

OASIS ebXML RegRep Version
4.0
Part 1: Registry Information Model (ebRIM)
Committee Specification Draft 01
24 March 2011
Specification URIs:
This Version:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/regrep/regrep-core/v4.0/csd01/regrep-core-rim-v4.0-csd01.odt
(Authoritative)
http://docs.oasis-open.org/regrep/regrep-core/v4.0/csd01/regrep-core-rim-v4.0-csd01.pdf
http://docs.oasis-open.org/regrep/regrep-core/v4.0/csd01/regrep-core-rim-v4.0-csd01.html
Previous Version:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/regrep/v3.0/specs/regrep-rim-3.0-os.pdf
Latest Version:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/regrep/regrep-core/v4.0/regrep-core-rim-v4.0.odt (Authoritative)
http://docs.oasis-open.org/regrep/regrep-core/v4.0/regrep-core-rim-v4.0.pdf
http://docs.oasis-open.org/regrep/regrep-core/v4.0/regrep-core-rim-v4.0.html
Chair(s):
Farrukh Najmi, Wellfleet Software
Editor(s):
Farrukh Najmi, Wellfleet Software
Related Work:
This specification replaces or supersedes the OASIS ebXML RegRep 3.0 specifications.
This specification consists of the following documents, schemas, and ontologies:
Part 0: Overview Document (this document) - provides a global overview and description of all the other parts
Part 1: Registry Information Model (ebRIM) - specifies the types of metadata and content that can be stored in an ebXML RegRep
Part 2: Services and Protocols (ebRS) - specifies the services and protocols for ebXML RegRep
Part 3: XML Schema - specifies the XML Schema for ebXML RegRep
Part 4: WSDL - specifies the WSDL interface descriptions for ebXML RegRep
Part 5: XML Definitions - specifies the canonical XML data for ebXML RegRep as well as example XML documents used in the specification
Declared XML Namespace(s):
See Part 0: Overview Document
Abstract:
This document defines the types of metadata and content that can be stored in an ebXML RegRep.
A separate document, OASIS ebXML RegRep Version 4.0 Part 2: Services and Protocols (ebRS), defines the services and protocols for an ebXML RegRep.
Status:
See Part 0: Overview Document
Citation Format:
When referencing this specification the following citation format should be used:
[regrep-rim-v4.0] OASIS ebXML RegRep Version 4.0 Part 1: Registry Information Model (ebRIM). 24 March 2011. OASIS Committee Specification Draft 01. http://docs.oasis-open.org/regrep/regrep-core/v4.0/csd01/regrep-core-rim-v4.0-csd01.odt.
Notices
Copyright © OASIS Open 2010-2011. All Rights Reserved.
All capitalized terms in the following text have the meanings assigned to them in the OASIS Intellectual Property Rights Policy (the "OASIS IPR Policy"). The full Policy may be found at the OASIS website.
This document and translations of it may be copied and furnished to others, and derivative works that comment on or otherwise explain it or assist in its implementation may be prepared, copied, published, and distributed, in whole or in part, without restriction of any kind, provided that the above copyright notice and this section are included on all such copies and derivative works. However, this document itself may not be modified in any way, including by removing the copyright notice or references to OASIS, except as needed for the purpose of developing any document or deliverable produced by an OASIS Technical Committee (in which case the rules applicable to copyrights, as set forth in the OASIS IPR Policy, must be followed) or as required to translate it into languages other than English.
The limited permissions granted above are perpetual and will not be revoked by OASIS or its successors or assigns.
This document and the information contained herein is provided on an "AS IS" basis and OASIS DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTY THAT THE USE OF THE INFORMATION HEREIN WILL NOT INFRINGE ANY OWNERSHIP RIGHTS OR ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
OASIS requests that any OASIS Party or any other party that believes it has patent claims that would necessarily be infringed by implementations of this OASIS Committee Specification or OASIS Standard, to notify OASIS TC Administrator and provide an indication of its willingness to grant patent licenses to such patent claims in a manner consistent with the IPR Mode of the OASIS Technical Committee that produced this specification.
OASIS invites any party to contact the OASIS TC Administrator if it is aware of a claim of ownership of any patent claims that would necessarily be infringed by implementations of this specification by a patent holder that is not willing to provide a license to such patent claims in a manner consistent with the IPR Mode of the OASIS Technical Committee that produced this specification. OASIS may include such claims on its website, but disclaims any obligation to do so.
OASIS takes no position regarding the validity or scope of any intellectual property or other rights that might be claimed to pertain to the implementation or use of the technology described in this document or the extent to which any license under such rights might or might not be available; neither does it represent that it has made any effort to identify any such rights. Information on OASIS' procedures with respect to rights in any document or deliverable produced by an OASIS Technical Committee can be found on the OASIS website. Copies of claims of rights made available for publication and any assurances of licenses to be made available, or the result of an attempt made to obtain a general license or permission for the use of such proprietary rights by implementers or users of this OASIS Committee Specification or OASIS Standard, can be obtained from the OASIS TC Administrator. OASIS makes no representation that any information or list of intellectual property rights will at any time be complete, or that any claims in such list are, in fact, Essential Claims.
The name "OASIS" is a trademark of OASIS, the owner and developer of this specification, and should be used only to refer to the organization and its official outputs. OASIS welcomes reference to, and implementation and use of, specifications, while reserving the right to enforce its marks against misleading uses. Please see http://www.oasis-open.org/who/trademark.php for above guidance.
Table of Contents
1.1 Terminology 9
1.2 XML Schema 9
1.3 Information Model Types: Inheritance View 9
1.5 Canonical ClassificationSchemes 11
2.1 InternationalStringType 13
2.1.1 Syntax 13
2.1.2 Example 14
2.1.3 Description 14
2.2.1 Syntax 14
2.2.2 Example 14
2.2.3 Description 14
2.3.1 Syntax 15
2.3.2 Example 15
2.3.3 Description 15
2.4 SlotType 15
2.4.1 Syntax 16
2.4.2 Example 16
2.4.3 Description 16
2.5 ValueType 16
2.5.1 Syntax 16
2.5.2 Description 17
2.6.1 Syntax 18
2.6.2 Example 18
2.6.3 Description 18
2.7.1 Syntax 18
2.7.2 Description 19
2.8.1 Syntax 21
2.8.2 Example 21
2.8.3 Description 21
2.9.1 Syntax 22
2.9.2 Example 22
2.9.3 Description 22
2.10 ObjectRefType 24
2.10.1 Syntax 24
2.10.2 Description 24
2.11.1 Syntax 25
2.11.2 Description 25
2.12.1 Syntax 25
2.12.2 Example 26
2.12.3 Description 26
2.13 CommentType 26
2.13.1 Syntax 27
2.13.2 Example 27
2.13.3 Description 27
2.14.1 Syntax 28
2.14.2 Example 28
2.14.3 Description 29
2.15 ExternalIdentifierType 29
2.15.1 Syntax 29
2.15.2 Example 29
2.15.3 Description 29
2.16 ExternalLinkType 30
2.16.1 Syntax 30
2.16.2 Example 30
2.16.3 Description 31
3 Association Information Model 32
3.1 Source and Target Objects 32
3.3.1 Syntax 32
3.3.2 Example 33
3.3.3 Description 33
4 Classification Information Model 34
4.1.1 Syntax 36
4.1.2 Description 36
4.2 ClassificationSchemeType 37
4.2.1 Syntax 37
4.2.2 Example 37
4.2.3 Description 37
4.3.1 Syntax 38
4.3.2 Description 38
4.3.3 Canonical Path Syntax 39
4.4.1 Syntax 40
4.4.2 Example 40
4.4.3 Description 40
5 Provenance Information Model 42
5.1.1 Syntax 42
5.1.2 Example 43
5.1.3 Description 43
5.2.1 Syntax 44
5.2.2 Example 44
5.2.3 Description 44
5.3.1 Syntax 45
5.3.2 Example 45
5.3.3 Description 45
5.4 PartyType 45
5.4.1 Syntax 45
5.4.2 Description 46
5.5 PersonType 46
5.5.1 Syntax 46
5.5.2 Example 46
5.5.3 Description 47
5.6.1 Syntax 47
5.6.2 Example 47
5.6.3 Description 47
5.7.1 Syntax 48
5.7.2 Example 48
5.7.3 Description 48
5.8 Associating Organization With Persons 49
5.9 Associating Organization With Organizations 49
5.10 Associating Organizations With RegistryObjects 49
6 Service Information Model 50
6.1 ServiceType 50
6.1.1 Syntax 50
6.1.2 Example 50
6.1.3 Description 51
6.2.1 Syntax 51
6.2.2 Example 51
6.2.3 Description 51
6.3.1 Syntax 52
6.3.2 Example 52
6.3.3 Description 52
6.4.1 Syntax 52
6.4.2 Example 53
6.4.3 Description 53
7.1.1 Syntax 54
7.1.2 Example 55
7.1.3 Description 55
7.2 ParameterType 55
7.2.1 Syntax 55
7.2.2 Example 56
7.2.3 Description 56
7.3.1 Syntax 57
7.3.2 Description 57
7.4 StringQueryExpressionType 58
7.4.1 Syntax 58
7.4.2 Example 58
7.4.3 Description 58
7.5.1 Syntax 58
7.5.2 Example 59
7.5.3 Description 59
7.6 QueryType 59
7.6.1 Syntax 59
7.6.2 Example 59
7.6.3 Description 59
8.1.1 Syntax 62
8.1.2 Example 62
8.1.3 Description 62
8.2 ActionType 63
8.2.1 Syntax 63
8.2.2 Description 63
8.3.1 Syntax 64
8.3.2 Example 64
8.3.3 Description 64
8.4.1 Syntax 66
8.4.2 Description 66
8.5.1 Syntax 67
8.5.2 Example 67
8.5.3 Description 67
9 Federation Information Model 69
9.1 Federation Configuration 69
9.2 RegistryType 69
9.2.1 Syntax 70
9.2.2 Example 70
9.2.3 Description 70
9.3.1 Syntax 71
9.3.2 Example 71
9.3.3 Description 72
10 Access Control Information Model 73
10.1 Defining an Access Control Policy 74
10.2 Assigning Access Control Policy to a RegistryObject 74
10.2.1 Default Access Control Policy for a RegistryObject 74
10.2.2 Access Control Policy Inheritance 75
10.2.3 Performance Implications 75
10.3 Defining a Contextual Role 75
10.3.1 RoleType 76
10.3.2 Example 76
10.3.3 Description 76
10.4 Assigning a Contextual Role to a Subject 76
10.5 Action Matching 77
10.5.1 Action Attribute: reference-source 78
10.5.2 Action Attribute: reference-source-attribute 78
10.6 Subject Matching 78
10.6.1 Matching Subjects By Id 79
10.6.2 Matching Subject By Role 79
10.7 Resource Matching 80
10.7.1 Matching a Resource By Id 81
10.7.2 Matching a Resource Using XPATH Expression 81
10.8 Canonical XACML Functions 82
10.8.1 Function AssociationExists 82
10.8.2 Function ClassificationNodeCompare 83
10.8.3 Function matches-role 83
Illustration Index
Illustration 1: Information Model Inheritance View 10
Illustration 2: Core Information Model 13
Illustration 3: Association Example 32
Illustration 4: Classification Example 35
Illustration 5: Classification Information Model 36
Illustration 6: Provenance Information Model 42
Illustration 7: Service Information Model 50
Illustration 8: Query Information Model 54
Illustration 9: Event Information Model 61
Illustration 10: Federation Information Model 69
Illustration 11: Assigning Access Control Policy to a RegistryObject 74
Index of Tables
All text is normative unless otherwise indicated.
This document specifies the ebXML RegRep registry information model. For a general overview of ebXML RegRep and other related parts of the specification please refer to Part 0 [RR-OVERVIEW].
The keywords "MUST", "MUST NOT", "REQUIRED", "SHALL", "SHALL NOT", "SHOULD", "SHOULD NOT", "RECOMMENDED", "MAY", and "OPTIONAL" in this specification are to be interpreted as described in IETF [RFC 2119].
The ebXML Registry Information Model is defined as an XML Schema in the file “/xsd/rim.xsd” in the specification distribution zip file. It defines the metadata types and their relationships within ebXML RegRep specifications.
The central type in the model is the RegistryObjectType. An instance of RegistryObjectType represents an ebRIM metadata object.
Illustration 1 shows the inheritance or “Is-A” relationships between the various types derived from RegistryObjectType in the information model. Note that it does not show the other types of relationships, such as “Has-A” relationships, as they will be presented in subsequent diagrams. The attributes and elements of each type are also not shown to conserve page space. Detailed description of attributes and elements of each type will be displayed in tabular form within the detailed description of each type.
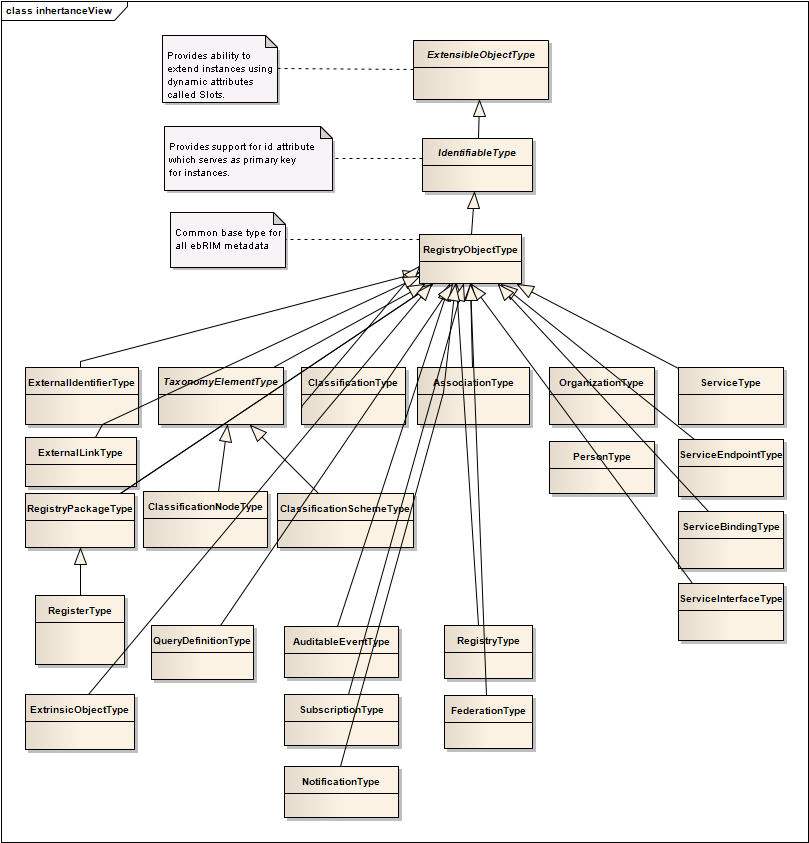
Illustration
1: Information Model Inheritance View
The XML Schema for ebRIM uses XML Schema type substitution feature to allow use of schema type extensions.
