| Template:— representing_typical_activity (rep_typ_act) | Date: 2008/01/18 08:58:19 Revision: 1.15 |
This section specifies the template representing_typical_activity.
NOTE An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is provided in the Template overview section.
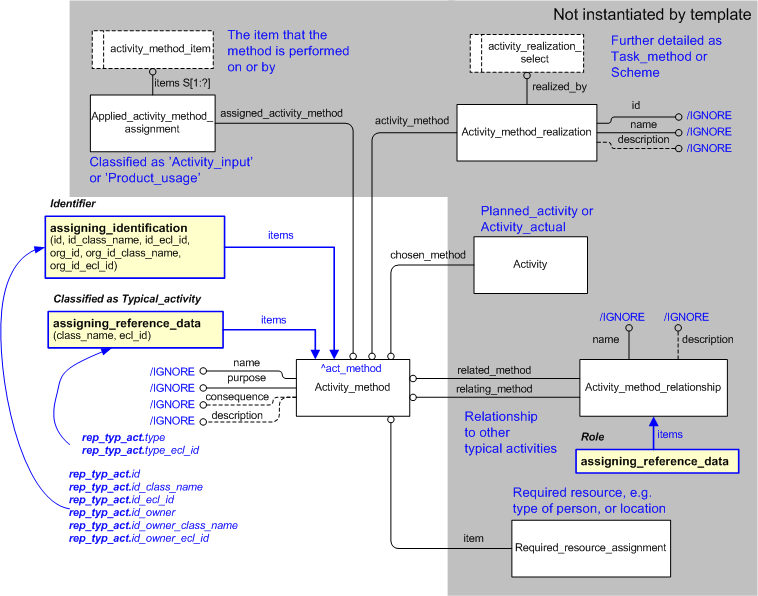
This template describes how to represent a typical activity that something or someone may undertake. A typical activity defines the approach to or method used for undertaking an activity.
For a typical activity that represents a structured set of processes, then the typical activity will be related to tasks which define the structured set of processes. For further details see: C015: representing_task (NB Capabilities are not documented in this release of the PLCS standard) . If the activities or tasks are to be scheduled, then the schedule is represented by a Scheme. For further details see: C062: representing_scheme (NB Capabilities are not documented in this release of the PLCS standard) .
The following templates are used to represent activities planned or undertaken in accordance with the typical activity. These activities are related back to the typical activity.


target
is the parameter to which the
Activity_method
is bound.
| Entity in path | Value | Inherited from |
| Activity_method.name | '/IGNORE' | — |
| Activity_method.purpose | '/IGNORE' | — |
| Activity_method.description | '/IGNORE' | — |
| Activity_method.consequence | '/IGNORE' | — |


NOTE this characterization is mandatory.
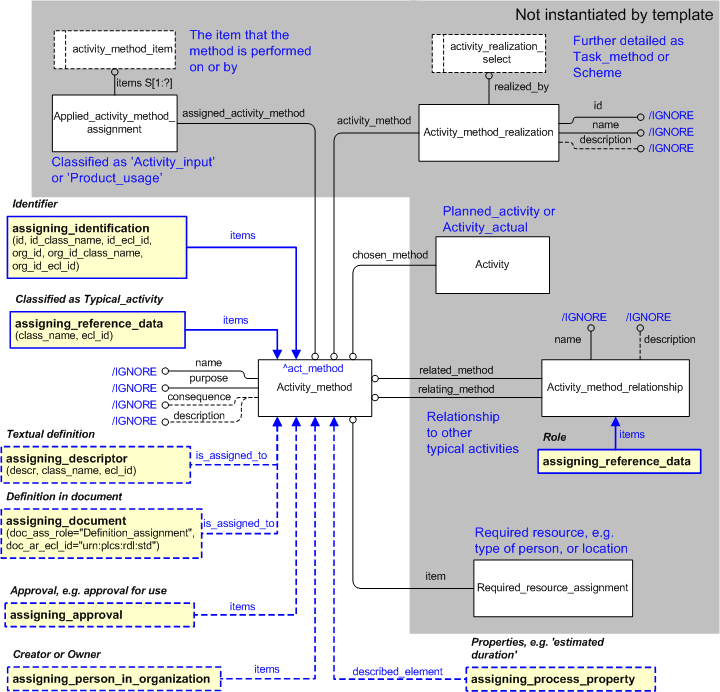
A typical activity must be specified in some way. There are several alternative routes to do this,
At least one of these alternatives must be used. See Figure 1 for an Express-G overview
A textual definition is represented by assigning a descriptor to the typical activity using the assigning_descriptor template.
