Code List Representation (Genericode) Version 1.0
Committee Draft 03
17 November 2007
Specification URIs:
This Version:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/cd3-genericode-1.0/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-genericode.html
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/cd3-genericode-1.0/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-genericode.odt
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/cd3-genericode-1.0/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-genericode.pdf
Previous Version:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/cd2-genericode-1.0/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-genericode.html
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/cd2-genericode-1.0/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-genericode.odt
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/cd2-genericode-1.0/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-genericode.pdf
Latest Version:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/genericode/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-genericode.html
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/genericode/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-genericode.odt
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/genericode/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-genericode.pdf
Latest Approved Version:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/approved/genericode/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-genericode.html
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/approved/genericode/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-genericode.odt
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/approved/genericode/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-genericode.pdf
Technical Committee:
OASIS Code List Representation TC
Chair(s):
G. Ken Holman, Associate Member, gkholman@CraneSoftwrights.com
Editor(s):
Anthony B. Coates, Miley Watts LLP, abcoates@mileywatts.com
Declared XML Namespace(s):
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/
(genericode)
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/rule/1.0/
(rule annotations in genericode Schema)
Abstract:
This document describes the OASIS Code List
Representation model and W3C XML Schema, known collectively as "genericode"[1].
Status:
This document was last revised or
approved by the Code List Representation TC on the above date. The level of
approval is also listed above. Check the "Latest Version" or "Latest Approved
Version" location noted above for possible later revisions of this document.
Technical Committee members should send
comments on this specification to the Technical Committee's email list. Others
should send comments to the Technical Committee by using the "Send A Comment"
button on the Technical Committee's web page at http://www.oasis-open.org/committees/codelist/.
For information on whether any patents have
been disclosed that may be essential to implementing this specification, and any
offers of patent licensing terms, please refer to the Intellectual Property Rights
section of the Technical Committee web page (http://www.oasis-open.org/committees/codelist/ipr.php).
The non-normative errata page for this
specification is located at http://www.oasis-open.org/committees/codelist/.
Copyright © OASIS® 2007. All
Rights Reserved.
All capitalized terms in the following text have the meanings
assigned to them in the OASIS Intellectual Property Rights Policy (the "OASIS IPR
Policy"). The full Policy may be found at the OASIS website.
This document and translations of it may be copied and
furnished to others, and derivative works that comment on or otherwise explain it
or assist in its implementation may be prepared, copied, published, and
distributed, in whole or in part, without restriction of any kind, provided that
the above copyright notice and this section are included on all such copies and
derivative works. However, this document itself may not be modified in any way,
including by removing the copyright notice or references to OASIS, except as needed
for the purpose of developing any document or deliverable produced by an OASIS
Technical Committee (in which case the rules applicable to copyrights, as set forth
in the OASIS IPR Policy, must be followed) or as required to translate it into
languages other than English.
The limited permissions granted above are perpetual and will
not be revoked by OASIS or its successors or assigns.
This document and the information contained herein is provided
on an "AS IS" basis and OASIS DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTY THAT THE USE OF THE INFORMATION HEREIN
WILL NOT INFRINGE ANY OWNERSHIP RIGHTS OR ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
OASIS requests that any OASIS Party or any other party that
believes it has patent claims that would necessarily be infringed by
implementations of this OASIS Committee Specification or OASIS Standard, to notify
OASIS TC Administrator and provide an indication of its willingness to grant patent
licenses to such patent claims in a manner consistent with the IPR Mode of the
OASIS Technical Committee that produced this specification.
OASIS invites any party to contact the OASIS TC Administrator
if it is aware of a claim of ownership of any patent claims that would necessarily
be infringed by implementations of this specification by a patent holder that is
not willing to provide a license to such patent claims in a manner consistent with
the IPR Mode of the OASIS Technical Committee that produced this specification.
OASIS may include such claims on its website, but disclaims any obligation to do
so.
OASIS takes no position regarding the validity or scope of any
intellectual property or other rights that might be claimed to pertain to the
implementation or use of the technology described in this document or the extent to
which any license under such rights might or might not be available; neither does
it represent that it has made any effort to identify any such rights. Information
on OASIS' procedures with respect to rights in any document or deliverable produced
by an OASIS Technical Committee can be found on the OASIS website. Copies of claims
of rights made available for publication and any assurances of licenses to be made
available, or the result of an attempt made to obtain a general license or
permission for the use of such proprietary rights by implementers or users of this
OASIS Committee Specification or OASIS Standard, can be obtained from the OASIS TC
Administrator. OASIS makes no representation that any information or list of
intellectual property rights will at any time be complete, or that any claims in
such list are, in fact, Essential Claims.
The names "OASIS", [insert specific trademarked names,
abbreviations, etc. here] are trademarks of OASIS, the owner and developer of this
specification, and should be used only to refer to the organization and its
official outputs. OASIS welcomes reference to, and implementation and use of,
specifications, while reserving the right to enforce its marks against misleading
uses. Please see http://www.oasis-open.org/who/trademark.php
for above guidance.
Table of Contents
1
Introduction...................................................................................................................
7
1.1
Terminology..................................................................................................................
7
1.2
Normative
References...................................................................................................
7
1.3
Non-normative
References.............................................................................................
7
2
What is a Code
List?.....................................................................................................
8
3
Genericode Model & XML
Format.................................................................................
11
3.1
Tabular
Structure.........................................................................................................
11
3.2
Genericode Document
Types.......................................................................................
11
Column Set
Documents............................................................................................................
12
Code List
Documents...............................................................................................................
12
Code List
Set
Documents.........................................................................................................
12
3.3
Column Sets - Columns and
Keys................................................................................
13
3.4
Code
lists...................................................................................................................
18
7.2.1 Simple
CodeLists and CodeList
Metadata......................................................................
19
3.5
Code list
sets..............................................................................................................
21
3.6
Namespaces...............................................................................................................
25
4
Genericode XML Schema
Reference.............................................................................
26
4.1
Notation......................................................................................................................
26
4.2
Table of Schema
Definitions........................................................................................
26
Global
Elements.......................................................................................................................
26
Global
Complex
Types..............................................................................................................
26
Global
Simple
Types.................................................................................................................
27
Global Model
Groups................................................................................................................
27
Global
Attribute
Groups............................................................................................................
28
4.3
Global Schema Definitions in Alphabetic
Order.............................................................
28
Agency
(Complex
Type)............................................................................................................
28
Annotation
(Complex
Type).......................................................................................................
28
AnyOtherContent (Complex
Type)..............................................................................................
29
AnyOtherLanguageContent (Complex
Type)...............................................................................
29
CodeList
(Element)...................................................................................................................
29
CodeListDocument (Complex
Type)...........................................................................................
29
CodeListRef
(Complex
Type).....................................................................................................
30
CodeListSet
(Element)..............................................................................................................
32
CodeListSetChoice (Model
Group).............................................................................................
32
CodeListSetDocument (Complex
Type)......................................................................................
33
CodeListSetRef (Complex
Type)................................................................................................
33
Column
(Complex
Type)............................................................................................................
35
ColumnChoice
(Model
Group)....................................................................................................
36
ColumnRef
(Complex
Type).......................................................................................................
37
ColumnReference (Attribute
Group)............................................................................................
39
ColumnSet
(Element)................................................................................................................
39
ColumnSet
(Complex
Type).......................................................................................................
39
ColumnSetChoice (Model
Group)...............................................................................................
40
ColumnSetContent (Model
Group).............................................................................................
41
ColumnSetDocument (Complex
Type)........................................................................................
41
ColumnSetRef
(Complex
Type)..................................................................................................
43
Data
(Complex
Type)................................................................................................................
44
DataRestrictions (Complex
Type)...............................................................................................
45
DatatypeFacet (Complex
Type).................................................................................................
46
DefaultDatatypeLibrary (Attribute
Group)....................................................................................
46
DocumentHeader (Model
Group)...............................................................................................
47
ExternalReference (Attribute
Group)...........................................................................................
47
GeneralIdentifier (Complex
Type)...............................................................................................
47
IdDefinition
(Attribute
Group).....................................................................................................
47
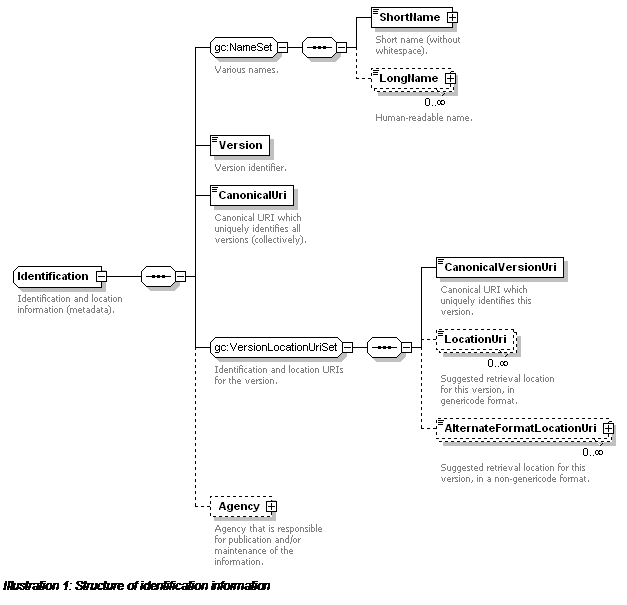
Identification (Complex
Type)....................................................................................................
47
IdentificationRefUriSet (Model
Group)........................................................................................
49
IdentificationVersionUriSet (Model
Group)..................................................................................
49
Key (Complex
Type).................................................................................................................
50
KeyChoice
(Model
Group).........................................................................................................
51
KeyColumnRef
(Complex
Type).................................................................................................
51
KeyRef
(Complex
Type)............................................................................................................
52
Language
(Attribute
Group).......................................................................................................
53
LongName
(Complex
Type).......................................................................................................
53
MimeTypedUri
(Complex
Type)..................................................................................................
53
NameSet
(Model
Group)............................................................................................................
54
OptionalUseDefinition (Attribute
Group).....................................................................................
54
OuterCodeListChoice (Model
Group)..........................................................................................
54
RequiredUseDefinition (Attribute
Group).....................................................................................
54
Row (Complex
Type).................................................................................................................
55
ShortName
(Complex
Type).......................................................................................................
55
SimpleCodeList (Complex
Type)................................................................................................
55
SimpleCodeListSequence (Model
Group)...................................................................................
56
SimpleValue
(Complex
Type).....................................................................................................
56
UseType
(Simple
Type).............................................................................................................
56
Value
(Complex
Type)...............................................................................................................
56
ValueChoice
(Model
Group).......................................................................................................
57
ValueIdentification (Attribute
Group)...........................................................................................
58
VersionLocationUriSet (Model
Group)........................................................................................
58
4.4
Conformance..............................................................................................................
59
Category:
document.................................................................................................................
59
Category:
application................................................................................................................
61
Appendix A.
Acknowledgments.........................................................................................................
65
Appendix B.
Example Code Lists in Genericode
Format.....................................................................
66
Code lists, or enumerated values, have been with us since long
before computers. They should be well understood and easily dealt with by now.
Unfortunately, they are not. As is often the case, if you take a fundamentally
simple concept, you find that everyone professes to understand it with complete
clarity. When you look more closely, you find that everybody has their own unique
view of what the problem is and how it should be solved.
If code lists were really so simple and obvious, there would
already be a single, well-known and accepted way of handling them in XML. There is
no such agreed solution, though. The problem is that while code lists are a well
understood concept, people don't actually agree exactly on what code lists are, and
how they should be used.
The OASIS Code List Representation format, "genericode", is a single model and XML format (with a W3C
XML Schema) that can encode a broad range of code list information. The XML format
is designed to support interchange or distribution of machine-readable code list
information between systems. Note that genericode is not designed as a run-time format for accessing code
list information, and is not optimized for such usage. Rather, it is designed
as an interchange format that can be transformed into formats suitable for run-time
usage, or loaded into systems that perform run-time processing using code list
information.
This version 1.0 of genericode implements the "Version 1.0
Requirements" from the OASIS Code List Representation Requirements document,
version 1.0.1 (
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/cd-genericode-1.0/doc/oasis-code-list-representation-requirements-1.0.1.pdf).
The requirements document also lists requirements for future versions of
genericode, which will not be discussed further in this version of this
document.
1.1 Terminology
The keywords "MUST", "MUST NOT", "REQUIRED", "SHALL", "SHALL
NOT", "SHOULD", "SHOULD NOT", "RECOMMENDED", "MAY", and "OPTIONAL" in this
specification are to be interpreted as described in IETF RFC 2119.
1.2 Normative
References
[RFC 2119] S. Bradner. Key
words for use in RFCs to Indicate Requirement Levels. IETF RFC 2119, March
1997. http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2119.txt.
[WXSTYPES] Paul V. Biron and
Ashok Malhotra (Eds), XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes
Second Edition. 28 October 2004.
http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/REC-xmlschema-2-20041028/
1.3 Non-normative
References
[XML2004] Anthony B. Coates.
Why are simple code lists so complex?
XML 2004 Conference. http://www.idealliance.org/proceedings/xml04/abstracts/paper86.html
This section is non-normative.
What is a code list, then? Most people would agree that the
following is a code list:
{'SUN', 'MON', 'TUE', 'WED', 'THU', 'FRI', 'SAT'}
Example 1: Days of the week: English, uppercase
This is a perfectly reasonable set of alphabetic codes for
representing days of the week. However, so is:
{'Sun', 'Mon', 'Tue', 'Wed', 'Thu', 'Fri', 'Sat'}
Example 2: Days of the week: English, mixed case
These two code lists are similar, but certainly not identical.