A deployment or profile specification of ebXML RegRep MAY define new types that extend the types defined in this specification as long as the XML Schema for ebRIM supports such extension.
A server MAY support the schema type extensibility feature. The following requirements are defined for a server that supports the schema type extensibility feature:
The server protocols as defined by [regrep-rs-v4.0] MUST support extended types in a manner equivalent to pre-defined types. Specifically they MUST support submit, update, versioning and removal of extended types derived directly or indirectly from RegistryObjectType
The server MUST be able to faithfully persist instances of extended types including all extension attributes and elements without any information loss
The server MUST be able to faithfully return instances of extension types including extension attributes and elements within a query response without any information loss
This specification does not prescribe how a server provides addition of new extension types to the server
ClassificationSchemes are defined in detail in the Classification Information Model. They are used by the specification for a wide variety of purposes within the ebXML RegRep specifications.
This specification uses several standard ClassificationSchemes referred to as canonical ClassificationSchemes. The values defined within canonical ClassificationSchemes are defined using standard ClassificationNodes that are referred to as canonical ClassificationNodes.
The directory “/xml/minDB” within the specification distribution zip file contains the canonical ClassificationSchemes defined by the ebXML RegRep specifications. The canonical ClassificationSchemes and ClassificationNodes are typically described using the rim:Description element within these files.
These canonical ClassificationSchemes MUST be present in all conforming ebXML RegRep servers. These Canonical ClassificationSchemes MAY be extended by adding additional ClassificationNodes. However, a ClassificationNode defined normatively in the canonical ClassificationScheme definitions MUST NOT be modified within a registry. In particular they MUST preserve their canonical id attributes in all servers.
The types in the information model are presented in related groups as follows:
Core Information Model: Defines core metadata types in the model including the abstract base types
Association Information Model: Defines types that enable objects to be associated with each other
Classification Information Model: Defines types that enable objects to be classified
Provenance Information Model: Defines types that enable the description of provenance or source information about an object
Service Information Model: Defines types that enable service description
Query Information Model: Defines types that enable definition and invocation of queries
Event Information Model: Defines types that enable the event subscription and notification feature defined in [regrep-rs-v4.0]
Federation Information Model: Defines types that enable the federated registries feature defined in [regrep-rs-v4.0]
Access Control Information Model: Defines types that enable access control and authorization for ebXML RegRep
The remainder of this document will describe each of the above related group of information model types in a dedicated chapter named accordingly.
The core information model is centered around the RegistryObjectType type as shown in figure below. Each type will be defined in detail in subsequent section.
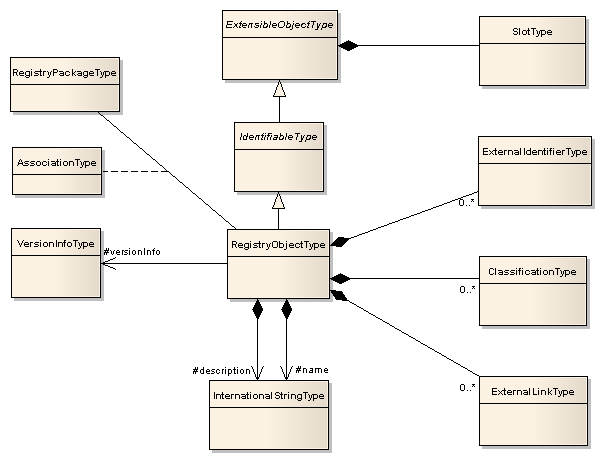
Illustration
2: Core Information Model
The InternationalStringType type is used throughout the schema whenever a textual value needs to be represented in one or more local languages.
The InternationalStringType has a sequence of LocalizedString instances, where each LocalizedString instance is specific to a particular locale.
<complexType name="InternationalStringType">
<sequence>
<element name="LocalizedString" type="tns:LocalizedStringType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" />
</sequence>
</complexType>
<rim:Name>
<rim:LocalizedString
xml:lang="en-US" value="freebXMLRegistry"/>
</rim:Name>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
LocalizedString |
LocalizedStringType |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
Element LocalizedString - An InternationalStringType instance MAY have zero or more LocalizedString elements where each defines a string value within a specific local language
This type allows the definition of a string value using the specified local language. It is used within the InternationalStringType as the type of the LocalizedString sub-element. Note that the character set for all LocalizedStringType instances in an XML document is defined by the charset attribute within the Content-Type mime header for the XML document as shown below:
Content-Type: text/xml; charset="UTF-8"
<complexType name="LocalizedStringType">
<attribute ref="xml:lang" default="en-US" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="value" type="tns:FreeFormText" use="required"/>
</complexType>
<rim:LocalizedString
xml:lang="en-US" value="freebXMLRegistry"/>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
xml:lang |
xs:language |
0..1 |
en-US |
Client |
Yes |
|
value |
rim:FreeFormText |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute xml:lang - Each LocalizedStringType instance MAY have a xml:lang attribute that specifies the language used by that LocalizedStringType instance. The xml:lang attribute and legal values for it are defined by [XML].
Attribute value - Each LocalizedStringType instance MUST have a value attribute that specifies the string value used by that LocalizedStringType instance
This type is the root type for most other types in rim.xsd. It allows extension properties called slots to be added to instances of this type using Slot sub-elements.
<complexType name="ExtensibleObjectType" abstract="true">
<sequence>
<element name="Slot" type="tns:SlotType" minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</sequence>
</complexType>
The following example shows how an OrganizationType instance which is of type ExtensibleObjectType MAY use Slot sub-elements to define a tax payer id for the organization.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:OrganizationType"
id="urn:freebxml:registry:Organization:freebXMLRegistry" ...>
<rim:Slot
name="urn:foo:slot:taxPayerId">
<rim:SlotValue
xsi:type="rim:StringValueType">
<rim:Value>1234567890</rim:Value>
</rim:SlotValue>
</rim:Slot>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
Slot |
SlotType |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
Element Slot – Allows an extension property to be added to any ExtensibleObjectType instance
Base Type: ExtensibleObjectType
The SlotType represents an extensible property for a RegistryObjectType instance . It can contain any type of information that may be represented in an XML document. It is an important extensibility mechanism with ebRIM.
A SlotType instance has a name and a value. The value is of type ValueType. ValueType is abstract and has several concrete sub-types defined within this specification.
Note that SlotType extends ExtensibleObjectType which means that a SlotType element may itself have SlotType sub-elements.
<complexType name="SlotType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ExtensibleObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="SlotValue" type="tns:ValueType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
</sequence>
<attribute name="name" type="tns:LongText" use="required"/>
<attribute name="type" type="tns:LongText" use="optional"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
The following example shows how a GML geometry value may be specified as a Slot.
<rim:Slot
name="geographicBoundingBox"
type="urn:ogc:def:dataType:ISO-19107:GM_Geometry">
<rim:SlotValue xsi:type="rim:AnyValueType">
<gml:Envelope srsName="urn:ogc:def:crs:OGC:2:WGS84">
<!--BB: POLYGON((0 0, 30 0, 30 30, 0 30, 0 0))-->
<gml:lowerCorner>0 0</gml:lowerCorner>
<gml:upperCorner>30 30</gml:upperCorner>
</gml:Envelope>
</rim:SlotValue>
</rim:Slot>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
name |
LongText |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
SlotValue |
ValueType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
type |
LongText |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute name – The name of this SlotType instance. The name of the slot MUST be unique within the universe of slot names for all sibling slots within its parent object
Element SlotValue – This element is the container for the actual value for the SlotType instance
Attribute type – A string that specifies the type for the SlotType instance. The type may be used to assign a category for the SlotType instance
This type is abstract base type for the value of a SlotType instance.
<complexType name="ValueType" abstract="true">
</complexType>
The ValueType is an abstract base type that does not define any attributes or elements. This specification defines several concrete sub-types that extend ValueType
AnyValueType – This concrete sub-type of ValueType is used as a container for any well-formed XML element value in any namespace
BooleanValueType - This concrete sub-type of ValueType is used as a container for a boolean value
CollectionValueType - This concrete sub-type of ValueType is used as a container for a collection of values. It may be used to represent a SlotValue that is a collection of values where each value is represented by a ValueType instance
Attribute collectionType – Defines the type of collection for the CollectionValueType. Must be an objectReferenceType that references a ClassificationNode in the canonical ClassificationScheme CollectionTypeScheme. A server MUST enforce the following semantics associated with the following canonical collection types:
List – Server MUST maintain the order of the values in the collection
Set – Server MUST NOT allow duplicate values in the collection
Sorted Set – Server MUST NOT allow duplicate values in the collection and MUST maintain a sort order according to the alphanumeric ordering of its elements according to the default locale associated with the server
Bag – Server MUST allow duplicate values and MAY not maintain order of values
DateTimeValueType - This concrete sub-type of ValueType is used as a container for a dateTime value
DurationValueType - This concrete sub-type of ValueType is used as a container for a duration value
FloatValueType - This concrete sub-type of ValueType is used as a container for a float value
IntegerValueType - This concrete sub-type of ValueType is used as a container for an integer value
InternationalStringValueType - This concrete sub-type of ValueType is used as a container for an InternationSringType value capable of holding strings in multiple locales
MapValueType - This concrete sub-type of ValueType is used as a container for a map value. A map consists of Entry sub-elements where each Entry consists of an EntryKey and EntryValue both of which are of type ValueType
SlotValueType – This concrete sub-type of ValueType is used as a container for a SlotType value
StringValueType – This concrete sub-type of ValueType is used as a container for a string value
VocabularyTermValueType - This concrete sub-type of ValueType is used as a container for a VocabularyTermType value. It is used to reference a term in some externally defined coded vocabulary (e.g. Dublin Core)
Base Type: ExtensibleObjectType
This type extends ExtensibleObjectType and allows its instances to be uniquely identifiable by a unique id.
<complexType name="IdentifiableType" abstract="true">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ExtensibleObjectType">
<attribute name="id" type="string" use="required"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:OrganizationType"
id="urn:freebxml:registry:Organization:freebXMLRegistry" ...>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
id |
xs:string |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute id – Specifies the unique identifier for an IdentifiableType instance.
Base Type: IdentifiableType
This type extends IdentifiableObjectType and is the common base type for all queryable metadata elements in ebRIM.
<complexType name="RegistryObjectType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:IdentifiableType">
<sequence>
<element name="Name" type="tns:InternationalStringType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<element name="Description" type="tns:InternationalStringType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<element name="VersionInfo" type="tns:VersionInfoType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<element name="Classification" type="tns:ClassificationType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
<element name="ExternalIdentifier" type="tns:ExternalIdentifierType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" />
<element name="ExternalLink" type="tns:ExternalLinkType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</sequence>
<attribute name="lid" type="string" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="objectType" type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="owner" type="string" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="status" type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
Classification |
ClassificationType |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
Description |
InternationalStringType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
ExternalIdentifer |
ExternalIdentifierType |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
ExternalLink |
ExternalLinkType |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
lid |
string |
0..1 |
|
Client or Server |
No |
|
Name |
InternationalStringType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
objectType |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client or Server |
No |
|
owner |
string |
0..1 |
|
Server |
Yes |
|
status |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Server |
Yes |
|
VersionInfo |
VersionInfoType |
0..1 |
|
Server |
No |
Element Classification - A RegistryObjectType instance MAY have zero or more ClassificationType instances that are composed within the RegistryObject. A ClassificationType instance classify the RegistryObject using a value within a ClassificationScheme
Element Description - A RegistryObjectType instance MAY have textual description in a human readable and user-friendly form. This element is of type InternationalStringType and therefor capable of containing textual values in multiple local languages and character sets.
Element ExternalIdentifier - A RegistryObjectType instance MAY have zero or more ExternalIdentifier instances that are composed within the RegistryObject. An ExternalIdentifier instance represents an alternate identifier for the RegistryObject in addition to the identifier specified by its id attribute value.
Attribute lid - A RegistryObjectType instance MUST have a lid (Logical Id) attribute. The lid is used to refer to a logical RegistryObject in a version independent manner.
All versions of a RegistryObject MUST have the same value for the lid attribute. Note that this is in contrast with the id attribute that MUST be unique for each version of the same logical RegistryObject.
The lid attribute MUST be specified by the client when creating the original version of a RegistryObject.
The lid attribute specified when submitting the original version of a RegistryObject MUST be globally unique and MUST NOT be already in use as lid by another object.
Element Name - A RegistryObjectType instance MAY have a human readable name. The name does not need to be unique with respect to other RegistryObjectType instances. This element is of type InternationalStringType and therefor capable of containing textual values in multiple local languages and character sets.
Attribute objectType - A RegistryObjectType instance has an objectType attribute.
The value of the objectType attribute MUST be a reference to a ClassificationNode in the canonical ObjectType ClassificationScheme.
A server MUST support the object types as defined by the canonical ObjectType ClassificationScheme. The canonical ObjectType ClassificationScheme may easily be extended by adding additional ClassificationNodes to the canonical ObjectType ClassificationScheme.
The objectType attribute MUST be assigned by the server for all RegistryObjectType instances that are not instances of ExtrinsicObjectType.
The objectType attribute MAY be assigned by the client for all RegistryObjectType instances that are instances of ExtrinsicObjectType
If the client does not specify an objectType for an ExtrinsicObject then the server MUST set its value to the id of the ClassificationNode representing ExtrinsicObject within the canonical ObjectType ClassificationScheme.
