| Template:— representing_part (rep_part) |
Date: 2008/02/27 09:14:09
Revision: 1.33
|
This section specifies the template representing_part.
NOTE
An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is
provided in the
Template overview
section.
This template describes how to represent a part. It
covers the minimum requirements to represent a Part,
Part_version and
Part_view_definition.
NOTE
If an organization does not version parts, it is recommended that the identification of the
Part_version
is set to "/NULL", i.e. the attribute
identifier
of entity Identification_assignment
contain the string "/NULL" (see C001: assigning_identifiers (NB Capabilities are not documented in this release of the PLCS standard)
), to indicate
that no version information is relevant or intended. In this case only a single part_version for the part is possible.
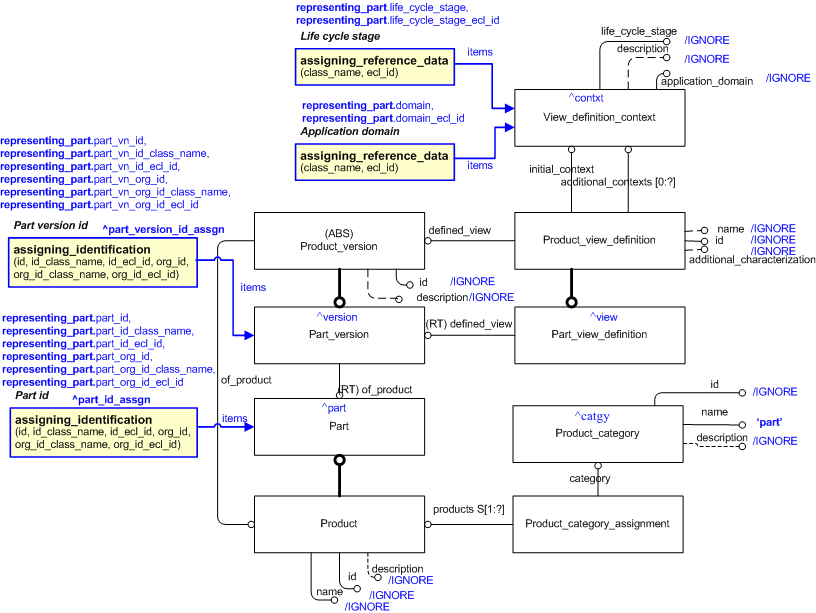
The EXPRESS-G diagram in
Figure
1
shows the templates and EXPRESS entities that are required
to represent the template
"representing_part".
The text highlighted in blue shows the template parameters.
The figure below shows the relevant aspects of the EXPRESS-G model for this part of AP239. It shows the setting
of the EXPRESS-G attributes and the
(re-)use of various subordinate templates. Most attributes of the EXPRESS model are set to '/IGNORE' and the equivalent
value is specified through a template,
where and when required. There is one exception to this - because of an inbuilt EXPRESS Rule which states that the
Product_category.name assigned to a
Part via a
Product_category_assignment
must be set to a specific value.
Hence 'part' is encoded into the template by default to enable a legal (EXPRESS-wise) population of instances.
The usage of the subordinate templates requires the capture of relevant input parameters to the representing_part
template.
The instantiation path uses the input parameters to establish the values
provided for the entities or other templates instantiated and then links them together following the EXPRESS-G model
in the appropriate manner.
Figure 1 — An EXPRESS-G representation of the Information model for representing_part
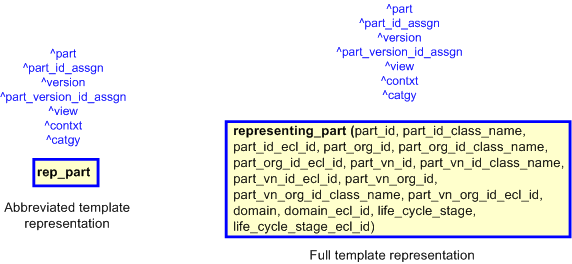
The graphic for the template to be used in other EXPRESS-G diagrams
is shown in Figure
2
below.
