| Template:— assigning_asserted_state (asg_ast_state) | Date: 2008/02/20 08:05:00 Revision: 1.20 |
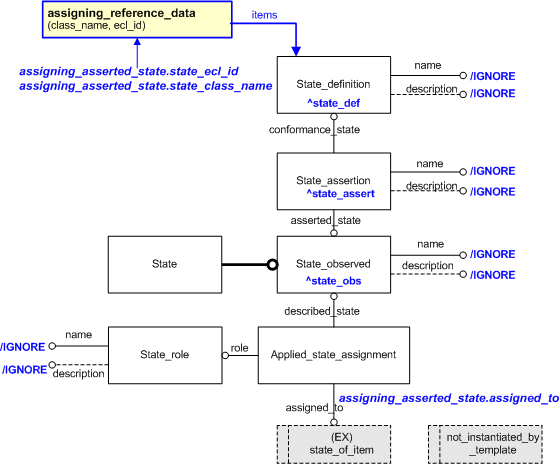
This section specifies the template assigning_asserted_state.
NOTE An explanation of a template and the associated instantiation path is provided in the Template overview section.
This template describes how to represent the fact that something has been observed to be in a given state and that this assertion has been confirmed by evidence such as a measurement.

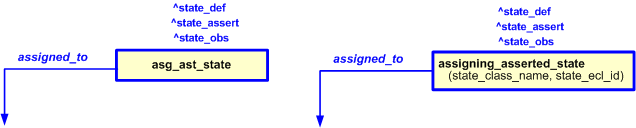
target
is the parameter to which the
State_observed
is bound.
target
is the parameter to which the
State_assertion
is bound.
target
is the parameter to which the
State_definition
is bound.
| Entity in path | Value | Inherited from |
| State_role.name | '/IGNORE' | — |
| State_role.description | '/IGNORE' | — |
| State_observed.name | '/IGNORE' | State.name |
| State_observed.description | '/IGNORE' | State.description |
| State_assertion.name | '/IGNORE' | — |
| State_assertion.description | '/IGNORE' | — |
| State_definition.name | '/IGNORE' | — |
| State_definition.description | '/IGNORE' | — |
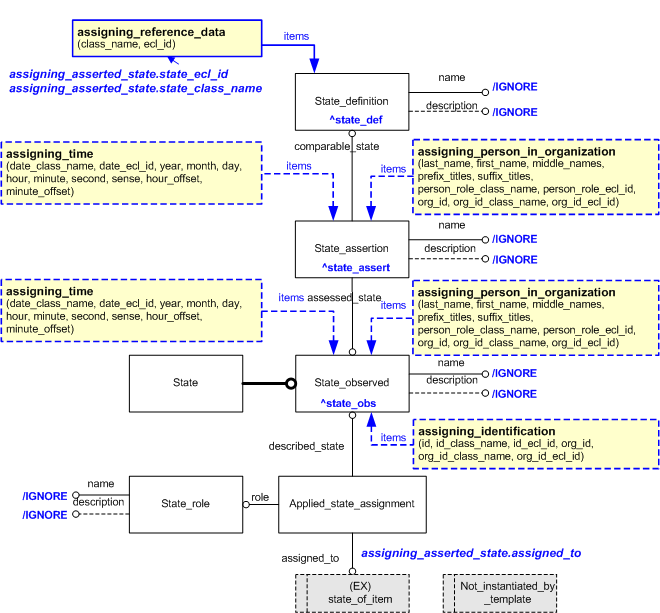
NOTE this characterization is optional.