A server MUST set the correct objectType on a RegistryObject when returning it as a response to a client request.
Attribute owner – Specifies the identifier associated with the registered user that owns the RegistryObjectType instance. It is used for access control and may be referenced within custom access control policies.
Attribute status - A RegistryObjectType instance MUST have a life cycle status indicator. The status is assigned by the server. Profiles MAY define additional status values if needed as slots on the RegistryObjectType instance. Such slots SHOULD have a type attribute with value “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:rim:Slot:type:status”.
A server MUST set the correct status on a RegistryObject when returning it as a response to a client request.
A client SHOULD NOT set the status on a RegistryObject when submitting the object as this is the responsibility of the server.
A server MUST ignore the status on a RegistryObject when it is set by the client during submission or update of the object.
The value of the status attribute SHOULD be a reference to a ClassificationNode in the canonical StatusType ClassificationScheme.
A Registry MUST support the status types as defined by the StatusType ClassificationScheme. The canonical StatusType ClassificationScheme MAY easily be extended by adding additional ClassificationNodes to the canonical StatusType ClassificationScheme.
Element VersionInfo - Provides information about the specific version of a RegistryObjectType instance. The VersionInfo element is set by the server.
This type represents information about a specific version of a RegistryObject or RepositoryItem. It is used as type for the RegistryObjectType/VersionInfo and ExtrinsicObjectType/ContentVersionInfo elements in the rim.xsd schema.
<complexType name="VersionInfoType">
type="tns:String16" use="optional" default="1.1"/>
<attribute name="userVersionName" type="string" use="optional"/>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:OrganizationType" ...>
...
<rim:VersionInfo versionName="1.1" userVersionName="1.1"/>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
userVersionName |
LongText |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
versionName |
String16 |
0..1 |
|
Server |
No |
Attribute userVersionName - Represents a client-specified version name associated with the VersionInfo for a specific RegistryObject version
A client MAY directly provide a value for the userVersionName attribute when submitting or updating an object
A server MUST persist any client specified userVersionName for an object without altering it in any form
Attribute versionName - Represents the registry assigned version name identifying the VersionInfo for a specific RegistryObject version.
The value for this attribute SHOULD NOT be specified by the client
A server MAY silently ignore the value for this attribute if specified by the client
The value for this attribute MUST be automatically generated by the server and MUST be defined for RegistryObjectType instances returned by server responses. The server is free to choose any scheme for generating the value for this attribute as long as the value is uniquely identifies a version for objects that have the same lid attribute value.
Base Type: xs:string
A RegistryObjectType instance typically has several references to other RegistryObjectType instances. These references are represented by attributes of type rim:objectReferenceType within the XML Schema for ebXML RegRep.
The RegistryObjectType instance that has a reference to another RegistryObjectType instance is referred to as the reference source object. The RegistryObjectType instance that is being referenced is referred to as the reference target object.
<simpleType name="objectReferenceType">
<restriction base="string"/>
</simpleType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:OrganizationType"
primaryContact="urn:acme:person:Danyal" ...>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
The reference source and target objects MAY be in different ebXML RegRep servers. In such cases the reference is referred to as a remote reference.
When a reference is fixed to a specific reference target it is referred to as a static reference. This specification also supports a dynamic reference where the reference target is determined dynamically by a query at the time the reference is resolved. Such a reference is referred to as a dynamic reference.
Both static and dynamic references may be to a local or remote object. Static references to local reference targets are the most typical form of reference.
A client MUST specify values for reference attributes of type objectReferenceType to be encoded as described below:
A static reference to a local
reference target SHOULD be encoded as the value of the id attribute
of the reference target.
The following example shows the
reference attribute named primaryContact within Organization
element. Its value is the value of the id attribute of a Person
element.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:OrganizationType"
primaryContact="urn:acme:person:Danyal" ...>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
<rim:RegistryObject
xsi:type="rim:PersonType" id="urn:acme:person:Danyal"
...>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
A dynamic reference to a local
reference target SHOULD be encoded to contain the id of a
DynamicObjectRefType instance. The reference target is determined by
the singleton result returned by the Query within the
DynamicObjectRef instance.
The following example shows the
reference attribute named primaryContact within Organization
element. Its value is the value of the id attribute of a
DynamicObjectRefType instance. The DynamicObjectRefType instance has
a Query that gets the latest version of the object identified
by the lid parameter of the Query. The query when invoked
matches the latest version of the Person object representing
Danyal.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:OrganizationType"
primaryContact="urn:acme:dynamicRef:LatestVersionOfDanyal" ...>
...
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
<rim:ObjectRef xsi:type="rim:ObjectRefType"
id="urn:acme:dynamicRef:LatestVersionOfDanyal">
<rim:Query queryDefinition="urn:acme:QueryDefinition:FindLatestVersion">
<rim:Slot
name="lid">
<rim:SlotValue
xsi:type="rim:StringValueType">
<rim:Value>urn:acme:person:Danyal</rim:Value>
</rim:SlotValue>
</rim:Slot>
</rim:Query>
</rim:ObjectRef>
<rim:RegistryObject
xsi:type="rim:PersonType"
lid="urn:acme:person:Danyal" id="urn:acme:person:Danyal:1.8"...>
<!-- latest version of object with lid "urn:acme:person:Danyal" -->
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
A static or dynamic reference to a local reference target MAY be encoded to contain a Canonical URL for the local object as defined by the REST binding in [regrep-rs-v4.0].
A
static or dynamic reference to a remote reference target MUST be
encoded to contain a Canonical URL for the local object as defined
by the REST binding in [regrep-rs-v4.0].
The
following example shows the reference attribute named primaryContact
within Organization element. Its value is the HTTP GET URL for a
remote PersonType instance. Note that the URL is not encoded to
handle special characters for sake of clarity.
<!-- Following object is in local server -->
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:OrganizationType"
primaryContact="http://www.remoteRegistry.com/query?id=urn:remoteServer:person:Danyal" ...>
...
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
<!--
Following object is in a remote server -->
<rim:RegistryObject
xsi:type="rim:PersonType"
id="urn:remoteServer:person:Danyal" ...>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
Base Type: ExtensibleObjectType
This type represents an object reference as does the objectReferenceType. However, the two are used in different situations. The objectReferenceType is used as the type for all reference attributes in ebRIM. The ObjectRefType is used as type for elements rather than attributes. This type is used when there is a need to have multiple object references within a schema type. An example of this is the ObjectRefList element which is used in several places in the schema where a list of references to RegistryObjectType instances are needed.
<complexType name="ObjectRefType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ExtensibleObjectType">
<attribute name="id" type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="required"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<complexType name="ObjectRefListType">
<sequence>
<element name="ObjectRef"
type="tns:ObjectRefType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</sequence>
</complexType>
<element name="ObjectRefList" type="tns:ObjectRefListType"/>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
id |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute id - Every ObjectRef instance MUST have an id attribute. The id attribute MUST contain the value of the id attribute of the RegistryObject being referenced.
Base Type: ObjectRefType
This type represents a dynamic object reference. It extends the ObjectRefType and add a Query sub-element. This query is used to determine the reference target at the time the reference is resolved.
<complexType name="DynamicObjectRefType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ObjectRefType">
<sequence>
<element name="Query" type="tns:QueryType"
minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/>
</sequence>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
Query |
QueryType |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Element Query – Specifies the query that MUST be invoked in order to determine the reference target.
This query MUST match zero or one RegistryObjectType instances.
When the query matches zero RegistryObjectType instances, the dynamic object reference is considered to be unresolved.
A server MUST return a ConfigurationException fault message if the query matches more than 1 RegistryObjectType instances.
Extends:RegistryObjectType
This type is a common base type for new extended types defined by profiles of ebRIM or by clients. The ExtrinsicObjectType also allows arbitrary content to be associated with it. Such arbitrary content is referred to as a Repository Item.
<complexType name="ExtrinsicObjectType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="ContentVersionInfo" type="tns:VersionInfoType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1">
<element name="RepositoryItemRef" type="tns:SimpleLinkType"/>
<element name="RepositoryItem"
xmime:expectedContentTypes="*/*" type="base64Binary">
</choice>
</sequence>
<attribute name="mimeType" type="tns:LongText" use="optional" />
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:ExtrinsicObjectType" mimeType="text/xml"
objectType="urn:freebxml:registry:sample:profile:cpp:objectType:cppa:CPP"
lid="urn:freebxml:registry:sample:profile:cpp:instance:cpp1"
id="urn:freebxml:registry:sample:profile:cpp:instance:cpp1" >
<ContentVersionInfo versionName="311" userVersionName="1.1"/>
<RepositoryItem>...binary encoding of repository item</RepositoryItem>
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
ContentVersionInfo |
VersionInfoType |
0..1 |
|
Server |
No |
|
mimeType |
LongText |
0..1 |
application/octet-stream |
Client |
No |
|
RepositoryItem |
xs:base64Binary |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
RepositoryItemRef |
SimpleLinkType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
No |
Element ContentVersionInfo - Provides information about the specific version of a RepositoryItem that is associated with an ExtrinsicObjectType instance. The ContentVersionInfo element is set by the server.
A server MUST NOT set a ContentVersionInfo element for an ExtrinsicObjectType instance that does not have a RepositoryItem.
A server MUST set a ContentVersionInfo element for an ExtrinsicObjectType instance that has a RepositoryItem. The ContentVersionInfo element MUST contain a versionName attribute whose value MUST be unique for all versions of that RepositoryItem.
Attribute mimeType - An ExtrinsicObjectType instance MAY have a mimeType attribute defined. The mimeType provides information on the type of repository item cataloged by the ExtrinsicObject instance. The value of this attribute SHOULD be a registered MIME media type at http://www.iana.org/assignments/media-types.
Element repositoryItem – Provides a base64 binary encoded representation of the repository item associated with the ExtrinsicObjectType instance (if any).
Element repositoryItemRef – This element MAY be specified as an alternative to the repositoryItem element. Its type is SimpleLinkType. It uses xlink:simpleAttrs to specify a reference to a file on the client's local file system. This provides client libraries an alternative way to specify local files as repository item. The client library MUST convert a repositoryItemRef element to a repositoryItem element prior to submitting it to the server.
Extends:ExtrinsicObjectType
This type represents a comment that may be associated with a RegistryObjectType instance. A comment associated with a RegistryObject models the familiar yellow POST-IT note metaphor used in attaching comments to paper documents.
<complexType name="CommentType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ExtrinsicObjectType">
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:CommentType"
lid="urn:freebxml:registry:sample:comment1"
id="urn:freebxml:registry:sample:comment1" >
<rim:Description>
<rim:LocalizedString
xml:lang="en-US" value="This change request is rejected because it is too complex a change."/>
</rim:Description>
</rim:RegistryObject>
No new attributes or elements are added by this type. The following requirements are defined for this type:
An authorized client MAY attach one or more comments to any RegistryObjectType instance using an Association between the RegistryObjectType instance and the CommentType instance
The type of the Association MUST reference the canonical HasComment ClassificationNode within the Canonical AssociationType ClassificationScheme
The sourceObject of the Association MUST be the RegistryObjectType instance
The targetObject of the Association MUST be the CommentType instance
Extends:RegistryObjectType
This type allows for grouping of related RegistryObjectType instances. It serves a similar role as a folder in the familiar file-folder metaphor available in most operating systems.
A RegistyObjectType instance MAY be a member of multiple RegistryPackageType instances.
A RegistryPackageType instance MAY have multiple RegistryObjectType instances as its members.
Membership of a RegistryObjectType instance in a RegistryPackageType instance is established via an AssociationType instance where the type attribute references the canonical “HasMember” AssociationType within the canonical AssociationTypeScheme ClassificationScheme.
As a convenience, the RegistryPackageType allows a RegistryObjectList to be specified by the client as a sub-element during submission of a RegistryPackage. The RegistryObjectList contains the set of RegistryObjectType instances that are members of the RegistryPackageType instance.
<complexType name="RegistryPackageType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="RegistryObjectList" type="tns:RegistryObjectListType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
</sequence>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
The following example shows the use of a RegistryObjectList to specify the members of a RegistryPackageType instance during submission.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:RegistryPackageType"
id="urn:acme:RegistryPackage:photos" ...>
...
<rim:RegistryObjectList>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:ExtrinsicObjectType" mimeType="image/jpeg" id="urn:acme:RegistryPackage:photos:summer-2008:wellfleet-beach.jpg"
<repositoryItem>
...binary encoding of photo repository item
</repositoryItem>
</rim:RegistryObject>
</rim:RegistryObjectList>
</rim:RegistryObject>
The following example shows the equivalent syntax for representing the membership relationship between a RegistryPackage and its members. This representation uses “HasMember” AssociationType instances to establish the membership relationship.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:RegistryPackageType"
id="urn:acme:RegistryPackage:photos" .../>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:ExtrinsicObjectType" mimeType="image/jpeg" id="urn:acme:RegistryPackage:photos:summer-2008:wellfleet-beach.jpg"
<repositoryItem>
...binary encoding of photo repository item
</repositoryItem>
</rim:RegistryObject>
sourceObject="urn:acme:RegistryPackage:photos"
targetObject="urn:acme:RegistryPackage:photos:summer-2008:wellfleet-beach.jpg"
type="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:AssociationType:HasMember"/>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
RegistryObjectList |
RegistryObjectListType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Element RegistryObjectList – This element allows clients to specify members of the RegistryPackage instance using a simpler alternative to “HasMember” AssociationType instances.
A server MUST replace the RegistryObjectList with AssociationType instances such that each RegistryObjectType instance is replaced with an AssociationType instance with type “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:AssociationType:HasMember”, with sourceObject specifying the id of the RegistryPackage instance and with targetObject specifying the id of the RegistryObjectType instance
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
This type allows any number of additional identifiers to be specified for a RegistryObjectType instance. The identifier value is defined using the value attribute within the context of a ClassificationScheme referenced via the identificationScheme attribute.
<complexType name="ExternalIdentifierType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<attribute name="registryObject"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="identificationScheme"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="required"/>
<attribute name="value" type="tns:LongText" use="required"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
The following examples shows an Organization instance with its tax payer id specified using an ExternalIdentifierType instance.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:OrganizationType" ...>
...
