The current set of Web service specifications [WSDL][SOAP11][
SOAP12] defines protocols for Web service interoperability. Web
services increasingly tie together a number of participants forming large
distributed applications. The resulting activities may have complex structure
and relationships.
The WS-Coordination [WSCOOR] specification defines an extensible framework for defining
coordination types. This specification provides the definition of an
atomic transaction coordination type used to coordinate activities having an "all
or nothing" property. Atomic transactions commonly require a high level of
trust between participants and are short in duration. The Atomic
Transaction specification defines protocols that enable existing transaction
processing systems to wrap their proprietary protocols and interoperate across
different hardware and software vendors.
To understand the protocol described in this specification, the following
assumptions are made:
-
The reader is familiar with existing standards for two-phase commit protocols
and with commercially available implementations of such protocols.
Therefore this section includes only those details that are essential to
understanding the protocols described.
-
The reader is familiar with the WS-Coordination specification that defines the
framework for the WS-AtomicTransaction coordination protocols.
-
The reader is familiar with WS-Addressing [WSADDR] and WS-Policy
[WSPOLICY].
Atomic transactions have an all-or-nothing property. The actions taken
prior to commit are only tentative (i.e., not persistent and not visible to
other activities). When an application finishes, it requests the
coordinator to determine the outcome for the transaction. The coordinator
determines if there were any processing failures by asking the participants to
vote. If the participants all vote that they were able to execute
successfully, the coordinator commits all actions taken. If a participant
votes that it needs to abort or a participant does not respond at all, the
coordinator aborts all actions taken. Commit makes the tentative actions
visible to other transactions. Abort makes the tentative actions appear as
if the actions never happened. Atomic transactions have proven to be
extremely valuable for many applications. They provide consistent failure
and recovery semantics, so the applications no longer need to deal with the
mechanics of determining a mutually agreed outcome decision or to figure out how
to recover from a large number of possible inconsistent states.
Atomic Transaction defines protocols that govern the outcome of atomic
transactions. It is expected that existing transaction processing systems
wrap their proprietary mechanisms and interoperate across different vendor
implementations.
By using the XML [XML], SOAP [SOAP11] [SOAP12]
and WSDL [WSDL] extensibility model, SOAP-based and WSDL-based
specifications are designed to work together to define a rich Web services
environment. As such, WS-AtomicTransaction by itself does not define all
features required for a complete solution. WS-AtomicTransaction is a building
block used with other specifications of Web services (e.g., WS-Coordination, WS-Security)
and application-specific protocols that are able to accommodate a wide variety
of coordination protocols related to the coordination actions of distributed
applications.
The key words “MUST”, “MUST NOT”, “REQUIRED”,
“SHALL”, “SHALL NOT”, “SHOULD”, “SHOULD
NOT”, “RECOMMENDED”, “MAY”, and “OPTIONAL”
in this document are to be interpreted as described in RFC2119 [KEYWORDS].
Namespace URIs of the general form "some-URI" represents some application-dependent
or context-dependent URI as defined in RFC3986 [URI].
This specification uses an informal syntax to describe the XML grammar of the
XML fragments below:
·
The syntax appears as an XML instance, but the values indicate the data types
instead of values.
·
Element names ending in "..." (such as <element.../> or <element...>)
indicate that elements/attributes irrelevant to the context are being omitted.
·
Attributed names ending in "..." (such as name=...) indicate that the values are
specified below.
·
Grammar in bold has not been introduced earlier in the document, or is of
particular interest in an example.
·
<-- description --> is a placeholder for elements from some "other"
namespace (like ##other in XSD).
·
Characters are appended to elements, attributes, and <!-- descriptions -->
as follows: "?" (0 or 1), "*" (0 or more), "+" (1 or more). The characters "["
and "]" are used to indicate that contained items are to be treated as a group
with respect to the "?", "*", or "+" characters.
·
The XML namespace prefixes (defined below) are used to indicate the namespace of
the element being defined.
·
Examples starting with <?xml contain enough information to conform to this
specification; others examples are fragments and require additional information
to be specified in order to conform.
XSD schemas and WSDL definitions are provided as a formal definition of grammars
[XML-Schema1] [WSDL].
The XML namespace URI that MUST be used by implementations of this specification
is:
This is also used as the CoordinationContext type for atomic transactions.
If an action URI is used then the action URI MUST consist of the wsat namespace
URI concatenated with the "/" character and the element name. For example:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-tx/wsat/2006/06/Commit
The following links hold the XML schema and the WSDL declarations defined in
this document.