That said, they can both be used to represent the days of the week. Of course, you
could also use:
{'Dim', 'Lun', 'Mar', 'Mer', 'Jeu', 'Ven', 'Sam'}
Example 3: Days of the week: French, mixed case
which is created from abbreviations for the days of the week in
French. Then again, you could use:
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Example 4: Days of the week: numeric
which is suitable as a computer representation, e.g. for a
database column. On the other hand:
{'S', 'M', 'T', 'W', 'T', 'F', 'S'}
Example 5: Days of the week: English, single character
is not suitable as a code list for the days of the week,
because the values are not unique.
Now suppose that you are using codes to represent days of the
week in an application, and you are displaying the days of the week using 3-letter
abbreviations in English or French. In that context, should Example 2 and Example 3 be
considered to be code lists, or should they be considered to be display values that
would be keyed to either the Example 1 or Example 4 codes? The fact is, they could be either code
lists or display values. A value which is a code in one context might only be an
associated value for that code in another context. Nothing privileges any of these
code lists over the others in terms of ability or suitability to be the code list
(except the Example 5 values which are not suitable).
There is a choice of code lists that can be used, and the answer to the question
"which choice is the best?" depends on the needs of each particular situation.
What the above examples show is that for each distinct entry in a code list, there are many possible
associated values (we use the term distinct entry
to express the idea that we are talking a single item that needs to be represented
in the code list, rather than about the code value(s) that can be used to identify
that item). Some of those associated values are suitable for use in code lists,
some are not. This leads to a tabular model, where each row of the table represents
a conceptual code, and each column represents an associated value (code list
metadata), as follows:
|
Numeric (key)
|
English, uppercase (key)
|
English, mixed case (key)
|
French, mixed case (key)
|
English, single character
|
|
0
|
SUN
|
Sun
|
Dim
|
S
|
|
1
|
MON
|
Mon
|
Lun
|
M
|
|
2
|
TUE
|
Tue
|
Mar
|
T
|
|
3
|
WED
|
Wed
|
Mer
|
W
|
|
4
|
THU
|
Thu
|
Jeu
|
T
|
|
5
|
FRI
|
Fri
|
Ven
|
F
|
|
6
|
SAT
|
Sat
|
Sam
|
S
|
Table 1: Days of the week
Notice that the first 4 of the 5 columns have been labeled as
"key" columns. This means that the values in those
columns can be used to uniquely identify the rows, and hence they can be used as
code list values. The term key is used here
similarly to a relational database table.
This is the most common case, where a single column can be used
as a key. However, consider the following modification:
|
Numeric (key)
|
English, uppercase (key)
|
English, single character #1
|
English, single character #2
|
|
0
|
SUN
|
S
|
U
|
|
1
|
MON
|
M
|
O
|
|
2
|
TUE
|
T
|
U
|
|
3
|
WED
|
W
|
E
|
|
4
|
THU
|
T
|
H
|
|
5
|
FRI
|
F
|
R
|
|
6
|
SAT
|
S
|
A
|
Table 2: Days of the week, version 2
Here, the first two columns are each a key column. The last two
columns are not individually key columns, but together they form a compound key, i.e. while the individual columns do not
contain unique values, the pair of values is unique within each row. This is again
similar to what happens in some relational databases, that a key for the rows need
not be constructed from a single column, but instead may be constructed by
combining two or more columns.
Finally, there is no reason why a column should only contain
simple values like strings or numbers. A column could also contain a complex
compound group of data, such as a fragment of XML:
|
Numeric (key)
|
English, uppercase (key)
|
XHTML
|
|
0
|
SUN
|
<a
href="http://days.of.week/SUN"><b>Sunday</b></a>
|
|
1
|
MON
|
<a
href="http://days.of.week/MON"><i>Monday</i></a>
|
|
2
|
TUE
|
<a
href="http://days.of.week/TUE"><b>Tuesday</b></a>
|
|
3
|
WED
|
<a
href="http://days.of.week/WED"><i>Wednesday</i></a>
|
|
4
|
THU
|
<a
href="http://days.of.week/THU"><b>Thursday</b></a>
|
|
5
|
FRI
|
<a
href="http://days.of.week/FRI"><i>Friday</i></a>
|
|
6
|
SAT
|
<a
href="http://days.of.week/SAT"><b>Saturday</b></a>
|
Table 3: Days of the week, version 3
Notice that the final XHTML column is not marked as a key
column. The values are unique, so it certainly could be used as a key column.
However, sometimes you may not wish to mark a column as a key column, even if the
values are unique. The values in the column may not make particularly suitable
keys. They might be too long to process quickly and conveniently, or they might not
be able to be used in a particular context, such as for an XML attribute value.
Also, it may be that while the values in a particular column are unique now, there
is no guarantee or expectation that they will remain unique as the code list grows
or changes in the future.
Once you see the tabular nature that underlies the information
that can be associated with code lists, it becomes clear why they can be a source
of so much debate. Different users need different subsets of the code list
information, and people often assume that the information they need is all the
information that anyone needs.
That kind of thinking doesn't work well with code lists,
because code lists are sufficiently generic a concept that they are used across
messages/documents, applications, and databases. The code list details that you
need for the XML schemas often will not be exactly the same as the details that you
need for your database or your application. If the code list information cannot be
shared easily across these different areas, the result is duplication of effort and
potential loss of synchronization between different implementations of the same
code list.
The XML schema may only require a set of 3-letter codes to
represent the code list. The database may require a set of numeric codes, plus
display labels (possibly in different languages). The application may need to know
which 3-letter code corresponds to which numeric code, so that it can process the
XML and update the database. Also, some information related to a code list might
not be appropriate for the XML format. For example, if you have a different image
file for each code, it isn't ideal to include this image inline in the code list
XML, since it vastly increases the size of the XML, and makes it more difficult to
read. So in an XML representation, you are more likely to include some reference
(e.g. a URL) to the image. For a database, however, it may be feasible to store the
image in a BLOB[2] column in a database.
One last piece of experience from databases is that support for
undefined values will be required. Sometimes users will have values that need to be
associated with some of the codes in a code list, but won't have values to
associate with every code. In that case, the concept of a undefined (nil or null)
value is needed.
3 Genericode Model
& XML Format
The text of this section is normative. The illustrations,
Schema subsets and examples are not normative.
This section describes the genericode model and XML format for
representing code lists. The "gc" XML prefix refers
to the namespace URI
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/
If you are reading this section for the first time, you may
find it helpful to review the examples in the appendices before continuing.
3.1 Tabular
Structure
Genericode has a tabular structure for code list information.
Each row in the table represents a single distinct
entry in the code list, i.e. each row represents a single uniquely
identifiable item in the code list.
Each column in the table represents a metadata value that can
be defined for each distinct entry in the code list. Each column is either required or optional. A
required column does not allow any row to have an
undefined (nil or null) value. An optional column
allows undefined values.
A genericode key is a set of
one or more required columns that together uniquely identify each distinct entry in
the code list. Optional columns cannot be used for keys. Each code list must have
at least one key. Genericode keys are equivalent to what people usually mean when
they talk about the "codes" in a code list. However, genericode allows multiple
keys for each code list, and there is no single preferred key. For code lists that have multiple keys,
it is assumed that the choice of which key to use is a late binding choice that is specific to the application,
technology and/or context in which the code list is used.
3.2 Genericode
Document Types
There are 3 kinds of genericode documents, all supported by the
one W3C XML Schema:
· Column
Set documents;
· Code List
documents;
· Code List
Set documents.
A column set document has the root element <gc:ColumnSet>. It contain definitions of genericode
columns or keys that can be imported into code list documents or into other column
set documents.
A code list document has the root element <gc:CodeList>. It contains metadata describing the
code list as a whole, as well as explicit code list data - codes and associated
values.
A code list set document has the root element <gc:CodeListSet>. It contains references to
particular versions of code lists, and can also contain version-independent
references to code lists. A code list set document can be used to define a
particular configuration of versions of code lists
that are used by a project, application, standard, etc.
3.3 Column Sets - Columns and Keys
A column set is a set of definitions of genericode columns
and/or keys. A column defines a particular metadata value that can be defined for
each distinct entry in a code list. A key defines a set of one or more columns.
It is not necessary to use separate column set documents. A
genericode code list document can contain all of the required column and key
definitions. Column set documents are provided as a convenience mechanism for
sharing column and/or key definitions between multiple code lists.
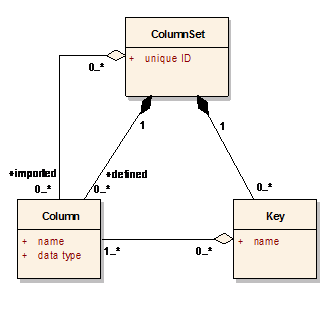
|
|
|
|
 |
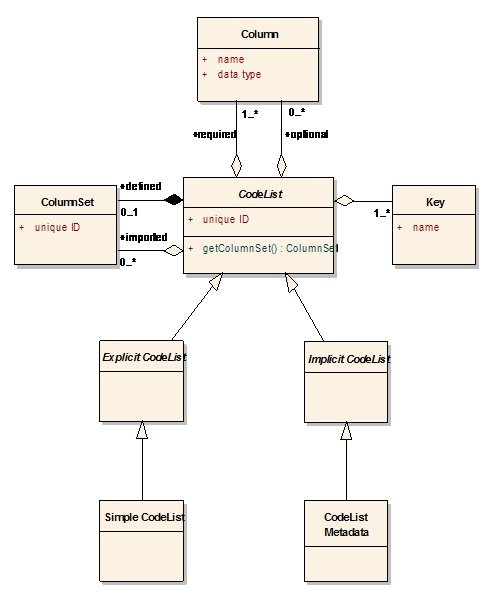
This figure is in UML notation. Each column set must have a unique ID. For a column
set defined within a code list document, the code list document's unique identifier
is used. A column set can define any number of columns. It can also reference any
number of columns from other column sets (in column set documents or code list
documents). A column set can also define any number of keys. Each key is defined by
one or more of the columns in the column set (either defined or imported). Keys are
used to uniquely identify the rows (distinct entries) of code lists. Columns and
keys are uniquely named within the column set that defines them, and each can also
be uniquely identified using a specific URI if required additionally.
The matching genericode W3C XML Schema (WXS) representation of
column set content is:
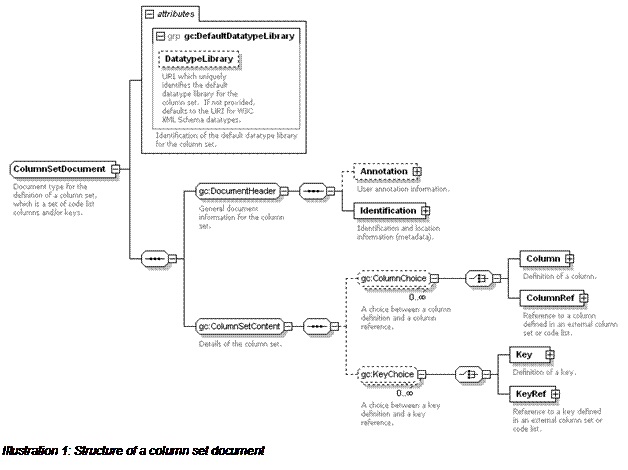
This figure is in XML Spy® notation. A default datatype library URI can be
provided to identify which datatype library should be used for columns which do not
explicitly specify a datatype library. If this URI is not provided, the datatype
library defaults to the W3C XML Schema (WXS) datatype library.
A column set definition contains optional user annotation information (
Annotation), and then identification and location
information (
Identification). A column set has a
short name, any number of long names and a version.
A column set is uniquely identified by a canonical URI. Particular versions of the
column set are uniquely identified by a canonical version URI. Location URIs can
also be provided to suggest URLs from which an XML genericode column set instance
may be retrieved (at the discretion of an application).
Alternative location URIs can be provided to suggest URLs
from which non-genericode representations of the column set can be retrieved.
Canonical URIs and canonical version URIs must not be used as
de facto location URIs for retrieving column set instances
(nor anything else). The column set definition can also list the details of
the agency which is responsible for publishing and/or maintaining the column set
information.
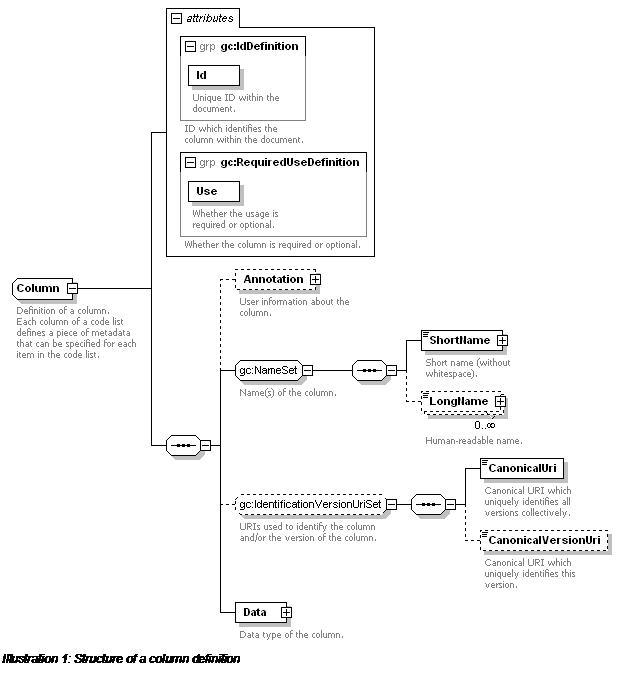
A column definition (
Column) contains a unique ID
for the column and its use (required or optional). It also contains a short name
(token) for the column, any number of long names, and optional extra canonical
identification URIs. The datatype information for the column is contained in its
Data element.