<rim:ExternalIdentifier ...
identificationScheme="urn:acme:ClassificationScheme:TaxPayerId"
value="1234567890"/>
</rim:ExternalIdentifier>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
identificationScheme |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
registryObject |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
No |
|
value |
LongText |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute identificationScheme - Each ExternalIdentifier instance MUST have an identificationScheme attribute that references a ClassificationScheme. This ClassificationScheme defines the namespace within which an identifier is defined using the value attribute for the RegistryObjectType instance referenced by the RegistryObject attribute.
Attribute registryObject - Each ExternalIdentifier instance MAY have a registryObject attribute specified. This attribute references the parent RegistryObjectType instance for which this is an ExternalIdentifier.
This attribute MUST be specified when a client submits an ExternalIdentifier separately from its parent RegistryObjectType instance
This attribute MAY be unspecified when a client submits an ExternalIdentifier as a sub-element of its parent RegistryObjectType instance. In such cases the server MUST set this attributes value to the value of the id attribute of the parent RegistryObjectType instance.
Attribute value - Each ExternalIdentifier instance MUST have a value attribute that provides the identifier value for this ExternalIdentifier (e.g., the tax payer id in example above).
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
This type allows a link to external content to be added to a RegistryObjectType instance.
<complexType name="ExternalLinkType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="ExternalRef"
type="tns:SimpleLinkType" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/>
</sequence>
<attribute name="registryObject"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
The following examples shows an Organization instance with an ExternalLink that links to its web site URL via its ExternalRef sub-element.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:OrganizationType" ...>
...
<rim:ExternalLink ...
objectType="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:ObjectType:RegistryObject:ExtrinsicObject:XML:WSDL"
mimeType="text/xml"/>
<ExternalRef xlink:href="http://www.acme.com"/>
</rim:ExternalLink>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
ExternalRef |
SimpleLinkType |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
registryObject |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client or Server |
No |
Element ExternalRef - Each ExternalLink instance MUST have an ExternalRef sub-element defined. This element provides a URI to the external resource pointed to by this ExternalLink instance.
Attribute registryObject – references the parent RegistryObjectType instance within which the ExtrnalLinkType instance is composed. The value MUST be provided by client when an ExtrenalLink is submitted separate from its parent object. The value MUST be set by the server if the ExternalLink is submitted as part of the submission of its parent object.
A RegistryObjectType instance MAY be associated or related with zero or more RegistryObjectType instances. The information model defines the AssociationType type, an instance of which MAY be used to associate any two RegistryObjectType instances. It also defines an Association element for that type.
In the example below, an AssociationType instance with type “...Supercedes” is used to indicate that the NAICS2001 ClassificationScheme supercedes the NAICS1997 ClassificationScheme.

Illustration
3: Association Example
An AssociationType instance represents an association between a source RegistryObjectType instance and a target RegistryObjectType instance. These are referred to as sourceObject and targetObject for the AssociationType instance. It is important which object is the sourceObject and which is the targetObject as it determines the directional semantics of an Association.
An AssociationType instance MUST have a type attribute that identifies the type of that association. The value of this attribute is typically the id of a ClassificationNode under the canonical AssociationType ClassificationScheme.
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
<complexType name="AssociationType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<attribute name="type"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="required"/>
<attribute name="sourceObject"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="required"/>
<attribute name="targetObject"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="required"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
The following examples shows an Organization instance that has an “OffersService” association with a Service that it offers.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:OrganizationType"
id="urn:acme:Organization:acme-inc" ... />
<rim:RegistryObject
xsi:type="rim:ServiceType"
id="urn:acme:Service:stock-quote" ... />
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:AssociationType"
id="urn:acme:Association:acme-example-relationship"
sourceObject="urn:acme:Organization:acme-inc"
targetObject="urn:acme:Service:stock-quote"
type="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:AssociationType:OffersService" .../>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
sourceObject |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
targetObject |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
type |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute sourceObject - Each Association MUST have a sourceObject attribute that references the RegistryObjectType instance that is the source of that Association.
Attribute targetObject - Each Association MUST have a targetObject attribute that references the RegistryObjectType instance that is the target of that Association.
Attribute type - Each Association MUST have a type attribute that identifies the type of that association.
The value of the type attribute MUST be a reference to a ClassificationNode within the canonical AssociationType ClassificationScheme.
A server MUST support the canonical association types as defined by the canonical AssociationType ClassificationScheme. Deployments and profiles may extend the canonical AssociationType ClassificationScheme by adding additional ClassificationNodes to it.
A client MAY create an AssociationType instance between any two RegistryObjectType instances assuming the access control policies associated with the source and target object permit the client to create a reference to them. The default access control policy permits any client to create a reference to an object.
The ebRIM information model supports classification of RegistryObjectType instances using values defined by a taxonomy or controlled vocabulary. A taxonomy is represented in ebRIM by the ClassificationSchemeType type. Values in a taxonomy are represented by the ClassificationNode type. A classification instance is represented in ebRIM by the ClassificationType type.
This specification specifies a set of canonical ClassificationSchemes. Deployments and profiles MAY extends these canonical ClassificationSchemes by adding additional ClassificationNodes to them. They MAY also define new ClassificationSchemes. A RegistryObjectType instance MAY be classified using any ClassificationNode in any ClassificationScheme supported by the server. A RegistryObjectType instance MAY have any number of classifications defined for it.
A general ClassificationScheme can be viewed as a tree structure where the ClassificationScheme is the root and ClassificationNodes are either intermediate or leaf nodes in the tree.
Illustration 4 below shows RegistryObjectType instances representing Organizations as grey boxes. Each Organization represents an automobile manufacturer. Organization is classified by the ClassificationNode named “Automotive” under the ClassificationScheme instance with name “IndustryScheme”. Furthermore, the US Automobile manufacturers are classified by the “US” ClassificationNode under the ClassificationScheme with name “GeographyScheme”. Similarly, a European automobile manufacturer is classified by the “Europe” ClassificationNode under the ClassificationScheme with name “GeographyScheme”.
The example shows how a RegistryObject may be classified by multiple ClassificationNodeType instances under multiple ClassificationScheme instances (e.g., IndustryScheme, GeographyScheme).
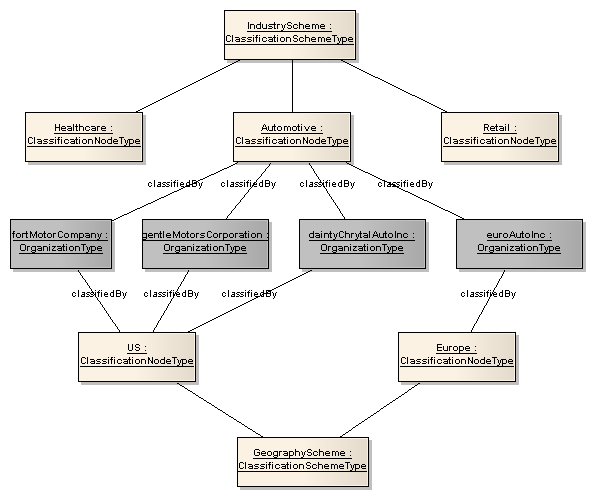
Illustration
4: Classification Example
Illustration 5 shows the Classification information model.
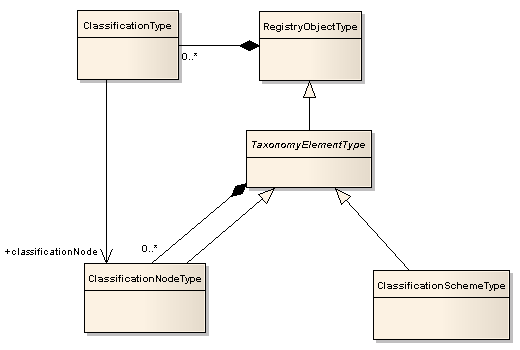
Illustration
5: Classification Information Model
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
This abstract type is the common base type for ClassificationSchemeType and ClassificationNodeType.
<complexType name="TaxonomyElementType" abstract="true">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="ClassificationNode" type="tns:ClassificationNodeType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</sequence>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
ClassificationNode |
ClassificationNodeType |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
Element ClassificationNode – This element represents a ClassificationNode child of a parent TaxonomyElementType instance. A TaxonomyElementType instance MAY have any number of ClassificationNode child elements.
Base Type: TaxonomyElementType
A ClassificationScheme instance represents a taxonomy.
The taxonomy hierarchy may be defined internally to the server using instances of ClassificationNodeType type, or it may be defined externally to the server, in which case the structure and values of the taxonomy elements are not known to the Registry.
In the first case the classification scheme is said to be internal and in the second case the classification scheme is said to be external.
<complexType name="ClassificationSchemeType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:TaxonomyElementType">
<attribute name="isInternal" type="boolean" use="required"/>
<attribute name="nodeType"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="required"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
The following examples shows a ClassificationScheme representing gender values.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:ClassificationSchemeType"
id="urn:acme:GenderScheme" isInternal="true"
nodeType="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:NodeType:UniqueCode" ...>
<Name>
<LocalizedString value="GenderScheme"/>
</Name>
<rim:ClassificationNode id="urn:acme:Gender:Male" code="Male" .../>
<rim:ClassificationNode id="urn:acme:Gender:Female" code="Female" .../>
<rim:ClassificationNode id="urn:acme:Gender:Other" code="Other" .../>
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
isInternal |
xs:boolean |
1 |
|
Client |
No |
|
nodeType |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Client |
No |
Attribute isInternal - When submitting a ClassificationSchemeType instance the client MUST declare whether the ClassificationSchemeType instance represents an internal or an external taxonomy. This allows the server to validate the subsequent submissions of ClassificationNodeType and ClassificationType instances in order to maintain the type of ClassificationScheme consistent throughout its lifecycle.
Attribute nodeType
- When submitting a ClassificationScheme instance the client
MUST declare the structure of taxonomy nodes within the
ClassificationScheme via the nodeType attribute. The value of the
nodeType attribute MUST be a reference to a ClassificationNodeType
instance within the canonical NodeType ClassificationScheme. A
server MUST support the node types as defined by the canonical
NodeType ClassificationScheme. The canonical NodeType
ClassificationScheme MAY easily be extended by adding additional
ClassificationNodes to it.
The following table lists the
canonical ClassificationNode defined as values for the NodeType
ClassificationScheme:
|
Name |
Description |
|
UniqueCode |
Indicates that the code for each ClassificationNode in the ClassificationScheme is unique within the scope of the ClassificationScheme |
|
EmbeddedPath |
Indicates that the code assigned to each node of the taxonomy also encodes its path. |
|
NonUniqueCode |
Indicates that the code for each ClassificationNode in the ClassificationScheme is not unique within the scope of the ClassificationScheme. For example, in a geography taxonomy Moscow could be under both Russia and the USA, where there are five cities of that name in different states. |
Base Type: TaxonomyElementType
ClassificationNodeType instances are used to define values for a taxonomy represented by ClassificationSchemeType instance.
<complexType name="ClassificationNodeType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:TaxonomyElementType">
<attribute name="parent" type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="path" type="string" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="code" type="tns:LongText" use="required"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
code |
LongText |
1 |
|
Client |
No |
|
parent |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
No |
|
path |
xs:string |
0..1 |
|
Registry |
No |
Attribute code - A ClassificationNodeType instance MUST have a code attribute. The code attribute contains a code that represents a value within a ClassificationScheme.
The code attribute of a ClassificationNodeType instance MUST be unique with respect to all sibling ClassificationNodes that are immediate children of the same parent TaxonomyElementType instance.
Attribute parent - A ClassificationNodeType instance MAY have a parent attribute. The parent attribute references the parent TaxonomyElementType instance. This is either another ClassificationNodeType instance or the ClassificationSchemeType instance.
Attribute path - A ClassificationNodeType instance MAY have a path attribute. The path attribute represents a hierarchical path from the root ClassificationSchemeType to the ClassificationNodeType instance. The syntax of the path attribute value is defined in 4.3.3.
A server MUST set the path attribute for any ClassificationNodeType instance when it is submitted by a client.
The path attribute MUST be ignored by the server if it is specified by the client during the submission of the ClassificationNodeType instance.
The path attribute of a ClassificationNode MUST be unique within a server.
The path attribute of the ClassificationNodeType instance contains an absolute path in a canonical representation that uniquely identifies the path leading from the root ClassificationSchemeType instance to that ClassificationNodeType instance.
The canonical path representation is defined by the following BNF grammar:
canonicalPath ::= '/' rootTaxonomyElementId nodePath
nodePath ::= '/' nodeCode
| '/' nodeCode ( nodePath )?
In the above grammar, rootTaxonomyElementId is the id attribute of the root ClassificationSchemeType or ClassificationNodeType instance, and nodeCode is defined by NCName production as defined by http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml-names/#NT-NCName.
The following canonical path represents the path attribute value for the ClassificationNode with code “Male” in the sample Gender ClassificationScheme presented earlier.
/urn:acme:GenderScheme/Male
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
A ClassificationType instance classifies a RegistryObjectType instance by using a value defined within a particular ClassificationScheme. An internal Classification specifies the value by referencing the ClassificationNodeType instance within a ClassificationSchemeType instance. An external Classification specifies the value using a string value that is defined in some external specification represented by an external ClassificationSchemeType instance.
<complexType name="ClassificationType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<attribute name="classificationScheme"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="classifiedObject"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="classificationNode"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="nodeRepresentation"
type="tns:LongText" use="optional"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
The following examples shows how a Person instance is classified using the sample Gender ClassificationScheme used in earlier examples.
<rim:RegistryObject
xsi:type="rim:PersonType"
id="urn:acme:person:Danyal" ...>
...
<Classification classifiedObject="urn:acme:person:Danyal"
classificationNode="urn:acme:Gender:Male"
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
classificationNode |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
No |
|
classifiedObject |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
No |
|
classificationScheme |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
No |
|
nodeRepresentation |
LongText |
0..1 |
|
Client |
No |
Attribute classificationNode - If the ClassificationType instance represents an internal classification, then the classificationNode attribute is required.
The classificationNode value MUST reference a ClassificationNodeType instance.
Attribute classifiedObject - For both internal and external classifications, the classifiedObject attribute is required and it references the RegistryObjectType instance that is classified by this Classification.