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-tx/wsat/2006/06/wsat.xsd
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-tx/wsat/2006/06/wsat.wsdl
SOAP bindings for the WSDL documents defined in this specification MUST use "document
" for the
style
attribute.
The protocol elements define various extensibility points that allow other child
or attribute content. Additional children and/or attributes MAY be added at the
indicated extension points but MUST NOT contradict the semantics of the parent
and/or owner, respectively. If a receiver does not recognize an extension, the
receiver SHOULD ignore the extension.
[KEYWORDS]
S. Bradner, "Key words for use in RFCs to Indicate Requirement Levels", RFC 2119,
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2119.txt,
Harvard University, March 1997
[SOAP11]
W3C Note, "SOAP: Simple Object Access Protocol 1.1", http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/NOTE-SOAP-20000508,
08 May 2000
[SOAP12]
W3C Recommendation, "SOAP Version 1.2 Part 1: Messaging Framework", http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope,
June 2003
[URI]
T. Berners-Lee, R. Fielding, L. Masinter, "Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI):
Generic Syntax", RFC 3986, http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3986.txt,
MIT/LCS, Day Software, Adobe Systems, January 2005
[WSADDR]
Web Services Addressing (WS-Addressing) 1.0, http://www.w3.org/2005/08/addressing,
W3C Recommendation, May 2006
[WSCOOR]
Web Services Coordination (WS-Coordination) 1.1, http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-tx/wscoor/2006/06,
OASIS, March 2006
[WSDL]
Web Services Description Language (WSDL) 1.1, http://www.w3.org/TR/2001/NOTE-wsdl-20010315
[WSPOLICY]
Web Services Policy Framework (WS-Policy), http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/09/policy,
VeriSign, Microsoft, Sonic Software, IBM, BEA Systems, SAP, September 2004
[WSPOLICYATTACH]
Web Services Policy Attachment (WS-PolicyAttachment), http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/09/policy,
VeriSign, Microsoft, Sonic Software, IBM, BEA Systems, SAP, September 2004
[WSSec]
OASIS Standard 200401, "Web Services Security: SOAP Message Security 1.0 (WS-Security
2004)", http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-soap-message-security-1.0.pdf,
March 2004
[WSSecConv]
Web Services Secure Conversation Language (WS-SecureConversation), http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/02/sc,
OpenNetwork, Layer7, Netegrity, Microsoft, Reactivity, IBM, VeriSign, BEA
Systems, Oblix, RSA Security, Ping Identity, Westbridge, Computer Associates,
February 2005
[WSSecPolicy]
Web Services Security Policy Language (WS-SecurityPolicy), http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/07/securitypolicy,
Microsoft, VeriSign, IBM, RSA Security, July 2005
[WSTrust]
Web Services Trust Language (WS-Trust), , http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/02/trust,
OpenNetwork, Layer7, Netegrity, Microsoft, Reactivity, VeriSign, IBM, BEA
Systems, Oblix, RSA Security, Ping Identity, Westbridge, Computer Associates,
February 2005
[XML]
W3C Recommendation, “Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 (Fourth Edition)”,
http://www.w3.org/TR/2006/REC-xml-20060816,
16 August 2006
[XML-ns]
W3C Recommendation, "Namespaces in XML (Second Edition)", http://www.w3.org/TR/2006/REC-xml-names-20060816,
16 August 2006
[XML-Schema1]
W3C Recommendation, " XML Schema Part 1: Structures Second Edition", http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/REC-xmlschema-1-20041028,
28 October 2004
[XML-Schema2]
W3C Recommendation, " XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes Second Edition", http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/REC-xmlschema-2-20041028,
28 October 2004
Atomic Transaction builds on WS-Coordination, which defines an activation and a
registration service. Example message flows and a complete
description of creating and registering for coordinated activities is found in
the WS-Coordination specification [WSCOOR].
The Atomic Transaction coordination context must flow on all application
messages involved with the transaction.
Atomic Transaction adds the following semantics to the CreateCoordinationContext
operation on the activation service.
-
If the request includes the CurrentContext element, the target coordinator is
interposed as a subordinate to the coordinator stipulated inside the
CurrentContext element.
-
If the request does not include a CurrentContext element, the target coordinator
creates a new transaction and acts as the root.
A coordination context MAY have an Expires element. This element specifies
the period, measured from the point in time at which the context was first
created or received, after which a transaction MAY be terminated solely due to
its length of operation. From that point forward, the coordinator MAY
elect to unilaterally roll back the transaction, so long as it has not made a
commit decision. Similarly a 2PC participant MAY elect to abort its work in the
transaction so long as it has not already decided to prepare.
The Atomic Transaction protocol is identified by the following coordination type:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-tx/wsat/2006/06
This specification defines the following protocols for atomic transactions.