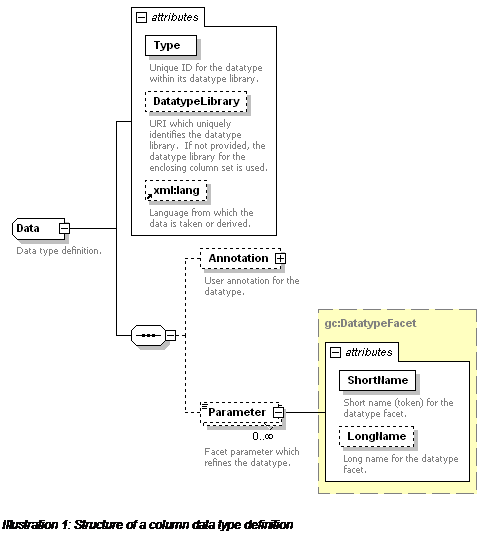
The Data structure is based on
the data element in RELAX NG. The datatype is
specified as a Type from a DatatypeLibrary. If the datatype library is not
specified, it is inherited from the DatatypeLibrary
attribute of the enclosing column set definition. It otherwise defaults to the W3C
XML Schema (WXS) datatype library.
If the data is XML (complex valued), the DataTypeLibrary is set to the namespace URI for the XML
(or to "*" if any namespace[3] is allowed), and the Type is set to the root element name for the XML data (or
to "*" if any root element is allowed).
Data definitions can contain
Parameter elements which define facets that refine the
datatype. When using the WXS datatype library, these are just the usual WXS
datatype facets.
If a column is defined in an external column set or code list document, it is
referenced using a
ColumnRef. The column reference
must have an ID just as a column definition would, but it also has an
ExternalRef which contains the column's ID in the
external document. The external column set or code list is identified by a
CanonicalVersionUri and/or by any
LocationUri information that is provided.
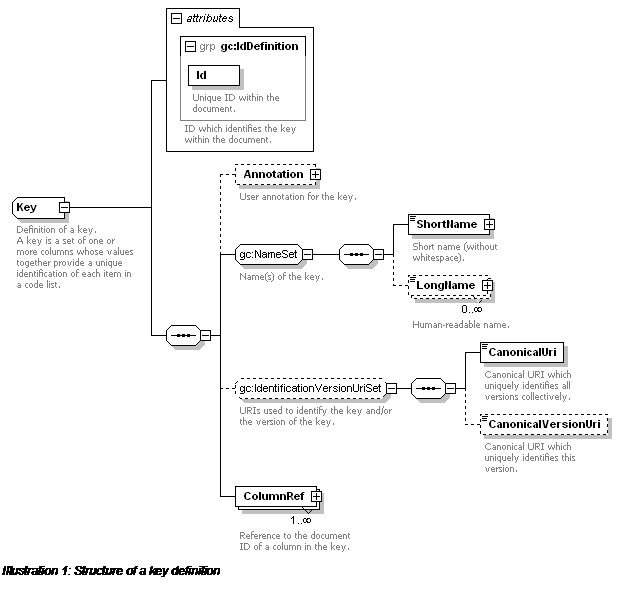
A key definition (
Key) contains an ID for the key.
It also contains a short name (token) for the key, any number of long names, and
optional extra canonical identification URIs. The columns which
together form the key are referenced using one or
more
ColumnRef elements. The
Ref attribute of each contains the ID of either a
Column or
ColumnRef in
the column set. Only required (not optional) columns may be used within a key (note
that this rule is not able to be enforced using the genericode WXS Schema
alone).
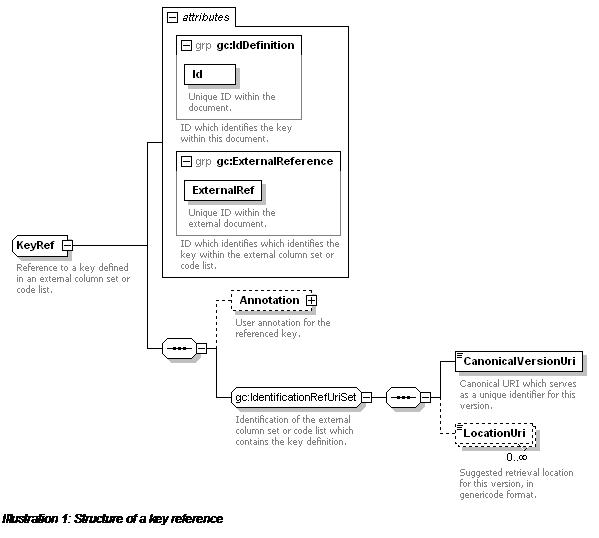
If a key is defined in an external column set or code list
document, it can be referred to using a KeyRef. The
key reference must have an ID, and also has an ExternalRef which contains the key's ID in the external
document. The external column set or code list is identified by a CanonicalVersionUri and/or by any LocationUri information that is provided.
3.4 Code lists
A code list can contain its own embedded column set definition.
It can also import columns and keys from any number of external column sets (in
column set documents and/or code list documents). In the simplest case, what a code
list provides is information (metadata) about the code list and (optionally) a set
of rows, where each row defines a distinct entry in the
code list.

A code list document that contains only information (metadata) about the code list
as a whole is known as a CodeList Metadata document. If
the code list document defines (zero or more) row, it is a Simple CodeList. These are the only kinds of code list that
are supported in this version of the specification.
There is an important difference between a CodeList Metadata document and Simple
CodeList that contains zero rows (zero distinct entries). The former does
not provide information on how many distinct entries
are contained in the code list. The latter explicitly indicates that a
particular version of the code list contains zero distinct entries, i.e. the
particular version of the code list is empty. A CodeList Metadata document
does not provide any indication about whether a code list is empty or not.
A CodeList Metadata document is a
special case of a Simple CodeList document. The
differences will be discussed explicitly where appropriate.
A Simple CodeList is modeled as follows:

A
Simple CodeList contains zero or more rows (it is necessary to support
empty code lists to allow for code lists that are empty now, but will be populated
in future versions). Each
Row defines a single
distinct
entry in the code list.
A Row contains one or more Values, where each of those values corresponds to a distinct
column in the code list. At least one value is required, because a code list has to
have at least one key, and each key requires at least one column. As a consequence,
a Row must have at least one Value. Additionally, a Row must contain a defined Value
for each of the required columns in the code list, i.e.
for those columns for which a Value must be defined
(non-null) for each Row (distinct entry) in the code
list.
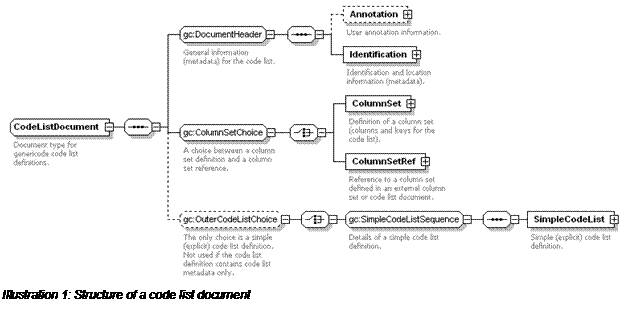
Each Value is associated with a single distinct column of the code list. For
each Key in the code list, the values associated with the columns for that
key must form a unique set, i.e. no two rows are allowed to have the same set of
values for the same key columns. Note that this uniqueness requirement cannot be
enforced using the genericode WXS Schema for code list documents, which is
structured as follows:
Many of these elements and types have appeared already in
section 3.3 , so the explanations will not
be repeated here. A code list document can either define its own embedded ColumnSet, or refer to an externally defined column set
using a ColumnSetRef.
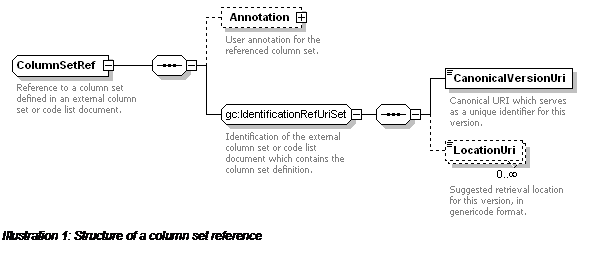
A
ColumnSetRef contains the canonical version URI
which uniquely identifies a referenced column set or code list document which
contains the column set. It can also contain suggested URLs from which to retrieve
the column set or code list. Canonical version URIs must not be used as
de facto location URIs for retrieving column set instances
(nor anything else).
A code list document that contains a SimpleCodeList element is a Simple
CodeList. If the code list document does not contain a SimpleCodeList element, then it is a CodeList Metadata document.
The genericode WXS Schema representation of a SimpleCodeList is
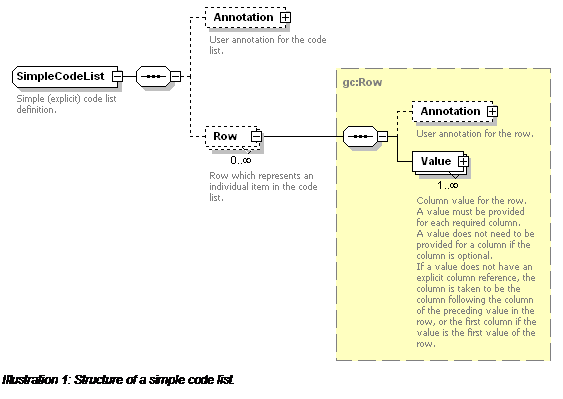
A SimpleCodeList contains zero
or more Row elements. Each Row contains one or more Value elements.
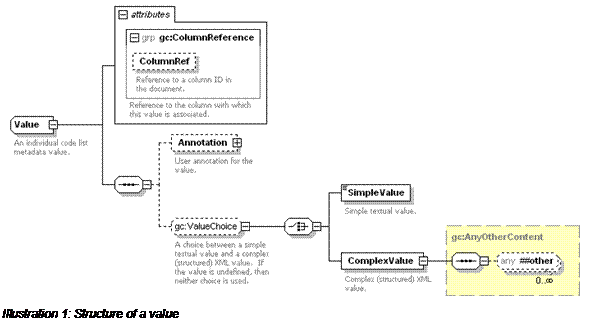
The
Value container element is needed to allow
optional user annotations of individual values in the code list. It has a
ColumnRef attribute which contains the unique document ID
of the associated column. A
Value element can contains
either a
SimpleValue containing a textual value, or
a
ComplexValue containing a balanced (well-formed)
XML fragment from a namespace
other than the
genericode namespace.
If a Value element does not
contain either a SimpleValue element or a ComplexValue element, then the value is undefined.
Only optional columns are allowed to have undefined
values. Also, if a Row element does not contain
a Value element corresponding to a particular column,
then the row's value for that column is undefined.
Note that the ColumnRef
attribute of a Value is optional. If it is not
provided, it is assumed that the column is the one which follows the column
associated with the previous value in the row. If the first Value in a Row does not
have a ColumnRef, it is assumed to be associated
with the first column in the column set. It is an error if a row contains more than
one value for the same column, or if it does not contain a value for a required
column.
The genericode WXS Schema is not able to validate that the
contents of a Value match the datatype of the
associated column. Other validation mechanisms should be used to perform
datatype validation.
3.5 Code list
sets
A CodeList Set lists a
configuration of code lists and/or codelist versions. CodeList Sets can be used to provide lists of the code lists
or code list versions that are associated with a particular version of an
application or specification. The genericode WXS Schema structure for CodeList Set documents is:
Many of these elements and types have appeared already in section
3.3 , so the explanations will not be repeated
here. A code list set document contains a series of zero or more
CodeListRef,
CodeListSet, or
CodeListSetRef elements.
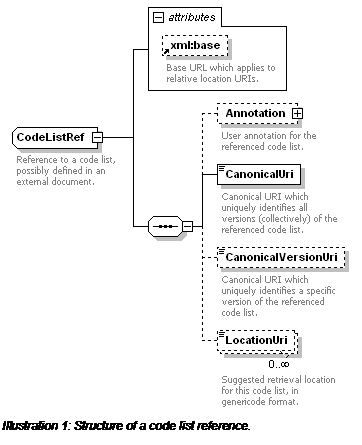
A CodeListRef is a reference to a code list or to a
version of a code list. If the CanonicalVersionUri is
defined, then the LocationUri elements (if any)
contain retrieval URIs for genericode CodeList
documents. If the CanonicalVersionUri is not defined, then the LocationUri elements (if any) contain retrieval URIs for
genericode CodeList Metadata documents. Note that
canonical URIs and canonical version URIs must not be used as de facto location URIs for retrieving code list instances
(nor anything else).
A CodeListSet element is used to
define an embedded code list set within a larger code list set document. It
allows a single CodeList Set documnent to carry
information on multiple code list sets. Each embedded CodeListSet element has the same structure as a
CodeListSet document.
A
CodeListSetRef is a reference to a code list set
or to a version of a code list set. If the
CanonicalVersionUri is defined, then the
LocationUri elements (if any) contain retrieval URIs for
genericode
CodeList Set documents. If the
CanonicalVersionUri is
not defined, then the
LocationUri elements (if any) contain retrieval URIs for
genericode
CodeList Set Metadata documents. Just as for
code list references, canonical URIs and canonical version URIs must not be
used as
de facto location URIs for retrieving code
list instances (nor anything else).
A CodeList Set does not contain
definitions of code lists, it only refers to the code list and code list versions
which are a part of the particular version of the CodeList
Set. It should also be noted that a code list set may contain a reference to
a code list or code list set without specifying a particular version of the code
list or code list set, and it may contain a reference to a code list or code list
version or code list set or code list set version without specifying a location for
retrieving a genericode definition of that code list (metadata) or code list
version or code list set (metadata) or code list set version. This is to support
situations where
· the code
list definition or code list set definition is known to the users, and no location
needs to be published. This may be because users have an application which maps the
canonical URI or canonical version URI to a local definition;
· the code
list or code list set is sufficiently well-known (e.g. ISO 3-letter country codes)
that users only need to have it uniquely identified, and do not need to have it
enumerated or defined for them.