Attribute classificationScheme - If the ClassificationType instance represents an external classification, then the classificationScheme attribute is required.
The classificationScheme value MUST reference a ClassificationScheme instance.
Attribute nodeRepresentation - If the ClassificationType instance represents an external classification, then the nodeRepresentation attribute is required. It is a representation of a taxonomy value from a classification scheme.
A canonical slot with name “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:rim:Classification:context” may be optionally specified to provide additional context for a ClassificationType instance
The term provenance in the English language implies the origin and history of ownership and custodianship of things of value. When applied to the ebXML RegRep, provenance implies information about the origin, history of ownership, custodianship, and other relationships between entities such as people, organizations and information represented by RegistryObjectType instances.
The ebRIM information model supports types and relationships that MAY be used to represent the provenance of RegistryObjectType instances.
The following figure presents the
significant types defined by the provenance information model.
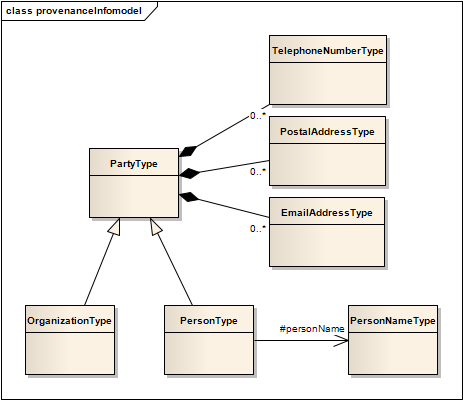
Illustration
6: Provenance Information Model
Base Type: ExtensibleObjectType
This type represents a postal or mailing address.
<complexType name="PostalAddressType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ExtensibleObjectType">
<attribute name="city" type="tns:ShortText" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="country" type="tns:ShortText" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="postalCode" type="tns:ShortText" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="stateOrProvince" type="tns:ShortText" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="street" type="tns:ShortText" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="streetNumber" type="tns:String32" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="type" type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:PersonType" id="urn:acme:person:Danyal" ...>
...
<rim:PostalAddress streetNumber="10" street="Street 1" city="Islamabad"
stateOrProvince="Punjab" country="Pakistan" postalCode="12345"/>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
city |
ShortText |
No |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
country |
ShortText |
No |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
postalCode |
ShortText |
No |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
stateOrProvince |
ShortText |
No |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
street |
ShortText |
No |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
streetNumber |
String32 |
No |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute city - A PostalAddressType instance MAY have a city attribute identifying the city for that address.
Attribute country - A PostalAddressType instance MAY have a country attribute identifying the country for that address.
Attribute postalCode - A PostalAddressType instance MAY have a postalCode attribute identifying the postal code (e.g., zip code) for that address.
Attribute stateOrProvince - A PostalAddressType instance MAY have a stateOrProvince attribute identifying the state, province or region for that address.
Attribute street - A PostalAddressType instance MAY have a street attribute identifying the street name for that address.
Attribute streetNumber - A PostalAddressType instance MAY have a streetNumber attribute identifying the street number (e.g., 65) for the street address.
Base Type: ExtensibleObjectType
This type defines attributes of a telephone number.
<complexType name="TelephoneNumberType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ExtensibleObjectType">
<attribute name="areaCode" type="tns:String8" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="countryCode" type="tns:String8" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="extension" type="tns:String8" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="number" type="tns:String16" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="type" type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:PersonType" id="urn:acme:person:Danyal" ...>
...
<rim:TelephoneNumber countryCode="92" areaCode="51" number="123-4567"
type="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:PhoneType:MobilePhone"/>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
areaCode |
String8 |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
countryCode |
String8 |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
extension |
String8 |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
number |
String16 |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
type |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute areaCode - A TelephoneNumberType instance MAY have an areaCode attribute that provides the area code for that telephone number.
Attribute countryCode - A TelephoneNumberType instance MAY have a countryCode attribute that provides the country code for that telephone number.
Attribute extension - A TelephoneNumberType instance MAY have an extension attribute that provides the extension number, if any, for that telephone number.
Attribute number - A TelephoneNumberType instance MAY have a number attribute that provides the local number (without area code, country code and extension) for that telephone number.
Attribute type - A TelephoneNumberType instance MAY have a type attribute that provides the type for the TelephoneNumber. The value of the phoneType attribute MUST be a reference to a ClassificationNode in the canonical PhoneType ClassificationScheme.
Base Type: ExtensibleObjectType
This type defines attributes of an email address.
<complexType name="EmailAddressType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ExtensibleObjectType">
<attribute name="address" type="tns:ShortText" use="required"/>
<attribute name="type" type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:PersonType" id="urn:acme:person:Danyal" ...>
...
<rim:EmailAddress address="danyal@play.com"
type="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:EmailType:HomeEmail"/>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
address |
ShortText |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
type |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute address - An EmailAddressType instance MUST have an address attribute that provides the actual email address.
Attribute type - An EmailAddressType instance MAY have a type attribute that provides the type for that email address. The value of the type attribute MUST be a reference to a ClassificationNode in the canonical EmailType ClassificationScheme.
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
This abstract type represents a party that has contact information such as PostalAddress, EmailAddress, TelephoneNumber etc. It is used as a common base type for PersonType and OrganizationType.
<complexType name="PartyType" abstract="true">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="PostalAddress" type="tns:PostalAddressType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
<element name="TelephoneNumber" type="tns:TelephoneNumberType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
<element name="EmailAddress" type="tns:EmailAddressType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</sequence>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
EmailAddress |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
|
PostalAddress |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
|
TelephoneNumber |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
Element EmailAddress - A PartyType instance MAY have any number of EmailAddress sub-elements. Each EmailAddress provides an email address for that PartyType instance. A PartyType instance SHOULD have at least one EmailAddress.
Element PostalAddress - A PartyType instance MAY have any number of PostalAddress sub-elements. Each PostalAddress element provides a postal address for that PartyType instance. A PartyType instance SHOULD have at least one PostalAddress.
Element TelephoneNumber - A PartyType instance MAY have any number of TelephoneNumber sub-elements. Each TelephoneNumber element provides a TelephoneNumber for that PartyType instance. A PartyType instance SHOULD have at least one TelephoneNumber.
Base Type: PartyType
This type represent a person.
<complexType name="PersonType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:PartyType">
<sequence>
<element name="PersonName" type="tns:PersonNameType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
</sequence>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:PersonType" id="urn:acme:person:Danyal" ...>
<rim:PersonName firstName="Danyal" middleName="Idris" lastName="Najmi"/>
<rim:PostalAddress streetNumber="10" street="Street 1" city="Islamabad"
stateOrProvince="Punjab" country="Pakistan" postalCode="12345"/>
<rim:TelephoneNumber countryCode="92" areaCode="51" number="123-4567"
type="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:PhoneType:MobilePhone"/>
<rim:EmailAddress address="danyal@play.com"
type="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:EmailType:HomeEmail"/>
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
PersonName |
0..1 |
|
Client |
No |
Element PersonName – A PersonType instance SHOULD have a PersonName sub-element that provides the name for that person.
Base Type: ExtensibleObjectType
This represents the name for a PersonType instance.
<complexType name="PersonNameType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ExtensibleObjectType">
<attribute name="firstName" type="tns:ShortText" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="middleName" type="tns:ShortText" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="lastName" type="tns:ShortText" use="optional"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:PersonType" id="urn:acme:person:Danyal" ...>
...
<rim:PersonName firstName="Danyal" middleName="Idris" lastName="Najmi"/>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
firstName |
ShortText |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
lastName |
ShortText |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
middleName |
ShortText |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute firstName - A PersonName instance SHOULD have a firstName attribute that is the given name of the person.
Attribute lastName - A PersonName instance SHOULD have a lastName attribute that is the family name of the person.
Attribute middleName - A PersonName instance SHOULD have a middleName attribute that is the middle name of the person.
This type represents an organization or entity.
<complexType name="OrganizationType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:PartyType">
<sequence>
<element
name="Organization" type="tns:OrganizationType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</sequence>
<attribute name="primaryContact" type="tns:objectReferenceType"
use="optional"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject
xsi:type="rim:OrganizationType"
id="urn:acme:Organization:acme"
primaryContact="urn:acme:person:Danyal" ...>
<rim:PostalAddress streetNumber="1" street="Grand Trunk Rd."
city="Hasan Abdal"
stateOrProvince="Punjab" country="Pakistan" postalCode="12345"/>
<rim:TelephoneNumber countryCode="92" areaCode="52" number="123-4567"
type="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:PhoneType:OfficePhone"/>
<rim:EmailAddress address="info@acme.com"
type="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:EmailType:OfficeEmail"/>
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
Organization |
OrganizationType |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
primaryContact |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Element Organization – This element allows clients to specify sub-organizations of the Organization instance using a simpler alternative to specifying “HasMember” AssociationType instances between the parent and child Organizations.
A server MUST replace any nested Organization elements within an OrganizationType instance with AssociationType instances such that each nested Organization element is replaced with an AssociationType instance with type “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:AssociationType:HasMember”, with sourceObject specifying the id of the parent OrganizationType instance and with targetObject specifying the id of the nested Organization element
Attribute primaryContact - An OrganizationType instance SHOULD have a primaryContact attribute that references the Person instance for the person that is the primary contact for that organization.
There are many situation where a person is related to an organization. Such relationship SHOULD be defined by AssociationType instances between an OrganizationType instance and a PersonType instance as follows:
The type attribute of the Association references the canonical ClassificationNode with id “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:AssociationType:AffiliatedWith” or one of its descendants.
The sourceObject references the PersonType instance.
The targetObject references the OrganizationType instance.
There are many situation where an organization is related to another organization. Such relationship SHOULD be defined by AssociationType instances between an OrganizationType instance and another OrganizationType instance.
To represent parent-child relationship between organizations the type attribute of the Association SHOULD reference the canonical ClassificationNode with id “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:AssociationType:HasMember” or one of its descendants.
The sourceObject SHOULD reference the parent OrganizationType instance.
The targetObject SHOULD reference the child OrganizationType instance.
An organization MAY be associated with zero or more RegistryObjectType instances. Each such association is modeled in ebRIM using an Association instance between an Organization instance and a RegistryObjectType instance.
Associations between Organizations and RegistryObjectType instances do not entitle organizations to any special privileges with respect to those instances. Such privileges are defined by the Access Control Policies defined for the RegistryObjectType instances as described in the Access Control Information Model chapter.
This chapter describes the parts of the information model that support the description of services within an ebXML RegRep server. Although service information model aligns with [WSDL2] model, it may be used to describe any type of service in addition to web services.

Illustration
7: Service Information Model
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
This type represent a logical service. Physical service endpoints are represented by the ServiceEndpointType type. A ServiceType instance typically contains ServiceEndpoint sub-elements where each ServiceEndpoint sub-element represents an alternate endpoint for a service.
<complexType name="ServiceType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="ServiceEndpoint" type="tns:ServiceEndpointType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</sequence>
<attribute name="serviceInterface"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional" />
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:ServiceType"
id="urn:acme:Service:StockQuoteService" ...>
...
<rim:ServiceEndpoint
id="urn:acme:ServiceEndpoint:StockQuoteService:free" .../>
<rim:ServiceEndpoint
id="urn:acme:ServiceEndpoint:StockQuoteService:premium" .../>
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
ServiceEndpoint |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
|
serviceInterface |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Element ServiceEndpoint – Represents a physical endpoint for the service that MAY be used by clients to access the service
Attribute serviceInterface – References the abstract interface description for the service
MUST reference a ServiceInterfaceType instance if specified
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
This type represents a physical endpoint for the service that MAY be used by clients to access a service.
<complexType name="ServiceEndpointType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<attribute name="address" type="anyURI" use="optional" />
<attribute name="serviceBinding"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional" />
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:ServiceType"
id="urn:acme:Service:StockQuoteService" ...>
...
<rim:ServiceEndpoint id="urn:acme:ServiceEndpoint:StockQuoteService:free"
address="http://acme.com/StockQuoteService/free"
serviceBinding="urn:acme:ServiceBinding:soap:StockQuoteService">
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
address |
xs:anyURI |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
serviceBinding |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute address – Represents the endpoint address URI that a client of the service endpoint may use to access the service endpoint
Attribute serviceBinding – References the ServiceBindingType instance that represents protocol-specific binding information for the ServiceEndpointType instance
MUST reference a ServiceBindingType instance
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
This type represents protocol-specific binding information for a ServiceEndpointType instance. Example of a protocol-specific binding is a SOAP binding.
<complexType name="ServiceBindingType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<attribute name="serviceInterface"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="optional" />
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject
xsi:type="rim:ServiceBindingType"
id="urn:acme:ServiceBinding:soap:StockQuoteService"
serviceInterface="urn:acme:ServiceInterface:StockQuoteService" .../>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
serviceInterface |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute serviceInterface – References a ServiceInterfaceType instance which represents the abstract service interface for the service
MUST reference a ServiceInterfaceType instance if specified
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
This type represents an abstract service interface for a service.
<complexType name="ServiceInterfaceType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:ServiceInterfaceType"
id="urn:acme:ServiceInterface:StockQuoteService" .../>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
No attributes or elements beyond those inherited from RegistryObjectType are defined for this type.
This chapter describes the information model for defining and invoking parameterized queries in ebXML RegRep. The following significant types are defined by the Query Information Model:
QueryDefinitionType - Represents the definition of a parameterized query
QueryType – Represents the invocation of a parameterized query
Several canonical QueryDefinitionType instances are defined by the ebRS specification. Profiles of ebXML RegRep MAY define additional QueryDefinitionType instances as canonical queries for that profile. Deployments MAY also define additional QueryDefinitionType instances. Finally, clients MAY submit additional QueryDefinitionType instances.
A QueryDefinitionType instance MAY be invoked using a QueryType instance. The ebRS Query protocol allows clients to invoke a QueryDefinitionType instance using a QueryType instance within the Query protocol.
The following figure presents the significant types defined by the Query information model.