-
Completion
:
The completion protocol initiates commitment processing. Based on each
protocol's registered participants, the coordinator begins with Volatile 2PC
then proceeds through Durable 2PC. The final result is signaled to the
initiator.
-
Two-Phase Commit (2PC)
: The 2PC protocol coordinates registered participants to reach a commit or
abort decision, and ensures that all participants are informed of the final
result. The 2PC protocol has two variants:
-
-
Volatile 2PC:
Participants managing volatile resources such as a cache should register
for this protocol.
-
Durable 2PC:
Participants managing durable resources such as a database should register for
this protocol.
A participant can register for more than one of these protocols by sending
multiple Register messages.
The correct operation of the protocols requires that a number of preconditions
MUST be established prior to the processing:
-
The source MUST have knowledge of the destination's policies, if any, and the
source MUST be capable of formulating messages that adhere to this policy.
-
If a secure exchange of messages is required, then the source and destination
MUST have a security context.
The Completion protocol is used by an application to tell the coordinator to
either try to commit or abort an atomic transaction. After the transaction
has completed, a status is returned to the application.
An initiator registers for this protocol using the following protocol identifier:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-tx/wsat/2006/06/Completion
A Completion protocol coordinator must be the root coordinator of an atomic
transaction. The registration service for a subordinate coordinator MUST respond
to an attempt to register for this coordination protocol with the WS-Coordination
fault Cannot Register Participant.
The diagram below illustrates the protocol abstractly. Refer to the section
State Tables for a detailed description of this protocol.
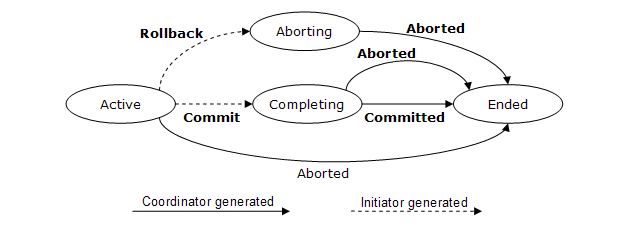
The coordinator accepts:
Commit
Upon receipt of this notification, the coordinator knows that the participant
has completed application processing and that it should attempt to commit the
transaction.
Rollback
Upon receipt of this notification, the coordinator knows that the participant
has terminated application processing and that it should abort the transaction.
The initiator accepts:
Committed
Upon receipt of this notification, the initiator knows that the coordinator
reached a decision to commit.
Aborted
Upon receipt of this notification, the initiator knows that the coordinator
reached a decision to abort.
A coordination service that supports an Activation service MUST support the
Completion protocol.
The Two-Phase Commit (2PC) protocol is a Coordination protocol that defines how
multiple participants reach agreement on the outcome of an atomic transaction.
The 2PC protocol has two variants: Durable 2PC and Volatile 2PC.
Upon receiving a Commit notification in the completion protocol, the root
coordinator begins the prepare phase of all participants registered for the
Volatile 2PC protocol. All participants registered for this protocol must
respond before a Prepare is issued to a participant registered for Durable 2PC.
Further participants may register with the coordinator until the coordinator
issues a Prepare to any durable participant. Once this has happened the
Registration Service for the coordinator MUST respond to any further Register
requests with a Cannot Register Participant fault message. A volatile recipient
is not guaranteed to receive a notification of the transaction's outcome.
Participants register for this protocol using the following protocol identifier:
After receiving a Commit notification in the completion protocol and upon
successfully completing the prepare phase for Volatile 2PC participants, the
root coordinator begins the Prepare phase for Durable 2PC participants.
All participants registered for this protocol must respond Prepared or ReadOnly
before a Commit notification is issued to a participant registered for either
protocol.
Participants register for this protocol using the following protocol identifier:
The diagram below illustrates the protocol abstractly. Refer to the section
State Tables for a detailed description of this protocol.
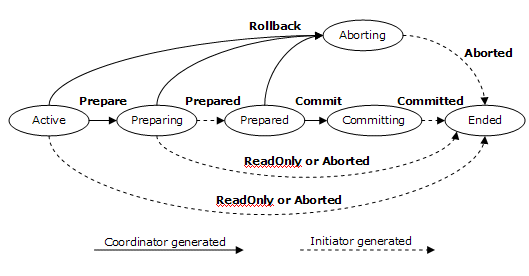
The participant accepts:
Prepare
Upon receipt of this notification, the participant knows to enter phase 1 and
vote on the outcome of the transaction. If the participant does not know
of the transaction, it must vote to abort. If the participant has already
voted, it should resend the same vote.