3.6 Namespaces
The genericode Schema makes use of two namespace URIs.
The "gc" XML prefix refers to the namespace URI
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/
which is the main genericode namespace URI. The "rule"
XML prefix refers to the namespace URI
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/rule/1.0/
which is used in the identification of auxiliary rules in the
Schema. These are rules that cannot be enforced using the XML Schema itself;
they appear in the Schema in <rule:text>
elements within <xsd:documentation>
elements.
4 Genericode XML Schema Reference
Schema version: 1.0
Target namespace:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/
4.1 Notation
|
Multiplicity
|
Minimum Occurrence
|
Maximum Occurrence
|
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
|
?
|
0
|
1
|
|
+
|
1
|
unbounded
|
|
*
|
0
|
unbounded
|
|
{m,n}
|
m
|
n
|
|
{m,}
|
m
|
unbounded
|
ANY - any element in any namespace.
ANY[##other] - any element in any namespace other than the
target namespace of the genericode XML Schema.
(A , B , C , ...) - sequence of items (A, B, C, etc.).
(A | B | C | ...) - choice between items (A, B, C, etc.).
4.2 Table of Schema
Definitions
· CodeList
(page 29)
·
CodeListSet (page 32)
· ColumnSet
(page 39)
· Agency
(page 28)
·
Annotation (page 28)
·
AnyOtherContent (page 29)
·
AnyOtherLanguageContent (page 29)
·
CodeListDocument (page 29)
·
CodeListRef (page 30)
·
CodeListSetDocument (page 33)
·
CodeListSetRef (page 33)
· Column
(page 35)
· ColumnRef
(page 37)
· ColumnSet
(page 39)
·
ColumnSetDocument (page 41)
·
ColumnSetRef (page 43)
· Data
(page 44)
·
DataRestrictions (page 45)
·
DatatypeFacet (page 46)
·
GeneralIdentifier (page 47)
·
Identification (page 47)
· Key
(page 50)
·
KeyColumnRef (page 51)
· KeyRef
(page 52)
· LongName
(page 53)
·
MimeTypedUri (page 53)
· Row
(page 55)
· ShortName
(page 55)
·
SimpleCodeList (page 55)
·
SimpleValue (page 56)
· Value
(page 56)
· UseType
(page 56)
·
CodeListSetChoice (page 32)
·
ColumnChoice (page 36)
·
ColumnSetChoice (page 40)
·
ColumnSetContent (page 41)
·
DocumentHeader (page 47)
·
IdentificationRefUriSet (page 49)
·
IdentificationVersionUriSet (page 49)
· KeyChoice
(page 51)
· NameSet
(page 54)
·
OuterCodeListChoice (page 54)
·
SimpleCodeListSequence (page 56)
·
ValueChoice (page 57)
·
VersionLocationUriSet (page 58)
·
ColumnReference (page 39)
·
DefaultDatatypeLibrary (page 46)
·
ExternalReference (page 47)
·
IdDefinition (page 47)
· Language
(page 53)
·
OptionalUseDefinition (page 54)
·
RequiredUseDefinition (page 54)
·
ValueIdentification (page 58)
4.3 Global Schema
Definitions in Alphabetic Order
Agency (Complex Type)
Details of an agency which produces code lists or related
artifacts.
Content Model: (ShortName?
, LongName* , Identifier*)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
ShortName
|
ShortName (page 55)
|
Short name (without whitespace) for the
agency.
|
|
LongName
|
LongName (page 53)
|
Human-readable name for the agency.
|
|
Identifier
|
GeneralIdentifier (page 47)
|
Identifier for the agency.
|
User annotation information.
Content Model:
(Description* , AppInfo?)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Description
|
AnyOtherLanguageContent (page 29)
|
Human-readable information.
|
|
AppInfo
|
AnyOtherContent (page 29)
|
Machine-readable information.
|
Container for any XML content which is in a different namespace
to the Schema's target namespace.
Content Model:
(ANY[##other]*)
Mixed Content: No
Container for any human-readable XML content which is in a
different namespace to the Schema's target namespace.
Extension of:
AnyOtherContent (page 29)
Content Model:
(ANY[##other]*)
Mixed Content: No
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
xml:lang
|
optional
|
|
Language for the human-readable XML content.
|
Top-level (root) element for a genericode code list
definition.
A code list definition defines the details of a particular
(version of a) code list.
Complex Type:
CodeListDocument (page 29)
Document type for genericode code list definitions.
Rules:
|
Rule R1 [document]
:
A code list must have at least one key, unless it is
a metadata-only definition without a 'SimpleCodeList' element.
|
Content Model:
((Annotation? , Identification) , (ColumnSet | ColumnSetRef) ,
((SimpleCodeList))?)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation (from DocumentHeader on page
47)
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation information.
DocumentHeader:
General information (metadata) for the code
list.
|
|
Identification (from DocumentHeader on
page 47)
|
Identification (page 47)
|
Identification and location information
(metadata).
DocumentHeader:
General information (metadata) for the code
list.
|
|
ColumnSet (from ColumnSetChoice on page
40)
|
ColumnSet (page 39)
|
Definition of a column set (columns and keys for the
code list).
ColumnSetChoice:
A choice between a column set definition and a
column set reference.
|
|
ColumnSetRef (from ColumnSetChoice on page
40)
|
ColumnSetRef (page 43)
|
Reference to a column set defined in an external
column set or code list document.
ColumnSetChoice:
A choice between a column set definition and a
column set reference.
|
|
SimpleCodeList (from SimpleCodeListSequence
on page 56)
|
SimpleCodeList (page 55)
|
Simple (explicit) code list definition.
SimpleCodeListSequence:
Details of a simple code list definition.
OuterCodeListChoice:
The only choice is a simple (explicit) code list
definition.
Not used if the code list definition contains
code list metadata only.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
xml:base
|
optional
|
|
Base URL which applies to relative location
URIs.
Rules:
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Reference to a code list, possibly defined in an external
document.
Rules:
|
Rule R3 [application]
:
The code list reference must be valid.
An application may use the CanonicalVersionUri to select
a local copy of the code list.
If there is no CanonicalVersionUri, the CanonicalUri may
be used to select a local copy of the code list.
Otherwise the LocationUri value(s) may be tried in order,
until a valid code list document is retrieved.
An application must signal an error to the user if it
is not able to retrieve a code list document to match the code list
reference.
|
Content Model: (Annotation?
, CanonicalUri , CanonicalVersionUri? , LocationUri*)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation for the referenced code
list.
|
|
CanonicalUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies all versions
(collectively) of the referenced code list.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
|
CanonicalVersionUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies a specific
version of the referenced code list.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
|
LocationUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Suggested retrieval location for this code list, in
genericode format.
Rules:
If the CanonicalVersionUri has been defined, the
LocationUri must reference a genericode CodeList document.
If the CanonicalVersionUri is undefined, the LocationUri
must reference a genericode CodeList Metadata document.
An application must signal an error to the user if a
LocationUri does not reference the appropriate type of genericode
document.
An application must signal an error to the user if a
document retrieved using a LocationUri is not in genericode format.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
xml:base
|
optional
|
|
Base URL which applies to relative location
URIs.
Rules:
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Top-level element for the definition of a code list set.
Complex Type:
CodeListSetDocument (page 33)
A choice between a code list reference, an inline code list
set, or a code list set reference.
Content Model: (CodeListRef
| CodeListSet | CodeListSetRef)
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
CodeListRef
|
CodeListRef (page 30)
|
|
|
CodeListSet
|
CodeListSetDocument (page 33)
|
|
|
CodeListSetRef
|
CodeListSetRef (page 33)
|
|
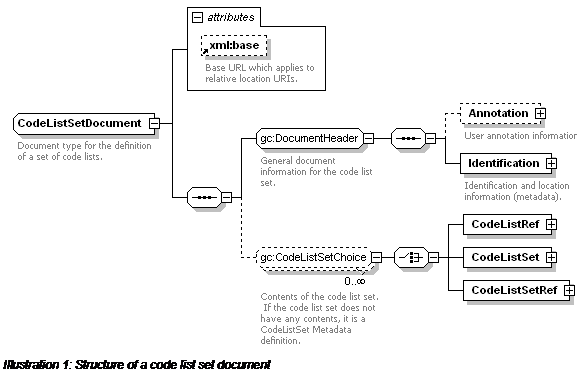
Document type for the definition of a set of code lists.
Content Model:
((Annotation? , Identification) , (CodeListRef | CodeListSet |
CodeListSetRef)*)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation (from DocumentHeader on page
47)
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation information.
DocumentHeader:
General document information for the code list
set.
|
|
Identification (from DocumentHeader on
page 47)
|
Identification (page 47)
|
Identification and location information
(metadata).
DocumentHeader:
General document information for the code list
set.
|
|
CodeListRef (from CodeListSetChoice on
page 32)
|
CodeListRef (page 30)
|
CodeListSetChoice:
Contents of the code list set. If the code list
set does not have any contents, it is a CodeListSet Metadata definition.
|
|
CodeListSet (from CodeListSetChoice on
page 32)
|
CodeListSetDocument (page 33)
|
CodeListSetChoice:
Contents of the code list set. If the code list
set does not have any contents, it is a CodeListSet Metadata definition.
|
|
CodeListSetRef (from CodeListSetChoice on
page 32)
|
CodeListSetRef (page 33)
|
CodeListSetChoice:
Contents of the code list set. If the code list
set does not have any contents, it is a CodeListSet Metadata definition.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
xml:base
|
optional
|
|
Base URL which applies to relative location
URIs.
Rules:
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
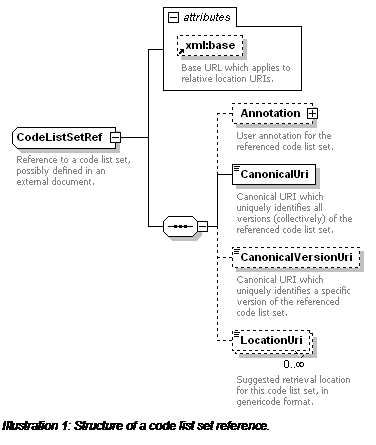
Reference to a code list set, possibly defined in an external
document.
Rules:
|
Rule R47 [application]
:
The code list set reference must be valid.
An application may use the CanonicalVersionUri to select
a local copy of the code list set.
If there is no CanonicalVersionUri, the CanonicalUri may
be used to select a local copy of the code list set.
Otherwise the LocationUri value(s) may be tried in order,
until a valid code list set document is retrieved.
An application must signal an error to the user if it
is not able to retrieve a code list set document to match the code list set
reference.
|
Content Model: (Annotation?
, CanonicalUri , CanonicalVersionUri? , LocationUri*)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation for the referenced code list
set.
|
|
CanonicalUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies all versions
(collectively) of the referenced code list set.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
|
CanonicalVersionUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies a specific
version of the referenced code list set.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
|
LocationUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Suggested retrieval location for this code list set,
in genericode format.
Rules:
If the CanonicalVersionUri has been defined, the
LocationUri must reference a genericode CodeListSet document.
If the CanonicalVersionUri is undefined, the LocationUri
must reference a genericode CodeListSet Metadata document.
An application must signal an error to the user if a
LocationUri does not reference the appropriate type of genericode
document.
An application must signal an error to the user if a
document retrieved using a LocationUri is not in genericode format.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
xml:base
|
optional
|
|
Base URL which applies to relative location
URIs.
Rules:
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Column (Complex Type)
Definition of a column.
Each column of a code list defines a piece of metadata that can
be specified for each item in the code list.
Content Model: (Annotation?
, (ShortName , LongName*) , (CanonicalUri , CanonicalVersionUri?)? , Data)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User information about the column.
|
|
ShortName (from NameSet on page 54)
|
ShortName (page 55)
|
Short name (without whitespace).
NameSet:
Name(s) of the column.
|
|
LongName (from NameSet on page 54)
|
LongName (page 53)
|
Human-readable name.
NameSet:
Name(s) of the column.
|
|
CanonicalUri (from IdentificationVersionUriSet
on page 49)
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies all versions
collectively.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
IdentificationVersionUriSet:
URIs used to identify the column and/or the
version of the column.
|
|
CanonicalVersionUri (from
IdentificationVersionUriSet on page 49)
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies this
version.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
IdentificationVersionUriSet:
URIs used to identify the column and/or the
version of the column.
|
|
Data
|
Data (page 44)
|
Data type of the column.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Id (from IdDefinition on page 47)
|
required
|
xsd:ID
|
Unique ID within the document.
IdDefinition:
ID which identifies the column within the
document.
|
|
Use (from RequiredUseDefinition on page
54)
|
required
|
UseType (page 56)
|
Whether the usage is required or optional.
RequiredUseDefinition:
Whether the column is required or optional.
|
A choice between a column definition and a column
reference.
Content Model: (Column |
ColumnRef)
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Column
|
Column (page 35)
|
Definition of a column.
|
|
ColumnRef
|
ColumnRef (page 37)
|
Reference to a column defined in an external
column set or code list.
|
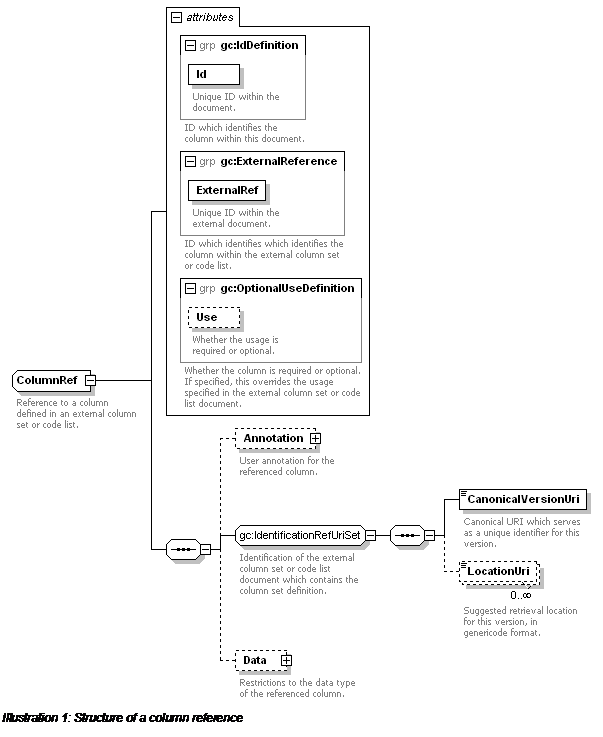
Reference to a column defined in an external column set or code
list.