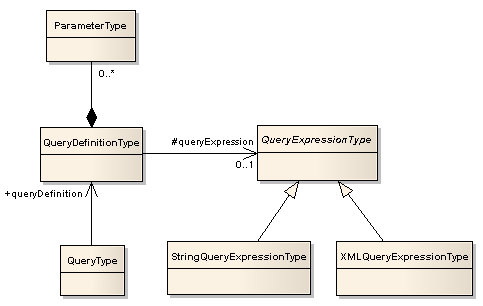
Illustration
8: Query Information Model
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
This type represents the definition of a parameterized query. The definition of a query includes the definition of its supported parameters and the definition of a parameterized query expression.
<complexType name="QueryDefinitionType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="Parameter"
type="tns:ParameterType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
<element name="QueryExpression"
type="tns:QueryExpressionType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
</sequence>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:QueryDefinitionType"
id="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:query:GetObjectById">
<rim:Parameter parameterName="id"
minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" defaultValue="%">
</Parameter>
<rim:QueryExpression xsi:type="rim:StringQueryExpressionType"
queryLanguage="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:QueryLanguage:EJBQL">
<Value>
SELECT Object(ro) FROM ...
</Value>
</QueryExpression>
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
Parameter |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
|
QueryExpression |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Element Parameter – Represents the definition of a query parameter for the QueryDefinitionType instance. A QueryDefinitionType instance MAY have any number of Parameter sub-elements
Element QueryExpression – Represents a query expression for the parameterized query.
MAY be omitted if the query is implemented as a Query plugin as defined by ebRS
Base Type: ExtensibleObjectType
This type represents the definition of a parameter within a QueryDefinitionType.
<complexType name="ParameterType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ExtensibleObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="Name" type="tns:InternationalStringType"
minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/>
<element name="Description" type="tns:InternationalStringType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
</sequence>
<attribute name="parameterName" type="string" use="required"/>
<attribute name="dataType" type="string" use="required" />
<attribute name="defaultValue" type="string" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="minOccurs" type="nonNegativeInteger" default="1"/>
<attribute name="maxOccurs" type="nonNegativeInteger" default="1"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:QueryDefinitionType"
id="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:query:GetObjectById">
<rim:Parameter parameterName="id" dataType="string" minOccurs="1"
maxOccurs="1" defaultValue="%" />
...
<rim:QueryExpression .../>
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
dataType |
xs:string |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
defaultValue |
xs:string |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
Description |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
|
minOccurs |
0..1 |
1 |
Client |
Yes |
|
|
maxOccurs |
xs:nonNegativeInteger |
0..1 |
1 |
Client |
Yes |
|
Name |
InternationalStringType |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
parameterName |
xs:string |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute dataType – Specifies the data type for the parameter.
The dataType MUST be “string” for parameters whose values are represented by a string value.
The dataType MUST be “boolean” for parameters whose values are represented by a boolean value.
The dataType MUST be “taxonomyElement” for parameters whose value is the id of a TaxonomyElement.
Attribute defaultValue - Specifies the default value for the parameter. This value MUST be used as parameter value when the query is invoked if the client does not specify a value for this parameter.
Element Description - Specifies a human-friendly description of the parameter that indicates what the parameter value represents and what kind of value is allowed. The description MAY be provided in multiple local languages and character sets.
Attribute minOccurs – Specifies the minimum number of values allowed for the parameter.
Attribute maxOccurs - Specifies the maximum number of values allowed for the parameter.
Element Name - Specifies a human-friendly name for the parameter. The name MAY be provided in multiple local languages and character sets.
Attribute parameterName – Specifies the canonical name of the parameter. The canonicalName identifies the parameter in a locale-insensitive manner
SHOULD match a declared parameter name within the query expression for the QueryDefinitionType instance
The parameterName MUST be unique across the universe of all sibling ParameterType instances within a QueryDefinitionType instance
Base Type: ExtensibleObjectType
This type represents a query expression in a specified query language that MAY be used by the server to invoke a query.
The QueryExpressionType is the abstract root of a type hierarchy for the following more specialized sub-types:
StringQueryExpressionType – This type MAY be used to represent non-XML query syntaxes such as SQL-92 and EJBQL.
XMLQueryExpressionType - This type MAY be used to represent XML query syntaxes such as OGC Filter Query.
This specification does not specify a specific query expression syntax that a server must support.
<complexType name="QueryExpressionType" abstract="true">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ExtensibleObjectType">
<attribute name="queryLanguage"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="required"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
queryLanguage |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute queryLanguage – Specifies the query language used by the QueryExpressionType instance.
MUST be a reference to a ClassificationNode in the canonical Query Language ClassificationScheme whose id is “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:classificationScheme:QueryLanguage”.
Base Type: QueryExpressionType
This type is used to represent non-XML query syntaxes such as SQL-92 and EJBQL.
<complexType name="StringQueryExpressionType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:QueryExpressionType">
<sequence>
<element name="Value" type="string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/>
</sequence>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:QueryDefinitionType"
id="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:query:GetObjectById">
<rim:Parameter ... />
...
<rim:QueryExpression xsi:type="rim:StringQueryExpressionType"
queryLanguage="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:QueryLanguage:EJBQL">
<Value>
SELECT Object(ro) FROM RegistryObjectType WHERE ...
</Value>
</rim:QueryExpression>
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
Value |
xs:string |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Element Value – Specifies the string value representing the actual query expression within the query language specified by the queryLanguage attribute inherited from base type QueryExpressionType.
Base Type: QueryExpressionType
This type is used to represent XML query syntaxes such as OGC Filter Query.
<complexType name="XMLQueryExpressionType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:QueryExpressionType">
<sequence>
<any namespace="##other"
processContents="lax" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/>
</sequence>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:QueryDefinitionType"
<rim:Parameter ... />
...
<rim:QueryExpression xsi:type="rim:XMLQueryExpressionType"
queryLanguage="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:QueryLanguage:EJBQL">
<ogc:Filter>
...
</ogc:Filter>
</rim:QueryExpression>
</rim:RegistryObject>
An XMLQueryExpressionType instance MAY contain any XML element from a namespace other than the name space for rim.xsd. In the example above we use an ogc:Filter element to represent an OGC Filter query.
Base Type: ExtensibleObjectType
This type represents the invocation of a parameterized query.
<complexType name="QueryType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ExtensibleObjectType">
<attribute name="queryDefinition"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="required"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:QueryType"
queryDefinition="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:query:GetObjectById">
<rim:Slot name="id">
<rim:SlotValue xsi:type="rim:StringValueType">
<rim:Value>urn:acme:person:Danyal</rim:Value>
</rim:SlotValue>
</rim:Slot>
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
queryDefinition |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute queryDefinition – References the parameterized query to be invoked by the server.
The value of this attribute MUST be a reference to a QueryDefinitionType instance that is supported by the server.
Element Slot (Inherited) - Each Slot element specifies a parameter value for a parameter supported by the QueryDefinitionType instance.
The slot name MUST match a parameterName attribute within a Parameter's definition within the QueryDefinitionType instance.
The slot value's type MUST match the dataType attribute for the Parameter's definition within the QueryDefinitionType instance.
A server MUST NOT treat the order of parameters as significant.
This chapter defines the information model types that supports the Event Notification feature for ebXML RegRep. These types include the following:
AuditableEventType – Represents a server event that is typically a consequence of a client request.
SubscriptionType – Represents a client's subscription to receive notification of AuditableEventType instances based upon a specified selection criteria.
QueryType – Represents a query invocation that is used to select events of interest within a SubscriptionType instance. This type has been specified previously in the Query Information Model.
NotificationType – Represents a notification sent by the server to a client regarding an event that matches the criteria specified by the client within a SubscriptionType instance.
Illustration 9 shows how a Subscription may be defined that uses a QueryType instance as a selector query to select the AuditableEvents of interest to the subscriber. The Subscription MAY also have zero or more DeliveryInfoType elements that specify the subscriber's endpoint to deliver the selected events to. The endpoint may be a REST or SOAP service endpoint or it may be an email address endpoint in case notification is to be delivered via email.
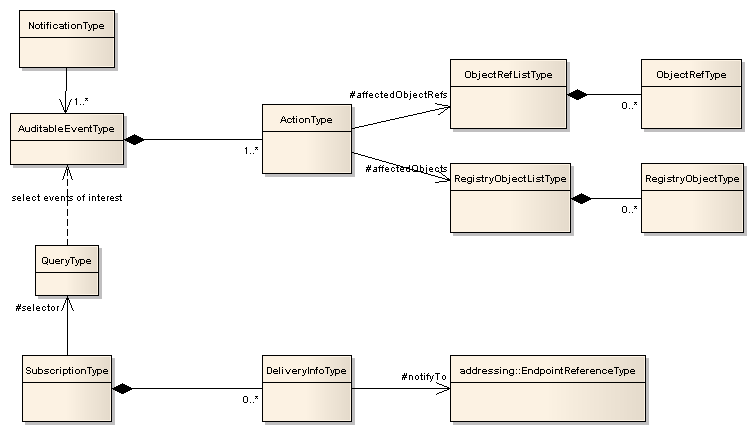
Illustration
9: Event Information Model
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
This type represents a server event. AuditableEventType instances provide a long-term record of events that effected changes in the state of a RegistryObjectType instance. AuditableEventType instances MUST be generated by the server and MUST NOT be submitted by clients.
AuditableEventType instances represent a change in the state of a RegistryObjectType instance. For example a client request could Create, Update, Deprecate or Delete a RegistryObjectType instance. An AuditableEventType instance is created when a request creates or alters the state of a RegistryObjectType instance. Read-only requests typically do not generate an AuditableEventType instance.
<complexType name="AuditableEventType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="Action" type="tns:ActionType"
minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</sequence>
<attribute name="timestamp" type="dateTime" use="required"/>
<attribute name="user" type="string" use="required"/>
<attribute name="requestId"
type="string" use="required"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
The following example shows an AuditableEventType instance that logs the creation of an object within the context of a client request.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:AuditableEventType"
requestid="urn:uuid:24cee176-9098-4931-894f-fea5dab1732a"
timestamp="2008-01-10T19:20:30+01:00" user="farid"
...>
<rim:Action eventType="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:EventType:Created">
<rim:AffectedObjectRefs>
<rim:ObjectRef id="urn:acme:person:Danyal" />
</rim:AffectedObjectRefs>
</rim:Action>
</AuditableEvent>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
Action |
1..* |
|
Registry |
No |
|
|
requestId |
xs:string |
1 |
|
Registry |
No |
|
timestamp |
xs:dateTime |
1 |
|
Registry |
No |
|
user |
xs:string |
1 |
|
Registry |
No |
Element Action – Represents an action taken by the server within the context of an AuditableEventType instance. An AuditableEventType instance MUST have one or more Action instances.
Attribute requestId – Specifies the id of the request that generated the AuditableEventType instance.
Attribute timestamp – Specifies the timestamp that represents the date and time the event occurred.
Attribute user – Specifies the id of the registered user associated with the client that made the request to the server that generated the AuditableEventType instance. Note that the inherited attribute owner SHOULD be set by a server to an internal system user since it is the server and not the user associated with the request that creates an AuditableEventType instance
Base Type: ExtensibleObjectType
Represents an action taken by the server within the context of an AuditableEventType instance.
<complexType name="ActionType">
<sequence>
<element name="AffectedObjects" type="tns:RegistryObjectListType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<element name="AffectedObjectRefs" type="tns:ObjectRefListType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
</sequence>
<attribute name="eventType" type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="required"/>
</complexType>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
AffectedObjects |
RegistryObjectListType |
0..1 |
|
Registry |
No |
|
AffectedObjectRefs |
ObjectRefListType |
0..1 |
|
Registry |
No |
|
eventType |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Registry |
No |
Element AffectedObject – Identifies the RegistryObjectType instances that were affected by the event. The AffectedObject element contains any number of elements of type RegistryObjectType, each of which is a RegistryObjectType instance affected by the event. If this element is present then AffectedObjectRefs element MUST NOT be present.
Element AffectedObjectRefs – Identifies the RegistryObjectType instances that were affected by the event. The AffectedObject element contains any number of ObjectRef elements each of which reference a RegistryObjectType instance that was affected by the event. If this element is present then AffectedObjects element MUST NOT be present.
Attribute eventType – Specifies the type of event associated with the Action within an AuditableEventType instance.
The value of the eventType attribute MUST be a reference to a ClassificationNode in the canonical EventType ClassificationScheme.
A Registry MUST support the event types as defined by the EventType ClassificationScheme.
The canonical EventType ClassificationScheme MAY easily be extended by adding additional ClassificationNodes to it
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
This type represents a subscription on behalf of a client to receive notifications by the server of events that are of interest to the client.
<complexType name="SubscriptionType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="DeliveryInfo"
type="tns:DeliveryInfoType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" />
<element name="Selector"
type="tns:QueryType" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" />
</sequence>
<attribute name="startTime" type="dateTime" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="endTime" type="dateTime" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="notificationInterval"
type="duration" use="optional"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
The following example shows a subscription to receive notification of changes to the object whose id value matches “urn:acme:person:Danyal”. The DeliveryInfo specifies the SOAP endpoint where the server should deliver the Notification.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:SubscriptionType"
id="urn:acme:Subscription:subscribeToDanyal"
startTime="2008-01-10T19:20:30+01:00" endTime="2009-01-10T19:20:30+01:00"
...>
<DeliveryInfo>
<NotifyTo>
<wsa:Address rim:endpointType="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:endPointType:soap">http://www.acme.com/notificationListener</wsa:Address>
</NotifyTo>
</DeliveryInfo>
<Selector queryDefinition="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:query:GetObjectById">
<Slot name="id">
<SlotValue xsi:type="rim:StringValueType">
<Value>urn:acme:person:Danyal</Value>
</SlotValue>
</Slot>
</Selector>
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
DeliverInfo |
0..* |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
|
endTime |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
|
notificationInterval |
xs:duration |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
Selector |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
|
startTime |
xs:dateTime |
0..1 |
Time of submission |
Client |
Yes |
Attribute startTime, endTime – Define the time window within which the subscription is valid.
A server MUST use the current time at the time of submission of Subscription as value for the startTime attribute if it is unspecified.
The Subscription validity window MUST be inclusive of the startTime and endTime.
If endTime is unspecified then a server MUST assume the Subscription is valid at any time any time since startTime inclusively.
Element DeliveryInfo – Specifies the information needed by the server to deliver notifications for the subscription. It includes the reference to the endpoint where notifications should be delivered.