A document describing the typical activity is assigned using template assigning_document with the Document_assignment classified as "Definition_assignment" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Definition_assignment).
A structured set of processes or steps of a typical activity is represented using Activity_method_realization to relate e.g. a Task_method or Scheme to the Activity_method.
NOTE These alternatives are not mutually exclusive, they can be used at the same time.
NOTE this characterization is optional.
A product or a group of products can be assigned to the typical activity, classified as e.g. "activity input" and "product usage". See Figure 1 for an Express-G overview.
For a typical activity to be performed on a product or group of products, an Applied_activity_method_assignment, classified as "Activity_input" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Activity_input), is used to relate the product to the activity as an "activity input".
This is done using template assigning_activity with the input parameter role_class_name given the value "Activity_input" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Activity_input).
For a typical activity to be performed by a product, an Applied_activity_method_assignment, classified as "Product_usage" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Product_usage), is used to relate the product to the activity as the product to be used ("product_usage").
This is done using template assigning_activity with the input parameter role_class_name given the value "Product_usage" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Product_usage).
NOTE this characterization is optional.
A typical activity may be approved, e.g. approved for use. See Figure 1 for an Express-G overview.
An approval of the typical activity is represented by assigning a Approval to the Activity_method using the assigning_approval template.
NOTE The assignment of approvals is described the capability C019: assigning_approvals (NB Capabilities are not documented in this release of the PLCS standard) .
NOTE this characterization is optional.
A person or organization may be assigned to a typical activity, classified as e.g. "creator" or "owner" of the activity. See Figure 1 for an Express-G overview.
NOTE This characterization is not intended to assign persons or organizations as a resource to an activity. To assign types of persons or organizations as a resource to an activity, see characterization "assigning resources".
An organization is associated to a typical activity by using the template assigning_organization. The assignment of the organization (Organization_or_person_in_organization_assignment) must be classified, e.g. as "Owner_of".
A person in an organization is associated to a typical activity by using the template assigning_person_in_organization. The assignment of the person (Organization_or_person_in_organization_assignment) must be classified, e.g. as "Creator".
NOTE this characterization is optional.
Required resources, such as required type of person, required location, etc, may be assigned to a typical activity. See Figure 1 for an Express-G overview.
An required resource is associated to a typical activity by using Required_resource_assignment, classified appropriately.
NOTE this characterization is optional.
Properties, e.g. estimated duration, can be assigned to a typical activity. See Figure 1 for an Express-G overview.
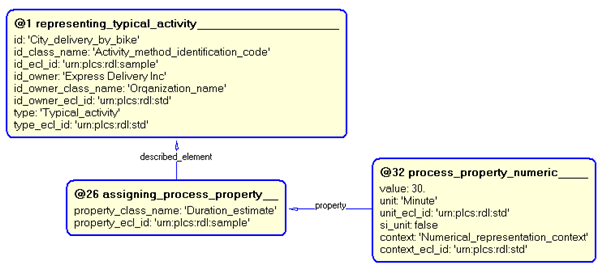
A property is represented by Activity_property assigned to the Activity_method, using template assigning_process_property.
NOTE The assignment of process properties are described further in capability C077: assigning_process_properties (NB Capabilities are not documented in this release of the PLCS standard) .
© OASIS 2008 — All rights reserved