Rollback
Upon receipt of this notification, the participant knows to abort, and forget,
the transaction. This notification can be sent in either phase 1 or phase
2. Once sent, the coordinator may forget all knowledge of this transaction.
Commit
Upon receipt of this notification, the participant knows to commit the
transaction. This notification can only be sent after phase 1 and if the
participant voted to commit. If the participant does not know of the
transaction, it must send a Committed notification to the coordinator.
The coordinator accepts:
Prepared
Upon receipt of this notification, the coordinator knows the participant is
prepared and votes to commit the transaction.
ReadOnly
Upon receipt of this notification, the coordinator knows the participant votes
to commit the transaction, and has forgotten the transaction. The
participant does not wish to participate in phase 2.
Aborted
Upon receipt of this notification, the coordinator knows the participant has
aborted, and forgotten, the transaction.
Committed
Upon receipt of this notification, the coordinator knows the participant has
committed the transaction. That participant may be safely forgotten.
Conforming implementations MUST implement the 2PC protocol.
WS-Policy Framework [WSPOLICY] and WS-Policy Attachment [WSPOLICYATTACH] collectively define a framework, model and
grammar for expressing the capabilities, requirements, and general
characteristics of entities in an XML Web services-based system. To enable a web
service to describe transactional capabilities and requirements of a service and
its operations, this specification defines a pair of Atomic Transaction policy
assertions that leverage the WS-Policy framework.
The AT policy assertion is provided by a web service to qualify the
transactional processing of messages associated with the particular operation to
which the assertion is scoped. The AT policy assertion indicates whether a
requester MAY or MUST include an AtomicTransaction CoordinationContext flowed
with the message.
The normative outline for the AT policy assertion is:
<wsat:ATAssertion [wsp:Optional="true"]? ... >
...
</wsat:ATAssertion>
The following describes additional, normative constraints on the outline listed
above:
/wsat:ATAssertion
A policy assertion that specifies that an atomic transaction MUST be flowed
inside a requester’s message. From the perspective of the requester, the
target service that processes the transaction MUST behave as if it had
participated in the transaction. The transaction MUST be represented as a SOAP
header in CoordinationContext format, as defined in WS-Coordination [WSCOOR].
/wsat:ATAssertion/@wsp:Optional="true"
Per WS-Policy [WSPOLICY], this is compact notation for two policy alternatives,
one with and one without the assertion.
Because the AT policy assertion indicates atomic transaction behavior for a
single operation, the assertion has Operation Policy Subject [WSPOLICYATTACH].
WS-PolicyAttachment defines two WSDL [WSDL] policy attachment points with Operation Policy Subject:
-
wsdl:portType/wsdl:operation – A policy expression containing the AT
policy assertion MUST NOT be attached to a wsdl:portType; the AT policy
assertion specifies a concrete behavior whereas the wsdl:portType is an abstract
construct.
-
wsdl:binding/wsdl:operation – A policy expression containing the AT policy
assertion SHOULD be attached to a wsdl:binding.
An example use of the AT policy assertion follows:
(01)
<wsdl:definitions
(02)
targetNamespace="bank.example.com"
(03)
xmlns:tns="bank.example.com"
(04)
xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
(05)
xmlns:wsp="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/09/policy"
(06)
xmlns:wsat="http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-tx/wsat/2006/06
"
(07)
xmlns:wsu="http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-wssecurity-utility-1.0.xsd
" >
(08)
<wsp:Policy wsu:Id="TransactedPolicy" >
(09)
<wsat:ATAssertion wsp:optional="true" />
(10)
<!-- omitted assertions -->
(11)
</wsp:Policy>
(12)
<!-- omitted elements -->
(13)
<wsdl:binding name="BankBinding" type="tns:BankPortType" >
(14)
<!-- omitted elements -->
(15)
<wsdl:operation name="TransferFunds" >
(16)
<wsp:PolicyReference URI="#TransactedPolicy
" wsdl:required="true" />
(17)
<!-- omitted elements -->
(18)
</wsdl:operation>
(19)
</wsdl:binding>
(20)
</wsdl:definitions>
Lines (8-11) are a policy expression that includes an AT policy assertion (Line
10) to indicate that an atomic transaction in WS-Coordination [WSCOOR] format MAY be used.
Lines (13-19) are a WSDL [WSDL] binding. Line (17) indicates that the policy in Lines (9-12)
applies to this binding, specifically indicating that an atomic transaction MAY
flow inside messages.
WS-AtomicTransaction faults MUST include as the [action] property the following
fault action URI:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-tx/wsat/2006/06/fault
The protocol faults defined in this section are generated if the condition
stated in the preamble is met. These faults are targeted at a destination
endpoint according to the protocol fault handling rules defined for that
protocol.
