| Help TOC > Introduction to DEXlib > DEX technology overview
|
| DEX technology overview |
Date: 2010/03/17 11:26:07
Revision: 1.19
|
This section provides a high level overview of the key concepts used to document the usage of
ISO 10303-239 PLCS (Product Life Cycle Support) standard.
ISO 10303-239 Product life cycle support
(PLCS
Product life cycle support
(PLCS ) specifies an
information model that defines
what information can be represented and exchanged to support a product
through life.
The information model is specified using the EXPRESS
) specifies an
information model that defines
what information can be represented and exchanged to support a product
through life.
The information model is specified using the EXPRESS information
modelling language. The EXPRESS based information model is used to derive an XML Schema
information
modelling language. The EXPRESS based information model is used to derive an XML Schema .
As well as XML conformant to the XML Schema (ISO 10303-28
.
As well as XML conformant to the XML Schema (ISO 10303-28 ed. 2),
ISO 10303
ed. 2),
ISO 10303 also defines structured text exchange formats
(ISO 10303-21
also defines structured text exchange formats
(ISO 10303-21 )
driven from the EXPRESS language.
)
driven from the EXPRESS language.
The role of ISO 10303-239 in data exchange is illustrated in Figure 1.
This shows how the ISO 10303-239 information model defines the scope of the information to be exchanged or shared,
and offers a range of exchange formats independent of technology
to support that exchange. These formats define the requirements for translators
applied to specific systems.
Figure 1 — The usage of ISO 10303-239
Because the information model defined by ISO 10303-239 (PLCS) is a generic model
supporting the whole life cycle of a product, it has a scope
that is wider than most applications, business processes or single data exchanges.
Consequently Data EXchange Specifications (DEXs) have been developed by the OASIS/PLCS TC members to support the
usage of subsets of the model.
have been developed by the OASIS/PLCS TC members to support the
usage of subsets of the model.
A DEX specifies the subset of, and associated usage guidance for, ISO 10303-239 (PLCS) required for
a specific business purpose, e.g.
DEX (D003):— Task set
. DEXs can be also used to
contract for information, and software applications may declare conformance to a DEX,
thus ensuring interoperability.
The OASIS DEXs, developed to support common information exchange requirements identified
by OASIS/PLCS TC members, are built from "Templates ".
The Templates describe and specify how common business concepts
should be represented using the PLCS information model.
Templates have been defined at a fine grained level to encourage maximum re-use
across different DEXs, hence ensuring consistent usage of the PLCS information model.
For example, the Template representing_organization
is used to represent an organization, and can be reused whenever this is required.
".
The Templates describe and specify how common business concepts
should be represented using the PLCS information model.
Templates have been defined at a fine grained level to encourage maximum re-use
across different DEXs, hence ensuring consistent usage of the PLCS information model.
For example, the Template representing_organization
is used to represent an organization, and can be reused whenever this is required.
Further usage guidance on how different business concepts should be represented
using Templates is provided by Capabilities .
Capabilities describe the business concepts themselves and
place the Template in the context of the overall PLCS information model.
.
Capabilities describe the business concepts themselves and
place the Template in the context of the overall PLCS information model.
NOTE
Capabilities are in development and will be included in a future release.
As previously discussed, the information model defined by ISO 10303-239 (PLCS) is generic.
It holds no business specific terms. Instead, business semantics are represented by extending the
PLCS information model through classification with so called Reference Data (RD).
This provides a mechanism for adapting the generic model to one more specialized for given
business domains.
The use of the Reference Data is identified within the DEXs, Templates and Capabilities.
(RD).
This provides a mechanism for adapting the generic model to one more specialized for given
business domains.
The use of the Reference Data is identified within the DEXs, Templates and Capabilities.
In summary:
-
A DEX identifies and documents a subset of the ISO 10303-239 (PLCS) information
model required for a specific business purpose;
-
The usage of the PLCS information model identified by a DEX is defined through Templates. The Templates provide
a precise specification of how the model should be used to represent a given concept;
-
Capabilities provide further guidance on how the
information model and Templates should be used.
-
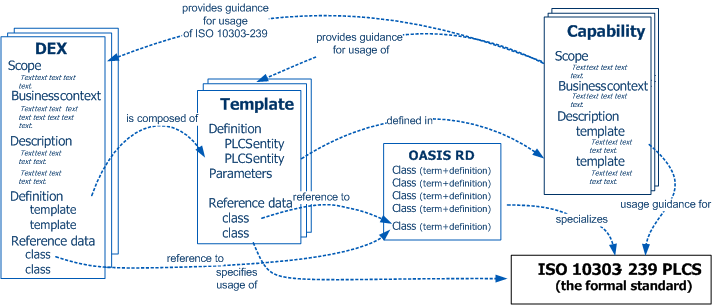
Reference Data provides an extensible vocabulary that adds business specific semantics to the information model.
This is illustrated in
Figure 2.
Further technical details of the
DEXlib components are provided in the
PLCS technical description
section.
components are provided in the
PLCS technical description
section.
Figure 2 — Relationships between the different DEX components, Reference Data and PLCS
 Product life cycle support
(PLCS
Product life cycle support
(PLCS ) specifies an
information model that defines
what information can be represented and exchanged to support a product
through life.
The information model is specified using the EXPRESS
) specifies an
information model that defines
what information can be represented and exchanged to support a product
through life.
The information model is specified using the EXPRESS information
modelling language. The EXPRESS based information model is used to derive an XML Schema
information
modelling language. The EXPRESS based information model is used to derive an XML Schema .
As well as XML conformant to the XML Schema (ISO 10303-28
.
As well as XML conformant to the XML Schema (ISO 10303-28 ed. 2),
ISO 10303
ed. 2),
ISO 10303 also defines structured text exchange formats
(ISO 10303-21
also defines structured text exchange formats
(ISO 10303-21 )
driven from the EXPRESS language.
)
driven from the EXPRESS language.