Rules:
|
Rule R12 [application]
:
The column reference must be valid.
An application may use the CanonicalVersionUri to select
a local copy of the code list or column set which contains the column
definition.
Otherwise the LocationUri value(s) may be tried in order,
until a valid code list or column set document (containing the necessary
column definition) is retrieved.
An application must signal an error to the user if it
is not able to retrieve a code list or column set document which contains the
necessary column definition.
|
Content Model: (Annotation?
, (CanonicalVersionUri , LocationUri*) , Data?)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation for the referenced column.
|
|
CanonicalVersionUri (from
IdentificationRefUriSet on page 49)
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which serves as a unique identifier
for this version.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
IdentificationRefUriSet:
Identification of the external column set or
code list document which contains the column set definition.
|
|
LocationUri (from IdentificationRefUriSet
on page 49)
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Suggested retrieval location for this version, in
genericode format.
Rules:
An application must signal an error to the user if a
document retrieved using a LocationUri is not in genericode format.
IdentificationRefUriSet:
Identification of the external column set or
code list document which contains the column set definition.
|
|
Data
|
DataRestrictions (page 45)
|
Restrictions to the data type of the referenced
column.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Id (from IdDefinition on page 47)
|
required
|
xsd:ID
|
Unique ID within the document.
IdDefinition:
ID which identifies the column within this
document.
|
|
ExternalRef (from ExternalReference on
page 47)
|
required
|
xsd:NCName
|
Unique ID within the external document.
Rules:
The external reference must not be prefixed with a '#'
symbol.
ExternalReference:
ID which identifies which identifies the column
within the external column set or code list.
|
|
Use (from OptionalUseDefinition on page
54)
|
optional
|
UseType (page 56)
|
Whether the usage is required or optional.
OptionalUseDefinition:
Whether the column is required or optional.
Rules:
|
Rule R13
[application] :
If specified, this overrides the usage
specified in the external column set or code list document.
|
|
|
xml:base
|
optional
|
|
Base URL which applies to relative location
URIs.
Rules:
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Attribute set for referring to a column definition.
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
ColumnRef
|
optional
|
xsd:IDREF
|
Reference to a column ID in the document.
|
Top-level element for the definition of a column set.
Complex Type:
ColumnSetDocument (page 41)
Definition of a column set (columns and keys for a code
list).
Content Model: ((Column |
ColumnRef)* , (Key | KeyRef)*)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Column (from ColumnChoice on page 36)
|
Column (page 35)
|
Definition of a column.
ColumnChoice:
A choice between a column definition and a column
reference.
ColumnSetContent:
Column set definitions.
|
|
ColumnRef (from ColumnChoice on page
36)
|
ColumnRef (page 37)
|
Reference to a column defined in an external column
set or code list.
ColumnChoice:
A choice between a column definition and a column
reference.
ColumnSetContent:
Column set definitions.
|
|
Key (from KeyChoice on page 51)
|
Key (page 50)
|
Definition of a key.
KeyChoice:
A choice between a key definition and a key
reference.
ColumnSetContent:
Column set definitions.
|
|
KeyRef (from KeyChoice on page 51)
|
KeyRef (page 52)
|
Reference to a key defined in an external column set
or code list.
KeyChoice:
A choice between a key definition and a key
reference.
ColumnSetContent:
Column set definitions.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
DatatypeLibrary (from DefaultDatatypeLibrary
on page 46)
|
optional
|
xsd:anyURI
|
URI which uniquely identifies the default datatype
library for the column set. If not provided, defaults to the URI for W3C XML
Schema datatypes.
DefaultDatatypeLibrary:
Identification of the default datatype library
for the column set.
|
|
xml:base
|
optional
|
|
Base URL which applies to relative location
URIs.
Rules:
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
A choice between a column set definition and a column set
reference.
Content Model: (ColumnSet |
ColumnSetRef)
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
ColumnSet
|
ColumnSet (page 39)
|
Definition of a column set (columns and keys for
the code list).
|
|
ColumnSetRef
|
ColumnSetRef (page 43)
|
Reference to a column set defined in an external
column set or code list document.
|
Specific details of a column set.
Content Model: ((Column |
ColumnRef)* , (Key | KeyRef)*)
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Column (from ColumnChoice on page 36)
|
Column (page 35)
|
Definition of a column.
ColumnChoice:
A choice between a column definition and a
column reference.
|
|
ColumnRef (from ColumnChoice on page
36)
|
ColumnRef (page 37)
|
Reference to a column defined in an external column
set or code list.
ColumnChoice:
A choice between a column definition and a
column reference.
|
|
Key (from KeyChoice on page 51)
|
Key (page 50)
|
Definition of a key.
KeyChoice:
A choice between a key definition and a key
reference.
|
|
KeyRef (from KeyChoice on page 51)
|
KeyRef (page 52)
|
Reference to a key defined in an external column set
or code list.
KeyChoice:
A choice between a key definition and a key
reference.
|
Document type for the definition of a column set, which is a
set of code list columns and/or keys.
Content Model:
((Annotation? , Identification) , ((Column | ColumnRef)* , (Key | KeyRef)*))
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation (from DocumentHeader on page
47)
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation information.
DocumentHeader:
General document information for the column
set.
|
|
Identification (from DocumentHeader on
page 47)
|
Identification (page 47)
|
Identification and location information
(metadata).
DocumentHeader:
General document information for the column
set.
|
|
Column (from ColumnChoice on page 36)
|
Column (page 35)
|
Definition of a column.
ColumnChoice:
A choice between a column definition and a column
reference.
ColumnSetContent:
Details of the column set.
|
|
ColumnRef (from ColumnChoice on page
36)
|
ColumnRef (page 37)
|
Reference to a column defined in an external column
set or code list.
ColumnChoice:
A choice between a column definition and a column
reference.
ColumnSetContent:
Details of the column set.
|
|
Key (from KeyChoice on page 51)
|
Key (page 50)
|
Definition of a key.
KeyChoice:
A choice between a key definition and a key
reference.
ColumnSetContent:
Details of the column set.
|
|
KeyRef (from KeyChoice on page 51)
|
KeyRef (page 52)
|
Reference to a key defined in an external column set
or code list.
KeyChoice:
A choice between a key definition and a key
reference.
ColumnSetContent:
Details of the column set.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
DatatypeLibrary (from DefaultDatatypeLibrary
on page 46)
|
optional
|
xsd:anyURI
|
URI which uniquely identifies the default datatype
library for the column set. If not provided, defaults to the URI for W3C XML
Schema datatypes.
DefaultDatatypeLibrary:
Identification of the default datatype library
for the column set.
|
|
xml:base
|
optional
|
|
Base URL which applies to relative location
URIs.
Rules:
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Reference to a column set defined in an external column set or
code list document.
Rules:
|
Rule R17 [application]
:
The column set reference must be valid.
An application may use the CanonicalVersionUri to select
a local copy of the column set or code list.
Otherwise the LocationUri value(s) may be tried in order,
until a valid column set or code list document is retrieved.
An application must signal an error to the user if it
is not able to retrieve a column set or code list document to match the
column set reference.
|
Content Model: (Annotation?
, (CanonicalVersionUri , LocationUri*))
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation for the referenced column
set.
|
|
CanonicalVersionUri (from
IdentificationRefUriSet on page 49)
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which serves as a unique identifier
for this version.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
IdentificationRefUriSet:
Identification of the external column set or
code list document which contains the column set definition.
|
|
LocationUri (from IdentificationRefUriSet
on page 49)
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Suggested retrieval location for this version, in
genericode format.
Rules:
An application must signal an error to the user if a
document retrieved using a LocationUri is not in genericode format.
IdentificationRefUriSet:
Identification of the external column set or
code list document which contains the column set definition.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
xml:base
|
optional
|
|
Base URL which applies to relative location
URIs.
Rules:
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Data (Complex Type)
Data type definition.
Content Model: (Annotation?
, Parameter*)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation for the datatype.
|
|
Parameter
|
DatatypeFacet (page 46)
|
Facet parameter which refines the datatype.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Type
|
required
|
xsd:token
|
Unique ID for the datatype within its datatype
library.
Rules:
The datatype ID must not include a namespace prefix.
For the W3C XML Schema datatypes, possible datatype IDs
are 'string', 'token', 'boolean', 'decimal', etc.
If the data is complex (i.e. XML), this value is set
to the root element name for the XML value, or '*' if the root element name
is not restricted.
|
|
DatatypeLibrary
|
optional
|
xsd:anyURI
|
URI which uniquely identifies the datatype
library.
Rules:
If this URI not explicitly provided, the datatype library
for the enclosing column set is used.
If the data is complex (i.e. XML), this value is set
to the namespace URI for the XML, or '*' if the namespace URI is not
restricted.
|
|
Lang (from Language on page 53)
|
optional
|
xsd:language
|
Language code which accepts the same values as
'xml:lang'.
Unlike 'xml:lang', the scope of the language
definition is not restricted to the XML content within the element where the
'lang' attribute appears.
Language:
Language from which the data is taken or
derived.
|
Restrictions to a data type.
Rules:
|
Rule R23 [document]
:
The 'gc:lang' attribute may be specified only if no
language is already set for the data type that is being restricted.
|
Content Model:
(Parameter*)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Parameter
|
DatatypeFacet (page 46)
|
Facet parameter which refines the datatype.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Lang (from Language on page 53)
|
optional
|
xsd:language
|
Language code which accepts the same values as
'xml:lang'.
Unlike 'xml:lang', the scope of the language
definition is not restricted to the XML content within the element where the
'lang' attribute appears.
Language:
Language from which the data is taken or
derived.
|
Facet information for refining a datatype.
Extension of:
xsd:string
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
ShortName
|
required
|
xsd:token
|
Short name (token) for the datatype facet.
|
|
LongName
|
optional
|
xsd:normalizedString
|
Long name for the datatype facet.
|
Identification of the default datatype library for a column
set.
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
DatatypeLibrary
|
optional
|
xsd:anyURI
|
URI which uniquely identifies the default
datatype library for the column set. If not provided, defaults to the URI for
W3C XML Schema datatypes.
|
(Model Group)
General document information (metadata).
Content Model: (Annotation?
, Identification)
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation information.
|
|
Identification
|
Identification (page 47)
|
Identification and location information
(metadata).
|
Attribute set used to identify a definition within an external
document.
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
ExternalRef
|
required
|
xsd:NCName
|
Unique ID within the external document.
Rules:
The external reference must not be prefixed with a
'#' symbol.
|
An identifier value. Typically not a long or short name.
Extension of:
xsd:normalizedString
Attribute set used to identify a definition within the
document.
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Id
|
required
|
xsd:ID
|
Unique ID within the document.
|
Identification and location information (metadata).
Content Model: ((ShortName
, LongName*) , Version , CanonicalUri , (CanonicalVersionUri , LocationUri* ,
AlternateFormatLocationUri*) , Agency?)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
ShortName (from NameSet on page 54)
|
ShortName (page 55)
|
Short name (without whitespace).
NameSet:
Various names.
|
|
LongName (from NameSet on page 54)
|
LongName (page 53)
|
Human-readable name.
NameSet:
Various names.
|
|
Version
|
xsd:token
|
Version identifier.
|
|
CanonicalUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies all versions
(collectively).
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
|
CanonicalVersionUri (from VersionLocationUriSet
on page 58)
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies this
version.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
VersionLocationUriSet:
Identification and location URIs for the
version.
|
|
LocationUri (from VersionLocationUriSet on
page 58)
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Suggested retrieval location for this version, in
genericode format.
Rules:
An application must signal an error to the user if a
document retrieved using a LocationUri is not in genericode format.
VersionLocationUriSet:
Identification and location URIs for the
version.
|
|
AlternateFormatLocationUri (from
VersionLocationUriSet on page 58)
|
MimeTypedUri (page 53)
|
Suggested retrieval location for this version, in a
non-genericode format.
Such alternative formats are intended only as
additional renditions of the code list information, not as a replacements nor
as alternatives for use in application processing.
VersionLocationUriSet:
Identification and location URIs for the
version.
|
|
Agency
|
Agency (page 28)
|
Agency that is responsible for publication
and/or maintenance of the information.
|
Identification and location URIs.
Content Model:
(CanonicalVersionUri , LocationUri*)
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
CanonicalVersionUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which serves as a unique identifier
for this version.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
|
LocationUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Suggested retrieval location for this version, in
genericode format.
Rules:
An application must signal an error to the user if a
document retrieved using a LocationUri is not in genericode format.
|
URIs used as unique identifiers.
Content Model:
(CanonicalUri , CanonicalVersionUri?)
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
CanonicalUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies all versions
collectively.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
|
CanonicalVersionUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies this
version.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
Key (Complex Type)
Definition of a key.
A key is a set of one or more columns whose values together
provide a unique identification of each item in a code list.
Rules:
|
Rule R34 [document]
:
Only required columns can be used for keys.
|
Content Model: (Annotation?
, (ShortName , LongName*) , (CanonicalUri , CanonicalVersionUri?)? ,
ColumnRef+)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation for the key.
|
|
ShortName (from NameSet on page 54)
|
ShortName (page 55)
|
Short name (without whitespace).