The definitions of faults in this section use the following properties:
[Code] The fault code.
[Subcode] The fault subcode.
[Reason] The English language reason element.
[Detail] The detail element. If absent, no detail element is defined for
the fault.
For SOAP 1.2, the [Code] property MUST be either "Sender" or "Receiver".
These properties are serialized into text XML as follows:
|
SOAP Version
|
Sender
|
Receiver
|
|
SOAP 1.2
|
S12:Sender
|
S12:Receiver
|
The properties above bind to a SOAP 1.2 fault as follows:
<S12:Envelope>
<S12:Header>
<wsa:Action>
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-tx/wsat/2006/06/fault
</wsa:Action>
<!-- Headers elided for clarity. -->
</S12:Header>
<S12:Body>
<S12:Fault>
<S12:Code>
<S12:Value>
[Code]
</S12:Value>
<S12:Subcode>
<S12:Value>
[Subcode]
</S12:Value>
</S12:Subcode>
</S12:Code>
<S12:Reason>
<S12:Text xml:lang="en">
[Reason]
</S12:Text>
</S12:Reason>
<S12:Detail>
[Detail]
...
</S12:Detail>
</S12:Fault>
</S12:Body>
</S12:Envelope>
The properties bind to a SOAP 1.1 fault as follows:
<S11:Envelope>
<S11:Body>
<S11:Fault>
<faultcode>
[Subcode]
</faultcode>
<faultstring xml:lang="en">
[Reason]
</faultstring>
</S11:Fault>
</S11:Body>
</S11:Envelope>
This fault is sent by a participant or coordinator to indicate that a protocol
violation has been detected after it is no longer possible to change the outcome
of the transaction. This is indicative of a global consistency failure and
is an unrecoverable condition.
Properties:
[Code] Sender
[Subcode] wsat:InconsistentInternalState
[Reason] A global consistency failure has occurred. This is an
unrecoverable condition.
[Detail] unspecified
This fault is sent by a coordinator to indicate that it has no knowledge of the
transaction and consequently cannot convey the outcome.
Properties:
[Code] Sender
[Subcode] wsat:UnknownTransaction
[Reason] The coordinator has no knowledge of the transaction. This is an
unrecoverable condition.
[Detail] unspecified
The security model for atomic transactions builds on the model defined in WS-Coordination
[WSCOOR]. That is, services have policies specifying their
requirements and requestors provide claims (either implicit or explicit) and the
requisite proof of those claims. Coordination context creation establishes
a base secret which can be delegated by the creator as appropriate.
Because atomic transactions represent a specific use case rather than the
general nature of coordination contexts, additional aspects of the security
model can be specified.
All access to atomic transaction protocol instances is on the basis of identity.
The nature of transactions, specifically the uncertainty of systems means that
the security context established to register for the protocol instance may not
be available for the entire duration of the protocol.
Consider for example the scenarios where a participant has committed its part of
the transaction, but for some reason the coordinator never receives
acknowledgement of the commit. The result is that when communication is re-established
in the future, the coordinator will attempt to confirm the commit status of the
participant, but the participant, having committed the transaction and forgotten
all information associated with it, no longer has access to the special keys
associated with the token.
The participant can only prove its identity to the coordinator when it indicates
that the specified transaction is not in its log and assumed committed.
This is illustrated in the figure below:

There are, of course, techniques to mitigate this situation but such options
will not always be successful. Consequently, when dealing with atomic
transactions, it is critical that identity claims always be proven to ensure
that correct access control is maintained by coordinators.
There is still value in coordination context-specific tokens because they offer
a bootstrap mechanism so that all participants need not be pre-authorized.
As well, it provides additional security because only those instances of an
identity with access to the token will be able to securely interact with the
coordinator (limiting privileges strategy). This is illustrated in the
figure below:

The "list" of authorized participants ensures that application messages having a
coordination context are properly authorized since altering the coordination
context ID will not provide additional access unless (1) the bootstrap key is
provided, or (2) the requestor is on the authorized participant "list" of
identities.
It is strongly RECOMMENDED that the communication between services be secured
using the mechanisms described in WS-Security [WSSec].
In order to properly secure messages, the body and all relevant headers need to
be included in the signature. Specifically, the
<wscoor:CoordinationContext>
header needs to be signed with the body and other key message headers in order
to "bind" the two together.
In the event that a participant communicates frequently with a coordinator, it
is RECOMMENDED that a security context be established using the mechanisms
described in WS-Trust [WSTrust] and WS-SecureConversation
[WSSecConv] allowing for potentially more efficient
means of authentication.
