the UML is encouraged to review one or more of
the many useful online resources and book publications available describing UML
(see, for example, www.uml.org).
A critical factors analysis (CFA) is an analysis of the key
properties of a project. A CFA is analyzed in terms of the goals of the
project, the critical factors that will lead to its success and the measurable
requirements of the project implementation that support the goals of the
project. CFA is particularly suitable for capturing quality attributes of a
project, often referred to as “non-functional” or “other-than-functional”
requirements: for example, security, scalability, wide-spread adoption, and so
on. As such, CFA complements rather than attempts to replace other requirements
capture techniques.
D.1 Goals
A goal is an overall target that you are trying to reach
with the project. Typically, goals are hard to measure by themselves. Goals are
often directed at the potential consumer of the product rather than the
technology developer.
D.2 Critical Success Factors
A critical success factor (CSF) is a property, sub-goal that
directly supports a goal and there is strong belief that without it the goal is
unattainable. CSFs themselves are not necessarily measurable in themselves.
D.3 Requirements
A requirement is a specific measurable property that
directly supports a CSF. The key here is measurability: it should be possible
to unambiguously determine if a requirement has been met. While goals are
typically directed at consumers of the specification, requirements are focused
on technical aspects of the specification.
D.4 CFA Diagrams
It can often be helpful to illustrate graphically the key
concepts and relationships between them. Such diagrams can act as effective
indices into the written descriptions of goals etc., but is not intended to replace
the text.
The legend:

illustrates the key elements of the graphical notation.
Goals are written in round ovals, critical success factors are written in
round-ended rectangles and requirements are written using open-ended
rectangles. The arrows show whether a CSF/goal/requirement is supported by
another element or opposed by it. This highlights the potential for conflict in
requirements.
The white paper “Navigating the SOA Open Standards Landscape
Around Architecture” issued jointly by OASIS, OMG, and The Open Group [SOA-NAV]
was written to help the SOA community at large navigate the myriad of
overlapping technical products produced by these organizations with specific
emphasis on the “A” in SOA, i.e., Architecture.
The white paper explains and positions standards for SOA reference
models, ontologies, reference architectures, maturity models, modeling
languages, and standards work on SOA governance. It outlines where the works
are similar, highlights the strengths of each body of work, and touches on how
the work can be used together in complementary ways. It is also meant as a
guide to users for selecting those specifications most appropriate for their
needs.
While the understanding of SOA and SOA Governance concepts
provided by these works is similar, the evolving standards are written from
different perspectives. Each specification supports a similar range of
opportunity, but has provided different depths of detail for the perspectives
on which they focus. Although the definitions and expressions may differ,
there is agreement on the fundamental concepts of SOA and SOA Governance.
The following is a summary taken from [SOA-NAV] of
the positioning and guidance on the specifications:
·
The OASIS Reference Model for SOA (SOA RM) is the most abstract
of the specifications positioned. It is used for understanding core SOA
concepts
·
The Open Group SOA Ontology extends, refines, and formalizes some
of the core concepts of the SOA RM. It is used for understanding core SOA
concepts and facilitates a model-driven approach to SOA development.
·
The OASIS Reference Architecture Foundation for SOA (this
document) is an abstract, foundational reference architecture addressing a
broader ecosystem viewpoint for building and interacting within the SOA
paradigm. It is used for understanding different elements of SOA, the
completeness of SOA architectures and implementations, and considerations for
reaching across ownership boundaries where there is no single authoritative
entity for SOA and SOA governance.
·
The Open Group SOA Reference Architecture is a layered
architecture from consumer and provider perspective with cross cutting concerns
describing these architectural building blocks and principles that support the
realizations of SOA. It is used for understanding the different elements of
SOA, deployment of SOA in enterprise, basis for an industry or organizational
reference architecture, implication of architectural decisions, and positioning
of vendor products in a SOA context.
·
The Open Group SOA Governance Framework is a governance domain
reference model and method. It is for understanding SOA governance in
organizations. The OASIS Reference Architecture for SOA Foundation contains an
abstract discussion of governance principles as applied to SOA across
boundaries
·
The Open Group SOA Integration Maturity Model (OSIMM) is a means
to assess an organization’s maturity within a broad SOA spectrum and define a
roadmap for incremental adoption. It is used for understanding the level of SOA
maturity in an organization
·
The Object Management Group SoaML Specification supports services
modeling UML extensions. It can be seen as an instantiation of a subset of the
Open Group RA used for representing SOA artifacts in UML.
Fortunately, there is a great deal of agreement on the foundational
core concepts across the many independent specifications and standards for SOA.
This could be best explained by broad and common experience of users of SOA and
its maturity in the marketplace. It also provides assurance that investing in
SOA-based business and IT transformation initiatives that incorporate and use
these specifications and standards helps to mitigate risks that might
compromise a successful SOA solution.

Figure 45 - SOA Reference
Architecture Positioning (from “Navigating the SOA Open Standards Landscape
Around Architecture, © OASIS, OMG, The Open Group)














