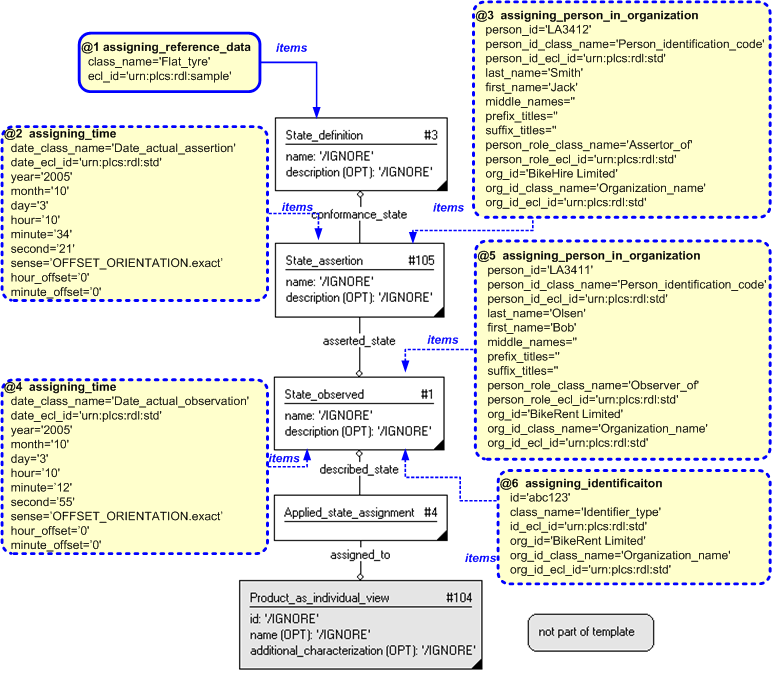
Dates and times can be associated with the assignment of an asserted state in a given role by using the template assigning_time.
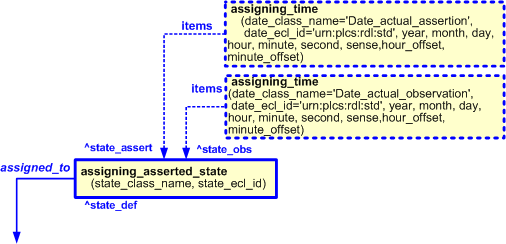
Several dates can be assigned to the template assigning_asserted_state, however two dates and times are commonly assigned these being the date and time on which the state was asserted and the date and time when the state was observed.
The date and time on which the state was asserted is represented by using the template assigning_time to assign a date and time to State_assertion. The date assignment is classified as: "Date_actual_assertion" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Date_actual_assertion) to indicate that it is the date when the state was asserted. This is illustrated in Figure 6.
The date and time on which the state was observed is represented by using the template assigning_time to assign a date and time to State_observed. The date assignment is classified as: "Date_actual_observation" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Date_actual_observation) to indicate that it is the date when the state was observed. This is illustrated in Figure 6.
NOTE this characterization is optional.
People can be associated with the assignment of an asserted state in a given role by using the template assigning_person_in_organization to assign a person to either a State_observed or a State_assertion .
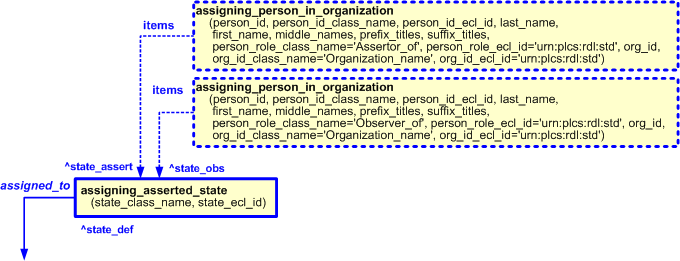
Several roles can be assigned to an asserted state. Two common roles in which people are assigned to the assignment of an asserted state are as an "Assessor of" the state and as an "Observer of" the state.
The person who asserted the state is represented by using the template assigning_person_in_organization to assign a person to State_assertion. The assignment of the person (Organization_or_person_in_organization_assignment) is classified as: "Assertor_of" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Assertor_of) to indicate that it is this person who has asserted the state. This is illustrated in Figure 7.
The person who observed the state is represented by using the template assigning_person_in_organization to assign a person to State_observed. The assignment of the person (Organization_or_person_in_organization_assignment) is classified as: "Observer_of" (urn:plcs:rdl:std:Observer_of) to indicate that it is this person who has observed the state. This is illustrated in Figure 7.
NOTE this characterization is optional.
Identifiers can be associated with the assignment of an asserted state by using the template assigning_identification to assign an identifier to a State_observed.
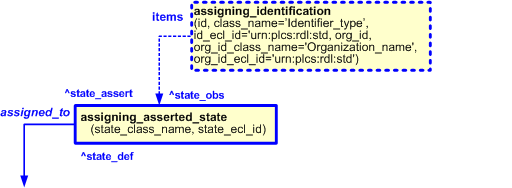
An example of the use of an identifier could be to identify the fault that is the reason for a repair activity.
© OASIS 2008 — All rights reserved