It is common for communication with coordinators to exchange multiple messages.
As a result, the usage profile is such that it is susceptible to key attacks.
For this reason it is strongly RECOMMENDED that the keys be changed frequently.
This "re-keying" can be effected a number of ways. The following list
outlines four common techniques:
-
Attaching a nonce to each message and using it in a derived key function with
the shared secret
-
Using a derived key sequence and switch "generations"
-
Closing and re-establishing a security context (not possible for delegated keys)
-
Exchanging new secrets between the parties (not possible for delegated keys)
It should be noted that the mechanisms listed above are independent of the SCT
and secret returned when the coordination context is created. That is, the
keys used to secure the channel may be independent of the key used to prove the
right to register with the activity.
The security context MAY be re-established using the mechanisms described in WS-Trust
[WSTrust] and WS-SecureConversation [WSSecConv]. Similarly, secrets can be exchanged using the
mechanisms described in WS-Trust. Note, however, that the current shared
secret SHOULD NOT be used to encrypt the new shared secret. Derived keys,
the preferred solution from this list, can be specified using the mechanisms
described in WS-SecureConversation.
The following list summarizes common classes of attacks that apply to this
protocol and identifies the mechanism to prevent/mitigate the attacks:
-
Message alteration
– Alteration is prevented by including signatures of the message
information using WS-Security [WSSec].
-
Message disclosure
– Confidentiality is preserved by encrypting sensitive data using WS-Security.
-
Key integrity
– Key integrity is maintained by using the strongest algorithms possible (by
comparing secured policies – see WS-Policy [WSPOLICY]
and WS-SecurityPolicy [WSSecPolicy]).
-
Authentication
– Authentication is established using the mechanisms described in WS-Security
and WS-Trust [WSTrust]. Each message is authenticated using the
mechanisms described in WS-Security [WSSec].
-
Accountability
– Accountability is a function of the type of and string of the key and
algorithms being used. In many cases, a strong symmetric key provides
sufficient accountability. However, in some environments, strong PKI
signatures are required.
-
Availability
– Many services are subject to a variety of availability attacks.
Replay is a common attack and it is RECOMMENDED that this be addressed as
described in the next bullet. Other attacks, such as network-level denial
of service attacks are harder to avoid and are outside the scope of this
specification. That said, care should be taken to ensure that minimal
processing be performed prior to any authenticating sequences.
-
Replay
– Messages may be replayed for a variety of reasons. To detect and
eliminate this attack, mechanisms should be used to identify replayed messages
such as the timestamp/nonce outlined in WS-Security [WSSec].
Alternatively, and optionally, other technologies, such as sequencing, can also
be used to prevent replay of application messages.
The protocols defined in WS-AtomicTransaction use a "one way" message exchange
pattern consisting of a sequence of notification messages between a Coordinator
and a Participant. There are two types of notification messages used in
these protocols:
-
A notification message is a terminal message when it indicates the end of a
coordinator/participant relationship.
Committed, Aborted
and
ReadOnly
are terminal messages, as are the protocol faults defined in this specification
and in [WSCOOR].
-
A notification message is a non-terminal message when it does not indicate the
end of a coordinator/participant relationship.
Commit, Rollback, Prepare
and
Prepared
are non-terminal messages.
The following statements define addressing interoperability requirements for the
WS-AtomicTransaction message types:
Non-terminal notification messages
·
MUST include a [source endpoint] property whose [address] property is not set to ‘http://www.w3.org/2005/08/addressing/anonymous’
or
'http://www.w3.org/2005/08/addressing/none’.
Both terminal and non-terminal notification messages
·
MUST include a [reply endpoint] property whose [address] property is set to 'http://www.w3.org/2005/08/addressing/none’.
Notification messages are addressed by both coordinators and participants using
the Endpoint References initially obtained during the Register-RegisterResponse
exchange. If a [source endpoint] property is present in a notification
message, it MAY be used by the recipient. For example, in cases where a
Coordinator or Participant has forgotten a transaction that is completed and
needs to respond to a resent protocol message, the [source endpoint] property
should be used as described in section 3.3 of WS-Addressing 1.0 – Core [WSADDR].
Permanent loss of connectivity between a coordinator and a participant in an in-doubt
state can result in data corruption.
Protocol faults raised by a Coordinator or Participant during the processing of
a notification message are terminal notifications and MUST be composed using the
same mechanisms as other terminal notification messages.
All messages are delivered using connections initiated by the sender.
The following state tables specify the behavior of coordinators and participants
when presented with protocol messages or internal events.