The figure below shows the full and abbreviated template for representing_part. The expanded (full) version exposes
the parameter list required by the template. The input parameters are specified below and where the term 'Default=' is found,
it indicates that the parameter is optional and that if no value is provided, then the default value specified will be used
instead.
Figure 2 — The graphical representation of the representing_part template
The following input parameters are defined for this template:
The identifier of the part
The name of the class being used to classify the identifier assigned (
Identification_assignment
) to the part (i.e. the part.id)
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The name or identifier of the organization that owns the part id.
The name of the class being used to classify the identification (
Identification_assignment)
of the organization responsible for creating the part representation
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The identifier of the part version
The name of the class being used to classify the identifier assigned (
Identification_assignment
) to the part version (i.e. the part_vn_id)
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The name or identifier of the organization owns the part version id.
The name of the class being used to classify the identification (
Identification_assignment)
of the organization responsible for providing the part version representation
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
domain (Default=Product_life_cycle_support,Type='CLASS', Optional)
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The following classes and their sub-classes can be used:
The following reference parameters are defined for this template:
Allow the
Part
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
Note: The
Part
entity can be referenced in a template path by:
%^target = $representing_part.part%
where
target
is the parameter to which the
Part
is bound.
%^target = $representing_part.part_id_assgn%
Allow the
Part_version
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
Note: The
Part_version
entity can be referenced in a template path by:
%^target = $representing_part.version%
where
target
is the parameter to which the
Part_version
is bound.
%^target = $representing_part.part_version_id_assgn%
Allow the
Part_view_definition
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
%^target = $representing_part.view%
%^target = $representing_part.contxt%
Allow the
Product_category
entity instantiated in this path to be referenced when this template is used.
%^target = $representing_part.catgy%
The following entity/attribute combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: Unique product_category
The following parameter combinations specify a uniqueness constraint:
Unique constraint: Unique part
Unique constraint: Unique part version
There shall be at most one instance of the
entity
(
Part_version)
within the data set uniquely identified
by a combination of the following parameters on this
template (representing_part) namely:
part_id,
part_id_class_name,
part_id_ecl_id,
part_org_id,
part_org_id_class_name,
part_org_id_ecl_id,
part_vn_id,
part_vn_id_class_name,
part_vn_id_ecl_id,
part_vn_org_id,
part_vn_org_id_class_name,
part_vn_org_id_ecl_id.
The
instance is
referenced by the following template parameter:
version.
This rule means that there can be only one version
(
Part_version)
of a part
(
Part)
with any given identifier.
Unique constraint: Unique part view
There shall be at most one instance of the
entity
(
Part_view_definition)
within the data set uniquely identified
by a combination of the following parameters on this
template (representing_part) namely:
part_id,
part_id_class_name,
part_id_ecl_id,
part_org_id,
part_org_id_class_name,
part_org_id_ecl_id,
part_vn_id,
part_vn_id_class_name,
part_vn_id_ecl_id,
part_vn_org_id,
part_vn_org_id_class_name,
part_vn_org_id_ecl_id,
domain,
domain_ecl_id,
life_cycle_stage,
life_cycle_stage_ecl_id.
The
instance is
referenced by the following template parameter:
view.
Unique constraint: Unique view_definition_context
The instantiation path shown below specifies the entities that are to be
instantiated by the template.