NameSet:
Name(s) of the key.
|
|
LongName (from NameSet on page 54)
|
LongName (page 53)
|
Human-readable name.
NameSet:
Name(s) of the key.
|
|
CanonicalUri (from IdentificationVersionUriSet
on page 49)
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies all versions
collectively.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
IdentificationVersionUriSet:
URIs used to identify the key and/or the version
of the key.
|
|
CanonicalVersionUri (from
IdentificationVersionUriSet on page 49)
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies this
version.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
IdentificationVersionUriSet:
URIs used to identify the key and/or the version
of the key.
|
|
ColumnRef
|
KeyColumnRef (page 51)
|
Reference to the document ID of a column in the
key.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Id (from IdDefinition on page 47)
|
required
|
xsd:ID
|
Unique ID within the document.
IdDefinition:
ID which identifies the key within the
document.
|
A choice between a key definition and a key reference.
Content Model: (Key |
KeyRef)
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Key
|
Key (page 50)
|
Definition of a key.
|
|
KeyRef
|
KeyRef (page 52)
|
Reference to a key defined in an external column
set or code list.
|
Reference to a column which forms part of a key.
Content Model:
(Annotation?)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation for the column.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Ref
|
required
|
xsd:IDREF
|
Reference to the ID of the column within the
document.
|
KeyRef (Complex Type)
Reference to a key defined in an external column set or code
list.
Rules:
|
Rule R35 [application]
:
The key reference must be valid.
An application may use the CanonicalVersionUri to select
a local copy of the code list or column set which contains the key
definition.
Otherwise the LocationUri value(s) may be tried in order,
until a valid code list or column set document (containing the necessary key
definition) is retrieved.
An application must signal an error to the user if it
is not able to retrieve a code list or column set document which contains the
necessary key definition.
|
Content Model: (Annotation?
, (CanonicalVersionUri , LocationUri*))
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation for the referenced key.
|
|
CanonicalVersionUri (from
IdentificationRefUriSet on page 49)
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which serves as a unique identifier
for this version.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
IdentificationRefUriSet:
Identification of the external column set or
code list which contains the key definition.
|
|
LocationUri (from IdentificationRefUriSet
on page 49)
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Suggested retrieval location for this version, in
genericode format.
Rules:
An application must signal an error to the user if a
document retrieved using a LocationUri is not in genericode format.
IdentificationRefUriSet:
Identification of the external column set or
code list which contains the key definition.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Id (from IdDefinition on page 47)
|
required
|
xsd:ID
|
Unique ID within the document.
IdDefinition:
ID which identifies the key within this
document.
|
|
ExternalRef (from ExternalReference on
page 47)
|
required
|
xsd:NCName
|
Unique ID within the external document.
Rules:
The external reference must not be prefixed with a '#'
symbol.
ExternalReference:
ID which identifies which identifies the key
within the external column set or code list.
|
|
xml:base
|
optional
|
|
Base URL which applies to relative location
URIs.
Rules:
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Language (Attribute Group)
Attributes which describe the language of a piece of text.
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Lang
|
optional
|
xsd:language
|
Language code which accepts the same values as
'xml:lang'.
Unlike 'xml:lang', the scope of the language
definition is not restricted to the XML content within the element where the
'lang' attribute appears.
|
A human-readable name.
Extension of:
xsd:normalizedString
URI for a resource, with support for specifying the MIME
type.
Extension of:
xsd:anyURI
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
MimeType
|
optional
|
xsd:normalizedString
|
MIME type of the resource which can be retrieved
from the URI.
|
Various names.
Content Model: (ShortName ,
LongName*)
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
ShortName
|
ShortName (page 55)
|
Short name (without whitespace).
|
|
LongName
|
LongName (page 53)
|
Human-readable name.
|
Attribute set which defines the usage (optional attribute).
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Use
|
optional
|
UseType (page 56)
|
Whether the usage is required or optional.
|
A choice which currently only allows a simple (explicit) code
list definition.
Content Model:
((SimpleCodeList))
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
SimpleCodeList (from SimpleCodeListSequence
on page 56)
|
SimpleCodeList (page 55)
|
Simple (explicit) code list definition.
SimpleCodeListSequence:
Details of a simple code list definition.
|
Attribute set which defines the usage (required attribute).
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Use
|
required
|
UseType (page 56)
|
Whether the usage is required or optional.
|
Row (Complex Type)
Row which represents an individual item in a code list.
Content Model: (Annotation?
, Value+)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation for the row.
|
|
Value
|
Value (page 56)
|
Column value for the row.
Rules:
A value must be provided for each required column.
A value does not need to be provided for a column if the
column is optional.
If a value does not have an explicit column
reference, the column is taken to be the column following the column of the
preceding value in the row, or the first column if the value is the first
value of the row.
|
A short name without whitespace that is suitable for use in
generating names for software artifacts.
Rules:
|
Rule R39 [document]
:
Must not contain whitespace characters.
|
Extension of: xsd:token
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
xml:lang
|
optional
|
|
The language from which the short name is taken
or derived.
|
Simple (explicit) code list definition.
Rules:
|
Rule R40 [application]
:
Applications must not have any dependency on the
ordering of the rows.
|
Content Model: (Annotation?
, Row*)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation for the code list.
|
|
Row
|
Row (page 55)
|
Row which represents an individual item in the
code list.
|
Details of a simple code list definition.
Content Model:
(SimpleCodeList)
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
SimpleCodeList
|
SimpleCodeList (page 55)
|
Simple (explicit) code list definition.
|
Simple textual value.
Extension of:
xsd:string
Indicates whether the usage is required or optional.
Restriction of:
xsd:token
Allowed Values:
·
optional
·
required
Value (Complex Type)
An individual code list metadata value.
Content Model: (Annotation?
, (SimpleValue | ComplexValue)?)
Mixed Content: No
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Annotation
|
Annotation (page 28)
|
User annotation for the value.
|
|
SimpleValue (from ValueChoice on page
57)
|
SimpleValue (page 56)
|
Simple textual value.
Rules:
The value must be valid with respect to the datatype and
restrictions of the matching column.
ValueChoice:
A choice between a simple textual value and a
complex (structured) XML value. If the value is undefined, then neither
choice is used.
|
|
ComplexValue (from ValueChoice on page
57)
|
AnyOtherContent (page 29)
|
Complex (structured) XML value.
Rules:
The names of all direct child elements of the
'ComplexValue' element must match the datatype ID for the matching column,
unless that ID is set to '*'.
The namespace URIs of all direct child elements of the
'ComplexValue' element must match the datatype library URI for the matching
column, unless that URI is set to '*'.
ValueChoice:
A choice between a simple textual value and a
complex (structured) XML value. If the value is undefined, then neither
choice is used.
|
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
ColumnRef (from ColumnReference on page
39)
|
optional
|
xsd:IDREF
|
Reference to a column ID in the document.
ColumnReference:
Reference to the column with which this value is
associated.
|
A choice between a simple textual value and a complex
(structured) XML value.
Content Model: (SimpleValue
| ComplexValue)
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
SimpleValue
|
SimpleValue (page 56)
|
Simple textual value.
Rules:
The value must be valid with respect to the datatype
and restrictions of the matching column.
|
|
ComplexValue
|
AnyOtherContent (page 29)
|
Complex (structured) XML value.
Rules:
The names of all direct child elements of the
'ComplexValue' element must match the datatype ID for the matching column,
unless that ID is set to '*'.
The namespace URIs of all direct child elements of
the 'ComplexValue' element must match the datatype library URI for the
matching column, unless that URI is set to '*'.
|
Information which identifies one of a set of alternate
values.
Attributes:
|
Attribute
|
Usage
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
Identifier
|
optional
|
xsd:normalizedString
|
A string which identifies one of a set of
alternate values.
|
|
xml:lang
|
optional
|
|
The language from which the value is taken or
derived.
|
Identification and location URIs for a version.
Content Model:
(CanonicalVersionUri , LocationUri* , AlternateFormatLocationUri*)
Elements:
|
Element
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
CanonicalVersionUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Canonical URI which uniquely identifies this
version.
Rules:
Must be an absolute URI, must not be relative.
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
|
LocationUri
|
xsd:anyURI
|
Suggested retrieval location for this version, in
genericode format.
Rules:
An application must signal an error to the user if a
document retrieved using a LocationUri is not in genericode format.
|
|
AlternateFormatLocationUri
|
MimeTypedUri (page 53)
|
Suggested retrieval location for this version, in a
non-genericode format.
Such alternative formats are intended only as
additional renditions of the code list information, not as a replacements nor
as alternatives for use in application processing.
|
4.4 Conformance
An XML instance conforms to the OASIS Code List Representation
genericode document model if it does not violate any constraints expressed in the
"genericode.xsd" schema associated with this version of the specification,
including auxiliary rules marked as "document" rules (see below). An application
conforms to the OASIS Code List Representation genericode processing rules if, in
addition, it does not violate any of auxiliary rules marked as "application" rules.
The auxiliary rules are:
Rule R1 [document:: complexType
CodeListDocument] :
|
A code list must have at least one key, unless
it is a metadata-only definition without a 'SimpleCodeList' element.
|
Rule R4 [document:: element
CanonicalUri in complexType CodeListRef] :
|
Must be an absolute URI, must not be
relative.
|
Rule R6 [document:: element
CanonicalVersionUri in complexType CodeListRef] :
|
Must be an absolute URI, must not be
relative.
|
Rule R19 [document:: attribute
Type in complexType Data] :
|
The datatype ID must not include a namespace
prefix.
For the W3C XML Schema datatypes, possible
datatype IDs are 'string', 'token', 'boolean', 'decimal', etc.
|
Rule R20 [document:: attribute
Type in complexType Data] :
|
If the data is complex (i.e. XML), this value is
set to the root element name for the XML value, or '*' if the root element
name is not restricted.
|
Rule R22 [document:: attribute
DatatypeLibrary in complexType Data] :
|
If the data is complex (i.e. XML), this value is
set to the namespace URI for the XML, or '*' if the namespace URI is not
restricted.
|
Rule R23 [document:: complexType
DataRestrictions] :
|
The 'gc:lang' attribute may be specified only if
no language is already set for the data type that is being restricted.
|
Rule R24 [document:: attribute
ExternalRef in attributeGroup ExternalReference] :
|
The external reference must not be prefixed with
a '#' symbol.
|
Rule R25 [document:: element
CanonicalUri in complexType Identification] :
|
Must be an absolute URI, must not be
relative.
|
Rule R27 [document:: element
CanonicalVersionUri in group IdentificationRefUriSet] :
|
Must be an absolute URI, must not be
relative.
|
Rule R30 [document:: element
CanonicalUri in group IdentificationVersionUriSet] :
|
Must be an absolute URI, must not be
relative.
|
Rule R32 [document:: element
CanonicalVersionUri in group IdentificationVersionUriSet] :
|
Must be an absolute URI, must not be
relative.
|
Rule R34 [document:: complexType
Key] :
|
Only required columns can be used for keys.
|
Rule R37 [document:: element
Value in complexType Row] :
|
A value must be provided for each required
column.
A value does not need to be provided for a
column if the column is optional.
|
Rule R38 [document:: element
Value in complexType Row] :
|
If a value does not have an explicit column
reference, the column is taken to be the column following the column of the
preceding value in the row, or the first column if the value is the first
value of the row.
|
Rule R39 [document:: complexType
ShortName] :
|
Must not contain whitespace characters.
|
Rule R41 [document:: element
SimpleValue in group ValueChoice] :
|
The value must be valid with respect to the
datatype and restrictions of the matching column.
|
Rule R42 [document:: element
ComplexValue in group ValueChoice] :
|
The names of all direct child elements of the
'ComplexValue' element must match the datatype ID for the matching column,
unless that ID is set to '*'.
|
Rule R43 [document:: element
ComplexValue in group ValueChoice] :
|
The namespace URIs of all direct child elements
of the 'ComplexValue' element must match the datatype library URI for the
matching column, unless that URI is set to '*'.
|
Rule R44 [document:: element
CanonicalVersionUri in group VersionLocationUriSet] :
|
Must be an absolute URI, must not be
relative.
|
Rule R48 [document:: element
CanonicalUri in complexType CodeListSetRef] :
|
Must be an absolute URI, must not be
relative.
|
Rule R50 [document:: element
CanonicalVersionUri in complexType CodeListSetRef] :
|
Must be an absolute URI, must not be
relative.
|
Rule R2 [application:: attribute
xml:base in complexType CodeListDocument] :
|
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Rule R3 [application::
complexType CodeListRef] :
|
The code list reference must be valid.
An application may use the CanonicalVersionUri to
select a local copy of the code list.
If there is no CanonicalVersionUri, the CanonicalUri
may be used to select a local copy of the code list.
Otherwise the LocationUri value(s) may be tried in
order, until a valid code list document is retrieved.
An application must signal an error to the user
if it is not able to retrieve a code list document to match the code list
reference.
|
Rule R5 [application:: element
CanonicalUri in complexType CodeListRef] :
|
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
Rule R7 [application:: element
CanonicalVersionUri in complexType CodeListRef] :
|
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
Rule R8 [application:: element
LocationUri in complexType CodeListRef] :
|
If the CanonicalVersionUri has been defined, the
LocationUri must reference a genericode CodeList document.
If the CanonicalVersionUri is undefined, the
LocationUri must reference a genericode CodeList Metadata document.
An application must signal an error to the user
if a LocationUri does not reference the appropriate type of genericode
document.
|
Rule R9 [application:: element
LocationUri in complexType CodeListRef] :
|
An application must signal an error to the user
if a document retrieved using a LocationUri is not in genericode format.
|
Rule R10 [application::
attribute xml:base in complexType CodeListRef] :
|
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Rule R11 [application::
attribute xml:base in complexType CodeListSetDocument] :
|
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Rule R12 [application::
complexType ColumnRef] :
|
The column reference must be valid.