A server MUST deliver notifications that match the Selector query for a valid SubscriptionType instance to the endpoint specified by each DeliveryInfo element of the SubscriptionType instance.
If no DeliveryInfo element is present then client MUST use the canonical query GetNotification via the Query protocol to “pull” the pending notification if any at a time of their choosing as defined in ebRS.
Attribute notificationInterval – Specifies the duration that a server MUST wait between delivering successive notifications to the client. The client specifies this attribute in order to control the frequency of notification communication between server and client.
A server MUST deliver any pending notifications within the interval specified by this attribute.
A server MUST NOT deliver the same event more than once for the same subscription.
Element Selector – Specifies the query that the server MUST invoke to determine whether an event matches a subscription or not. If the result of the query contains an object that is affected by an event that has not yet been delivered to the subscriber then the event matches the subscription.
Base Type: ExtensibleObjectType
This type provides the information needed by the server to deliver notifications for the subscription. It includes the reference to the endpoint where notifications should be delivered. The endpoint reference is typically one of the following types:
SOAP service endpoint
REST service endpoint
E-mail address endpoint
Software plugin endpoint that is configured within the same process as the registry server
<complexType name="DeliveryInfoType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:ExtensibleObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="NotifyTo"
type="wsa:EndpointReferenceType" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" />
</sequence>
<attribute name="notificationOption" type="tns:objectReferenceType"
default="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:NotificationOptionType:ObjectRefs"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
notificationOption |
objectReferenceType |
0..1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
|
NotifyTo |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute notificationOption – Specifies the modality of how notifications are to be delivered to the subscriber. Its value MUST reference a ClassificationNode in the canonical NotificationOptionType ClassificationScheme.
urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:NotificationOptionType:Objects – Indicates that the server MUST provide complete RegistryObjectType instances in notifications delivered to the subscriber when this mode is specified.
urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:NotificationOptionType:ObjectRefs – Indicates that the server MUST provide ObjectRefType instances rather than complete RegistryObjectType instances in notifications delivered to the subscriber when this mode is specified. A client MAY pull the complete RegistryObjectType instances using Query protocol after receiving the notification.
Element NotifyTo – Specifies the endpoint reference for the endpoint where the server should deliver notifications for the Subscription.
The type of this element is wsa:EndpointReferenceType as defined by [WSA-Core]
The content of this element is a string representing the endpoint address which SHOULD be a URI
The type of endpoint (SOAP, REST, email, ...) is indicated by an extension attribute rim:endpointType as follows:
If endpoint is a SOAP web service then the rim:endpointType attribute value MUST be “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:endPointType:soap”
If endpoint is a REST web service then the rim:endpointType attribute value MUST be “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:endPointType:rest”
If endpoint is an email address then the rim:endpointType attribute value MUST be “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:endPointType:mail”
If endpoint is a software plugin then the rim:endpointType attribute value MUST be “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:endPointType:plugin”
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
This type represents a notification that is sent by the server to a client to notify it of server events that are of interest to the client.
<complexType name="NotificationType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<sequence>
<element name="Event" type="tns:AuditableEventType"
minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</sequence>
<attribute name="subscription"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="required"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
<element name="Notification" type="tns:NotificationType"/>
The following example shows a Notification sent by the server for the subscription in earlier example. It notifies the subscriber that the object with id “urn:acme:person:Danyal” has changed.
<Notification subscription="urn:acme:Subscription:subscribeToDanyal" ...>
<Event
user="123456" timestamp="2008-10-17T15:44:29.637"
...>
<Action
eventType="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:EventType:Created">
<AffectedObjectRefs>
<ObjectRef
id="urn:acme:person:Danyal"/>
</AffectedObjectRefs>
</Action>
</Event>
</Notification>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
Event |
AuditableEventType |
1..* |
|
Server |
No |
|
subscription |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Server |
No |
Element Event – Represents an Event that is of interest to the subscriber.
Unlike an AuditableEvent element that contains all objects affected by it, the Event element MUST only contain objects that match the selector query of the SubscriptionType instance. It has only a subset of affected objects compared to the actual AuditableEvent it represents. The subset of affected objects MUST be those that match the selector query for the subscription.
The Action elements within the Event element MUST contain a RegistryObjectList element if subscription's notificationOption is “Push”.
The Action elements within the Event element MUST contain a RegistryObjectRefList element if subscription's notificationOption is “Pull”.
Attribute subscription – References the SubscriptionType instance for which this is a Notification.
This chapter describes the information model that support the definition of registry federations. A registry federation is a set of ebXML RegRep servers that have voluntarily agreed to form a loosely coupled union. Such a federation may be based on common business interests or membership in a community-of-interest. Registry federations enabled clients to query the content of their member servers using federated queries as if they are a single logical server.
A federation is created by the creation of a FederationType instance. A federation may have any number of registries as well as other federations as its members.
Membership of a registry or federation within a parent federation is established by creating an Association between the RegistryType or FederationType instance representing the registry or federation seeking membership, and the FederationType instance representing the parent federation as follows:
The Association MUST have its associationType be the id of the canonical ClassificationNode “HasFederationMember”
The Association MUST have as its sourceObject the FederationType instance representing the parent federation
The Association MUST have as its targetObject the RegistryType or FederationType instance that is seeking membership within the parent federation as shown in Illustration 10.
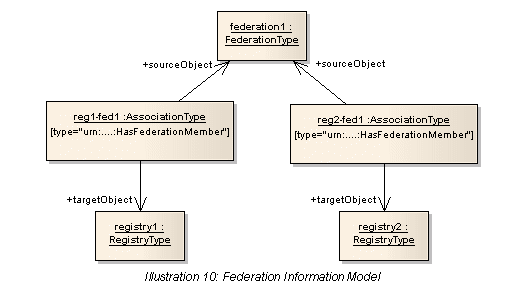
Thus a Federation is defined by a tree where a FederationType instances are root and intermediate n, RegistryType instances are leaf nodes and HasFederationMember AssociationType instances are the edges between the nodes. This tree is referred to as the federation membership tree.
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
RegistryType instances are used to represent an ebXML RegRep server. RegistryType instances are also used by a server to advertise the capabilities it supports. A client MAY read the RegistryType instance for a server to determine whether it is compatible with a server or not. Profiles of ebXML RegRep specifications MAY define canonical slots to represents support for the profile as well as optional features defined by the profile.
<complexType name="RegistryType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<attribute name="operator"
type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="required"/>
<attribute name="specificationVersion"
type="string" use="required"/>
<attribute default="P1D" name="replicationSyncLatency"
type="duration" use="optional"/>
<attribute default="PT0S" name="catalogingLatency"
type="duration" use="optional"/>
<attribute name="conformanceProfile"
use="optional" default="RegistryLite">
<simpleType>
<restriction base="NCName">
<enumeration value="RegistryFull"/>
<enumeration value="RegistryLite"/>
</restriction>
</simpleType>
</attribute>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
The following example describes an ebXML RegRep server operated by organization with id “urn:acme:Organization:acme-inc”, that implements the “RegistryFull” conformance level of version 4.0 of the ebXML RegRep specifications. The server performs replication synchronization once a day (P1D) and performs cataloging of submitted content immediately when content is submitted.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:RegistryType"
id="urn:acme:Registry:serviceRegistry"
operator="urn:acme:Organization:acme-inc"
specificationVersion="4.0"
conformanceProfile="RegistryFull"
replicationSyncLatency="P1D"
catalogingLatency="PT0S"
...>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
catalogingLatency |
xs:duration |
0..1 |
P1D (once a day) |
Server |
Yes |
|
conformanceProfile |
xs:string |
0..1 |
RegistryLite |
Server |
Yes |
|
operator |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Server |
Yes |
|
replicationSyncLatency |
xs:duration |
0..1 |
PT0S (immediately) |
Server |
Yes |
|
specificationversion |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Server |
Yes |
Attribute catalogingLatency - A RegistryType instance MAY have an attribute named catalogingLatency that specifies the maximum latency between the time a submission is made to the server and the time it gets cataloged by any cataloging services defined for the objects within the submission. The default value of PT0S indicates a duration of 0 seconds which implies that cataloging happens immediately when request is submitted.
Attribute conformanceProfile - A RegistryType instance MAY have an attribute named conformanceProfile that declares the conformance profile that the server supports. The conformance profiles choices are “RegistryLite” and “RegistryFull” as defined by [regrep-rs-v4.0].
Attribute operator - A RegistryType instance MUST have an attribute named operator that is a reference to the Organization instance representing the organization for the server’s operator. Since the same Organization MAY operate multiple registries, it is possible that the home registry for the Organization referenced by operator may not be the local registry.
Attribute replicationSyncLatency - A RegistryType instance MAY have an attribute named replicationSyncLatency that specifies the maximum latency between the time when an original object changes and the time when its replica object within the local server gets updated to synchronize with the new state of the original object. The default value of P1D indicates a duration of once a day.
Attribute specificationVersion - A RegistryType instance MUST have an attribute named specificationVersion that is the version of the ebXML RegReg Specifications it implements.
Federation instances are used to represent a registry federation. A FederationType instance has a set of RegistryType instances as its members. The membership of a RegistryType instance in a federationType instance is represented by an AssociationType instance whose type is HasFederationMember.
<complexType name="FederationType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<attribute name="replicationSyncLatency"
type="duration" use="optional" default="P1D" />
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
The following example shows a Federation with two independently-operated ebXML RegRep servers as members.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:FederationType"
id="urn:acme:Federation:supplierFederation"
replicationSyncLatency="P1D" ...>
...
</rim:RegistryObject>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:AssociationType"
sourceObject="urn:acme:Federation:supplierFederation"
targetObject="urn:widgetInc:Registry:widget-inc"
type="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:AssociationType:HasFederationMember"/>
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:AssociationType"
sourceObject="urn:acme:Federation:supplierFederation"
targetObject="urn:supplierInc:Registry:supplier-inc"
type="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:AssociationType:HasFederationMember"/>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
replicationSyncLatency |
xs:duration |
0..1 |
P1D (1 day) |
Client |
Yes |
Attribute replicationSyncLatency - A FederationType instance MAY specify a replicationSyncLatency attribute that describes the time duration that is the amount of time within which a member of this Federation MUST synchronize itself with the current state of the Federation. Members of the Federation MAY use this parameter to periodically synchronize the federation metadata they MUST cache locally about the state of the Federation and its members. Such synchronization MAY be based upon the registry event notification capability.
This chapter defines the Information Model used to control access to RegistryObjects and RepositoryItems managed by it. It also defines a normative profile of [XACML] for ebXML RegRep.
It is assumed that the reader is already familiar with [XACML]. This specification does not provide any introduction to [XACML].
A server MUST support the roles of both Enforcement Point (PEP) and a Policy Decision Point (PDP) as defined in [XACML].
The Access Control Model attempts to reuse terms defined by [XACML] wherever possible. The definitions of some key terms are duplicated here from [XACML] for convenience of the reader:
|
Term |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Access |
Performing an action. An example is a user performing a delete action on a RegistryObject. |
|
Access Control |
Controlling access in accordance with a policy. An example is preventing a user from performing a delete action on a RegistryObject that is not owned by that user. |
|
Action |
An operation on a resource. An example is the delete action on a RegistryObject. |
|
Attribute |
Characteristic of a subject, resource, action. Some examples are:
|
|
Policy |
A set of rules. May be a component of a policy set |
|
PolicySet |
A set of policies, other policy sets. May be a component of another policy set |
|
Resource |
Data, service or system component. Examples are:
|
|
Subject |
An actor whose attributes may be referenced by within a Policy definition. Examples of subject include:
|
A RegistryObjectType instance is associated with exactly one Access Control Policy that governs “who” is authorized to perform “what” action on that RegistryObject. This Access Control Policy is expressed as an [XACML] document which is the repositoryItem for an ExtrinsicObjectType instance. The Access Control Policy is published to the server as an ExtrinsicObject and repositoryItem pair using the Submit protocol defined by [regrep-rs-v4.0].
The objectType attribute of this ExtrinsicObject MUST reference a descendent of the “XACML” ClassificationNode (e.g. “Policy” or PolicySet”) in the canonical ObjectType ClassificationScheme.
An Access Control Policy MAY be assigned to a RegistryObjectType instance using the canonical slot “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:rim:RegistryObject:accessControlPolicy”. The value slot references the ExtrinsicObject representing the Access Control Policy and contains the id of that ExtrinsicObject.
If a RegistryObjectType instance does not have an Access Control Policy explicitly associated with it via the canonical slot with name “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:rim:RegistryObject:accessControlPolicy”, then it is implicitly associated with the default Access Control Policy defined for the server.
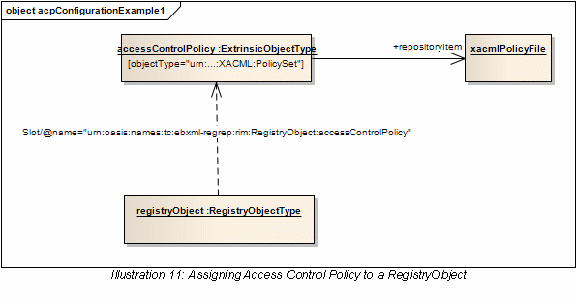
Illustration 11 shows a UML instance diagram where an Organization instance org references an ExtrinsicObject instance accessControlPolicy as its Access Control Policy object using the canonical accessControlPolicy slot.
A server MUST support a default Access Control Policy. A server MAY implement any default access control policy. The default Access Control Policy applies to all RegistryObjectType instances that do not explicitly have an Access Control Policy assigned.
This following specify the semantics of a suggested default Access Control Policy that a server SHOULD implement:
An unauthenticated client is permitted to perform read actions (that do not modify the state of resources) on any resource
An authenticated client with authentication credentials of a registered user is permitted all actions on RegistryObjects submitted by the user
A authenticated client with authentication credentials that are assigned the canonical subject role of "urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:SubjectRole:RegistryAdministrator" is permitted to perform any action on any object
A RegistryObjectType instance that does not explicit define an Access Control Policy MAY inherit an Access Control Policy from its nearest RegistryPackageType ancestor if it is in the membership hierarchy of a RegistryPackageType instance.