-- Part Part-- Mark the Part entity as referable when this template -- is used by binding by the reference parameter ^part %^part =
Part%
Part.id = '/IGNORE'
Part.name = '/IGNORE'
Part.description = '/IGNORE'
-- Identify the Part /
assigning_identification(
items=^part,
id=@part_id,
id_class_name=@part_id_class_name,
id_ecl_id=@part_id_ecl_id,
org_id=@part_org_id,
org_id_class_name=@part_org_id_class_name,
org_id_ecl_id=@part_org_id_ecl_id )/
-- establish the ref parameter %^part_id_assgn = $assigning_identification.id_assgn%
-- -- Product category assignment Product_category_assignment-- Not able to reference from outside -- Attach the assignment to the Part Product_category_assignment.products ->
Part-- -- Product category Product_categoryProduct_category.id = '/IGNORE'
Product_category.name = 'part'
Product_category.description = '/IGNORE'
%^catgy =
Product_category%
-- Attach the assignment to the Product_category Product_category_assignment.category ->
Product_category-- Part version -- Part_version-- Mark the Part_version entity as referable when this template -- is used by binding it to the reference parameter ^version %^version =
Part_version%
Part_version.id = '/IGNORE'
Part_version.description = '/IGNORE'
-- Relate the part_version to the part Part_version.of_product ->
Part-- Identify the Part_version /
assigning_identification(
items=^version,
id=@part_vn_id,
id_class_name=@part_vn_id_class_name,
id_ecl_id=@part_vn_id_ecl_id,
org_id=@part_vn_org_id,
org_id_class_name=@part_vn_org_id_class_name,
org_id_ecl_id=@part_vn_org_id_ecl_id )/
-- establish the ref parameter %^part_version_id_assgn = $assigning_identification.id_assgn%
-- Part_view_definition-- Mark the Part_view_definition entity as referable -- when this template is used by binding it to the reference -- parameter ^view %^view =
Part_view_definition%
Part_view_definition.id = '/IGNORE'
Part_view_definition.name = '/IGNORE'
Part_view_definition.additional_characterization = '/IGNORE'
-- Relate the part_version to the part Part_view_definition.defined_version ->
Part_version-- View_definition_context-- Mark the View_definition_context entity as referable when this -- template is used by binding it to the reference parameter ^contxt %^contxt =
View_definition_context%
-- Ignore the attributes View_definition_context.application_domain = '/IGNORE'
View_definition_context.life_cycle_stage = '/IGNORE'
View_definition_context.description = '/IGNORE'
-- provide the application domain of the view definition by classification /
assigning_reference_data(
items=^contxt,
class_name=@domain,
ecl_id=@domain_ecl_id)/
-- provide the life cycle stage of the view definition by classification /
assigning_reference_data(
items=^contxt,
class_name=@life_cycle_stage,
ecl_id=@life_cycle_stage_ecl_id)/
-- Relate the part_view_definition to the View_definition_context Part_view_definition.initial_context ->
View_definition_context
The following entities are instantiated with attributes as specified:
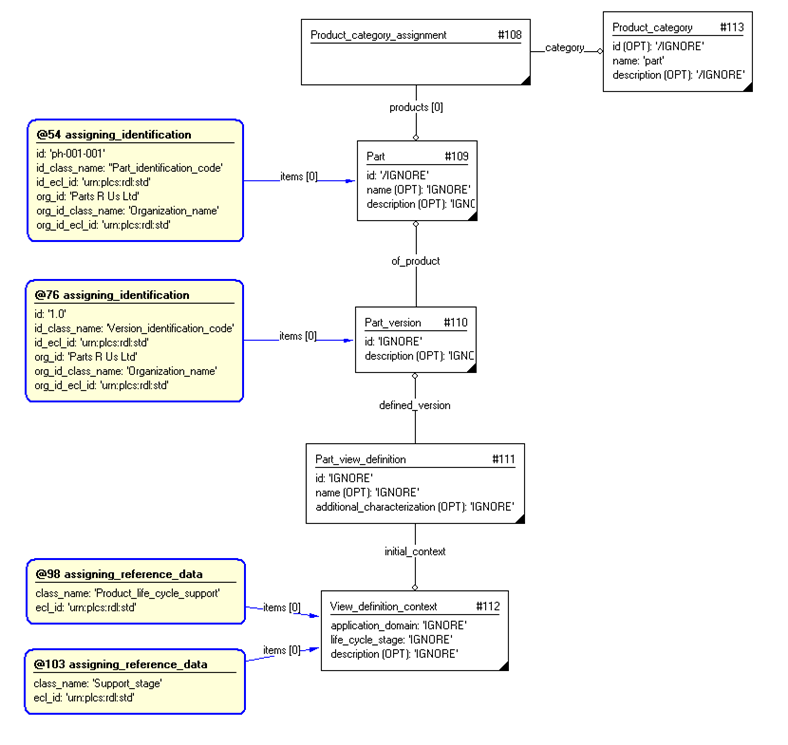
The instance diagram in Figure
3
shows an example of the EXPRESS entities and templates that are instantiated by the template:
/representing_part(part_id='ph-001-001', part_id_class_name='Part_identification_code', part_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', part_org_id='Parts R Us Ltd', part_org_id_class_name='Organization_name', part_org_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', part_vn_id='1.0', part_vn_id_class_name='Version_identification_code', part_vn_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', part_vn_org_id='Parts R Us Ltd', part_vn_org_id_class_name='Organization_name', part_vn_org_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', domain='Product_life_cycle_support', domain_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', life_cycle_stage='Support_stage', life_cycle_stage_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std')/
(an illustration of the consolidated representing_part template is shown in
Figure
4 below.)