An application may use the CanonicalVersionUri to
select a local copy of the code list or column set which contains the column
definition.
Otherwise the LocationUri value(s) may be tried in
order, until a valid code list or column set document (containing the
necessary column definition) is retrieved.
An application must signal an error to the user
if it is not able to retrieve a code list or column set document which
contains the necessary column definition.
|
Rule R13 [application::
attributeGroup gc:OptionalUseDefinition in complexType ColumnRef] :
|
If specified, this overrides the usage specified
in the external column set or code list document.
|
Rule R14 [application::
attribute xml:base in complexType ColumnRef] :
|
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Rule R15 [application::
attribute xml:base in complexType ColumnSet] :
|
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Rule R16 [application::
attribute xml:base in complexType ColumnSetDocument] :
|
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Rule R17 [application::
complexType ColumnSetRef] :
|
The column set reference must be valid.
An application may use the CanonicalVersionUri to
select a local copy of the column set or code list.
Otherwise the LocationUri value(s) may be tried in
order, until a valid column set or code list document is retrieved.
An application must signal an error to the user
if it is not able to retrieve a column set or code list document to match the
column set reference.
|
Rule R18 [application::
attribute xml:base in complexType ColumnSetRef] :
|
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Rule R21 [application::
attribute DatatypeLibrary in complexType Data] :
|
If this URI not explicitly provided, the
datatype library for the enclosing column set is used.
|
Rule R26 [application:: element
CanonicalUri in complexType Identification] :
|
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
Rule R28 [application:: element
CanonicalVersionUri in group IdentificationRefUriSet] :
|
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
Rule R29 [application:: element
LocationUri in group IdentificationRefUriSet] :
|
An application must signal an error to the user
if a document retrieved using a LocationUri is not in genericode format.
|
Rule R31 [application:: element
CanonicalUri in group IdentificationVersionUriSet] :
|
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
Rule R33 [application:: element
CanonicalVersionUri in group IdentificationVersionUriSet] :
|
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
Rule R35 [application::
complexType KeyRef] :
|
The key reference must be valid.
An application may use the CanonicalVersionUri to
select a local copy of the code list or column set which contains the key
definition.
Otherwise the LocationUri value(s) may be tried in
order, until a valid code list or column set document (containing the
necessary key definition) is retrieved.
An application must signal an error to the user
if it is not able to retrieve a code list or column set document which
contains the necessary key definition.
|
Rule R36 [application::
attribute xml:base in complexType KeyRef] :
|
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Rule R40 [application::
complexType SimpleCodeList] :
|
Applications must not have any dependency on the
ordering of the rows.
|
Rule R45 [application:: element
CanonicalVersionUri in group VersionLocationUriSet] :
|
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
Rule R46 [application:: element
LocationUri in group VersionLocationUriSet] :
|
An application must signal an error to the user
if a document retrieved using a LocationUri is not in genericode format.
|
Rule R47 [application::
complexType CodeListSetRef] :
|
The code list set reference must be valid.
An application may use the CanonicalVersionUri to
select a local copy of the code list set.
If there is no CanonicalVersionUri, the CanonicalUri
may be used to select a local copy of the code list set.
Otherwise the LocationUri value(s) may be tried in
order, until a valid code list set document is retrieved.
An application must signal an error to the user
if it is not able to retrieve a code list set document to match the code list
set reference.
|
Rule R49 [application:: element
CanonicalUri in complexType CodeListSetRef] :
|
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
Rule R51 [application:: element
CanonicalVersionUri in complexType CodeListSetRef] :
|
Must not be used as a de facto location URI.
|
Rule R52 [application:: element
LocationUri in complexType CodeListSetRef] :
|
If the CanonicalVersionUri has been defined, the
LocationUri must reference a genericode CodeListSet document.
If the CanonicalVersionUri is undefined, the
LocationUri must reference a genericode CodeListSet Metadata document.
An application must signal an error to the user
if a LocationUri does not reference the appropriate type of genericode
document.
|
Rule R53 [application:: element
LocationUri in complexType CodeListSetRef] :
|
An application must signal an error to the user
if a document retrieved using a LocationUri is not in genericode format.
|
Rule R54 [application::
attribute xml:base in complexType CodeListSetRef] :
|
xml:base does not apply to canonical URIs.
|
Appendix A. Acknowledgments
The following individuals have participated in the creation of
this specification and are gratefully acknowledged
Participants:
· Jon
Bosak, Sun Microsystems
· Anthony
Coates, Miley Watts LLP
· Ray
Denenberg, Library of Congress
· Marc
Gratacos, Associate Member
· Jim
Harris, National Center for State
Courts
· G. Ken
Holman, Associate Member
· Paul
Spencer, Associate Member
Appendix B. Example Code Lists in
Genericode Format
This section is non-normative.
B.1. UBL Example - Country Codes
This is an example of a single-key code list which includes
agency metadata. Notice that only the top-level "CodeList" element requires a "gc:" namespace prefix. There are 3 columns and 1 key
defined in the embedded ColumnSet:
· Code,
column, normalized string, required;
· Name,
column, string, optional;
·
NumericCode, column, string, optional;
· CodeKey,
key cased on "Code" column.
Note that the values in each row have an explicit reference
(ColumnRef) to the matching column (some of these
are highlighted in yellow).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<gc:CodeList xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:gc="http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/">
<Identification>
<ShortName>CountryIdentificationCode</ShortName>
<LongName xml:lang="en">Country</LongName>
<LongNameIdentifier="listID">ISO3166-1</LongName>
<Version>0.3</Version>
<CanonicalUri>urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:codelist:gc:CountryIdentificationCode</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:codelist:gc:CountryIdentificationCode-2.0</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/default/CountryIdentificationCode-2.0.gc</LocationUri>
<Agency>
<LongName xml:lang="en">United Nations Economic Commission for Europe</LongName>
<Identifier>6</Identifier>
</Agency>
</Identification>
<ColumnSet>
<Column Id="code" Use="required">
<ShortName>Code</ShortName>
<Data Type="normalizedString"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="name" Use="optional">
<ShortName>Name</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="numericcode" Use="optional">
<ShortName>NumericCode</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Key Id="codeKey">
<ShortName>CodeKey</ShortName>
<ColumnRef Ref="code"/>
</Key>
</ColumnSet>
<SimpleCodeList>
<Row>
<Value ColumnRef="code">
<SimpleValue>AF</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="name">
<SimpleValue>AFGHANISTAN</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="numericcode">
<SimpleValue>004</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value ColumnRef="code">
<SimpleValue>AL</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="name">
<SimpleValue>ALBANIA</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="numericcode">
<SimpleValue>008</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<!-- ... -->
<Row>
<Value ColumnRef="code">
<SimpleValue>ZM</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="name">
<SimpleValue>ZAMBIA</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="numericcode">
<SimpleValue>894</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value ColumnRef="code">
<SimpleValue>ZW</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="name">
<SimpleValue>ZIMBABWE</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="numericcode">
<SimpleValue>716</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
</SimpleCodeList>
</gc:CodeList>
This example could also have been implemented without explicit
column references on the values, as the column can be inferred based on the
position.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<gc:CodeList xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:gc="http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/"
xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/">
<Annotation>
<Description>
<html:p>This is an example based on a
UBL code list.
It is <html:strong>not</html:strong> an official UBL
document.</html:p>
</Description>
</Annotation>
<Identification>
<ShortName>CountryIdentificationCode</ShortName>
<LongName xml:lang="en">Country</LongName>
<LongName Identifier="listID">ISO3166-1</LongName>
<Version>0.3</Version>
<CanonicalUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/CountryIdentificationCode</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/CountryIdentificationCode-2.0</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/default/CountryIdentificationCode-2.0.gc</LocationUri>
<Agency>
<LongName xml:lang="en">United Nations Economic Commission for Europe</LongName>
<Identifier>6</Identifier>
</Agency>
</Identification>
<ColumnSet>
<Column Id="code" Use="required">
<ShortName>Code</ShortName>
<Data Type="normalizedString"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="name" Use="optional">
<ShortName>Name</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="numericcode" Use="optional">
<ShortName>NumericCode</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Key Id="codeKey">
<ShortName>CodeKey</ShortName>
<ColumnRef Ref="code"/>
</Key>
</ColumnSet>
<SimpleCodeList>
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>AF</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>AFGHANISTAN</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>004</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>AL</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ALBANIA</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>008</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<!-- ... -->
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZM</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZAMBIA</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>894</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZW</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZIMBABWE</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>716</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
</SimpleCodeList>
</gc:CodeList>
B.2. FpML Example - Business
Centers
This is an example of a single-key code list without agency
metadata, but with user metadata. Note that the column for each value is
inferred based on the position of the value in the row. Note also that only
the top-level "CodeList" element requires a "gcl:" namespace prefix. There are 3 columns and 1 key
defined in the embedded ColumnSet:
· Code,
column, token, required, maximum length = 60;
· Source,
column, string, optional;
·
Description, column, string, optional;
·
PrimaryKey, key cased on "Code" column.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<gcl:CodeList
xmlns:gcl="http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/"
xmlns:doc="http://www.fpml.org/coding-scheme/documentation"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<Annotation>
<Description>
<doc:definition>A financial business
center location</doc:definition>
<doc:description>
<doc:paragraph>In general, the
codes are based on the ISO country code and the English name of the
location.</doc:paragraph>
<doc:paragraph>Additional location
codes can be built according to the following rules. The first two characters
represent the ISO country code, the next two characters represent a) if the
location name is one word, the first two letters of the location b) if the location
name consists of at least two words, the first letter of the first word followed by
the first letter of the second word.</doc:paragraph>
<doc:paragraph>There are
exceptions to this rule. For example, the TARGET (Trans-European Automated
Real-time Gross settlement Express Transfer system) business center for Euro
settlement has a code of EUTA.</doc:paragraph>
<doc:paragraph>This coding scheme
is currently consistent with the S.W.I.F.T. Financial Center scheme used in the
MT340/MT360/MT361 message definitions, although FpML controls the Business Center
Scheme and it should not be assumed that both schemes will remain
synchronized.</doc:paragraph>
</doc:description>
</Description>
</Annotation>
<Identification>
<ShortName>businessCenterScheme</ShortName>
<Version>6-4</Version>
<CanonicalUri>http://www.fpml.org/coding-scheme/business-center</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.fpml.org/coding-scheme/business-center-6-4</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://www.fpml.org/coding-scheme/business-center-6-4.xml</LocationUri>
</Identification>
<ColumnSet>
<Column Id="Code" Use="required">
<ShortName>Code</ShortName>
<Data Type="token">
<ParameterShortName="maxLength">60</Parameter>
</Data>
</Column>
<Column Id="Source" Use="optional">
<ShortName>Source</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="Description" Use="optional">
<ShortName>Description</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Key Id="PrimaryKey">
<ShortName>key</ShortName>
<ColumnRef Ref="Code"/>
</Key>
</ColumnSet>
<SimpleCodeList>
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>AEAD</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>FpML</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>Abu Dhabi</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>AEDU</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>FpML</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>Dubai</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<!-- ... -->
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>VECA</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>FpML</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>Caracas,
Venezuela</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZAJO</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>FpML</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>Johannesburg</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
</SimpleCodeList>
</gcl:CodeList>
B.3. Multiple Key Example
This is an example of a code list with multiple alternative
keys for the distinct entries in the code list.
There are 3 alternative keys, one for each revision of the ISO639 standard.
Note that the columns have data types and facets (Parameter element) defined. Note also the (optional)
use of XHTML for human-readable annotations.