An Access Control Policy for members of a RegistryPackageType instance MAY be assigned to the RegistryPackageType instance using the canonical slot “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:rim:RegistryPackage:memberAccessControlPolicy”. The value slot references the ExtrinsicObject representing the Access Control Policy and contains the id of that ExtrinsicObject. The member Access Control Policy is implicitly inherited as the applicable Access Control Policy for any member RegistryObjectType instance that does not have an explicit Access Control Policy assigned to it.
In the event that a RegistryObjectType instance has a member Access Control Policy defined from two RegistryPackageType ancestors at the same ancestry level a server MAY choose any mechanism to select one of the two member Access Control Policies.
A server MUST implement the following algorithm for determining the applicable Access Control Policy for a RegistryObjectType instance:
If an Access Control Policy is explicitly assigned to the object then use it
If no Access Control Policy is explicitly assigned to the object then get the member Access Control Policy from a nearest RegistryPackageType ancestor of the object
If no Access Control Policy is explicitly assigned to the object or inherited from a RegistryPackageType ancestor of the object then use the system-wide default Access Control Policy
Excessive use of custom Access Control Policies MAY result in slower processing of registry requests in some registry implementations. It is therefor suggested that, whenever possible, a submitter SHOULD reuse an existing Access Control Policy. Submitters SHOULD use good judgment on when to reuse or extend an existing Access Control Policy and when to create a new one.
A contextual role may be define by a RoleType instance within a server as defined next.
Base Type: RegistryObjectType
<complexType name="RoleType">
<complexContent>
<extension base="tns:RegistryObjectType">
<attribute name="type" type="tns:objectReferenceType" use="required"/>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
The following examples shows a RoleType instances representing a contextual role of “ProjectLead” within the organizational context of an Organization TestSubmittingOrg1.
<rim:RegistryObject xsi:type="rim:RoleType"
type="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:SubjectRole:ProjectLead" ...>
<rim:Slot name="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:RoleAssociation:organizationContext">
<rim:SlotValue xsi:type="rim:StringValueType">
<rim:Value>urn:test:Organization:TestSubmittingOrg1</rim:Value>
</rim:SlotValue>
</rim:Slot>
</rim:RegistryObject>
|
Node |
Type |
Cardinality |
Default Value |
Specified By |
Mutable |
|
type |
objectReferenceType |
1 |
|
Client |
Yes |
Attribute type - Each RoleType instance MUST have a type attribute that identifies the type of role.
The value of the type attribute SHOULD be a reference to a ClassificationNode within the canonical SubjectRole ClassificationScheme.
A server MUST support the canonical subject role types as defined by the canonical SubjectRole ClassificationScheme. Deployments and profiles may extend the canonical SubjectRole ClassificationScheme by adding additional ClassificationNodes to it.
The RoleType instance may have any number of Slots that provide context for the role as a name/value pair. The name attribute of each such context slot provides the context key while the value of the Slot (typically a string) provides the context value
A subject such as a registered user MAY be assigned a contextual role by associating the id attribute value of the RoleType instance representing the contextual role with the id of the subject. This specification does not define how such an association is made. Implementations may provide this association in an implementation specific manner. For example, in an LDAP based identity management system this may be done by making the node representing the subject to be a member of a groupOfName node as illustrated below:
#person ProjectLead1 definition
dn: uid=ProjectLead1,...
objectclass: top
objectclass: person
objectclass: organizationalPerson
objectclass: inetOrgPerson
cn: Project Lead 1
sn: ProjectLead1
uid: ProjectLead1
#Role TestSubmittingOrg1ProjectLead definition
dn: cn=urn:test:Role:TestSubmittingOrg1ProjectLead,...
objectclass: top
objectclass: groupOfNames
cn: urn:test:Role:TestSubmittingOrg1ProjectLead
member: uid=ProjectLead1,ou=people,...
An XACML Access Control Policy MAY use an action identifier associated with the action as an action attribute within <xacml:ActionMatch> elements to match the action that is authorized for a subject on a resource.
The following requirements are defined for a server for action matching:
A server MUST specify the action identifier in the request context for an XACML decision request using a <xacmlc:Request>/<xacmlc:Action>/<xacmlc:Attribute> element
The <xacmlc:Attribute> element MUST have an AttributeId attribute with content "urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:action:action-id"
The <xacmlc:Attribute> element MUST have a DataType attribute with value “http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string”
The <xacmlc:Attribute> MUST have a <xacmlc:AttributeValue> element whose content MUST be the id attribute of the ClassificationNodeType instance within the canonical ActionTypeScheme that represent the requested action
The following requirements are defined for an Access Control Policy for action matching:
The policy MAY match an action using an <xacmlp:ActionMatch> element
The <xacmlp:ActionMatch> element MUST have a <xacmlp:AttributeValue DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"> element whose content MUST be the id attribute of a ClassificationNodeType instance within the canonical ActionTypeScheme
The <xacmlp:ActionMatch> element MUST have a <xacmlp:ActionAttributeDesignator AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:action:action-id" DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"/> element
The following example shows an Action that matches the “Read” action.
<Target>
<Actions>
<Action>
<ActionMatch
MatchId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:function:string-equal">
<AttributeValue
DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">
urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:ActionType:read
</AttributeValue>
<ActionAttributeDesignator
AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:action:action-id"
DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"/>
</ActionMatch>
</Action>
</Actions>
</Target>
This attribute is only relevant to the “Reference” action. This attribute MAY be used to specify the object from which the reference is being made to the resource being protected. The AttributeId of this attribute MUST be “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:rim:acp:subject:reference-source”. The value of this attribute MUST be the value of the id attribute for the object that is the source of the reference. A server MUST specify this attribute for a reference action.
This attribute is only relevant to the “Reference” action. This attribute MAY be used to specify the attribute name within the RegistryObjectype that the reference-source object is an instance of. A server MUST specify this attribute for a reference action. The AttributeId of this attribute MUST be “urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:rim:acp:subject: reference-source-attribute”. The value of this attribute MUST be the name of an attribute within the RIM type that is the type for the reference source object.
For example, if the reference source object is an Association instance then the reference-source-attribute MAY be used to specify the values “sourceObject” or “targetObject” to restrict the references to be allowed from only specific attributes of the source object. This enables, for example, a policy to only allow reference to objects under its protection only from the sourceObject attribute of an Association instance.
An XACML Access Control Policy MAY use the identity and roles associated with the subject as subject attributes within <xacml:SubjectMatch> elements to match the subject that is authorized for an action on a resource.
The following requirements are defined for a server for subject matching:
A server MUST specify the subject identifier in the request context for an XACML decision request using a <xacmlc:Request>/<xacmlc:Subject>/<xacmlc:Attribute> element
The <xacmlc:Attribute> element MUST have an AttributeId attribute with value "urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:subject:subject-id"
The <xacmlc:Attribute> element MUST have a DataType attribute with value “http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string”
The <xacmlc:Attribute> MUST have a <xacmlc:AttributeValue> element whose content MUST be the unique id associated with the requestor
A server MUST specify any subject roles in the request context for an XACML decision request using a <xacmlc:Request>/<xacmlc:Subject>/<xacmlc:Attribute> element. This specification does not define how roles are assigned to a subject. Implementations SHOULD provide that functionality in an implementation-specific manner.
The <xacmlc:Attribute> element MUST have an AttributeId attribute with value "urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:3.0:rim:acp:subject:role"
The <xacmlc:Attribute> element MUST have a DataType attribute with value “http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string”
The <xacmlc:Attribute> MUST have a <xacmlc:AttributeValue> element whose content MUST be the id attribute value of a RoleType instance associated with the requestor
The following requirements are defined for an Access Control Policy for subject matching by the subject id:
The policy MAY match a subject by id using an <xacmlp:SubjectMatch> element
The <xacmlp:SubjectMatch> element MUST have a <xacmlp:AttributeValue DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"> element whose content MUST be the unique id of the subject
The <xacmlp:SubjectMatch> element MUST have a <xacmlp:SubjectAttributeDesignator AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:subject:subject-id" DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"/> element
The following example shows a Subject that matches a registered user with id “urn:acme:person:Danyal”:
<Target>
<Subjects>
<Subject>
<SubjectMatch
MatchId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:function:string-equal">
<AttributeValue
DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">
urn:acme:person:Danyal
</AttributeValue>
<SubjectAttributeDesignator
AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:subject:subject-id"
DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"/>
</SubjectMatch>
</Subject>
</Subjects>
</Target>
The following requirements are defined for an Access Control Policy for subject matching by a subject role:
The policy MAY match a subject by a contextual role using an <xacmlp:Condition> element
The <xacmlp:Condition> element MUST use an <xacmlp:Apply/@FunctionId='urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:4.0:rim:acp:function:matches-role'> element to invoke the “matches-role” XACML function as defined by this specification
The following example shows a Subject that matches a subject role “ProjectLead” within the organizational context of Organization TestSubmittingOrg1 and register context of Register TestRegister1:
<Rule Effect="Permit" RuleId="urn:test:customACP1:rule:restricted-delete">
<Target/>
<Condition>
<Apply FunctionId="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:4.0:rim:acp:function:matches-role">
<SubjectAttributeDesignator AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:3.0:rim:acp:subject:role" DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"/>
<AttributeValue DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:SubjectRole:ProjectLead</AttributeValue>
<AttributeValue DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:RoleAssociation:organizationContext</AttributeValue>
<AttributeValue DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">urn:test:Organization:TestSubmittingOrg1</AttributeValue>
<AttributeValue DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:RoleAssociation:registerContext</AttributeValue>
<AttributeValue DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">urn:test:Register:TestRegister1</AttributeValue>
</Apply>
</Condition>
</Rule>
An XACML Access Control Policy MAY use the id associated with the resource as resource attributes within <xacml:ResourceMatch> elements to match a resource within an authorization decision for an action on the resource.
The following requirements are defined for a server for resource matching:
A server MUST specify the resource identifier in the request context for an XACML decision request using a <xacmlc:Request>/<xacmlc:Resource>/<xacmlc:Attribute> elementThe <xacmlc:Attribute> element MUST have an AttributeId attribute with value "urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:resource:resource-id"
The <xacmlc:Attribute> element MUST have a DataType attribute with value “http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string”
The <xacmlc:Attribute> MUST have a <xacmlc:AttributeValue> element whose content MUST be the unique id associated with the resource
A server MUST specify the owner attribute value of the RegistryObjectType resource in the request context for an XACML decision request using a <xacmlc:Request>/<xacmlc:Resource>/<xacmlc:Attribute> element
The <xacmlc:Attribute> element MUST have an AttributeId attribute with value "urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:3.0:rim:acp:resource:owner"
The <xacmlc:Attribute> element MUST have a DataType attribute with value “http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string”
The <xacmlc:Attribute> MUST have a <xacmlc:AttributeValue> element whose content MUST be the owner attribute value of the RegistryObjectType resource
The following requirements are defined for an Access Control Policy for resource matching by the resource's id:
The policy MAY match a resource by id using an <xacmlp:ResourceMatch> element
The <xacmlp:ResourceMatch> element MUST have a <xacmlp:AttributeValue DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"> element whose content MUST be the unique id of the resource
The <xacmlp:ResourceMatch> element MUST have a <xacmlp:ResourceAttributeDesignator AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:resource:resource-id" DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"/> element
The following example shows a ResourceMatch that matches a resource with id “urn:acme:person:Danyal”:
<Target>
<Resources>
<Resource>
<ResourceMatch
MatchId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:function:string-equal">
<AttributeValue
DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">
urn:acme:person:Danyal
</AttributeValue>
<ResourceAttributeDesignator
AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:subject:subject-id"
DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"/>
</ResourceMatch>
</Resource>
</Resources>
</Target>
An XACML Access Control Policy MAY use any node in the XML document representing a RegistryObjectType instance within an <xacml:ResourceMatch> element. In this case, the <xacml:ResourceMatch> element SHOULD use an XPATH expression to match any part of the XML element representing the RegistryObjectType instance.
The following example uses XPATH expression to match resource if it has a Slot with name “someSlotName”.
<Resource>
<ResourceMatch MatchId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:function:string-equal">
<AttributeValue DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">
urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:xsd:rim:4.0
</AttributeValue>
<ResourceAttributeDesignator
AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:2.0:resource:target-namespace"
DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"/>
</ResourceMatch>
MatchId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:function:xpath-node-match">
<AttributeValue DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">
//<rim:Slot>/@name="someSlotName"
</AttributeValue>
<ResourceAttributeDesignator
AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:resource:xpath"
DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string"/>
</ResourceMatch>
</Resource>
Section A.3 of [XACML] defines a set of standard functions. This section defines addition XACML functions that MUST be supported by an ebXML RegRep server that supports XACML based custom access control policies. XACML specifies the following functions. If an argument of one of these functions were to evaluate to "Indeterminate", then the function MUST be set to "Indeterminate".
Function ID: urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:rim:acp:function:AssociationExists
Function ID: urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:rim:acp:function:ClassificationNodeCompare
A client MAY use this XACML function to test whether a resource's objectType attribute matches a specific objectType or its sub-types.
Function ID: urn:oasis:names:tc:ebxml-regrep:4.0:rim:acp:function:matches-role
This specification normatively defines the following constraints on the binding of the Access Control Model to [XACML]. These constraints MAY be relaxed in future versions of this specification.
All Policy and PolicySet definitions MUST reside within an ebXML Registry as RepositoryItems.
An XACML PolicySet MAY reference XACML Policy objects defined outside the repository item containing the XACML PolicySet. A server implementation MUST be able to resolve such references. To resolve such references efficiently a server SHOULD be able to find the repository item containing the referenced Policy without having to load and search all Access Control Policies in the repository. This section describes the normative behavior that enables a server to resolve policy references efficiently.
A server SHOULD define a Content Cataloging Service for the canonical XACML PolicySet objectType. The PolicySet cataloging service MUST automatically catalog every PolicySet upon submission to contain a special Slot with name ComposedPolicies. The value of this Slot MUST be a Set where each element in the Set is the id for a Policy object that is composed within the PolicySet.
Thus a server is able to use an ad hoc query to find the repositoryItem representing an XACML PolicySet that contains the Policy that is being referenced by another PolicySet.