Note that the
assigning_reference_data and
assigning_identification templates are used in the diagram.
Namely:
/assigning_reference_data(items='#112', class_name='Support_stage', ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std')/
/assigning_reference_data(items='#112', class_name='Product_life_cycle_support', ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std')/
/assigning_identification(items='#109', id='ph-001-001', id_class_name='Part_identification_code', id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', org_id='Parts R Us Ltd', org_id_class_name='Organization_name', org_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std')/
/assigning_identification(items='#110', id='1.0', id_class_name='Version_identification_code', id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', org_id='Parts R Us Ltd', org_id_class_name='Organization_name', org_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std')/
Figure 3 — Entities instantiated by representing_part template
The instance diagram in
Figure
4
shows the graphic symbol for the template that is to be
used in other instance diagrams. The example template is:
/representing_part(part_id='ph-001-001', part_id_class_name='Part_identification_code', part_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', part_org_id='Parts R Us Ltd', part_org_id_class_name='Organization_name', part_org_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', part_vn_id='1.0', part_vn_id_class_name='Version_identification_code', part_vn_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', part_vn_org_id='Parts R Us Ltd', part_vn_org_id_class_name='Organization_name', part_vn_org_id_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', domain='Product_life_cycle_support', domain_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', life_cycle_stage='Support_stage', life_cycle_stage_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std')/
Figure 4 — Example instantiation of representing_part template
The following section details how the
representing_part
template can be optionally characterized by assigning
other constructs to it. These are characterizations commonly
applied to the template. The ISO 10303-239 EXPRESS model may enable
other assignments to the entities instantiated by the template.