Each cell in the tables uses the following convention:
|
Legend
|
|
Action to take
Next state
|
Each state supports a number of possible events. Expected events are
processed by taking the prescribed action and transitioning to the next state. Unexpected
protocol messages will result in a fault message, with a standard fault code
such as Invalid State or Inconsistent Internal State. Events that may not
occur in a given state are labeled as N/A.
Notes:
-
Transitions with a “N/A” as their action are inexpressible. A
TM should view these transitions as serious internal consistency issues, and
probably fatal.
-
The "Internal events" shown are those events, created either within a TM itself
or on its local system, that cause state changes and/or trigger the sending of a
protocol message.
|
Completion Protocol
(Coordinator View)
|
|
Inbound Events
|
States
|
|
None
|
Active
|
Completing
|
|
Commit
|
Unknown Transaction
None
|
Initiate user commit
Completing
|
Ignore
Completing
|
|
Rollback
|
Unknown Transaction
None
|
Initiate user rollback, send aborted
None
|
Invalid
State
Completing
|
|
Internal Events
|
|
|
Commit Decision
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Send committed
None
|
|
Abort Decision
|
N/A
|
Send aborted
None
|
Send aborted
None
|
These tables present the view of a coordinator or participant with respect to a
single partner. A coordinator with multiple participants can be understood
as a collection of independent coordinator state machines, each with its own
state.
|
Atomic Transaction 2PC Protocol
(Coordinator View)
|
|
Inbound Events
|
States
|
|
None
|
Active
|
Preparing
|
Prepared
|
PreparedSuccess
|
Committing
|
Aborting
|
|
Prepared
|
Durable: Send Rollback
Volatile: Unknown Transaction
None
|
Invalid
State
Aborting
|
Record Vote
Prepared
|
Ignore
Prepared
|
Ignore
PreparedSuccess
|
Resend Commit
Committing
|
Resend Rollback
Aborting
|
|
ReadOnly
|
Ignore
None
|
Forget
None
|
Forget
None
|
Inconsistent Internal State
Prepared
|
Inconsistent Internal State
PreparedSuccess
|
Inconsistent Internal State
Committing
|
Forget
None
|
|
Aborted
|
Ignore
None
|
Forget
None
|
Forget
None
|
Inconsistent Internal State
Prepared
|
Inconsistent Internal State
PreparedSuccess
|
Inconsistent Internal State
Committing
|
Forget
None
|
|
Committed
|
Ignore
None
|
Invalid
State
Aborting
|
Invalid
State
Aborting
|
Inconsistent Internal State
Prepared
|
Inconsistent Internal State
PreparedSuccess
|
Forget
None
|
Inconsistent Internal State
Aborting
|
|
Internal Events
|
|
|
User Commit
|
N/A
|
Send Prepare
Preparing
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
User Rollback
|
N/A
|
Send Rollback
Aborting
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
Expires Times Out
|
N/A
|
Send Rollback
Aborting
|
Send Rollback
Aborting
|
Send Rollback
Aborting
|
Ignore
PreparedSuccess
|
Ignore
Committing
|
Ignore
Aborting
|
|
Comms Times Out
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Resend Prepare
Preparing
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Resend Commit
Committing
|
N/A
|
|
Commit Decision
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Record Outcome
PreparedSuccess
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
Rollback Decision
|
N/A
|
Send Rollback
Aborting
|
Send Rollback
Aborting
|
Send Rollback
Aborting
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
Write Done
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Send Commit
Committing
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
Write Failed
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Send Rollback
Aborting
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
Participant Abandoned
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Durable: N/A
Volatile: None
|
None
|
“Forget” implies that the subordinate’s participation is
removed from the coordinator (if necessary), and otherwise the message is
ignored
|
Atomic Transaction 2PC Protocol
(Participant View)
|
|
Inbound Events
|
States
|
|
None
|
Active
|
Preparing
|
Prepared
|
PreparedSuccess
|
Committing
|
|
Prepare
|
Send Aborted
None
|
Gather Vote Decision
Preparing
|
Ignore
Preparing
|
Ignore
Prepared
|
Resend Prepared
PreparedSuccess
|