<?xml
version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<gc:CodeList xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:gc="http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/"
xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/">
<Annotation>
<Description>
<html:p>Example of ISO639-1
language codes with ISO639-2 and ISO639-3 alternatives.</html:p>
<html:p>See
"http://www.sil.org/iso639-3/codes.asp?order=639_1&letter=a".</html:p>
</Description>
</Annotation>
<Identification>
<ShortName>iso639-1</ShortName>
<Version>1.0</Version>
<CanonicalUri>http://www.example.com/languages/iso639-1</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.example.com/languages/iso639-1/1.0</CanonicalVersionUri>
<Agency>
<!-- TODO -->
</Agency>
</Identification>
<ColumnSet>
<Column Id="col-iso639-1" Use="required">
<ShortName>ISO639-1</ShortName>
<Data Type="string">
<ParameterShortName="pattern">[a-z]{2}</Parameter>
</Data>
</Column>
<Column Id="col-iso639-2" Use="required">
<ShortName>ISO639-2</ShortName>
<Data Type="string">
<ParameterShortName="pattern">[a-z]{3}</Parameter>
</Data>
</Column>
<Column Id="col-iso639-3" Use="required">
<ShortName>ISO639-3</ShortName>
<Data Type="string">
<ParameterShortName="pattern">[a-z]{3}</Parameter>
</Data>
</Column>
<Column Id="col-language-name" Use="required">
<ShortName>LanguageName</ShortName>
<LongName>Language
Name</LongName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="col-scope" Use="required">
<ShortName>Scope</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="col-type" Use="required">
<ShortName>Type</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Key Id="key-iso639-1">
<ShortName>Key-ISO639-1</ShortName>
<ColumnRef Ref="col-iso639-1"/>
</Key>
<Key Id="key-iso639-2">
<ShortName>Key-ISO639-2</ShortName>
<ColumnRef Ref="col-iso639-2"/>
</Key>
<Key Id="key-iso639-3">
<ShortName>Key-ISO639-3</ShortName>
<ColumnRef Ref="col-iso639-3"/>
</Key>
</ColumnSet>
<SimpleCodeList>
<Row>
<Value><SimpleValue>aa</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>aar</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>aar</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Afar</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Individual</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Living</SimpleValue></Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value><SimpleValue>ab</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>abk</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>abk</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Abkhazian</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Individual</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Living</SimpleValue></Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value><SimpleValue>ae</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>ave</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>ave</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Avestan</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Individual</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Ancient</SimpleValue></Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value><SimpleValue>af</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>afr</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>afr</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Afrikaans</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Individual</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Living</SimpleValue></Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value><SimpleValue>ak</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>aka</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>aka</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Akan</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Macrolanguage</SimpleValue></Value>
<Value><SimpleValue>Living</SimpleValue></Value>
</Row>
<!-- ... -->
</SimpleCodeList>
</gc:CodeList>
B.4. Undefined Values
Example
This example is a variation of the "Multiple Key Example" on
page 72. Some of the columns are optional, meaning that the value for that
column can be left undefined in a row. Some of the rows have defined values
for all of the columns, some do not (see, for example, the final Row element).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<gc:CodeList xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:gc="http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/"
xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/">
<Annotation>
<Description>
<html:p>Example of ISO639-2
language codes with ISO639-1 and ISO639-3 alternatives.</html:p>
<html:p>See
"http://www.sil.org/iso639-3/codes.asp?order=639_2&letter=a".</html:p>
</Description>
</Annotation>
<Identification>
<ShortName>iso639-2</ShortName>
<Version>1.0</Version>
<CanonicalUri>http://www.example.com/languages/iso639-2</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.example.com/languages/iso639-2/1.0</CanonicalVersionUri>
<Agency>
<!-- TODO -->
</Agency>
</Identification>
<ColumnSet>
<Column Id="col-iso639-1" Use="optional">
<ShortName>ISO639-1</ShortName>
<Data Type="string">
<ParameterShortName="pattern">[a-z]{2}</Parameter>
</Data>
</Column>
<Column Id="col-iso639-2" Use="required">
<ShortName>ISO639-2</ShortName>
<Data Type="string">
<ParameterShortName="pattern">[a-z]{3}</Parameter>
</Data>
</Column>
<Column Id="col-iso639-3" Use="optional">
<ShortName>ISO639-3</ShortName>
<Data Type="string">
<Parameter ShortName="pattern">[a-z]{3}</Parameter>
</Data>
</Column>
<Column Id="col-language-name" Use="required">
<ShortName>LanguageName</ShortName>
<LongName>Language
Name</LongName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="col-scope" Use="required">
<ShortName>Scope</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="col-type" Use="optional">
<ShortName>Type</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Key Id="key-iso639-2">
<ShortName>Key-ISO639-2</ShortName>
<ColumnRef Ref="col-iso639-2"/>
</Key>
</ColumnSet>
<SimpleCodeList>
<Row>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-1">
<SimpleValue>aa</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-2">
<SimpleValue>aar</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-3">
<SimpleValue>aar</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-language-name">
<SimpleValue>Afar</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-scope">
<SimpleValue>Individual</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-type">
<SimpleValue>Living</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-1">
<SimpleValue>ab</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-2">
<SimpleValue>abk</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-3">
<SimpleValue>abk</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-language-name">
<SimpleValue>Abkhazian</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-scope">
<SimpleValue>Individual</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-type">
<SimpleValue>Living</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-2">
<SimpleValue>ace</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-3">
<SimpleValue>ace</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-language-name">
<SimpleValue>Achinese</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-scope">
<SimpleValue>Individual</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-type">
<SimpleValue>Living</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-2">
<SimpleValue>ach</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-3">
<SimpleValue>ach</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-language-name">
<SimpleValue>Acoli</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-scope">
<SimpleValue>Individual</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-type">
<SimpleValue>Living</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-2">
<SimpleValue>ada</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-3">
<SimpleValue>ada</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-language-name">
<SimpleValue>Adangme</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-scope">
<SimpleValue>Individual</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-type">
<SimpleValue>Living</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-2">
<SimpleValue>ady</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-3">
<SimpleValue>ady</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-language-name">
<SimpleValue>Adyghe</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-scope">
<SimpleValue>Individual</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-type">
<SimpleValue>Living</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value ColumnRef="col-iso639-2">
<SimpleValue>afa</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-language-name">
<SimpleValue>Afro-Asiatic
(Other)</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value ColumnRef="col-scope">
<SimpleValue>Collective</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<!-- ... -->
</SimpleCodeList>
</gc:CodeList>
B.5. Complex (XML) Values
Example
This example is a variation of the second example from "UBL
Example - Country Codes" on page 66. An extra column has been added
containing XHTML markup to display an image for each country in the code list.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<gc:CodeList xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:gc="http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/"
xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/">
<Annotation>
<Description>
<html:p>This is an example based on a
UBL code list.
It
is <html:strong>not</html:strong> an official UBL document.</html:p>
</Description>
</Annotation>
<Identification>
<ShortName>CountryIdentificationCode</ShortName>
<LongName xml:lang="en">Country</LongName>
<LongNameIdentifier="listID">ISO3166-1</LongName>
<Version>0.3</Version>
<CanonicalUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/CountryIdentificationCode</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/CountryIdentificationCode-2.0</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/default/CountryIdentificationCode-2.0.gc</LocationUri>
<Agency>
<LongName xml:lang="en">United
Nations Economic Commission for Europe</LongName>
<Identifier>6</Identifier>
</Agency>
</Identification>
<ColumnSet>
<Column Id="code" Use="required">
<ShortName>Code</ShortName>
<Data Type="normalizedString"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="name" Use="optional">
<ShortName>Name</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="numericcode" Use="optional">
<ShortName>NumericCode</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="imagehtml" Use="required">
<ShortName>ImageHTML</ShortName>
<LongName>Satellite Image
(X)HTML</LongName>
<Data Type="img" DatatypeLibrary="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/"/>
</Column>
<Key Id="codeKey">
<ShortName>CodeKey</ShortName>
<ColumnRef Ref="code"/>
</Key>
</ColumnSet>
<SimpleCodeList>
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>AF</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>AFGHANISTAN</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>004</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<ComplexValue>
<html:img alt="Afghanistan" src="http://geology.com/world/satellite-image-of-afghanistan.jpg"
width="1189" height="895"/>
</ComplexValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>AL</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ALBANIA</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>008</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<ComplexValue>
<html:img alt="Albania" src="http://geology.com/world/satellite-image-of-albania.jpg"
width="454" height="912"/>
</ComplexValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<!-- ... -->
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZM</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZAMBIA</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>894</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<ComplexValue>
<html:img alt="Zambia" src="http://geology.com/world/satellite-image-of-zambia.jpg"
width="1068" height="924"/>
</ComplexValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZW</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZIMBABWE</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>716</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<ComplexValue>
<html:img alt="Zimbabwe" src="http://geology.com/world/satellite-image-of-zimbabwe.jpg"
width="1024" height="935"/>
</ComplexValue>
</Value>
</Row>
</SimpleCodeList>
</gc:CodeList>
B.6. External Column Set
Example
This example is a variation of the second example from "UBL
Example - Country Codes" on page 66. The embedded column set (column and key
definitions) has been moved to a separate genericode file. First the column
set:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<gc:ColumnSet xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:gc="http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/"
xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/">
<Annotation>
<Description>
<html:p>This is an example based on a
UBL code list.
It is <html:strong>not</html:strong> an official UBL
document.</html:p>
</Description>
</Annotation>
<Identification>
<ShortName>UBLCodeListColumnSet</ShortName>
<LongName xml:lang="en">UBL Code List Column Set (Example)</LongName>
<Version>0.1</Version>
<CanonicalUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/columnset/</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/columnset/1.0/</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/default/UBLColumnSet.gc</LocationUri>
</Identification>
<Column Id="code" Use="required">
<ShortName>Code</ShortName>
<Data Type="normalizedString"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="name" Use="optional">
<ShortName>Name</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Column Id="numericcode"Use="optional">
<ShortName>NumericCode</ShortName>
<Data Type="string"/>
</Column>
<Key Id="codeKey">
<ShortName>CodeKey</ShortName>
<ColumnRef Ref="code"/>
</Key>
</gc:ColumnSet>
Now the code list that refers to the column set. The column/key
references are highlighted in yellow:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<gc:CodeList xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:gc="http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/"
xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/">
<Annotation>
<Description>
<html:p>This is an example based on a
UBL code list.
It
is <html:strong>not</html:strong> an official UBL document.</html:p>
</Description>
</Annotation>
<Identification>
<ShortName>CountryIdentificationCode</ShortName>
<LongName xml:lang="en">Country</LongName>
<LongNameIdentifier="listID">ISO3166-1</LongName>
<Version>0.3</Version>
<CanonicalUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/CountryIdentificationCode</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/CountryIdentificationCode-2.0</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/default/CountryIdentificationCode-2.0.gc</LocationUri>
<Agency>
<LongName xml:lang="en">United Nations Economic Commission for Europe</LongName>
<Identifier>6</Identifier>
</Agency>
</Identification>
<ColumnSet>
<ColumnRef Id="code" ExternalRef="code">
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/columnset/1.0/</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/default/UBLColumnSet.gc</LocationUri>
</ColumnRef>
<ColumnRef Id="name" ExternalRef="name">
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/columnset/1.0/</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/default/UBLColumnSet.gc</LocationUri>
</ColumnRef>
<ColumnRef Id="numericcode" ExternalRef="numericcode">
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/columnset/1.0/</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/default/UBLColumnSet.gc</LocationUri>
</ColumnRef>
<KeyRef Id="codeKey" ExternalRef="codeKey">
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/columnset/1.0/</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/default/UBLColumnSet.gc</LocationUri>
</KeyRef>
</ColumnSet>
<SimpleCodeList>
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>AF</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>AFGHANISTAN</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>004</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>AL</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ALBANIA</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>008</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<!-- ... -->
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZM</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZAMBIA</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>894</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
<Row>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZW</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>ZIMBABWE</SimpleValue>
</Value>
<Value>
<SimpleValue>716</SimpleValue>
</Value>
</Row>
</SimpleCodeList>
</gc:CodeList>
B.7. Code List Set Example
This example is a code list set derived from the code lists
distributed with UBL 2.0.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<gc:CodeListSet xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/"
xmlns:gc="http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/">
<Annotation>
<Description>
<html:p>This is an example based on UBL
2.0.
It is <html:strong>not</html:strong> an official UBL
document.</html:p>
</Description>
</Annotation>
<Identification>
<ShortName>UBL-CodeListSet-2-0</ShortName>
<Version>2.0</Version>
<CanonicalUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/codelistset/</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/codelistset/2.0/</CanonicalVersionUri>
</Identification>
<CodeListRef>
<CanonicalUri>urn:un:unece:uncefact:codelist:specification:IANA_7_04</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>urn:un:unece:uncefact:codelist:specification:IANA_7_04:MIMEMediaType:2003</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/cefact/BinaryObjectMimeCode-2.0.gc</LocationUri>
</CodeListRef>
<CodeListRef>
<CanonicalUri>urn:un:unece:uncefact:codelist:specification:54217</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>urn:un:unece:uncefact:codelist:specification:54217:2001</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/cefact/CurrencyCode-2.0.gc</LocationUri>
</CodeListRef>
<!-- ... -->
<CodeListRef>
<CanonicalUri>urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:codelist:gc:ContainerSizeTypeCode</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:codelist:gc:ContainerSizeTypeCode-2.0</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/special-purpose/ContainerSizeTypeCode-2.0.gc</LocationUri>
</CodeListRef>
<CodeListRef>
<CanonicalUri>urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:codelist:gc:PortCode</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:codelist:gc:PortCode-2.0</CanonicalVersionUri>
<LocationUri>http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/os-ubl-2.0/cl/gc/special-purpose/PortCode-2.0.gc</LocationUri>
</CodeListRef>
</gc:CodeListSet>
The full version of the example was generated using the
following XQuery and the Saxon XSLT processor.
declare namespace html = "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/";
declare namespace cls = "http://www.example.com/xquery/genericode/codelistset/";
declare namespace gc = "http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/";
(: UBL 2.0 uses an older, draft version of
genericode. :)
declare namespace ublgc = "http://genericode.org/2006/ns/CodeList/0.4/";
declare variable $UBLCodeListDirectoryUrl as xs:anyURI
external;
declare function cls:list-code-lists() as node()*
{
for $file
in collection(concat($UBLCodeListDirectoryUrl, '?recurse=yes;select=*.gc'))
return
cls:reference-code-list($file)
};
declare function cls:reference-code-list($file as node()) as node()*
{
for $identification in $file/ublgc:CodeList/Identification
return
<CodeListRef>
<CanonicalUri>
{ $identification/CanonicalUri/text() }
</CanonicalUri>
{
if (exists($identification/CanonicalVersionUri))
then
element CanonicalVersionUri { $identification/CanonicalVersionUri/text() }
else ()
}
{
if (exists($identification/LocationUri))
then
for $location in $identification/LocationUri
return
element LocationUri { $location/text() }
else
element LocationUri { document-uri($file) }
}
</CodeListRef>
};
<gc:CodeListSet
xmlns:gc="http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/"
xmlns:html="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://docs.oasis-open.org/codelist/ns/genericode/1.0/
../xsd/CodeList.xsd">
<Annotation>
<Description>
<html:p>This is
an example based on UBL 2.0.
It is <html:strong>not</html:strong> an official UBL document.</html:p>
</Description>
</Annotation>
<Identification>
<ShortName>UBL-CodeListSet-2-0</ShortName>
<Version>2.0</Version>
<CanonicalUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/codelistset/</CanonicalUri>
<CanonicalVersionUri>http://www.example.com/ubl/codelist/genericode/codelistset/2.0/</CanonicalVersionUri>
</Identification>
{ cls:list-code-lists() }
</gc:CodeListSet>