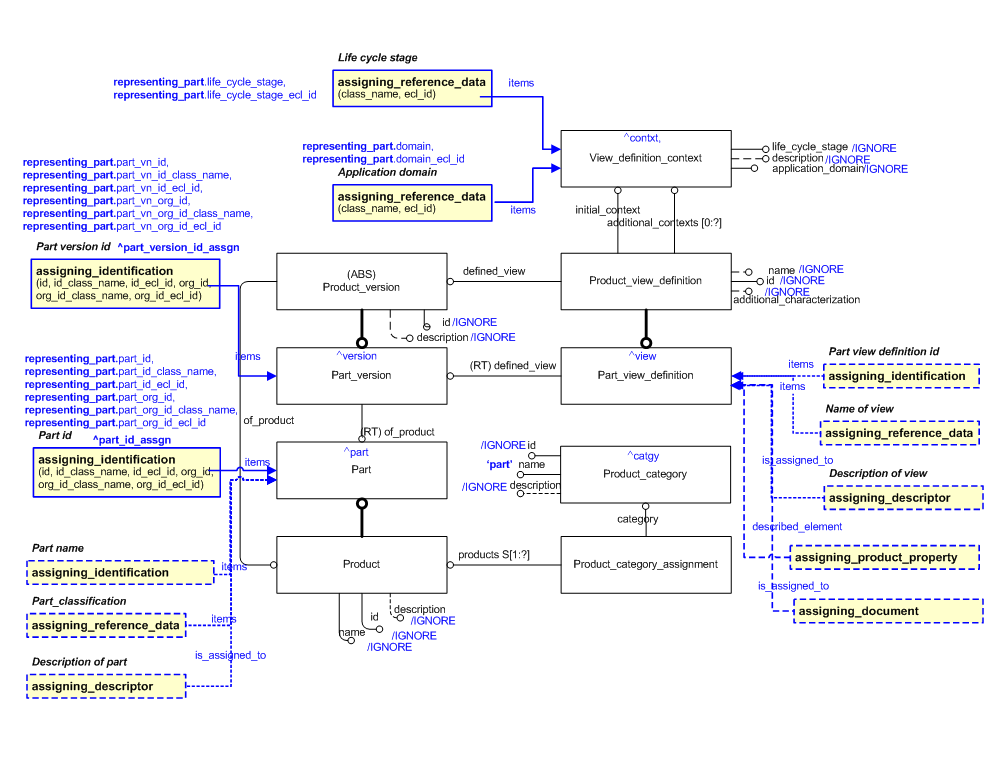
The EXPRESS-G diagram in Figure
5
shows the possible characterizations of the template
"representing_part".
Figure 5 — Characterizations for representing_part template
The following characterizations may apply:
Characterization Assigning name
NOTE this characterization is optional.
A name of the part can be provided using the template
assigning_identification. Part names are identifiers that are classifed
using external reference data as
"Part_name"
(urn:plcs:rdl:std:Part_name) or any subclass of this class.
This is then applied to the ^part reference parameter. See Figure 5 for the an abstract view of this.
The following template call shows how this might be instantiated with respect to Figure 5.
/assigning_identification(id='gasket', class_name='Part_name', ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', org_id='Parts R Us', org_id_class_name='Organization_name', org_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', items='@53')/
Characterization Assigning descriptor
NOTE this characterization is optional.
A description of the part can be provided using the template assigning_descriptor.
This is applied to the ^part, ^version or ^view reference parameters. See Figure 5 for the an abstract view of this.
The following template call shows how this might be instantiated with respect to Figure 5.
/assigning_descriptor(descr='This describes the part or a view of the part', class_name='Description', ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', is_assigned_to='@53')/
Characterization Assigning identification
NOTE this characterization is optional.
An identification of the part can be provided using the template
assigning_identification.
This is applied to the ^part, ^version or ^view reference parameters. See Figure 5 for the an abstract view of this.
The following template call shows how this might be instantiated with respect to Figure 5.
/assigning_identification(id='ph-001-001', class_name='Part_identification_code', ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', org_id='Parts R Us', org_id_class_name='Organization_name', org_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', items='@53')/
Characterization Assigning reference data
NOTE this characterization is optional.
Classification or reference data can be applied to the part using the template assigning_reference_data.
This is applied to the ^part, ^version or ^view reference parameters. See Figure 5 for the an abstract view of this.
The following template call shows how this might be instantiated with respect to Figure 5.
/assigning_reference_data(class_name='Part_classification', ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', items='@53')/
Characterization Assignments of properties and documents
NOTE this characterization is optional.
A part may have specific properties and documents assigned to it, through the use of the following templates:
assigning_product_property and
assigning_document. These are applied to the ^view reference parameter.
See Figure 5 for the an abstract view of this. The following template calls show how these characterizations
might be instantiated with respect to Figure 5.
/assigning_product_property(property_class_name='Wheel_diameter', property_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:sample', described_element='#53')/
/assigning_document(assigned_document='#??', doc_ass_role='Document_assignment_role', doc_ar_ecl_id='urn:plcs:rdl:std', is_assigned_to='#53')/