Ignore
Committing
|
|
Commit
|
Send Committed
None
|
Invalid
State
None
|
Invalid
State
None
|
Invalid
State
None
|
Initiate Commit Decision
Committing
|
Ignore
Committing
|
|
Rollback
|
Send Aborted
None
|
Initiate Rollback and Send Aborted
None
|
Initiate Rollback and Send Aborted
None
|
Initiate Rollback and Send Aborted
None
|
Initiate Rollback and Send Aborted
None
|
Inconsistent Internal State
Committing
|
|
Internal Events
|
|
|
Expires Times Out
|
N/A
|
Initiate Rollback and Send Aborted
None
|
Initiate Rollback and Send Aborted
None
|
Ignore
Prepared
|
Ignore
PreparedSuccess
|
Ignore
Committing
|
|
Comms Times Out
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Resend Prepared
PreparedSuccess
|
N/A
|
|
Commit Decision
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Record Commit
Prepared
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Send Committed
None
|
|
Rollback Decision
|
N/A
|
Send Aborted
None
|
Send Aborted
None
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
Write Done
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Send Prepared
PreparedSuccess
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
Write Failed
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Initiate Rollback and Send Aborted
None
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
ReadOnlyDecision
|
N/A
|
Send ReadOnly
None
|
Send ReadOnly
None
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
This document is based on initial contributions to the OASIS WS-TX Technical
Committee by the following authors: Luis Felipe Cabrera (Microsoft), George
Copeland (Microsoft), Max Feingold (Microsoft), Robert W Freund (Hitachi), Tom
Freund (IBM), Sean Joyce (IONA), Johannes Klein (Microsoft), David Langworthy (Microsoft),
Mark Little (Arjuna Technologies), Frank Leymann (IBM), Eric Newcomer (IONA),
David Orchard (BEA Systems), Ian Robinson (IBM), Tony Storey (IBM), Satish
Thatte (Microsoft).
The following individuals have provided invaluable input into the initial
contribution: Francisco Curbera (IBM), Doug Davis (IBM), Gert Drapers (Microsoft),
Don Ferguson (IBM), Kirill Gavrylyuk (Microsoft), Dan House (IBM), Oisin Hurley
(IONA), Thomas Mikalsen (IBM), Jagan Peri (Microsoft), John Shewchuk (Microsoft),
Stefan Tai (IBM).
The following individuals have participated in the creation of this
specification and are gratefully acknowledged:
Participants:
Martin Chapman, Oracle
Kevin Conner, JBoss Inc.
Paul Cotton, Microsoft Corporation
Doug Davis, IBM
Colleen Evans, Microsoft Corporation
Max Feingold, Microsoft Corporation
Thomas Freund, IBM
Robert Freund, Hitachi, Ltd.
Peter Furniss, Associate Member
Marc Goodner, Microsoft Corporation
Alastair Green, Choreology Ltd.
Daniel House, IBM
Ram Jeyaraman, Microsoft Corporation
Paul Knight, Nortel Networks Limited
Mark Little, JBoss Inc.
Jonathan Marsh, Microsoft Corporation
Monica Martin, Sun Microsystems
Joseph Fialli, Sun Microsystems
Eric Newcomer, IONA Technologies
Eisaku Nishiyama, Hitachi, Ltd.
Alain Regnier, Ricoh Company, Ltd.
Ian Robinson, IBM
Tom Rutt, Fujitsu Limited
Andrew Wilkinson, IBM
|
Revision
|
yy-mm-dd
|
Editor
|
Changes Made
|
|
01
|
05-11-22
|
Mark Little
Andrew Wilkinson
|
Initial Working Draft
|
|
02
|
06-02-12
|
Mark Little
|
Updated for issue i017
|
|
03
|
06-03-02
|
Andrew Wilkinson
|
Updated for issue i015
|
|
04
|
06-03-10
|
Andrew Wilkinson
|
Updated for issue i009
|
|
cd-01
|
06-03-15
|
Andrew Wilkinson
|
Updates to produce CD-01
|
|
05
|
06-05-23
|
Mark Little
|
Updates for i023, i026, i027, i028, i030
|
|
06
|
06-06-01
|
Andrew Wilkinson
|
Updates for i039, i043, i045, i052, i053, i055
|
|
cd-02
|
06-06-13
|
Andrew Wilkinson
|
Updates to produce CD-02
|
|
07
|
06-07-13
|
Mark Little
|
Editorial changes.
|
|
08
|
06-07-24
|
Andrew Wilkinson
|
Updates for i036, i037. Update namespace to 2006/06
|
|
09
|
06-08-18
|
Mark Little
Andrew Wilkinson
|
Updates for i038, i041, i047, i049, i050, i056, i057, i062, i083, i084.
|
|
10
|
06-08-25
|
Andrew Wilkinson
|
Updates for i061, i065, i078, i080, i081, i089
|
|
11
|
06-08-30
|
Andrew Wilkinson
|
Editorial changes
Updates for i090, i091
|
|
cd-03
|
06-08-30
|
Andrew Wilkinson
|
Updates to produce CD-03
|




